DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-024-01447-9
PMID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38884840
تاريخ النشر: 2024-06-17
رسائل النانو والميكرو
(2024) 16:221
تم القبول: 18 مايو 2024
نُشر على الإنترنت: 17 يونيو 2024
© المؤلف(ون) 2024
استراتيجية التجميع ذات الأبعاد المختلطة لبناء هياكل مختلطة من أكسيد الجرافين المخفف/رغوات الكربون لامتصاص الميكروويف، ومقاومة التآكل، والعزل الحراري
النقاط البارزة
- تم تصنيع هياكل فانديرفالز (vdWs) من أكسيد الجرافين المخفض/رغوات الكربون (RGO/CFs) بكفاءة من خلال استراتيجية تجميع بسيطة ذات أبعاد مختلطة.
- تأثير الربط بين تحسين مطابقة المقاومة وزيادة قدرات فقدان العزل يمنح أداءً ممتازًا في امتصاص الميكروويف لهياكل RGO/CFs vdWs.
- يمكن دمج وظائف متعددة مثل أداء مقاومة التآكل الجيد وقدرات العزل الحراري الممتازة في هياكل RGO/CFs vdWs.
الملخص
نظرًا لمشاكل تلوث الموجات الكهرومغناطيسية (EMW) الخطيرة وظروف التطبيق المعقدة، هناك حاجة ملحة لدمج وظائف متعددة ضمن مادة واحدة. ومع ذلك، لا تزال عملية الدمج الفعّال لوظائف متنوعة في مواد امتصاص EMW المصممة تواجه تحديات كبيرة. هنا، تم هندسة وتصنيع أكسيد الجرافين المخفف/رغوات الكربون (RGO/CFs) مع هياكل غير متجانسة من نوع فان der Waals (vdWs) ثنائية الأبعاد/ثلاثية الأبعاد (2D/3D) بدقة باستخدام منهجية فعالة تشمل التجفيف بالتجميد، والغمر في الامتصاص، والتجفيف بالتجميد الثانوي، تليها معالجة الكربنة. بفضل تأثير الربط الممتاز لفقدان العزل المعزز وتطابق المعاوقة المحسن، أظهرت هياكل RGO/CFs vdWs ثنائية/ثلاثية الأبعاد المصممة امتصاصًا جديرًا بالملاحظة للموجات الكهرومغناطيسية.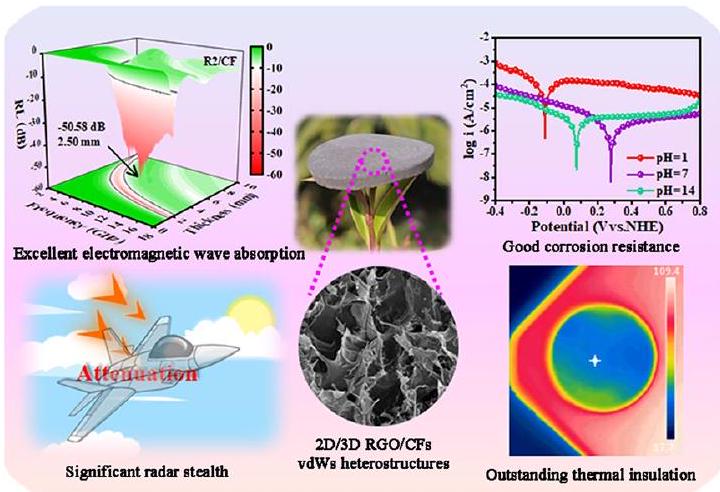 الأداءات، محققة عرض نطاق امتصاص واسع يبلغ 6.2 جيجاهرتز وخسارة انعكاس تبلغ -50.58 ديسيبل مع سماكات مطابقة منخفضة. علاوة على ذلك، عرضت الهياكل غير المتجانسة RGO/CFs ثنائية وثلاثية الأبعاد التي تم الحصول عليها أيضًا خصائص تخفي رادارية ملحوظة، وأداء جيد لمقاومة التآكل بالإضافة إلى قدرات عزل حراري استثنائية، مما يظهر الإمكانيات الكبيرة في البيئات المعقدة والمتغيرة. وبناءً عليه، لم تُظهر هذه الدراسة فقط طريقة مباشرة لتصنيع الهياكل غير المتجانسة ثنائية وثلاثية الأبعاد، بل وضعت أيضًا استراتيجية تجميع مختلطة الأبعاد قوية لتصميم رغوات متعددة الوظائف للحماية الكهرومغناطيسية، والفضاء، وظروف معقدة أخرى.
الأداءات، محققة عرض نطاق امتصاص واسع يبلغ 6.2 جيجاهرتز وخسارة انعكاس تبلغ -50.58 ديسيبل مع سماكات مطابقة منخفضة. علاوة على ذلك، عرضت الهياكل غير المتجانسة RGO/CFs ثنائية وثلاثية الأبعاد التي تم الحصول عليها أيضًا خصائص تخفي رادارية ملحوظة، وأداء جيد لمقاومة التآكل بالإضافة إلى قدرات عزل حراري استثنائية، مما يظهر الإمكانيات الكبيرة في البيئات المعقدة والمتغيرة. وبناءً عليه، لم تُظهر هذه الدراسة فقط طريقة مباشرة لتصنيع الهياكل غير المتجانسة ثنائية وثلاثية الأبعاد، بل وضعت أيضًا استراتيجية تجميع مختلطة الأبعاد قوية لتصميم رغوات متعددة الوظائف للحماية الكهرومغناطيسية، والفضاء، وظروف معقدة أخرى.
1 المقدمة
المواد غير المتبلورة النقية والمعدنية العارية، أظهرت المركبات المصممة عرض نطاق امتصاص فعال (EAB)، والذي تم نسبه إلى الواجهة غير المتجانسة التي توفرها الهياكل الطورية المختلفة. وبالمثل، نجح رضا بيمانفار وفريق زانغ في تعزيز أداء امتصاص الموجات الكهرومغناطيسية.
وستكون المواد الممتصة لموجات الكهرومغناطيسية ذات النطاق الترددي الواسع، والمثالية، والتي تتمتع باستقرار ممتاز ومرونة لتلبية الطلبات المتزايدة في البيئة العملية المتغيرة، اتجاهًا بحثيًا رئيسيًا في المستقبل. ومع ذلك، لا يزال دمج الوظائف المتعددة بما في ذلك قدرة امتصاص الموجات الكهرومغناطيسية، والحماية من الحرارة، ومقاومة التآكل في المواد الكربونية يواجه تحديات كبيرة حتى الآن.
2 القسم التجريبي
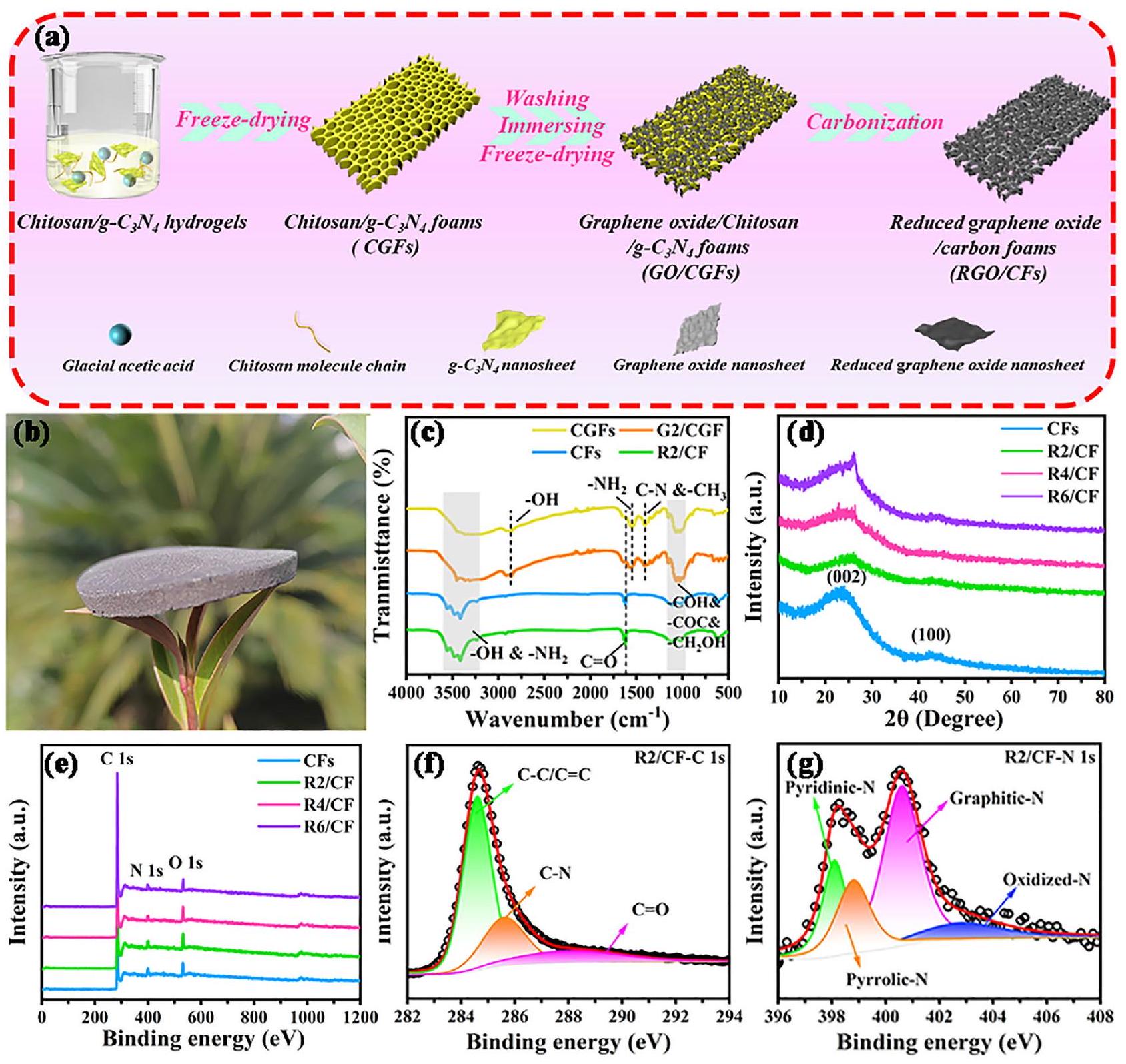
2.1 تصنيع شيتوزان/جرافين ثلاثي الأبعاد
تمت إزالته بعد معالجة التجفيف بالتجميد للحصول على CGFs خلوية ثلاثية الأبعاد.
