DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-92108-3
PMID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40025120
تاريخ النشر: 2025-02-28
تقارير علمية
افتح
التنقيب الجيوفيزيائي المتكامل للكشف عن المعادن العميقة في منطقة تعدين الذهب يونغشين، هيلونغجيانغ، الصين
الملخص
تلعب تقنيات الاستكشاف الجيوفيزيائي دورًا محوريًا في تعزيز دقة توقعات التنقيب عن المعادن. ومع ذلك، فإن الاعتماد فقط على طرق فردية غالبًا ما يقدم عدم اليقين. تقدم هذه الدراسة دراسة حالة من رواسب الذهب في يونغشين، حيث قمنا بدمج طرق المغناطيسية الصوتية (AMT) مع المسح الجاذبي والتصوير المغناطيسي عالي الدقة للتغلب على هذا التحدي. تم استخدام تقنيات النمذجة ثلاثية الأبعاد المتقدمة لتحديد التغيرات الصخرية وخصائص التمعدن العميقة الموجودة في المنطقة بدقة. قدمت عملية عكس وتفسير بيانات AMT العرضية رؤى حول الهيكل تحت السطحي حتى عمق 1.5 كم. تم تحقيق موثوقية البيانات المعززة من خلال تفسير متكامل مقيد ببيانات متعددة، مما أتاح استنتاجًا أكثر دقة للإطار الجيولوجي الأعمق. علاوة على ذلك، من خلال دمج مجموعات بيانات متنوعة، اكتشفنا خصائص التمعدن العميق، والتكوين ثلاثي الأبعاد للكتل الصخرية المرتبطة بالتمعدن، والتوجه المكاني لرواسب الخام المعروفة. سهل هذا النهج الشامل