2.2 تصنيع هياكل فريدة من نوعها من GO/CGFs ثنائية وثلاثية الأبعاد وRGO/CFs
2.3 توصيف
تم إجراء (XPS) ومقياس حيود الأشعة السينية (XRD) بشكل متتابع. للتحقيق في خصائص امتصاص EMW، تم الحصول على العينات (15، 20، و
3 النتائج والمناقشة
3.1 التركيب، البنية المجهرية، خصائص امتصاص EM و EMW لهياكل RGO/CFs vdWs عن طريق تنظيم محتوى GO
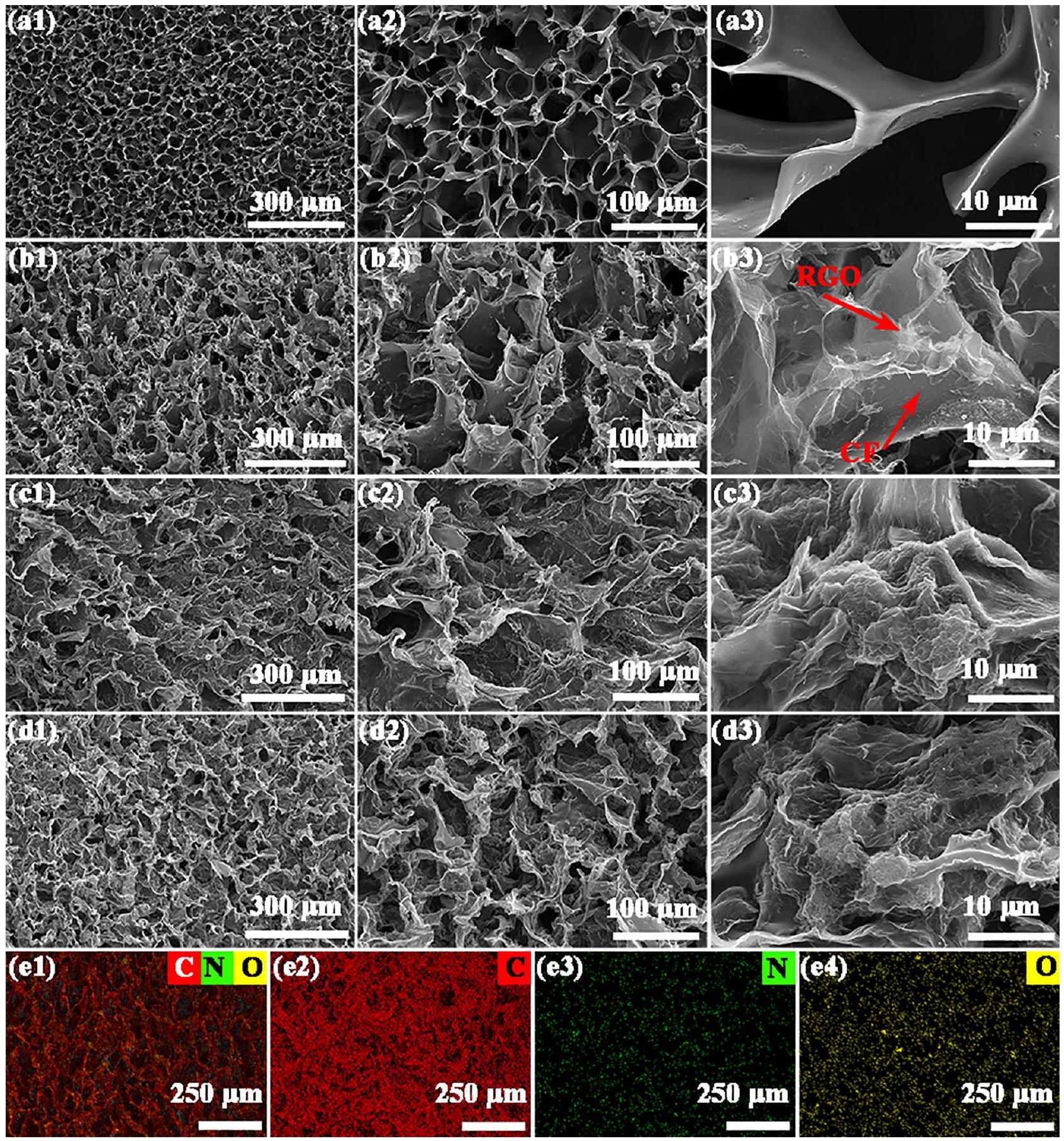
تمتلك الهياكل الهجينة RGO/CFs vdWs كثافة منخفضة جدًا تبلغ حوالي
دون أي تغيير في شكلها الخارجي، مما يؤكد الميزات الفائقة الخفة لهياكل RGO/CFs. توضح الشكل 1c طيف FIIR لـ CGFs و G2/CGF و CFs و R2/CF. يكشف تحليل منحنيات FIIR لـ CGFs و G2/CGF أن قمم -OH تخضع لانزياح أحمر واضح من حوالي 3430 إلى حوالي.
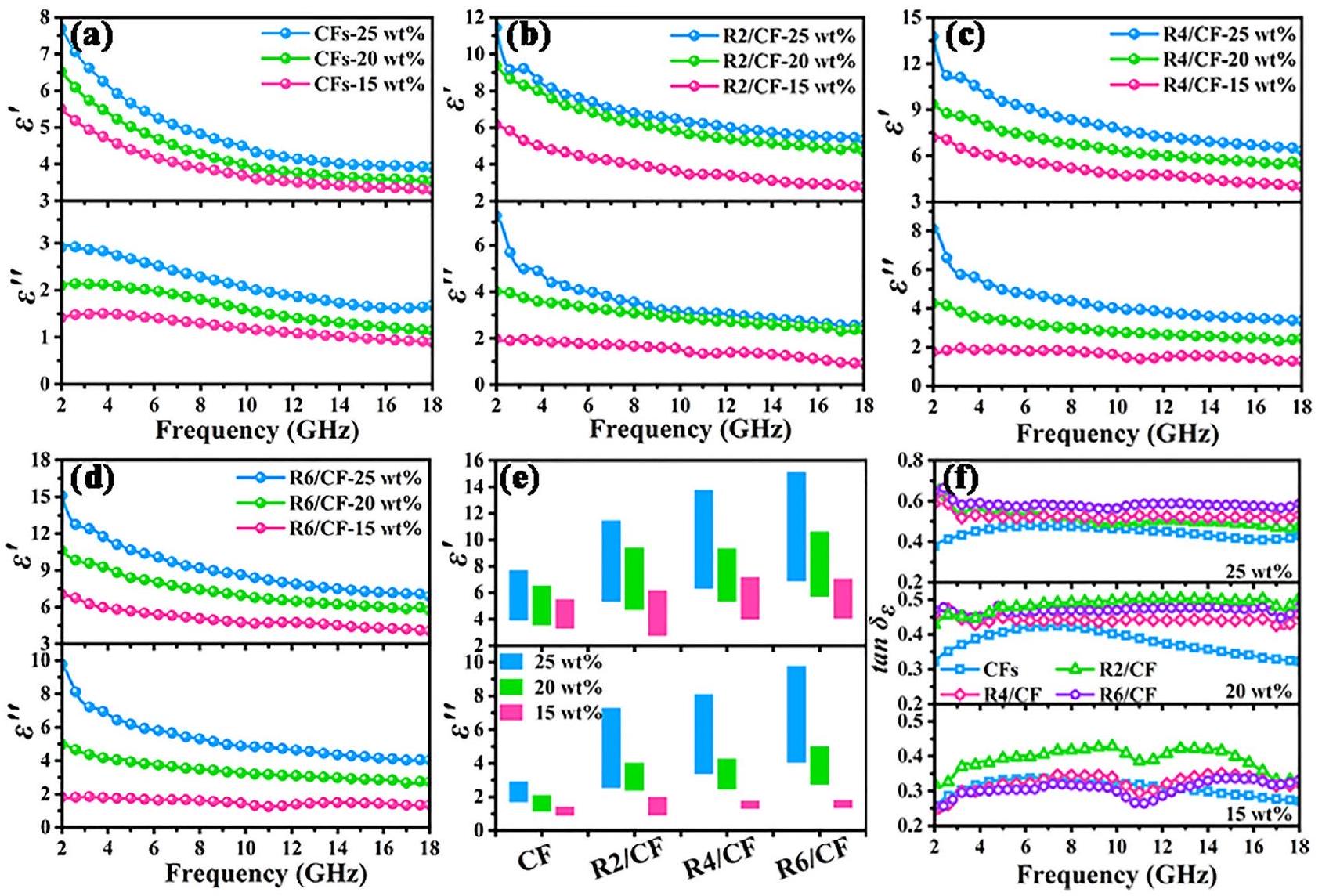
1.984-0.907، 9.385-4.695 و 4.019-2.370، 11.449-5.319 و 7.268-2.540. وعينة R2/CF المصممة تقدم قيمًا أعلى بكثير من