فهمًا كاملاً للتكوينات الجيولوجية الأعمق. أدت التحليلات التفصيلية للهياكل المسيطرة على الخام وعلامات الاستكشاف إلى تطوير نموذج جيولوجي-جيوفيزيائي مصمم خصيصًا للتنقيب عن المعادن داخل منطقة الدراسة، مما يمثل مرجعًا قيمًا لجهود الاستكشاف العميق المستقبلية.
الإعداد الجيولوجي الجيولوجيا الإقليمية
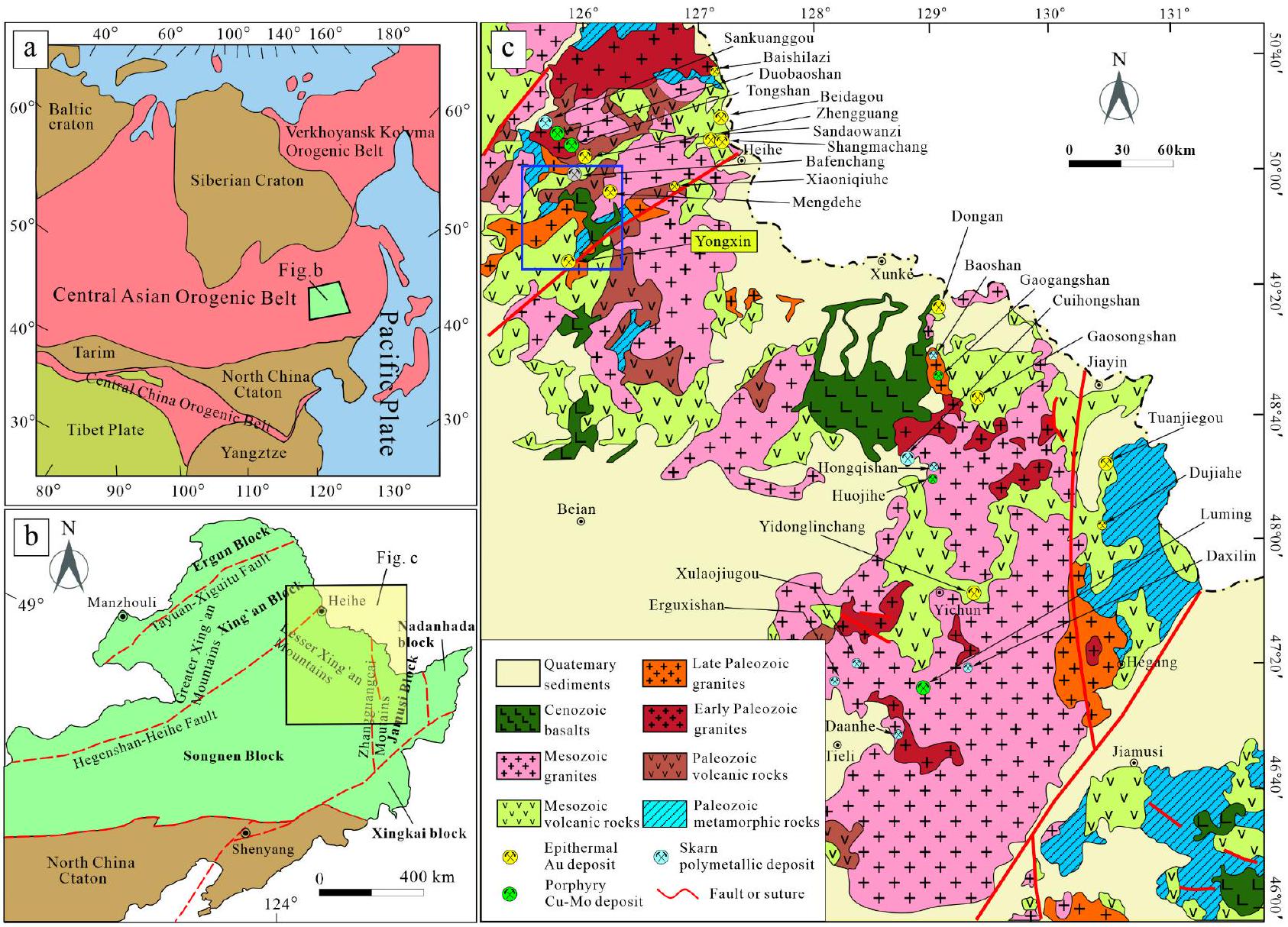
جيولوجيا رواسب الخام
طرق تحليلية
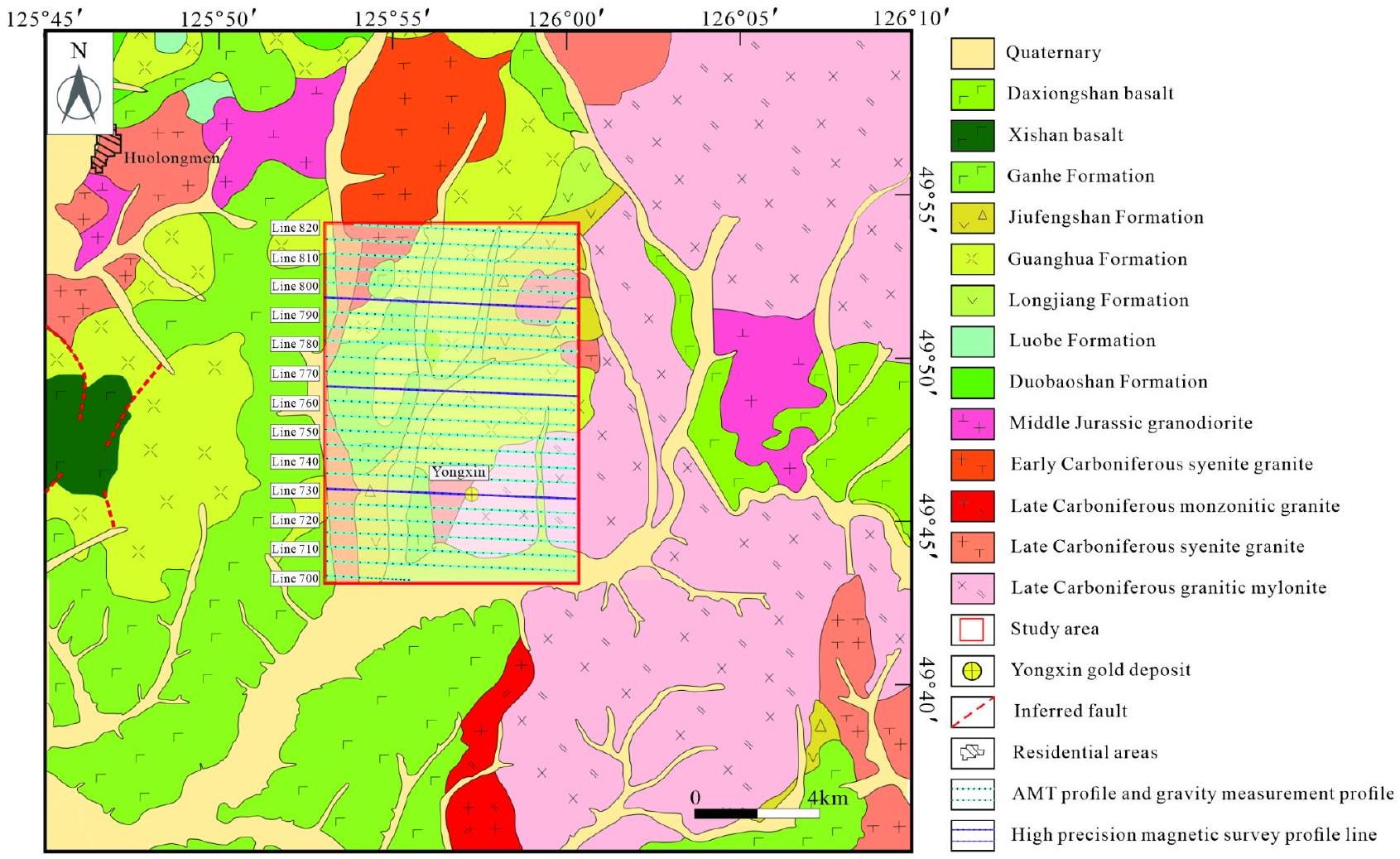
النتيجة
الخصائص الفيزيائية
| نوع | الصخور | المقاومية (
|
النفاذية المغناطيسية (10-5 SI) | الكثافة (
|
|||
| نطاق التباين | القيمة المتوسطة | نطاق التباين | القيمة المتوسطة | نطاق التباين | القيمة المتوسطة | ||
| صخر متداخل | جرانوديوريت من العصر الجوراسي الأوسط | ٣٤٣٥.٤-١٤٩٧٧.٩ | ٥١٧٨.٤ | 80.0-357.0 | 224.5 | 2.4-2.8 | 2.6 |
| جرانيت مونزونيتي من أواخر العصر الكربوني | 1183.5-25,096.5 | 5880.8 | 42.0-772.0 | 431.8 | 2.4-2.7 | 2.6 | |
| سيينوجرانيت من أواخر العصر الكربوني | ٣٤٣.٧-٣٣,٢٣٢.٧ | ٥٩٢١.٨ | ٢٠.٠-٤٨٠.٠ | ٢٢٣.٠ | 2.4-2.6 | 2.6 | |
| ميوليت جرانيتية من أواخر العصر الكربوني | 1922.9-8214.9 | ٤٠٩٠.٣ | 4.0-299.0 | ٣٥.٤ | 2.3-2.7 | 2.5 | |
| ديوريت منتصف الأورودوفيشي | 436.3-20,533.5 | 6118.2 | ٢٧.٠-٢٥٦٤.٠ | ١٠٣١.٢ | 2.5-2.9 | ٢.٧ | |
| طبقة | بازلت تشكيل غاني | 83.5-57,754.7 | 5773.6 | ٣٨٧.٠-٢٠٥٩.٠ | 865.0 | 2.1-2.7 | 2.6 |
| ريولايت تشكيل جوانغوا | 888.5-4826.0 | ٢٨٥٧.٣ | 13.0-554.0 | ١٤٥.٦ | 2.1-2.7 | 2.5 | |
| تكوين جيوفنغشان التوف الحمضي المتوسط | 118.4-5877.9 | 1485.7 | 40.0-235.0 | 100.6 | 2.3-2.9 | 2.6 | |
| انديسايت تشكيل لونغجيانغ | 795.7-3745.7 | 1875.7 | – | – | 2.08-2.63 | ٢.٤ | |
| رملية تشكيل لوخه | 706.5-31,699.2 | 5400.3 | 12.0-481.0 | ٨٨.٢ | 2.2-2.6 | ٢.٤ | |
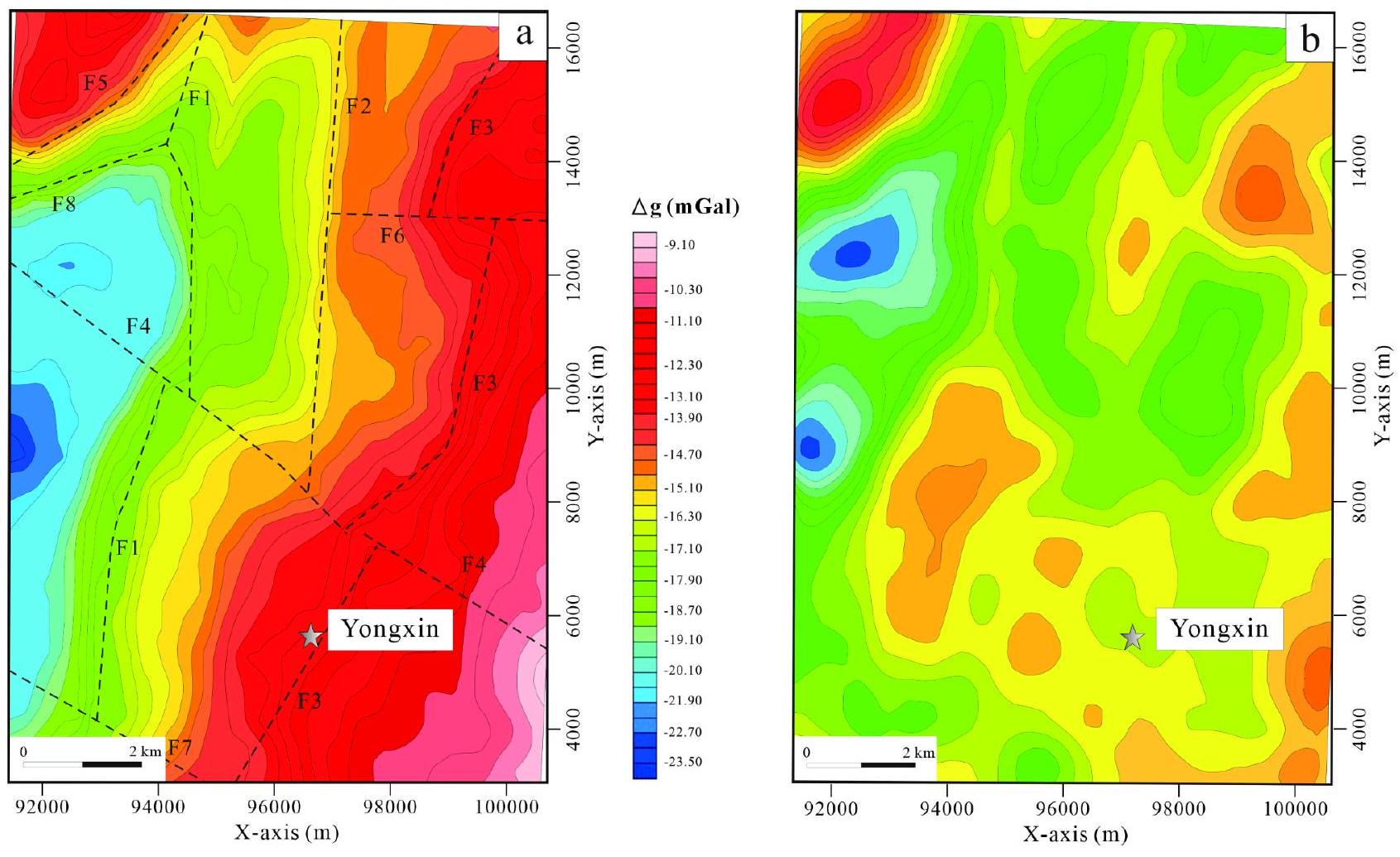
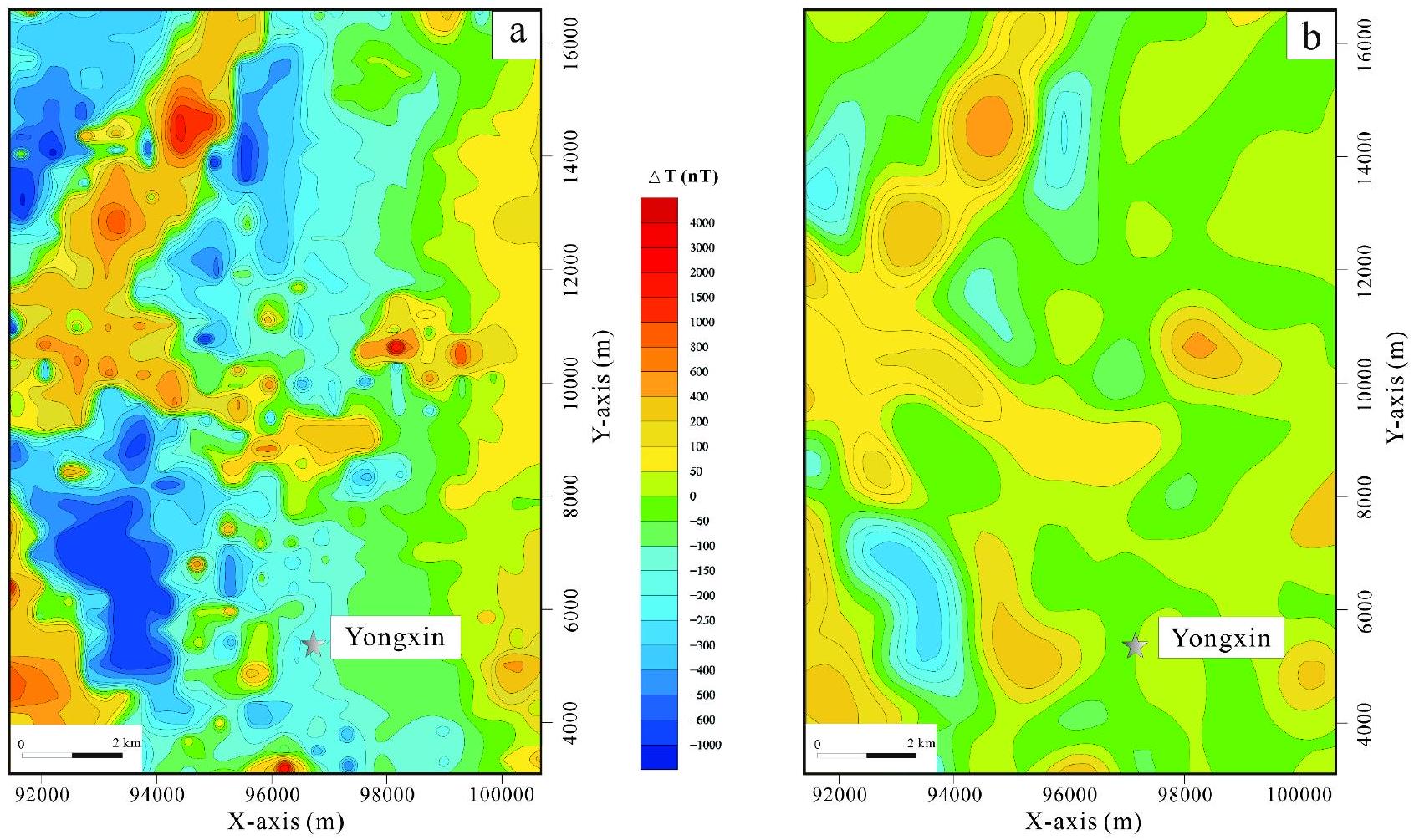
خصائص الشذوذ الجاذبي الإقليمي
خصائص الشذوذ المغناطيسي الإقليمي
الميزات الجيولوجية المتكاملة لملفات AMT
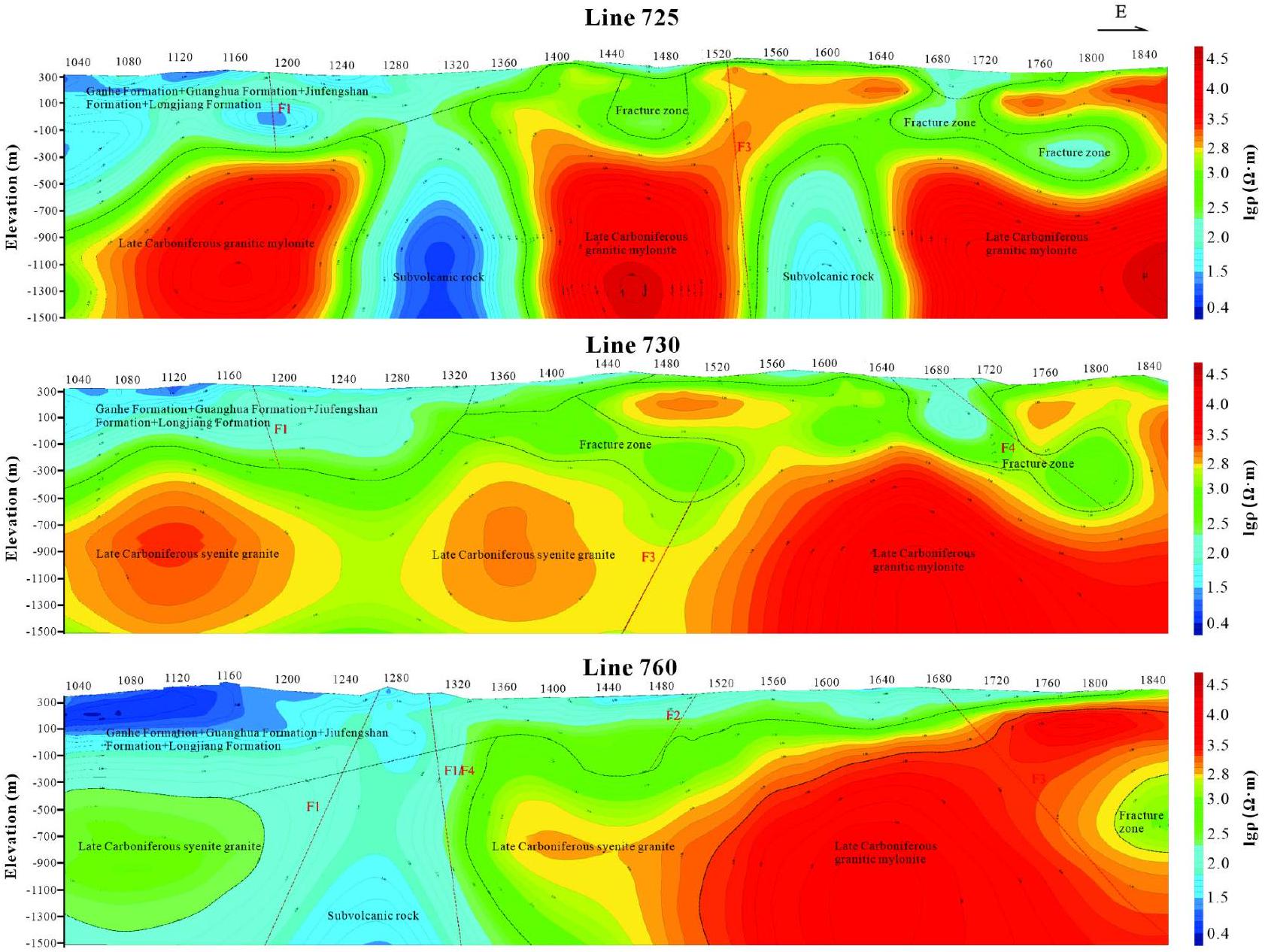
نقاش
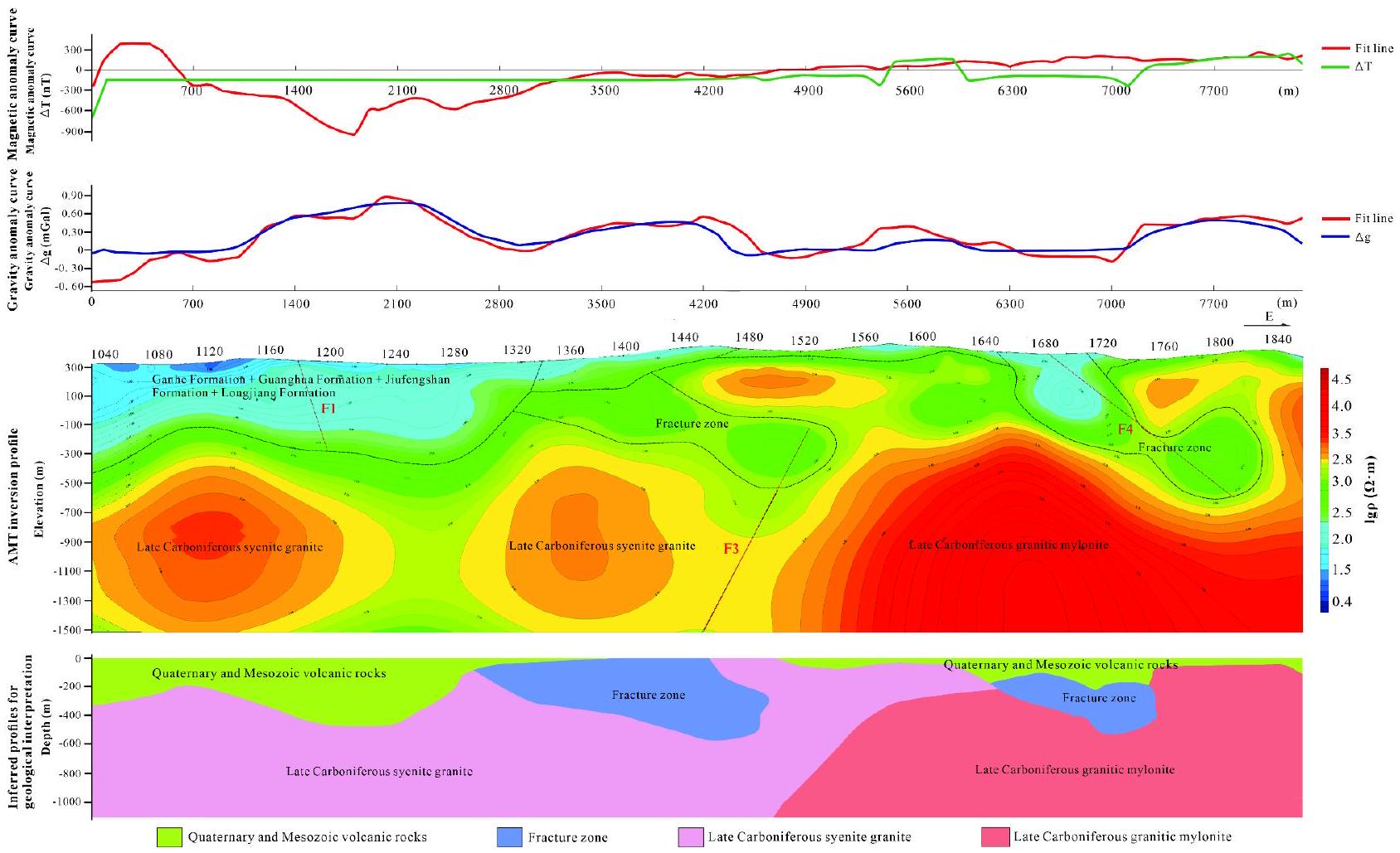
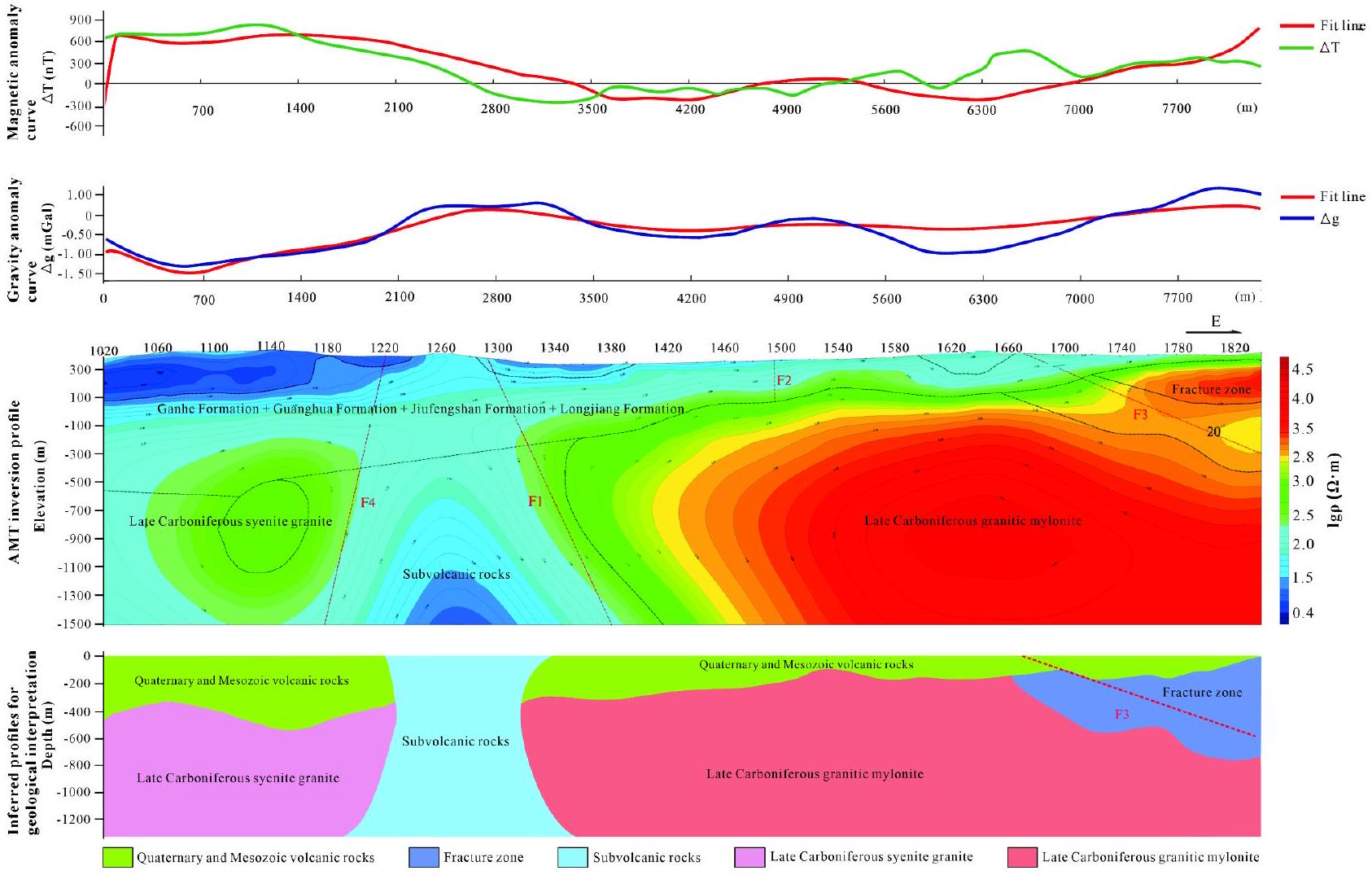
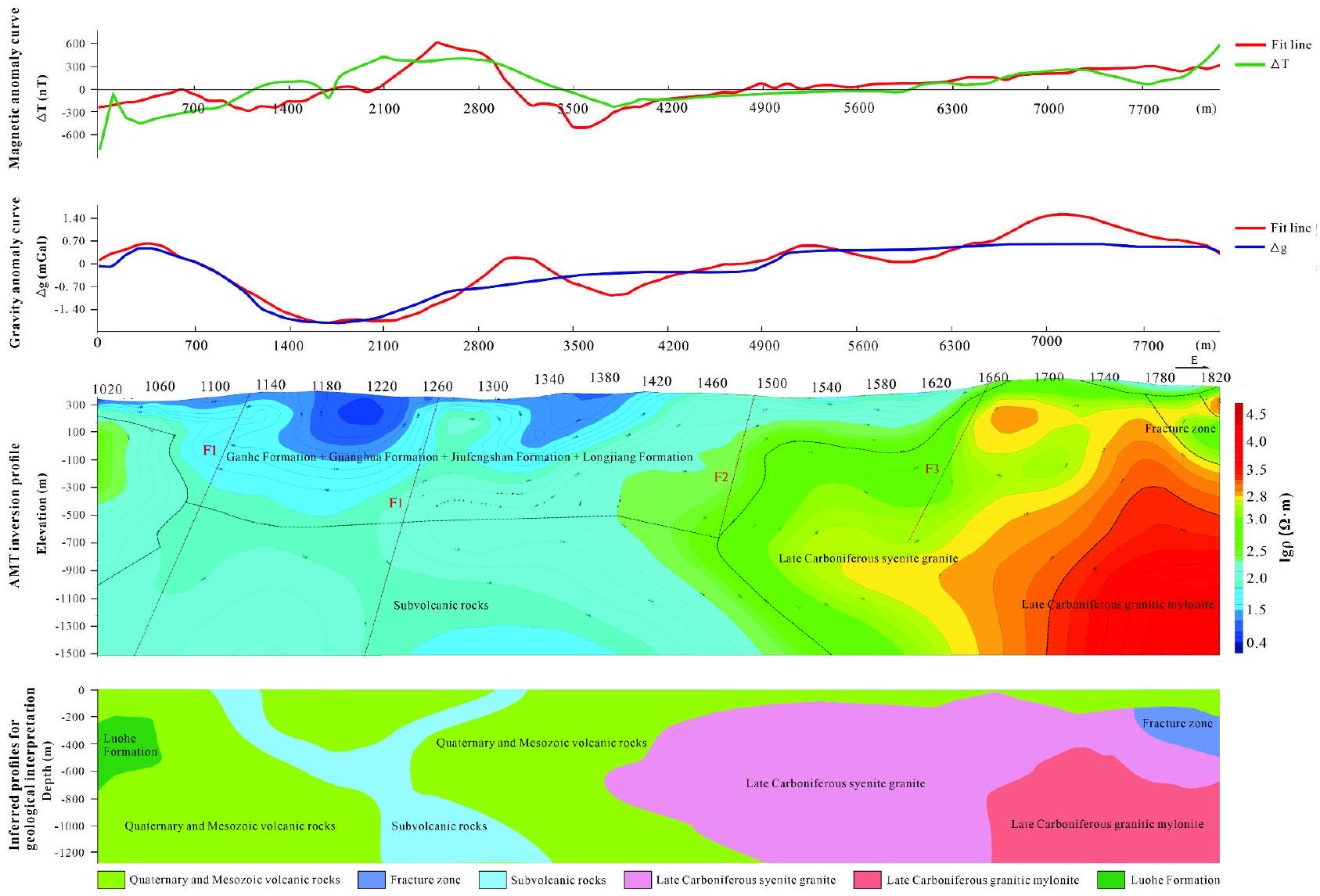
الانعكاس المشترك للبيانات الجاذبية والمغناطيسية والكهربائية
تضمن توافقًا مثاليًا للمعلمات لكل من الشذوذ النظري والمقاس، بينما يتوافق متوسط مربع الخطأ لنتائج المحاكاة مع متطلباتنا المستهدفة
تحليل الظروف الملائمة للتعدين