تعديل فعال للمعلمات الكهرومغناطيسية بعد دمج RGO. كما تشير قيم معامل فقدان العزل الكهربائي إلى أن CFs و RGO/CFs تظهر اتجاهًا تصاعديًا مستمرًا عندما يزيد نسبة التعبئة من 15 إلى
قيم CF
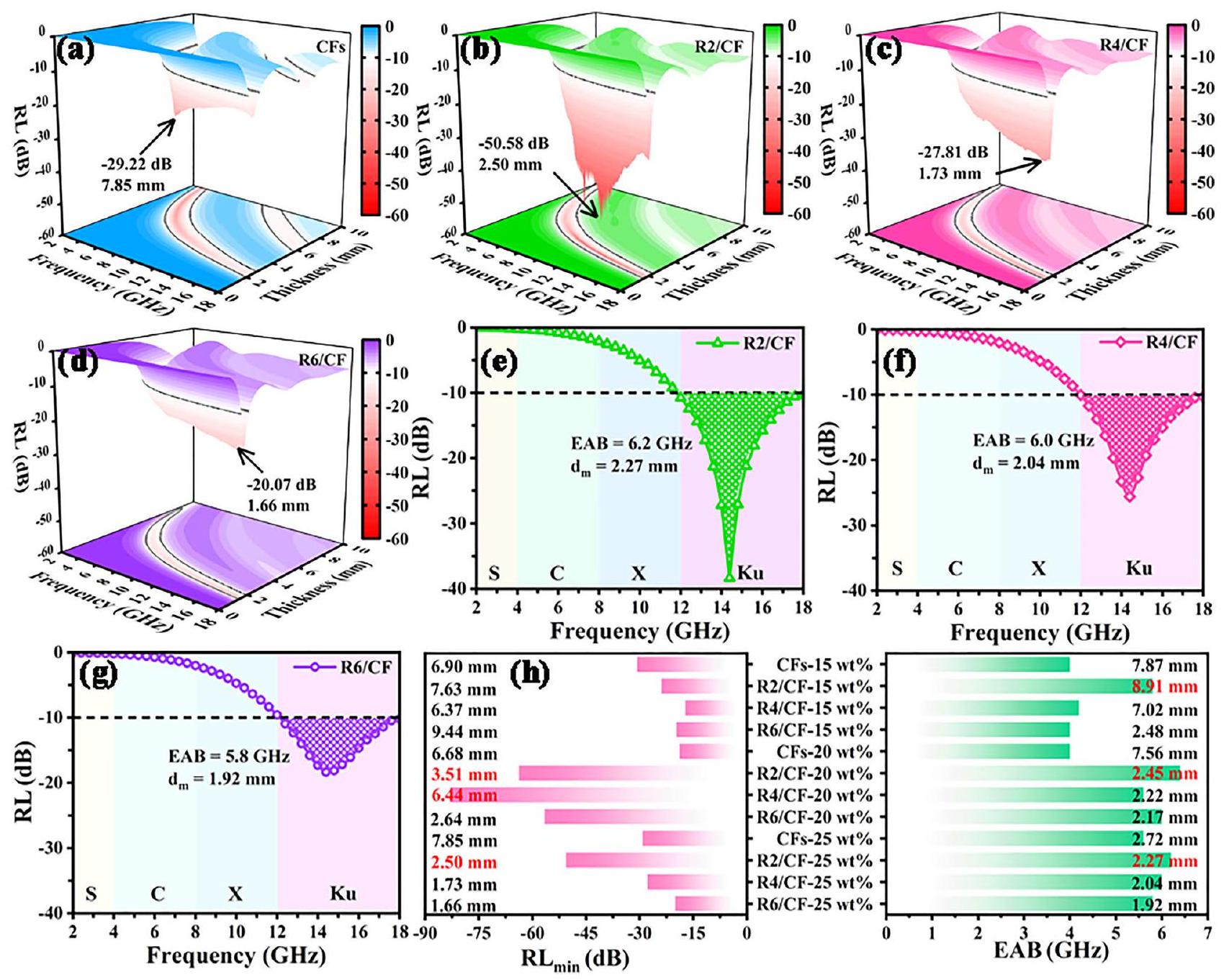
القدرات، EAB الواسع بالإضافة إلى سماكات مطابقة صغيرة، والتي هي ماصات EMW جديدة للغاية.
3.2 تأثير درجة حرارة المعالجة الحرارية
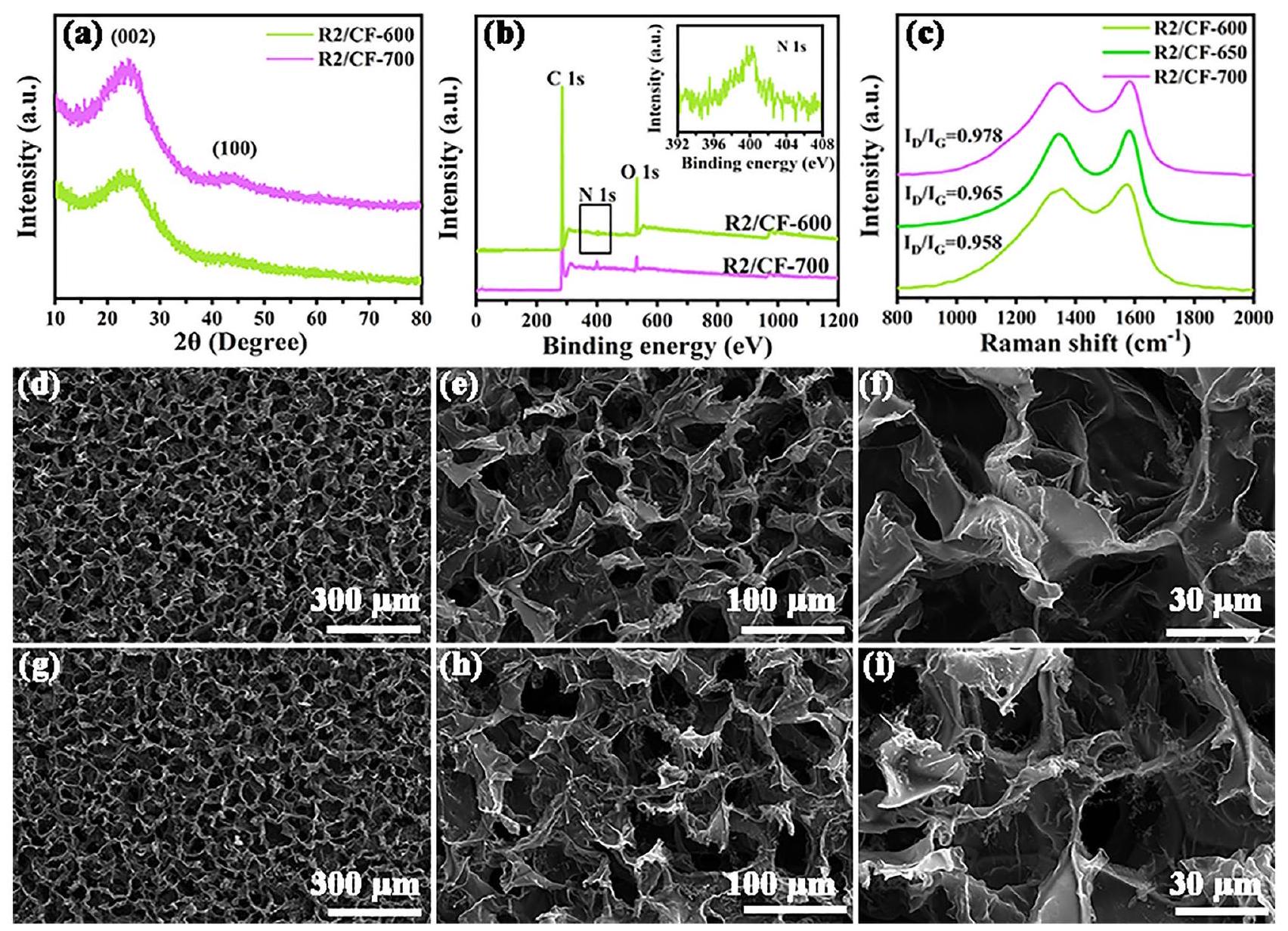
لتأكيد تأثير درجة حرارة الكربنة على أدائها، تم أيضًا دراسة معايير EM لعينات R2/CF-600 و R2/CF-700. كما تقدم عينات R2/CF-600 (الشكل 6أ) و R2/CF-700 (الشكل 6ب) القيم المتزايدة تدريجيًا لـ
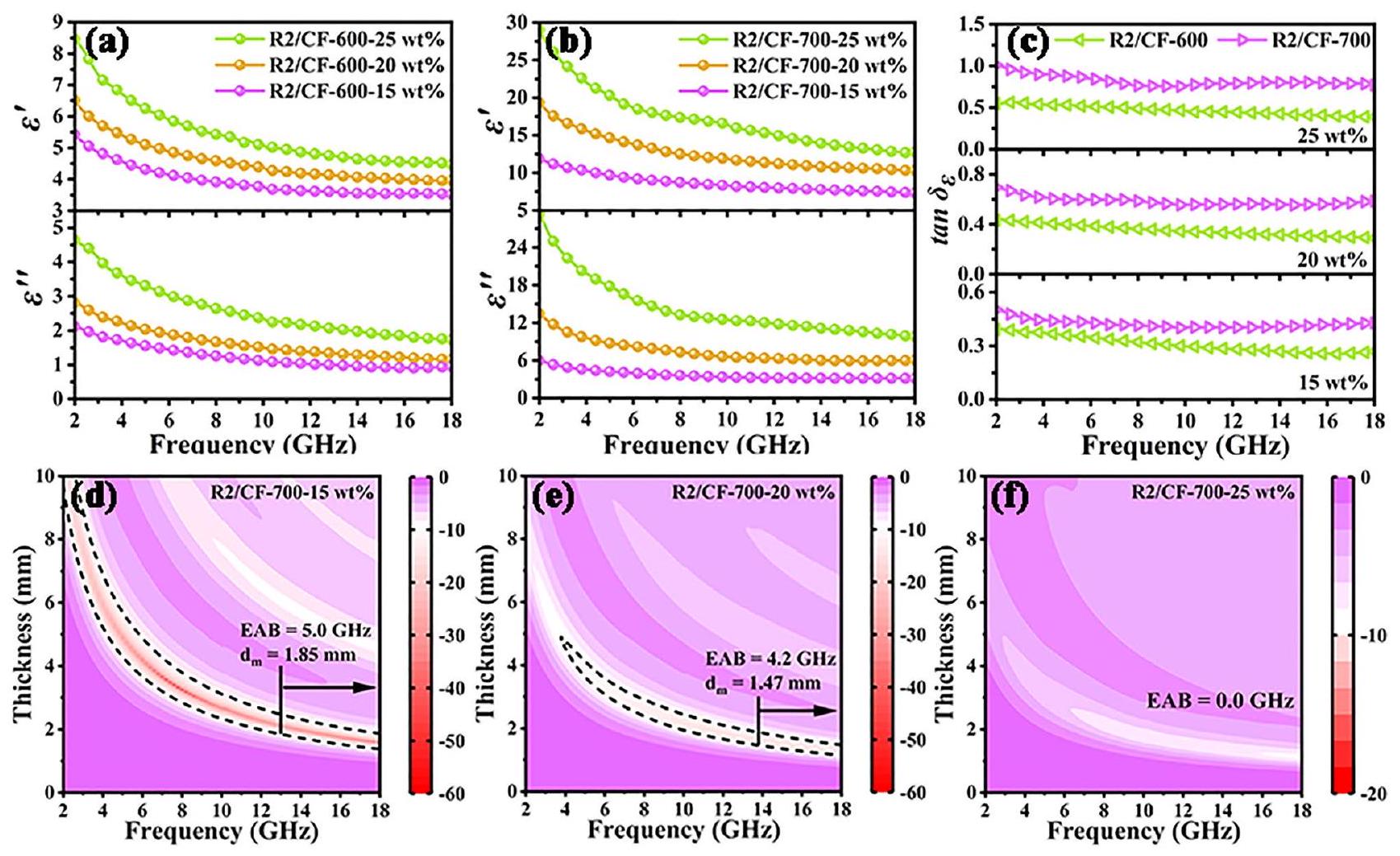
[48]. في الوقت نفسه، يتم تلخيص المعلمات التفصيلية الأخرى لـ EM وأداء الامتصاص لكل من العينات عند نسب تعبئة مختلفة في الجدول S1. وفقًا للنتائج المكتسبة، من الواضح أن أداء امتصاص EMW الممتاز للهياكل غير المتجانسة 2D/3D RGO/CFs التي تم الحصول عليها يتم أيضًا تعديلها عن طريق تنظيم درجة حرارة المعالجة الحرارية.
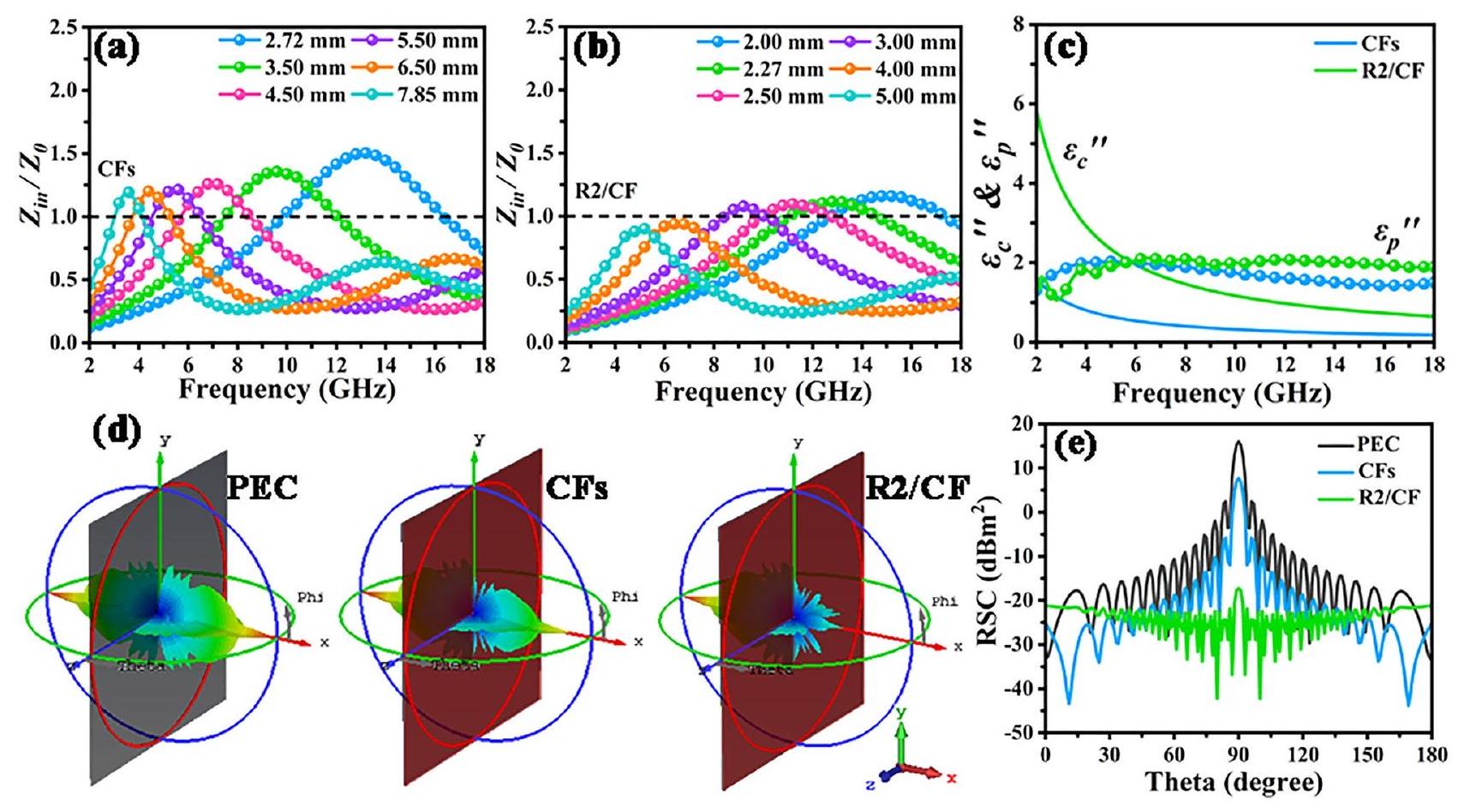
أن معظم طاقة EMW يتم تخفيفها بشكل فعال بواسطة الهياكل غير المتجانسة 2D/3D RGO/CFs. كما هو مقارن في الشكل 7هـ، تعرض عينة R2/CF التي تم الحصول عليها أدنى قيم RCS (أقل من
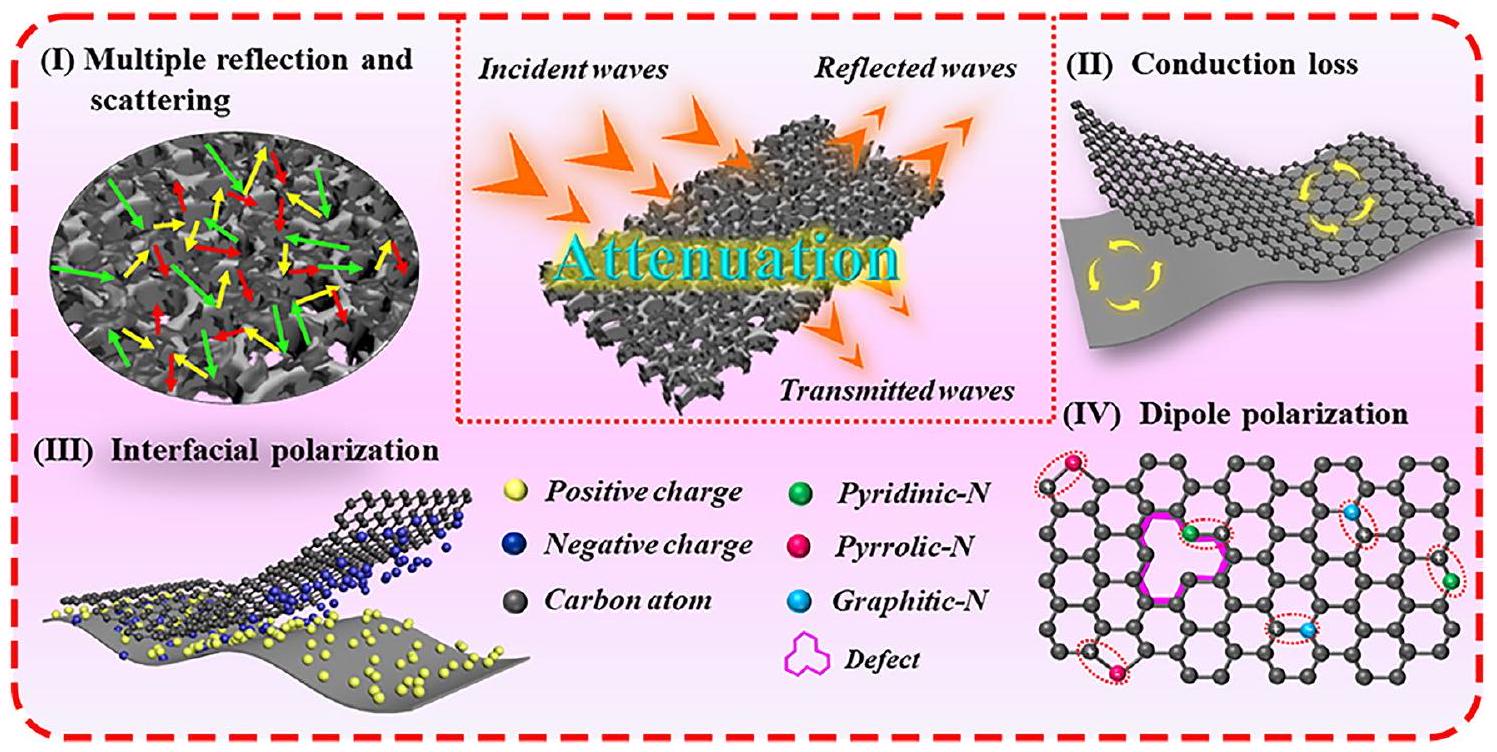
3.4 التعددية وآفاق التطبيق المحتملة
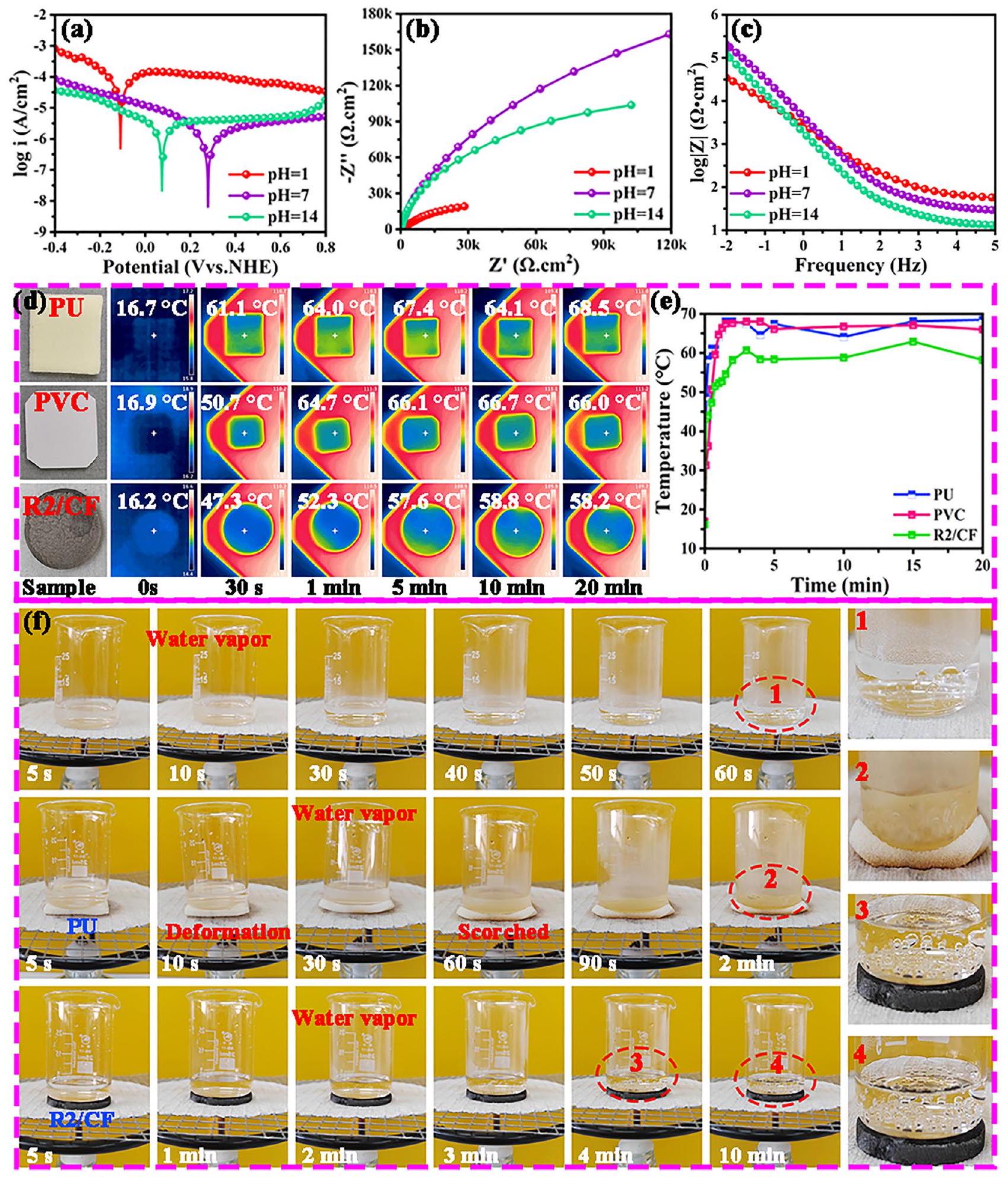
الظروف المحايدة والقلوية. بناءً على النتائج المذكورة أعلاه، يجب أن تُعزى الأداء الممتاز ضد التآكل إلى الاستقرار الفيزيائي/الكيميائي العالي لمواد الكربون، والهياكل الكثيفة، والخصائص الهيدروفوبية الممتازة. وتجنب الهيدروفوبية القوية لـ R2/CF (زاوية تماس الماء تصل إلى حوالي
4 الاستنتاجات
إعلانات
References
- J. Shu, Y. Wang, M. Cao, PEDOT:PSS-patched magnetic graphene films with tunable dielectric genes for electromagnetic interference shielding and infrared stealth. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 186, 28-36 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2023. 10.046
- M. He, J. Hu, H. Yan, X. Zhong, Y. Zhang et al., Shape anisotropic chain-like coni/polydimethylsiloxane composite films with excellent low-frequency microwave absorption and high thermal conductivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. (2024). https://doi. org/10.1002/adfm. 202316691
- H. Lv, J. Cui, B. Li, M. Yuan, J. Liu et al., Insights into civilian electromagnetic absorption materials: challenges and innovative solutions. Adv. Funct. Mater. (2024). https://doi.org/10. 1002/adfm. 202315722
- L. Yao, Y. Wang, J. Zhao, Y. Zhu, M. Cao, Multifunctional nanocrystalline-assembled porous hierarchical material and device for integrating microwave absorption, electromagnetic interference shielding, and energy storage. Small 19(25), 2208101 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll. 202208101
- R. Peymanfar, A. Mirkhan, Biomass-derived materials: promising, affordable, capable, simple, and lightweight microwave absorbing structures. Chem. Eng. J. 446, 136903 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.136903
- P. Liu, S. Gao, Y. Wang, Y. Huang, W. He et al., Carbon nanocages with N -doped carbon inner shell and
-doped carbon outer shell as electromagnetic wave absorption materials. Chem. Eng. J. 381, 122653 (2020). https://doi.org/10. 1016/j.cej.2019.122653 - R. Peymanfar, A. Ahmadi, E. Selseleh-Zakerin, A. Ghaffari, M.M. Mojtahedi et al., Electromagnetic and optical characteristics of wrinkled ni nanostructure coated on carbon microspheres. Chem. Eng. J. 405, 126985 (2021). https://doi.org/10. 1016/j.cej.2020.126985
- Z. Zhang, J. Wang, J. Shang, Y. Xu, Y.J. Wan et al., A throughthickness arrayed carbon fibers elastomer with horizontal segregated magnetic network for highly efficient thermal management and electromagnetic wave absorption. Small 19(4), 2205716 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll. 202205716
- L. Xiang, A.K. Darboe, Z. Luo, X. Qi, J.-J. Shao et al., Constructing two-dimensional/two-dimensional reduced graphene oxide/
and S van der Waals heterojunctions: a combined composition modulation and interface engineering strategy for microwave absorption. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 6, 215 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/ s42114-023-00793-3 - Y. Wu, Y. Zhao, M. Zhou, S. Tan, R. Peymanfar et al., Ultrabroad microwave absorption ability and infrared stealth property of nano-micro
lightweight aerogels.
11. Z. Wu, H.W. Cheng, C. Jin, B. Yang, C. Xu et al., Dimensional design and core-shell engineering of nanomaterials for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Mater. 34, 2107538 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma. 202107538
12. Y. Wang, Y. Yang, M. Miao, X. Feng, Carbon nanotube arrays@cobalt hybrids derived from metal-organic framework ZIF-67 for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. Mater. Today Phys. 35, 101110 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j. mtphys.2023.101110
13. J. Yan, Z. Ye, W. Chen, P. Liu, Y. Huang, Metal Mo and nonmetal N, S co-doped 3D flowers-like porous carbon framework for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 216, 118563 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2023.118563
14. M. Zhang, C. Han, W. Cao, M. Cao, H. Yang et al., A nanomicro engineering nanofiber for electromagnetic absorber, green shielding and sensor. Nano-Micro Lett. 13, 27 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-020-00552-9
15. B. Zhao, Y. Du, H. Lv, Z. Yan, H. Jian et al., Liquid-metalassisted programmed galvanic engineering of core-shell nanohybrids for microwave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33(34), 2302172 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm. 202302172
16. P. Wu, X. Kong, Y. Feng, W. Ding, Z. Sheng et al., Phase engineering on amorphous/crystalline
17. S. Seyedian, A. Ghaffari, A. Mirkhan, G. Ji, S. Tan et al., Manipulating the phase and morphology of
18. H. Zhang, J. Cheng, H. Wang, Z. Huang, Q. Zheng et al., Initiating VB-group laminated
19. J. Liu, L. Zhang, H. Wu, Anion-doping-induced vacancy engineering of cobalt sulfoselenide for boosting electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32(26), 2200544 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm. 202200544
20. L. Liang, W. Gu, Y. Wu, B. Zhang, G. Wang et al., Heterointerface engineering in electromagnetic absorbers: new insights and opportunities. Adv. Mater. 34(4), 2106195 (2021). https:// doi.org/10.1002/adma. 202106195
21. J. Wang, L. Liu, S. Jiao, K. Ma, J. Lv et al., Hierarchical carbon fiber@MXene@MoS2 core-sheath synergistic microstructure for tunable and efficient microwave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30(45), 2002595 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/ adfm. 202002595