(1) الظروف الجيولوجية. يكشف النموذج الجيولوجي-الفيزيائي لمنطقة دراستنا عن طبقات تمتد عبر العصور الحديثة (سينوزوي) والوسطى (ميزوزوي) والقديمة (باليزوئي). تعمل الطبقات الحديثة والوسطى، بما في ذلك الرواسب النهرية وتكوينات مثل جوانغhua، لونغجيانغ، غانخه، وجيوفينغشان، كطبقات تغطية.
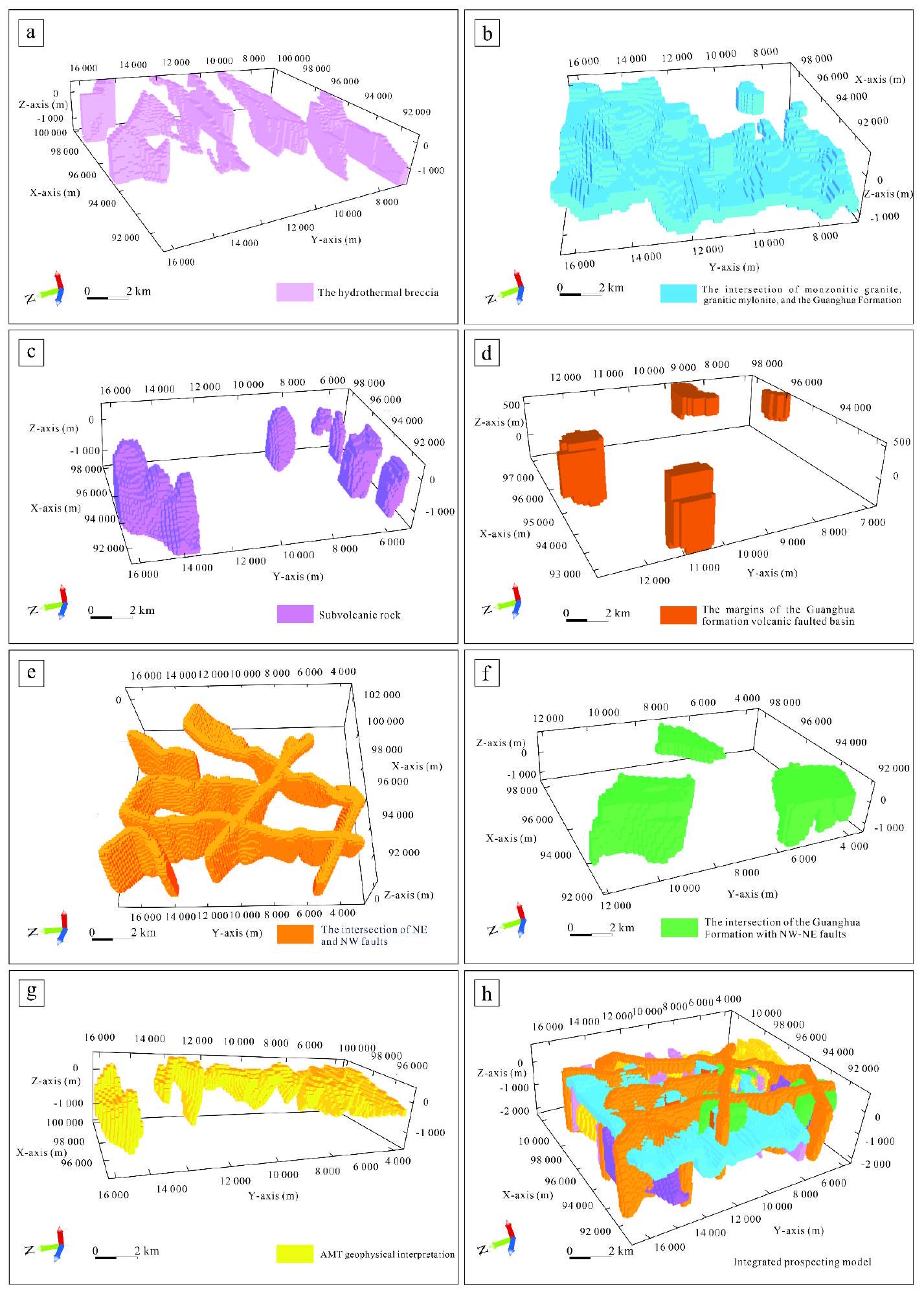
| أنواع رواسب المعادن | عوامل مواتية للتعدين | متغيرات الميزة |
| إيداع الذهب الإيبيثيرمال | ميزات جيولوجية ملائمة | الخرسانة الهيدروحرارية (الشكل 9أ) |
| تقاطع الجرانيت المونزونيتي، والجرانيت المايلونيت، وتكوين جوانغhua (الشكل 9ب) | ||
| صخور تحت بركانية (الشكل 9ج) | ||
| هوامش حوض غوانغوا التكتوني البركاني (الشكل 9د) | ||
| هياكل التمعدن المواتية | تقاطع الفوالق الشمالية الشرقية والشمالية الغربية (الشكل 9e) | |
| تقاطع تشكيل جوانغوا مع الفوالق NW-NE (الشكل 9f) | ||
| خصائص جيولوجية جغرافية ملائمة للتعدين | تفسير الجيوفيزياء AMT (الشكل 9g) |
(3) الظروف الجيوفيزيائية ونموذج الاستكشاف المتكامل. تم تحديد سبعة شذوذات جاذبية من خلال المسوحات الجاذبية والمغناطيسية. تحدث هذه الشذوذات بشكل أساسي في منطقة الاتصال بين الصخور البركانية والبركانية تحت السطحية من العصر الوسيط والشيرتات الجرانوديوريتية من العصر الكربوني المتأخر، والتي يمكن ملاحظتها في مناطق التدرج أو المناطق ذات الكثافة المغناطيسية المنخفضة.