22. Y. Zhao, X. Zuo, Y. Guo, H. Huang, H. Zhang et al., Structural engineering of hierarchical aerogels comprised of multidimensional gradient carbon nanoarchitectures for highly
efficient microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 13(1), 144 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00667-7
23. S. Wang, X. Zhang, S. Hao, J. Qiao, Z. Wang et al., Nitrogendoped magnetic-dielectric-carbon aerogel for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 16(1), 16 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-023-01244-w
24. S. Zhang, X. Liu, C. Jia, Z. Sun, H. Jiang et al., Integration of multiple heterointerfaces in a hierarchical 0D@2D@1D structure for lightweight, flexible, and hydrophobic multifunctional electromagnetic protective fabrics. Nano-Micro Lett. 15(1), 204 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-023-01179-2
25. X. Tang, C. Liu, X. Chen, Y. Deng, X. Chen et al., Graphene aerogel derived by purification-free graphite oxide for high performance supercapacitor electrodes. Carbon 146, 147-154 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.01.096
26. Y.Y. Wang, Z.H. Zhou, C.G. Zhou, W.J. Sun, J.F. Gao et al., Lightweight and robust carbon nanotube/polyimide foam for efficient and heat-resistant electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(7), 8704-8712 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami. 9b21048
27. X. Chen, M. Zhou, Y. Zhao, W. Gu, Y. Wu et al., Morphology control of eco-friendly chitosan-derived carbon aerogels for efficient microwave absorption at thin thickness and thermal stealth. Green Chem. 24(13), 5280-5290 (2022). https://doi. org/10.1039/d2gc01604d
28. W. Gu, J. Sheng, Q. Huang, G. Wang, J. Chen et al., Environmentally friendly and multifunctional shaddock peel-based carbon aerogel for thermal-insulation and microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 13(1), 102 (2021). https://doi.org/10. 1007/s40820-021-00635-1
29. R. Peymanfar, E. Selseleh-Zakerin, A. Ahmadi, Tailoring energy band gap and microwave absorbing features of graph-ite-like carbon nitride (
30. C. Wei, M. He, M. Li, X. Ma, W. Dang et al., Hollow Co/
31. L. He, F. Weniger, H. Neumann, M. Beller, Synthesis, characterization, and application of metal nanoparticles supported on nitrogen-doped carbon: catalysis beyond electrochemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55(41), 12582-12594 (2016). https:// doi.org/10.1002/anie. 201603198
32. J. Tao, L. Xu, C. Pei, Y. Gu, Y. He et al., Catfish effect induced by anion sequential doping for microwave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33(8), 2211996 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/ adfm. 202211996
33. L. Liang, Q. Li, X. Yan, Y. Feng, Y. Wang et al., Multifunctional magnetic
34. J. Xiao, B. Zhan, M. He, X. Qi, X. Gong et al., Interfacial polarization loss improvement induced by the hollow
engineering of necklace-like pan/carbon nanofibers for boosted microwave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. (2024). https://doi. org/10.1002/adfm. 202316722
35. X. Jiang, X. Zeng, Y. Ning, F. Hu, B. Fan, Construction of dual heterogeneous interface between zigzag-like Mo-MXene nanofibers and small CoNi@NC nanoparticles for electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Adv. Ceram. 12(8), 1562-1576 (2023). https://doi.org/10.26599/jac.2023.9220772
36. Z. Wu, X. Tan, J. Wang, Y. Xing, P. Huang et al., MXene hollow spheres supported by a C-Co exoskeleton grow MWCNTs for efficient microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 16, 107 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-024-01326-3
37. X. Huang, G. Yu, Y. Zhang, M. Zhang, G. Shao, Design of cellular structure of graphene aerogels for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 426, 131894 (2021). https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.cej.2021.131894
38. M. Qin, L. Zhang, H. Wu, Dielectric loss mechanism in electromagnetic wave absorbing materials. Adv Sci (Weinh) 9(10), e2105553 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/advs. 202105553
39. X. Zhang, K. Qian, J. Fang, S. Thaiboonrod, M. Miao et al., Synchronous deprotonation-protonation for mechanically robust chitin/aramid nanofibers conductive aerogel with excellent pressure sensing, thermal management, and electromagnetic interference shielding. Nano Res. 17(3), 2038-2049 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6189-6
40. Y. Li, X. Liu, X. Nie, W. Yang, Y. Wang et al., Multifunctional organic-inorganic hybrid aerogel for self-cleaning, heat-insulating, and highly efficient microwave absorbing material. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29(10), 1807624 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/ adfm. 201807624
41. Q. Liang, L. Wang, X. Qi, Q. Peng, X. Gong et al., Hierarchical engineering of
42. T. Hou, Z. Jia, Y. Dong, X. Liu, G. Wu, Layered 3D structure derived from MXene/magnetic carbon nanotubes for ultrabroadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 431, 133919 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021. 133919
43. J. Yan, Y. Wang, W. Liu, P. Liu, W. Chen, Two-dimensional metal organic framework derived nitrogen-doped graphenelike carbon nanomesh toward efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 643, 318-327 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2023.04.040
44. W. Gu, J. Tan, J. Chen, Z. Zhang, Y. Zhao et al., Multifunctional bulk hybrid foam for infrared stealth, thermal insulation, and microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(25), 28727-28737 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami. 0c09202