تنبؤ التمعدن
الاستنتاجات
(2) يدمج هذا البحث بشكل مبتكر بين قياسات المغناطيسية الصوتية (AMT) والاستطلاعات الجاذبية والتصوير المغناطيسي العالي، مستفيدًا من تقنيات النمذجة ثلاثية الأبعاد لتحديد التغيرات الصخرية والميزات الجيولوجية العميقة التي تشكل خامات في منطقة الدراسة بشكل فعال. تُظهر هذه الطريقة أسلوب تفسير شامل وفعال للغاية.
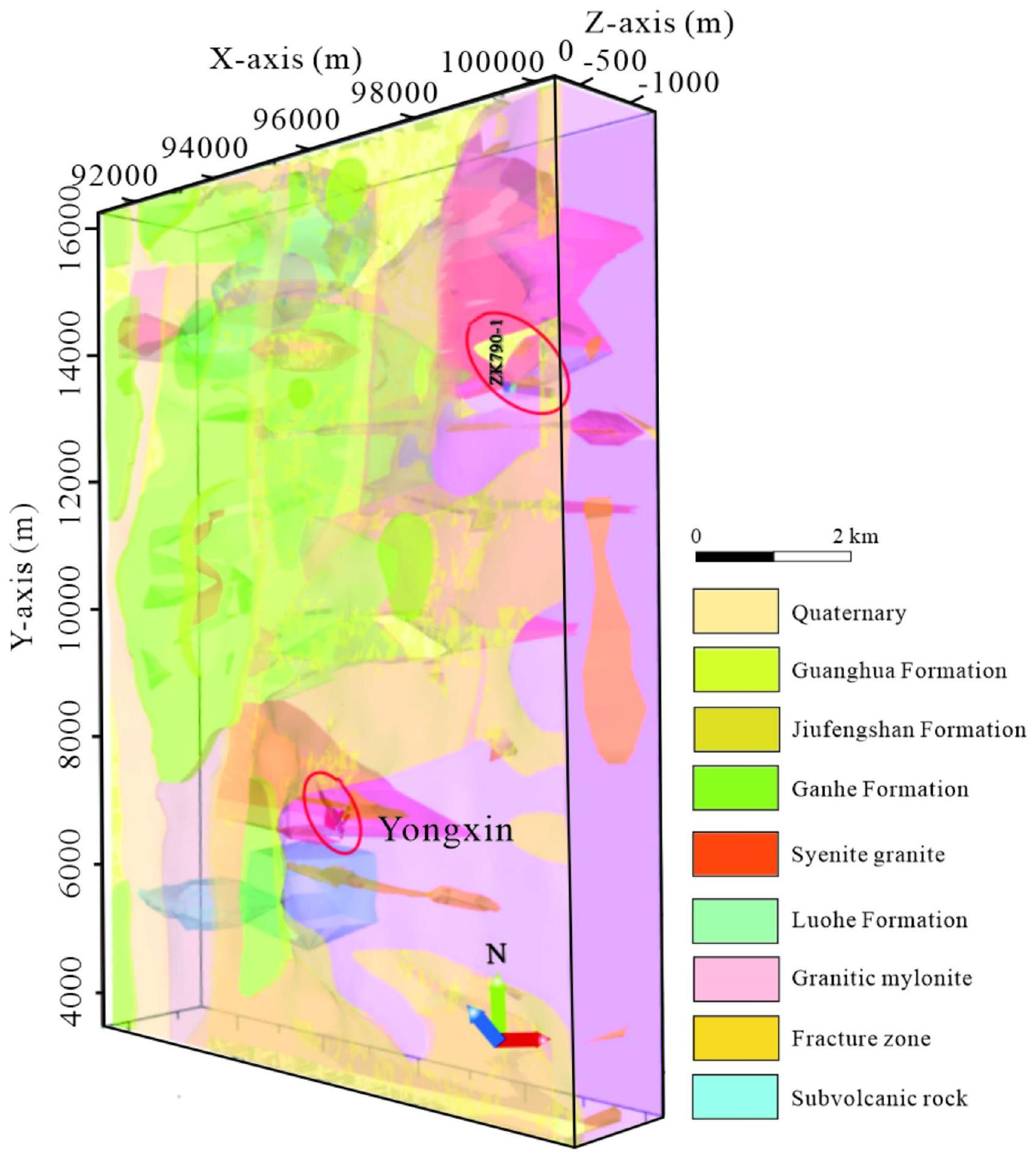
(3) من خلال بناء نموذج جيولوجي ثلاثي الأبعاد، حققنا “شفافية” الهيكل الجيولوجي ضمن نطاق عمق يبلغ 1.5 كم في منطقة الدراسة. من خلال دمج الظروف الجيولوجية المكونة للخامات مع نتائج التفسير الجيوفيزيائي، قمنا بتلخيص ظروف التمعدن المواتية لمنطقة تعدين الذهب يونغشين وطورنا نموذجًا شاملًا لاستكشاف الخامات. وقد أكدت التحقق من الحفر بنجاح على تحديد مناطق متعددة متمعدنة في العمق، مما يؤكد التآزر بين الاستكشاف الجيوفيزيائي المتكامل.
توفر البيانات
تم النشر عبر الإنترنت: 01 مارس 2025
References
- Bellefleur, G., de Kemp, E., Goutier, J., Allard, M. & Adam, E. Seismic imaging of the geologic framework and structures related to volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits in the Archean Rouyn-Noranda District, Quebec Canada. Econ. Geol. 109, 103-119 (2014).
- Liu, S. F. et al. Adoption of a mineral system model in successful deep exploration at Erdaogou, China’s deepest gold mine, on the northeastern margin of the North China Craton. Ore Geol. Rev. 131, 104060 (2021).
- Han, S. et al. Integrated geophysical exploration of the coupling of a concealed rock body and metallogenic structures-
mining area case study in Jilinbaolige, Inner Mongolia. China. J. Appl. Geophys. 178, 104048 (2020). - Ogah, A. J. & Abubakar, F. Solid mineral potential evaluation using integrated aeromagnetic and aeroradiometric datasets. Sci. Rep. 14, 1637 (2024).
- Olierook, H. K. H. et al. Emplacement of the Argyle diamond deposit into an ancient rift zone triggered by supercontinent breakup. Nat. Commun. 14, 5274 (2023).
- Yang, J., Liu, S. & Hu, X. Inversion of high-amplitude magnetic total field anomaly: An application to the Mengku iron-ore deposit, northwest China. Sci. Rep. 10, 11949 (2020).
- Zhang, G. et al. Joint interpretation of geological, magnetic, AMT, and ERT data for mineral exploration in the northeast of Inner Mongolia, China. Pure Appl. Geophys. 175, 989-1002 (2017).
- Lahti, I., Kontinen, A. & Nykänen, V. AMT survey in the Outokumpu ore belt, eastern Finland. Explor. Geophys. 50, 351-363 (2019).
- Cushing, E. M. et al. Building a three dimensional model of the active Plio-Quaternary basin of Argostoli (Cephalonia Island, Greece): An integrated geophysical and geological approach. Eng. Geol. 265, 105441 (2020).
- Qi, G., Meng, G. X., Yan, J. Y., Tang, H. J. & Xue, R. H. Three-dimensional geological-geophysical modeling and prospecting indications of the ashele ore concentration area in Xinjiang based on irregular sections. Minerals 13, 984 (2023).
- Anderson, E. D. et al. Geophysical data provide three dimensional insights into porphyry copper systems in the Silverton caldera, Colorado, USA. Ore Geol. Rev. 152, 105223 (2023).
- Eldougdoug, A. et al. Exploring gold mineralization in altered ultramafic rocks in south Abu Marawat, Eastern Desert, Egypt. Sci. Rep. 13, 7293 (2023).
- Tominaga, M. et al. Multi-scale magnetic mapping of serpentinite carbonation. Nat. Commun. 8, 1870 (2017).
- Wang, Q. Y., Liu, H. D., Chen, J. P., Wang, L. J. & Zhu, D. C. 3D geological modeling and metallogenic prognosis of Jiaojia gold metallogenic belt in Shandong. J. Geol. 38, 412-420 (2014).
- Zheng, X. M., Ni, J. C., Guo, G., Fang, W. X. & Wang, H. W. Application of audio frequency magnetotelluric sounding in 3D geological modeling in Hongshishan ophiolitic melange belt Gansu. Miner. Explor. 12, 1602-1609 (2021).
- Wang, L. et al. Geology and genesis of the Early Paleozoic Zhengguang intermediate-sulfidation epithermal Au-Zn deposit, northeast China. Ore Geol. Rev. 124, 103602 (2020).
- Zhang, A. Q. et al. Lithosphere-asthenosphere interactions beneath northeast China and the origin of its intraplate volcanism. Geology 50, 210-215 (2021).
- Wu, F. Y. et al. The Heilongjiang Group: A Jurassic accretionary complex in the Jiamusi Massif at the western Pacific margin of northeastern China. Island Arc 16, 156-172 (2007).
- Gong, M. Y., Tian, W., Fu, B., Wang, S. Y. & Dong, J. L. Zircon Hf-O isotopic constraints on the origin of Late Mesozoic felsic volcanic rocks from the Great Xing’an Range, NE China. Lithos 308, 412-427 (2018).
- Zhang, L. S. et al. Petrogenesis and tectonic settingof granitoids in the Fuanpu molybdenum deposit, Lesser Xing ar-Zhangguangcai range metallogenic belt: Constraints from element geochemistry, zircon U-Pb geochronology and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes. Acta Geol. Sin. 95, 2471-2492 (2021).
- Shu, Q. H., Chang, Z. S. & Mavrogenes, J. Fluid compositions reveal fluid nature, metal deposition mechanisms, and mineralization potential: An example at the Haobugao Zn-Pb skarn, China. Geology 49, 473-477 (2021).
- Mao, J. W. et al. Mesozoic large-scale metallogenic pulses in North China and corresponding geodynamic settings. Acta Petrol. Sin. 21, 171-190 (2005).
- Xu, M. J., Xu, W. L., Wang, F., Gao, F. H. & Yu, J. J. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Early Jurassic granitoids in the central Lesser Xing’an Range, NE China and its tectonic implications. Acta Petrol. Sin. 29, 354-368 (2013).
- Shu, Q. H. et al. Regional metallogeny of Mo-bearing deposits in northeastern China, with new Re-Os dates of porphyry Mo deposits in the northern Xilamulun district. Econ. Geol. 111, 1783-1798 (2016).
- Shu, Q. H. et al. Zircon trace elements and magma fertility: insights from porphyry (-skarn) Mo deposits in NE China. Miner. Depos. 54, 645-656 (2019).
- Xing, K., Shu, Q. H. & Lentz, D. R. Constraints on the formation of the giant Daheishan porphyry Mo deposit (NE China) from whole-rock and accessory mineral geochemistry. J. Petrol. 62, 1-26 (2021).
- Cheng, G. H. et al. Zircon U-Pb ages, Hf isotopes of the granitoids and Re-Os ages of the molybdenites in Luming molybdenum ore area, Heilongjiang Province, and its geological significance. Acta Petrol. Sin. 31, 2450-2464 (2015).
- Zhai, D. G. et al. The genesis of the giant Shuangjianzishan epithermal Ag-Pb-Zn deposit, Inner Mongolia, Northeastern China. Econ. Geol. 115, 101-128 (2020).
- Zhang, C. P. et al. Geochronology and isotope geochemistry studies of an epithermal gold deposit in the northern Lesser Khingan Range, NE China: The Gaosongshan example. Ore Geol. Rev. 105, 356-374 (2019).
- Liu, Y. et al. Origin and evolution of ore-forming fluid for the Gaosongshan gold deposit, Lesser Xing’an Range: Evidence from fluid inclusions, H-O-S-Pb isotopes. Geosci. Front. 10, 1961-1980 (2019).
- Zhao, Z. H. et al. Age of the Yongxin Au deposit in the Lesser Xing’an Range: Implications for an Early Cretaceous geodynamic setting for gold mineralization in NE China. Geol. J. 54, 2525-2544 (2019).
- Zhao, Z. H. et al. Genesis of the Yidonglinchang gold deposit, Lesser Xing’an Range, China: Insights from fluid inclusions, H-O-SPb isotopes, and
and geochronology. Ore Geol. Rev. 163 (2023). - Zhao, Z. H. et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic constraints on the timing and origin of the Early Cretaceous igneous rocks in the Yongxin gold deposit in the Lesser Xing’an Range, NE China. Geol. J. 55, 2684-2703 (2019).
- Yuan, M. W. et al. Geochemical and isotopic composition of auriferous pyrite from the Yongxin gold deposit, Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Implication for ore genesis. Ore Geol. Rev. 93, 255-267 (2018).
- Pitiya, R. et al. Audio magnetotellurics study of the geoelectric structure across the Zhugongtang giant lead-zinc deposit, NW Guizhou Province, China. Minerals 12 (2022).
- Singh, S. et al. Audio-magnetotelluric investigation of sulfide mineralization in Proterozoic-Archean greenstone belts of Eastern Indian Craton. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 127 (2018).
- Ugbor, C. C., Arinze, I. J. & Emedo, C. O. Analysis of aeromagnetic data of Ikwo and Environs, Southeastern Nigeria: A mineral and hydrocarbon exploration guide. Nat. Resour. Res. 29, 2915-2932 (2020).
- Di Paolo, F. et al. La Palma island (Spain) geothermal system revealed by 3D magnetotelluric data inversion. Sci. Rep. 10, 18181 (2020).
- Darabi-Golestan, F., Ghavami-Riabi, R., Khalokakaie, R., Asadi-Haroni, H. & Seyedrahimi-Nyaragh, M. Interpretation of lithogeochemical and geophysical data to identify the buried mineralized area in Cu-Au porphyry of Dalli-Northern Hill. Arab. J. Geosci. 6, 4499-4509 (2012).
- Maharaj, D., Elbra, T. & Pesonen, L. J. Physical properties of the drill core from the Elgygytgyn impact structure, NE Russia. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 48, 1130-1142 (2013).
- Zhang, R. Z. et al. 3-D joint inversion of gravity and magnetic data using data-space and truncated Gauss-Newton methods. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 19, 1-5 (2022).
- Li, W. B., Qian, J. L. & Li, Y. G. Joint inversion of surface and borehole magnetic data: A level-set approach. Geophysics 85, 15-32 (2020).
- Xiao, B. et al. Rare earth element characteristics of shales from Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in deep-buried areas of the Northern Sichuan Basin, Southern China: Implications for provenance, depositional conditions, and paleoclimate. ACS Omega 9, 2088-2103 (2024).
- Vatankhah, S., Renaut, R. A., Huang, X. G., Mickus, K. & Gharloghi, M. Large-scale focusing joint inversion of gravity and magnetic data with Gramian constraint. Geophys. J. Int. 230, 1585-1611 (2022).
- Zhang, S. et al. A facile approach to ultralight and recyclable 3D self-assembled copolymer/graphene aerogels for efficient oil/water separation. Sci. Total Environ. 694, 133671 (2019).
- Yang, Z. W., Tan, H. D., Peng, M., Kong, W. X. & Wu, P. P. Three-dimensional joint inversion of gravity, magnetic and magnetotelluric data based on cross-gradient theory. Chin. J. Geophys. Chin. Ed. 63, 736-752 (2020).
- Li, C. L. et al. Study on pyrite thermoelectricity, ore-forming fluids and H-O-Rb-Sr isotopes of the Yongxin gold deposit, Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Implications for ore genesis and exploration. Ore Geol. Rev. 121 (2020).
- Behrendt, J. C. The aeromagnetic method as a tool to identify Cenozoic magmatism in the West Antarctic Rift System beneath the West Antarctic Ice Sheet-A review; Thiel subglacial volcano as possible source of the ash layer in the WAISCORE. Tectonophysics 585, 124-136 (2013).
- Ross, P. S. et al. High-resolution physical properties, geochemistry, and alteration mineralogy for the host rocks of the Archean Lemoine auriferous volcanogenic massive sulfide deposit, Canada. Econ. Geol. 111, 1561-1574 (2016).
- Caballero-Miranda, C. I. et al. Vertical AMS variation within basalt flow profiles from the Xitle volcano (Mexico) as indicator of heterogeneous strain in lava flows. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 311, 9-28 (2016).
- Sakr, S. M., Bamousa, A. O., Gougazeh, M. H. & Zaman, H. Petromagnetic investigations of the volcanic rocks in southern part of Al-Madinah, Saudi Arabia: Differentiation of different lava types. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 14, 1009-1022 (2020).
- Liang, K. W., Zhao, Z. H. & Guo, Y. Application of primary halo in deep metallogenic prediction: A case study of Yongxin gold deposit in Heihe Area. Geol. Resour. 28, 512-518 (2019).
- Li, C. L. et al. Discovery and geological significance of gold-silver bearing minerals and tellurides in the Yongxin gold deposit in the northeastern Great Xing’an Range. Earth Sci. Front. 27, 244-254 (2020).
- Deng, C. Z. et al. Geochemistry of Early Cretaceous volcanic rocks in the Northeastern Great Xing’an Range, northeast China and implication for geodynamic setting. Int. Geol. Rev. 61, 1594-1612 (2018).