45. Z. Wu, K. Tian, T. Huang, W. Hu, F. Xie et al., Hierarchically porous carbons derived from biomasses with excellent microwave absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10(13), 11108-11115 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami. 7b17264
46. J. Cheng, L. Cai, Y. Shi, F. Pan, Y. Dong et al., Polarization loss-enhanced honeycomb-like
47. Y. Tian, D. Estevez, H. Wei, M. Peng, L. Zhou et al., Chitosanderived carbon aerogels with multiscale features for efficient microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 421, 129781 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129781
48. T. Li, D. Zhi, Y. Chen, B. Li, Z. Zhou et al., Multiaxial electrospun generation of hollow graphene aerogel spheres for broadband high-performance microwave absorption. Nano Res. 13(2), 477-484 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/ s12274-020-2632-0
49. X. Huang, X. Liu, Y. Zhang, J. Zhou, G. Wu et al., Construction of
50. H. Zhao, Y. Cheng, Z. Zhang, B. Zhang, C. Pei et al., Bio-mass-derived graphene-like porous carbon nanosheets towards ultralight microwave absorption and excellent thermal infrared properties. Carbon 173, 501-511 (2021). https://doi.org/10. 1016/j.carbon.2020.11.035
51. D. Zhi, T. Li, Z. Qi, J. Li, Y. Tian et al., Core-shell heterogeneous graphene-based aerogel microspheres for high-performance broadband microwave absorption via resonance loss and sequential attenuation. Chem. Eng. J. 433, 134496 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.134496
52. T. Zhao, Z. Jia, J. Liu, Y. Zhang, G. Wu et al., Multiphase interfacial regulation based on hierarchical porous molybdenum selenide to build anticorrosive and multiband tailorable absorbers. Nano-Micro Lett. 16, 6 (2023). https://doi.org/10. 1007/s40820-023-01212-4
53. A. Feng, D. Lan, J. Liu, G. Wu, Z. Jia, Dual strategy of a-site ion substitution and self-assembled
54. K. Qian, S. Li, J. Fang, Y. Yang, S. Cao et al.,
55. L. Yu, Q. Zhu, Z. Guo, Y. Cheng, Z. Jia et al., Unique electromagnetic wave absorber for three-dimensional framework engineering with copious heterostructures. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 170, 129-139 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2023. 06.024
56. H. Lv, Y. Yao, S. Li, G. Wu, B. Zhao et al., Staggered circular nanoporous graphene converts electromagnetic waves into electricity. Nat. Commun. 14, 1982 (2023). https://doi.org/ 10.1038/s41467-023-37436-6
57. S.H. Kim, S.Y. Lee, Y. Zhang, S.J. Park, J. Gu, Carbon-based radar absorbing materials toward stealth technologies. Adv.
58. X. Zhong, M. He, C. Zhang, Y. Guo, J. Hu et al., Heterostructured BN@Co-C@C endowing polyester composites excellent thermal conductivity and microwave absorption at C band. Adv. Funct. Mater. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/ adfm. 202313544
59. Y. Li, Y. Qing, Y. Zhang, H. Xu, Simultaneously tuning structural defects and crystal phase in accordion-like
60. X. Zeng, C. Zhao, X. Jiang, R. Yu, R. Che, Functional tailoring of multi-dimensional pure MXene nanostructures for significantly accelerated electromagnetic wave absorption. Small 19(41), 2303393 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll. 20230 3393
61. J. Zhou, D. Lan, F. Zhang, Y. Cheng, Z. Jia et al., Self-assembled
62. H. Cheng, Y. Pan, X. Wang, C. Liu, C. Shen et al., Ni flower/ MXene-melamine foam derived 3D magnetic/conductive networks for ultra-efficient microwave absorption and infrared stealth. Nano-Micro Lett. 14(1), 63 (2022). https://doi.org/10. 1007/s40820-022-00812-w
63. Z. Guo, P. Ren, J. Wang, X. Hou, J. Tang et al., Methylene blue adsorption derived thermal insulating N, S-co-doped TiC/ carbon hybrid aerogel for high-efficient absorption-dominant electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 451, 138667 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.138667
Xiaosi Qi, xsqi@gzu.edu.cn; Hualiang Lv, lv_hl@fudan.edu.cn
College of Physics, Guizhou Province Key Laboratory for Photoelectrics Technology and Application, Guizhou University, Guiyang City 550025, People’s Republic of China
College of Materials and Metallurgy, Guizhou University, Guiyang City 550025, People’s Republic of China
National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures and Jiangsu Provincial Laboratory for NanoTechnology, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, People’s Republic of China
Department of Materials Science and Laboratory of Advanced Materials, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, People’s Republic of China
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-024-01447-9
PMID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38884840
Publication Date: 2024-06-17
Nano-Micro Lett.
(2024) 16:221
Accepted: 18 May 2024
Published online: 17 June 2024
© The Author(s) 2024
Mixed-Dimensional Assembly Strategy to Construct Reduced Graphene Oxide/Carbon Foams Heterostructures for Microwave Absorption, Anti-Corrosion and Thermal Insulation
HIGHLIGHTS
- Reduced graphene oxide/carbon foams (RGO/CFs) vdWs heterostructures are efficiently fabricated via a simple mixed-dimensional assembly strategy.
- Linkage effect of optimized impedance matching and enhanced dielectric loss abilities endows the excellent microwave absorption performances of RGO/CFs vdWs heterostructures.
- Multiple functions such as good corrosion resistance performances and outstanding thermal insulation capabilities can be integrated into RGO/CFs vdWs heterostructures.