- Liu, R. P. et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and petrogeochemistry of host igneous rocks of the Dong’an gold deposit in Heilongjiang Province, NE China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 31, 1391-1408 (2015).
- Zhang, M. M. et al. Tellurium and gold enrichment aided by melts and pyrite crystallization kinetics: Insights from the Yongxin gold deposit, northeast China. Ore Geol. Rev. 156, 105370 (2023).
- Zhao, Z. H. et al. Early Cretaceous gold mineralization in the Lesser Xing’an Range of NE China: The Yongxin example. Int. Geol. Rev. 61, 1522-1548 (2018).
الشكر والتقدير
مساهمات المؤلفين
الإعلانات
المصالح المتنافسة
معلومات إضافية
معلومات إعادة الطبع والتصاريح متاحة على www.nature.com/reprints.
ملاحظة الناشر تظل Springer Nature محايدة فيما يتعلق بالمطالبات القضائية في الخرائط المنشورة والانتماءات المؤسسية.
© المؤلفون 2025
كلية التعدين، جامعة لياونينغ التقنية، فوكسي، لياونينغ 123000، الصين. مختبر لياونينغ الرئيسي للتنمية الخضراء للموارد المعدنية، LNTU، فوكسي، لياونينغ 123000، الصين. معهد هيلونغجيانغ لمسح الموارد الطبيعية، هاربين، هيلونغجيانغ 150036، الصين. البريد الإلكتروني: zhaozhonghai@Intu.edu.cn
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-92108-3
PMID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40025120
Publication Date: 2025-02-28
scientific reports
OPEN
Integrated geophysical prospecting for deep ore detection in the Yongxin gold mining area, Heilongjiang, China
Abstract
Geophysical exploration techniques play a pivotal role in enhancing the accuracy of mineral prospecting predictions. However, relying solely on individual methods often introduces uncertainties. This study presents a case study from the Yongxin gold deposit, where we integrated audio-frequency magnetotelluric (AMT) methods with gravimetric surveying and high-resolution magnetic profiling to overcome this challenge. Advanced three-dimensional modeling techniques were utilized to precisely delineate lithological variations and deep-seated mineralization features inherent to the area. The inversion and interpretation of cross-sectional AMT data provided insights into the subsurface structure down to a depth of 1.5 km . This enhanced data reliability was achieved through an integrated interpretation constrained by multiple datasets, enabling a more accurate inference of the deeper geological framework. Furthermore, by amalgamating various datasets, we uncovered characteristics of deep mineralization, the three-dimensional configuration of mineralization-related rock masses, and the spatial orientation of known ore deposits. This holistic approach facilitated a comprehensive understanding of the deeper geological formations. A detailed analysis of ore-controlling structures and exploration markers led to the development of a tailored geological-geophysical model for mineral exploration within the study area, serving as a valuable reference for future deep exploration efforts.
Geological setting Regional geology

Ore deposit geology
Analytical methods

Result
Physical properties
| Type | Lithology | Resistivity (
|
Magnetic susceptibility (10-5 SI) | Density (
|
|||
| Variation range | Average value | Variation range | Average value | Variation range | Average value | ||
| Intrusive rock | Middle Jurassic granodiorite | 3435.4-14,977.9 | 5178.4 | 80.0-357.0 | 224.5 | 2.4-2.8 | 2.6 |
| Late Carboniferous monzonitic granite | 1183.5-25,096.5 | 5880.8 | 42.0-772.0 | 431.8 | 2.4-2.7 | 2.6 | |
| Late Carboniferous Syenogranite | 343.7-33,232.7 | 5921.8 | 20.0-480.0 | 223.0 | 2.4-2.6 | 2.6 | |
| Late Carboniferousgranitic mylonite | 1922.9-8214.9 | 4090.3 | 4.0-299.0 | 35.4 | 2.3-2.7 | 2.5 | |
| Middle Ordovician diorite | 436.3-20,533.5 | 6118.2 | 27.0-2564.0 | 1031.2 | 2.5-2.9 | 2.7 | |
| Stratum | Ganhe Formation basalt | 83.5-57,754.7 | 5773.6 | 387.0-2059.0 | 865.0 | 2.1-2.7 | 2.6 |
| Guanghua Formation rhyolite | 888.5-4826.0 | 2857.3 | 13.0-554.0 | 145.6 | 2.1-2.7 | 2.5 | |
| Jiufengshan Formation intermediate-acid tuff | 118.4-5877.9 | 1485.7 | 40.0-235.0 | 100.6 | 2.3-2.9 | 2.6 | |
| Longjiang Formation andesite | 795.7-3745.7 | 1875.7 | – | – | 2.08-2.63 | 2.4 | |
| Luohe Formation sandstone | 706.5-31,699.2 | 5400.3 | 12.0-481.0 | 88.2 | 2.2-2.6 | 2.4 | |
Regional gravity anomaly characteristics
Regional magnetic anomaly characteristics
Integrated geological features of AMT profiles



Discussion
The joint inversion of gravity, magnetic, and electrical data
ensures optimal parameter fitting for both theoretical and measured anomalies, while the mean square error of the simulation results meets our target requirements



Analysis of favorable conditions for mineralization
(1) Geological conditions. The geological-geophysical model of our study area reveals strata spanning the Cenozoic, Mesozoic, and Paleozoic eras. The Cenozoic and Mesozoic strata, including river alluvium and formations like Guanghua, Longjiang, Ganhe, and Jiufengshan, serve as cover layers

| Types of mineral deposit | Favorable factors for mineralization | Feature variables |
| Epithermal gold deposit | Favorable geological features | The hydrothermal breccia (Fig. 9a) |
| The intersection of monzonitic granite, granitic mylonite, and the Guanghua Formation (Fig. 9b) | ||
| Subvolcanic rock (Fig. 9c) | ||
| The margins of the Guanghua formation volcanic faulted basin (Fig. 9d) | ||
| Favorable mineralization structures | The intersection of NE and NW faults (Fig. 9e) | |
| The intersection of the Guanghua Formation with NW-NE faults (Fig. 9f) | ||
| Favorable geophysical characteristics for mineralization | AMT geophysical interpretation (Fig. 9g) |
(3) Geophysical conditions and integrated prospecting model. Seven gravity anomalies were identified through gravity and magnetic surveys. These anomalies primarily occur at the contact zone between Mesozoic vol-canic-subvolcanic rocks and Late Carboniferous granodioritic cherts, observable in gradient zones or regions of low magnetic intensity.
Mineralization prediction
Conclusions
(2) This research innovatively integrates audio-frequency magnetotelluric (AMT) sounding, gravity surveys, and high-magnetic profiling, leveraging 3D modeling techniques to effectively identify lithological variations and deep ore-forming geological features within the study area. This approach demonstrates a highly efficient and comprehensive interpretation method.
(3) By constructing a 3D geological model, we have achieved “transparency” of the geological structure within a 1.5 km depth range in the study area. Combining ore-forming geological conditions with geophysical interpretation results, we have summarized the favorable mineralization conditions of the Yongxin gold mining area and developed a comprehensive ore-prospecting model. Drilling verification has successfully identified multiple mineralized zones at depth, confirming the synergy between integrated geophysical ex-

Data availability
Published online: 01 March 2025
References
- Bellefleur, G., de Kemp, E., Goutier, J., Allard, M. & Adam, E. Seismic imaging of the geologic framework and structures related to volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits in the Archean Rouyn-Noranda District, Quebec Canada. Econ. Geol. 109, 103-119 (2014).
- Liu, S. F. et al. Adoption of a mineral system model in successful deep exploration at Erdaogou, China’s deepest gold mine, on the northeastern margin of the North China Craton. Ore Geol. Rev. 131, 104060 (2021).
- Han, S. et al. Integrated geophysical exploration of the coupling of a concealed rock body and metallogenic structures-
mining area case study in Jilinbaolige, Inner Mongolia. China. J. Appl. Geophys. 178, 104048 (2020). - Ogah, A. J. & Abubakar, F. Solid mineral potential evaluation using integrated aeromagnetic and aeroradiometric datasets. Sci. Rep. 14, 1637 (2024).
- Olierook, H. K. H. et al. Emplacement of the Argyle diamond deposit into an ancient rift zone triggered by supercontinent breakup. Nat. Commun. 14, 5274 (2023).
- Yang, J., Liu, S. & Hu, X. Inversion of high-amplitude magnetic total field anomaly: An application to the Mengku iron-ore deposit, northwest China. Sci. Rep. 10, 11949 (2020).
- Zhang, G. et al. Joint interpretation of geological, magnetic, AMT, and ERT data for mineral exploration in the northeast of Inner Mongolia, China. Pure Appl. Geophys. 175, 989-1002 (2017).
- Lahti, I., Kontinen, A. & Nykänen, V. AMT survey in the Outokumpu ore belt, eastern Finland. Explor. Geophys. 50, 351-363 (2019).
- Cushing, E. M. et al. Building a three dimensional model of the active Plio-Quaternary basin of Argostoli (Cephalonia Island, Greece): An integrated geophysical and geological approach. Eng. Geol. 265, 105441 (2020).
- Qi, G., Meng, G. X., Yan, J. Y., Tang, H. J. & Xue, R. H. Three-dimensional geological-geophysical modeling and prospecting indications of the ashele ore concentration area in Xinjiang based on irregular sections. Minerals 13, 984 (2023).
- Anderson, E. D. et al. Geophysical data provide three dimensional insights into porphyry copper systems in the Silverton caldera, Colorado, USA. Ore Geol. Rev. 152, 105223 (2023).
- Eldougdoug, A. et al. Exploring gold mineralization in altered ultramafic rocks in south Abu Marawat, Eastern Desert, Egypt. Sci. Rep. 13, 7293 (2023).