Abstract
Considering the serious electromagnetic wave (EMW) pollution problems and complex application condition, there is a pressing need to amalgamate multiple functionalities within a single substance. However, the effective integration of diverse functions into designed EMW absorption materials still faces the huge challenges. Herein, reduced graphene oxide/carbon foams (RGO/CFs) with two-dimensional/three-dimensional (2D/3D) van der Waals (vdWs) heterostructures were meticulously engineered and synthesized utilizing an efficient methodology involving freeze-drying, immersing absorption, secondary freeze-drying, followed by carbonization treatment. Thanks to their excellent linkage effect of amplified dielectric loss and optimized impedance matching, the designed 2D/3D RGO/CFs vdWs heterostructures demonstrated commendable EMW absorption  performances, achieving a broad absorption bandwidth of 6.2 GHz and a reflection loss of -50.58 dB with the low matching thicknesses. Furthermore, the obtained 2D/3D RGO/CFs vdWs heterostructures also displayed the significant radar stealth properties, good corrosion resistance performances as well as outstanding thermal insulation capabilities, displaying the great potential in complex and variable environments. Accordingly, this work not only demonstrated a straightforward method for fabricating 2D/3D vdWs heterostructures, but also outlined a powerful mixeddimensional assembly strategy for engineering multifunctional foams for electromagnetic protection, aerospace and other complex conditions.
performances, achieving a broad absorption bandwidth of 6.2 GHz and a reflection loss of -50.58 dB with the low matching thicknesses. Furthermore, the obtained 2D/3D RGO/CFs vdWs heterostructures also displayed the significant radar stealth properties, good corrosion resistance performances as well as outstanding thermal insulation capabilities, displaying the great potential in complex and variable environments. Accordingly, this work not only demonstrated a straightforward method for fabricating 2D/3D vdWs heterostructures, but also outlined a powerful mixeddimensional assembly strategy for engineering multifunctional foams for electromagnetic protection, aerospace and other complex conditions.
1 Introduction
the pure amorphous and bare crystalline, the designed composites exhibited an effective absorption bandwidth (EAB), which was attributed to heterointerface provided by different phase structures [16]. Similarly, Reza Peymanfar et al. and Zhang’s team successfully promoted the EMW absorption performances of
and wide bandwidth, perfect EMW absorbing materials with excellent stability and versatility to satisfy the everincreasing demands in the changeable practical environment will be a key research direction in the future. However, effectively incorporating the multiple functionalities including EMW absorption capability, heat protection, and resistant to corrosion into carbon materials still faces huge challenges so far.
2 Experimental Section
2.1 Fabrication of 3D Cellular Chitosan/g-C3
removed after the vacuum freeze-drying treatment to obtain 3D cellular CGFs.
2.2 Fabrication of 2D/3D GO/CGFs and RGO/CFs vdWs Heterostructures
2.3 Characterization
(XPS) and X-ray powder diffractometer (XRD) were successively carried out. To investigate EMW absorption properties, the obtained specimens ( 15,20 , and
3 Results and Discussion
3.1 Composition, Microstructure, EM and EMW Absorption Properties of RGO/CFs vdWs Heterostructures by Regulating Content of GO


low-density EMW absorbers [26], RGO/CFs vdWs heterostructures have a very low density of ca.
without any alteration of its external form, confirming the ultra-lightweight features of RGO/CFs heterostructures. Figure 1c shows the FIIR spectra of CGFs, G2/CGF, CFs, and R2/CF. The analysis of FIIR curves for CGFs and G2/ CGF reveals that the -OH peaks undergo an evident red shift from ca. 3430 to ca.

1.984-0.907, 9.385-4.695 and 4.019-2.370, 11.449-5.319 and 7.268-2.540. And the designed R2/CF sample presents much higher values of
effective modulation of EM parameters after incorporation of RGO. And their dielectric loss tangent values also indicate that the CFs and RGO/CFs present the steadily upward trend when the filling ratio increases from 15 to
values of CF s,

capabilities, broad EAB as well as small matching thicknesses, which is a super-duper novel EMW absorbers.
3.2 Impact of Thermal Treatment Temperature

bonds in graphite nanocrystals generate a 2D plane and thus decrease the electrical resistivity [47]. One can see that the Raman spectra are accorded with the above-mentioned XRD and XPS outcomes. Same to R2/CF, the SEM investigations reveal that both the obtained R2/CF-600 (Fig. 5d-f) and R2/ CF-700 (Fig. 5g-i) display the representative 2D/3D vdWs heterostructures in which 2D RGO nanosheets firm anchoring to 3D cellular structure, which implies that the influence of heat treatment temperature on the morphology can be ignored. In short, the content of graphitic carbon is modulated by regulating the heat treatment temperature, facilitating the optimization of their EM parameters and EMW absorption properties.

3.3 Analyses on the Difference in EMW Absorption Properties, Radar Cross Section Simulation and Possible EMW Absorption Mechanism

prove that most of EMW energy is effectively attenuated by 2D/3D RGO/CFs vdWs heterostructures. As compared in Fig. 7e, the obtained R2/CF sample exhibits the lowest RCS values (less than

3.4 Versatility and Possible Application Prospects
neutral and alkaline condition. Based on the above findings, the outstanding anti-corrosion performance should be attributed to the high physical/chemical stability of carbon materials, dense heterostructures and excellent hydrophobicity. And strong hydrophobicity of R2/CF (water contact angle up to ca.

4 Conclusions
Declarations
References
- J. Shu, Y. Wang, M. Cao, PEDOT:PSS-patched magnetic graphene films with tunable dielectric genes for electromagnetic interference shielding and infrared stealth. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 186, 28-36 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2023. 10.046
- M. He, J. Hu, H. Yan, X. Zhong, Y. Zhang et al., Shape anisotropic chain-like coni/polydimethylsiloxane composite films with excellent low-frequency microwave absorption and high thermal conductivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. (2024). https://doi. org/10.1002/adfm. 202316691
- H. Lv, J. Cui, B. Li, M. Yuan, J. Liu et al., Insights into civilian electromagnetic absorption materials: challenges and innovative solutions. Adv. Funct. Mater. (2024). https://doi.org/10. 1002/adfm. 202315722
- L. Yao, Y. Wang, J. Zhao, Y. Zhu, M. Cao, Multifunctional nanocrystalline-assembled porous hierarchical material and device for integrating microwave absorption, electromagnetic interference shielding, and energy storage. Small 19(25), 2208101 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll. 202208101
- R. Peymanfar, A. Mirkhan, Biomass-derived materials: promising, affordable, capable, simple, and lightweight microwave absorbing structures. Chem. Eng. J. 446, 136903 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.136903
- P. Liu, S. Gao, Y. Wang, Y. Huang, W. He et al., Carbon nanocages with N -doped carbon inner shell and
-doped carbon outer shell as electromagnetic wave absorption materials. Chem. Eng. J. 381, 122653 (2020). https://doi.org/10. 1016/j.cej.2019.122653 - R. Peymanfar, A. Ahmadi, E. Selseleh-Zakerin, A. Ghaffari, M.M. Mojtahedi et al., Electromagnetic and optical characteristics of wrinkled ni nanostructure coated on carbon microspheres. Chem. Eng. J. 405, 126985 (2021). https://doi.org/10. 1016/j.cej.2020.126985
- Z. Zhang, J. Wang, J. Shang, Y. Xu, Y.J. Wan et al., A throughthickness arrayed carbon fibers elastomer with horizontal segregated magnetic network for highly efficient thermal management and electromagnetic wave absorption. Small 19(4), 2205716 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll. 202205716
- L. Xiang, A.K. Darboe, Z. Luo, X. Qi, J.-J. Shao et al., Constructing two-dimensional/two-dimensional reduced graphene oxide/
and S van der Waals heterojunctions: a combined composition modulation and interface engineering strategy for microwave absorption. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 6, 215 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/ s42114-023-00793-3 - Y. Wu, Y. Zhao, M. Zhou, S. Tan, R. Peymanfar et al., Ultrabroad microwave absorption ability and infrared stealth property of nano-micro
lightweight aerogels.
11. Z. Wu, H.W. Cheng, C. Jin, B. Yang, C. Xu et al., Dimensional design and core-shell engineering of nanomaterials for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Mater. 34, 2107538 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma. 202107538
12. Y. Wang, Y. Yang, M. Miao, X. Feng, Carbon nanotube arrays@cobalt hybrids derived from metal-organic framework ZIF-67 for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. Mater. Today Phys. 35, 101110 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j. mtphys.2023.101110
13. J. Yan, Z. Ye, W. Chen, P. Liu, Y. Huang, Metal Mo and nonmetal N, S co-doped 3D flowers-like porous carbon framework for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 216, 118563 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2023.118563
14. M. Zhang, C. Han, W. Cao, M. Cao, H. Yang et al., A nanomicro engineering nanofiber for electromagnetic absorber, green shielding and sensor. Nano-Micro Lett. 13, 27 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-020-00552-9
15. B. Zhao, Y. Du, H. Lv, Z. Yan, H. Jian et al., Liquid-metalassisted programmed galvanic engineering of core-shell nanohybrids for microwave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33(34), 2302172 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm. 202302172
16. P. Wu, X. Kong, Y. Feng, W. Ding, Z. Sheng et al., Phase engineering on amorphous/crystalline
17. S. Seyedian, A. Ghaffari, A. Mirkhan, G. Ji, S. Tan et al., Manipulating the phase and morphology of
18. H. Zhang, J. Cheng, H. Wang, Z. Huang, Q. Zheng et al., Initiating VB-group laminated
19. J. Liu, L. Zhang, H. Wu, Anion-doping-induced vacancy engineering of cobalt sulfoselenide for boosting electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32(26), 2200544 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm. 202200544
20. L. Liang, W. Gu, Y. Wu, B. Zhang, G. Wang et al., Heterointerface engineering in electromagnetic absorbers: new insights and opportunities. Adv. Mater. 34(4), 2106195 (2021). https:// doi.org/10.1002/adma. 202106195
21. J. Wang, L. Liu, S. Jiao, K. Ma, J. Lv et al., Hierarchical carbon fiber@MXene@MoS2 core-sheath synergistic microstructure for tunable and efficient microwave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30(45), 2002595 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/ adfm. 202002595
22. Y. Zhao, X. Zuo, Y. Guo, H. Huang, H. Zhang et al., Structural engineering of hierarchical aerogels comprised of multidimensional gradient carbon nanoarchitectures for highly
efficient microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 13(1), 144 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00667-7
23. S. Wang, X. Zhang, S. Hao, J. Qiao, Z. Wang et al., Nitrogendoped magnetic-dielectric-carbon aerogel for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 16(1), 16 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-023-01244-w
24. S. Zhang, X. Liu, C. Jia, Z. Sun, H. Jiang et al., Integration of multiple heterointerfaces in a hierarchical 0D@2D@1D structure for lightweight, flexible, and hydrophobic multifunctional electromagnetic protective fabrics. Nano-Micro Lett. 15(1), 204 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-023-01179-2
25. X. Tang, C. Liu, X. Chen, Y. Deng, X. Chen et al., Graphene aerogel derived by purification-free graphite oxide for high performance supercapacitor electrodes. Carbon 146, 147-154 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.01.096
26. Y.Y. Wang, Z.H. Zhou, C.G. Zhou, W.J. Sun, J.F. Gao et al., Lightweight and robust carbon nanotube/polyimide foam for efficient and heat-resistant electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(7), 8704-8712 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami. 9b21048
27. X. Chen, M. Zhou, Y. Zhao, W. Gu, Y. Wu et al., Morphology control of eco-friendly chitosan-derived carbon aerogels for efficient microwave absorption at thin thickness and thermal stealth. Green Chem. 24(13), 5280-5290 (2022). https://doi. org/10.1039/d2gc01604d
28. W. Gu, J. Sheng, Q. Huang, G. Wang, J. Chen et al., Environmentally friendly and multifunctional shaddock peel-based carbon aerogel for thermal-insulation and microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 13(1), 102 (2021). https://doi.org/10. 1007/s40820-021-00635-1
29. R. Peymanfar, E. Selseleh-Zakerin, A. Ahmadi, Tailoring energy band gap and microwave absorbing features of graph-ite-like carbon nitride (
30. C. Wei, M. He, M. Li, X. Ma, W. Dang et al., Hollow Co/
31. L. He, F. Weniger, H. Neumann, M. Beller, Synthesis, characterization, and application of metal nanoparticles supported on nitrogen-doped carbon: catalysis beyond electrochemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55(41), 12582-12594 (2016). https:// doi.org/10.1002/anie. 201603198
32. J. Tao, L. Xu, C. Pei, Y. Gu, Y. He et al., Catfish effect induced by anion sequential doping for microwave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33(8), 2211996 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/ adfm. 202211996
33. L. Liang, Q. Li, X. Yan, Y. Feng, Y. Wang et al., Multifunctional magnetic
34. J. Xiao, B. Zhan, M. He, X. Qi, X. Gong et al., Interfacial polarization loss improvement induced by the hollow
engineering of necklace-like pan/carbon nanofibers for boosted microwave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. (2024). https://doi. org/10.1002/adfm. 202316722
35. X. Jiang, X. Zeng, Y. Ning, F. Hu, B. Fan, Construction of dual heterogeneous interface between zigzag-like Mo-MXene nanofibers and small CoNi@NC nanoparticles for electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Adv. Ceram. 12(8), 1562-1576 (2023). https://doi.org/10.26599/jac.2023.9220772
36. Z. Wu, X. Tan, J. Wang, Y. Xing, P. Huang et al., MXene hollow spheres supported by a C-Co exoskeleton grow MWCNTs for efficient microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 16, 107 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-024-01326-3
37. X. Huang, G. Yu, Y. Zhang, M. Zhang, G. Shao, Design of cellular structure of graphene aerogels for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 426, 131894 (2021). https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.cej.2021.131894
38. M. Qin, L. Zhang, H. Wu, Dielectric loss mechanism in electromagnetic wave absorbing materials. Adv Sci (Weinh) 9(10), e2105553 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/advs. 202105553
39. X. Zhang, K. Qian, J. Fang, S. Thaiboonrod, M. Miao et al., Synchronous deprotonation-protonation for mechanically robust chitin/aramid nanofibers conductive aerogel with excellent pressure sensing, thermal management, and electromagnetic interference shielding. Nano Res. 17(3), 2038-2049 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6189-6
40. Y. Li, X. Liu, X. Nie, W. Yang, Y. Wang et al., Multifunctional organic-inorganic hybrid aerogel for self-cleaning, heat-insulating, and highly efficient microwave absorbing material. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29(10), 1807624 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/ adfm. 201807624
41. Q. Liang, L. Wang, X. Qi, Q. Peng, X. Gong et al., Hierarchical engineering of
42. T. Hou, Z. Jia, Y. Dong, X. Liu, G. Wu, Layered 3D structure derived from MXene/magnetic carbon nanotubes for ultrabroadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 431, 133919 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021. 133919
43. J. Yan, Y. Wang, W. Liu, P. Liu, W. Chen, Two-dimensional metal organic framework derived nitrogen-doped graphenelike carbon nanomesh toward efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 643, 318-327 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2023.04.040
44. W. Gu, J. Tan, J. Chen, Z. Zhang, Y. Zhao et al., Multifunctional bulk hybrid foam for infrared stealth, thermal insulation, and microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(25), 28727-28737 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami. 0c09202
45. Z. Wu, K. Tian, T. Huang, W. Hu, F. Xie et al., Hierarchically porous carbons derived from biomasses with excellent microwave absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10(13), 11108-11115 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami. 7b17264
46. J. Cheng, L. Cai, Y. Shi, F. Pan, Y. Dong et al., Polarization loss-enhanced honeycomb-like
47. Y. Tian, D. Estevez, H. Wei, M. Peng, L. Zhou et al., Chitosanderived carbon aerogels with multiscale features for efficient microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 421, 129781 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129781
48. T. Li, D. Zhi, Y. Chen, B. Li, Z. Zhou et al., Multiaxial electrospun generation of hollow graphene aerogel spheres for broadband high-performance microwave absorption. Nano Res. 13(2), 477-484 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/ s12274-020-2632-0
49. X. Huang, X. Liu, Y. Zhang, J. Zhou, G. Wu et al., Construction of
50. H. Zhao, Y. Cheng, Z. Zhang, B. Zhang, C. Pei et al., Bio-mass-derived graphene-like porous carbon nanosheets towards ultralight microwave absorption and excellent thermal infrared properties. Carbon 173, 501-511 (2021). https://doi.org/10. 1016/j.carbon.2020.11.035
51. D. Zhi, T. Li, Z. Qi, J. Li, Y. Tian et al., Core-shell heterogeneous graphene-based aerogel microspheres for high-performance broadband microwave absorption via resonance loss and sequential attenuation. Chem. Eng. J. 433, 134496 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.134496
52. T. Zhao, Z. Jia, J. Liu, Y. Zhang, G. Wu et al., Multiphase interfacial regulation based on hierarchical porous molybdenum selenide to build anticorrosive and multiband tailorable absorbers. Nano-Micro Lett. 16, 6 (2023). https://doi.org/10. 1007/s40820-023-01212-4
53. A. Feng, D. Lan, J. Liu, G. Wu, Z. Jia, Dual strategy of a-site ion substitution and self-assembled
54. K. Qian, S. Li, J. Fang, Y. Yang, S. Cao et al.,
55. L. Yu, Q. Zhu, Z. Guo, Y. Cheng, Z. Jia et al., Unique electromagnetic wave absorber for three-dimensional framework engineering with copious heterostructures. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 170, 129-139 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2023. 06.024
56. H. Lv, Y. Yao, S. Li, G. Wu, B. Zhao et al., Staggered circular nanoporous graphene converts electromagnetic waves into electricity. Nat. Commun. 14, 1982 (2023). https://doi.org/ 10.1038/s41467-023-37436-6
57. S.H. Kim, S.Y. Lee, Y. Zhang, S.J. Park, J. Gu, Carbon-based radar absorbing materials toward stealth technologies. Adv.
58. X. Zhong, M. He, C. Zhang, Y. Guo, J. Hu et al., Heterostructured BN@Co-C@C endowing polyester composites excellent thermal conductivity and microwave absorption at C band. Adv. Funct. Mater. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/ adfm. 202313544
59. Y. Li, Y. Qing, Y. Zhang, H. Xu, Simultaneously tuning structural defects and crystal phase in accordion-like
60. X. Zeng, C. Zhao, X. Jiang, R. Yu, R. Che, Functional tailoring of multi-dimensional pure MXene nanostructures for significantly accelerated electromagnetic wave absorption. Small 19(41), 2303393 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll. 20230 3393
61. J. Zhou, D. Lan, F. Zhang, Y. Cheng, Z. Jia et al., Self-assembled
62. H. Cheng, Y. Pan, X. Wang, C. Liu, C. Shen et al., Ni flower/ MXene-melamine foam derived 3D magnetic/conductive networks for ultra-efficient microwave absorption and infrared stealth. Nano-Micro Lett. 14(1), 63 (2022). https://doi.org/10. 1007/s40820-022-00812-w
63. Z. Guo, P. Ren, J. Wang, X. Hou, J. Tang et al., Methylene blue adsorption derived thermal insulating N, S-co-doped TiC/ carbon hybrid aerogel for high-efficient absorption-dominant electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 451, 138667 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.138667
Xiaosi Qi, xsqi@gzu.edu.cn; Hualiang Lv, lv_hl@fudan.edu.cn
College of Physics, Guizhou Province Key Laboratory for Photoelectrics Technology and Application, Guizhou University, Guiyang City 550025, People’s Republic of China
College of Materials and Metallurgy, Guizhou University, Guiyang City 550025, People’s Republic of China
National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures and Jiangsu Provincial Laboratory for NanoTechnology, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, People’s Republic of China
Department of Materials Science and Laboratory of Advanced Materials, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, People’s Republic of China