- Tominaga, M. et al. Multi-scale magnetic mapping of serpentinite carbonation. Nat. Commun. 8, 1870 (2017).
- Wang, Q. Y., Liu, H. D., Chen, J. P., Wang, L. J. & Zhu, D. C. 3D geological modeling and metallogenic prognosis of Jiaojia gold metallogenic belt in Shandong. J. Geol. 38, 412-420 (2014).
- Zheng, X. M., Ni, J. C., Guo, G., Fang, W. X. & Wang, H. W. Application of audio frequency magnetotelluric sounding in 3D geological modeling in Hongshishan ophiolitic melange belt Gansu. Miner. Explor. 12, 1602-1609 (2021).
- Wang, L. et al. Geology and genesis of the Early Paleozoic Zhengguang intermediate-sulfidation epithermal Au-Zn deposit, northeast China. Ore Geol. Rev. 124, 103602 (2020).
- Zhang, A. Q. et al. Lithosphere-asthenosphere interactions beneath northeast China and the origin of its intraplate volcanism. Geology 50, 210-215 (2021).
- Wu, F. Y. et al. The Heilongjiang Group: A Jurassic accretionary complex in the Jiamusi Massif at the western Pacific margin of northeastern China. Island Arc 16, 156-172 (2007).
- Gong, M. Y., Tian, W., Fu, B., Wang, S. Y. & Dong, J. L. Zircon Hf-O isotopic constraints on the origin of Late Mesozoic felsic volcanic rocks from the Great Xing’an Range, NE China. Lithos 308, 412-427 (2018).
- Zhang, L. S. et al. Petrogenesis and tectonic settingof granitoids in the Fuanpu molybdenum deposit, Lesser Xing ar-Zhangguangcai range metallogenic belt: Constraints from element geochemistry, zircon U-Pb geochronology and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes. Acta Geol. Sin. 95, 2471-2492 (2021).
- Shu, Q. H., Chang, Z. S. & Mavrogenes, J. Fluid compositions reveal fluid nature, metal deposition mechanisms, and mineralization potential: An example at the Haobugao Zn-Pb skarn, China. Geology 49, 473-477 (2021).
- Mao, J. W. et al. Mesozoic large-scale metallogenic pulses in North China and corresponding geodynamic settings. Acta Petrol. Sin. 21, 171-190 (2005).
- Xu, M. J., Xu, W. L., Wang, F., Gao, F. H. & Yu, J. J. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Early Jurassic granitoids in the central Lesser Xing’an Range, NE China and its tectonic implications. Acta Petrol. Sin. 29, 354-368 (2013).
- Shu, Q. H. et al. Regional metallogeny of Mo-bearing deposits in northeastern China, with new Re-Os dates of porphyry Mo deposits in the northern Xilamulun district. Econ. Geol. 111, 1783-1798 (2016).
- Shu, Q. H. et al. Zircon trace elements and magma fertility: insights from porphyry (-skarn) Mo deposits in NE China. Miner. Depos. 54, 645-656 (2019).
- Xing, K., Shu, Q. H. & Lentz, D. R. Constraints on the formation of the giant Daheishan porphyry Mo deposit (NE China) from whole-rock and accessory mineral geochemistry. J. Petrol. 62, 1-26 (2021).
- Cheng, G. H. et al. Zircon U-Pb ages, Hf isotopes of the granitoids and Re-Os ages of the molybdenites in Luming molybdenum ore area, Heilongjiang Province, and its geological significance. Acta Petrol. Sin. 31, 2450-2464 (2015).
- Zhai, D. G. et al. The genesis of the giant Shuangjianzishan epithermal Ag-Pb-Zn deposit, Inner Mongolia, Northeastern China. Econ. Geol. 115, 101-128 (2020).
- Zhang, C. P. et al. Geochronology and isotope geochemistry studies of an epithermal gold deposit in the northern Lesser Khingan Range, NE China: The Gaosongshan example. Ore Geol. Rev. 105, 356-374 (2019).
- Liu, Y. et al. Origin and evolution of ore-forming fluid for the Gaosongshan gold deposit, Lesser Xing’an Range: Evidence from fluid inclusions, H-O-S-Pb isotopes. Geosci. Front. 10, 1961-1980 (2019).
- Zhao, Z. H. et al. Age of the Yongxin Au deposit in the Lesser Xing’an Range: Implications for an Early Cretaceous geodynamic setting for gold mineralization in NE China. Geol. J. 54, 2525-2544 (2019).
- Zhao, Z. H. et al. Genesis of the Yidonglinchang gold deposit, Lesser Xing’an Range, China: Insights from fluid inclusions, H-O-SPb isotopes, and
and geochronology. Ore Geol. Rev. 163 (2023). - Zhao, Z. H. et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic constraints on the timing and origin of the Early Cretaceous igneous rocks in the Yongxin gold deposit in the Lesser Xing’an Range, NE China. Geol. J. 55, 2684-2703 (2019).
- Yuan, M. W. et al. Geochemical and isotopic composition of auriferous pyrite from the Yongxin gold deposit, Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Implication for ore genesis. Ore Geol. Rev. 93, 255-267 (2018).
- Pitiya, R. et al. Audio magnetotellurics study of the geoelectric structure across the Zhugongtang giant lead-zinc deposit, NW Guizhou Province, China. Minerals 12 (2022).
- Singh, S. et al. Audio-magnetotelluric investigation of sulfide mineralization in Proterozoic-Archean greenstone belts of Eastern Indian Craton. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 127 (2018).
- Ugbor, C. C., Arinze, I. J. & Emedo, C. O. Analysis of aeromagnetic data of Ikwo and Environs, Southeastern Nigeria: A mineral and hydrocarbon exploration guide. Nat. Resour. Res. 29, 2915-2932 (2020).
- Di Paolo, F. et al. La Palma island (Spain) geothermal system revealed by 3D magnetotelluric data inversion. Sci. Rep. 10, 18181 (2020).
- Darabi-Golestan, F., Ghavami-Riabi, R., Khalokakaie, R., Asadi-Haroni, H. & Seyedrahimi-Nyaragh, M. Interpretation of lithogeochemical and geophysical data to identify the buried mineralized area in Cu-Au porphyry of Dalli-Northern Hill. Arab. J. Geosci. 6, 4499-4509 (2012).
- Maharaj, D., Elbra, T. & Pesonen, L. J. Physical properties of the drill core from the Elgygytgyn impact structure, NE Russia. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 48, 1130-1142 (2013).
- Zhang, R. Z. et al. 3-D joint inversion of gravity and magnetic data using data-space and truncated Gauss-Newton methods. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 19, 1-5 (2022).
- Li, W. B., Qian, J. L. & Li, Y. G. Joint inversion of surface and borehole magnetic data: A level-set approach. Geophysics 85, 15-32 (2020).
- Xiao, B. et al. Rare earth element characteristics of shales from Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in deep-buried areas of the Northern Sichuan Basin, Southern China: Implications for provenance, depositional conditions, and paleoclimate. ACS Omega 9, 2088-2103 (2024).
- Vatankhah, S., Renaut, R. A., Huang, X. G., Mickus, K. & Gharloghi, M. Large-scale focusing joint inversion of gravity and magnetic data with Gramian constraint. Geophys. J. Int. 230, 1585-1611 (2022).
- Zhang, S. et al. A facile approach to ultralight and recyclable 3D self-assembled copolymer/graphene aerogels for efficient oil/water separation. Sci. Total Environ. 694, 133671 (2019).
- Yang, Z. W., Tan, H. D., Peng, M., Kong, W. X. & Wu, P. P. Three-dimensional joint inversion of gravity, magnetic and magnetotelluric data based on cross-gradient theory. Chin. J. Geophys. Chin. Ed. 63, 736-752 (2020).
- Li, C. L. et al. Study on pyrite thermoelectricity, ore-forming fluids and H-O-Rb-Sr isotopes of the Yongxin gold deposit, Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Implications for ore genesis and exploration. Ore Geol. Rev. 121 (2020).
- Behrendt, J. C. The aeromagnetic method as a tool to identify Cenozoic magmatism in the West Antarctic Rift System beneath the West Antarctic Ice Sheet-A review; Thiel subglacial volcano as possible source of the ash layer in the WAISCORE. Tectonophysics 585, 124-136 (2013).
- Ross, P. S. et al. High-resolution physical properties, geochemistry, and alteration mineralogy for the host rocks of the Archean Lemoine auriferous volcanogenic massive sulfide deposit, Canada. Econ. Geol. 111, 1561-1574 (2016).
- Caballero-Miranda, C. I. et al. Vertical AMS variation within basalt flow profiles from the Xitle volcano (Mexico) as indicator of heterogeneous strain in lava flows. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 311, 9-28 (2016).
- Sakr, S. M., Bamousa, A. O., Gougazeh, M. H. & Zaman, H. Petromagnetic investigations of the volcanic rocks in southern part of Al-Madinah, Saudi Arabia: Differentiation of different lava types. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 14, 1009-1022 (2020).
- Liang, K. W., Zhao, Z. H. & Guo, Y. Application of primary halo in deep metallogenic prediction: A case study of Yongxin gold deposit in Heihe Area. Geol. Resour. 28, 512-518 (2019).
- Li, C. L. et al. Discovery and geological significance of gold-silver bearing minerals and tellurides in the Yongxin gold deposit in the northeastern Great Xing’an Range. Earth Sci. Front. 27, 244-254 (2020).
- Deng, C. Z. et al. Geochemistry of Early Cretaceous volcanic rocks in the Northeastern Great Xing’an Range, northeast China and implication for geodynamic setting. Int. Geol. Rev. 61, 1594-1612 (2018).
- Liu, R. P. et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and petrogeochemistry of host igneous rocks of the Dong’an gold deposit in Heilongjiang Province, NE China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 31, 1391-1408 (2015).
- Zhang, M. M. et al. Tellurium and gold enrichment aided by melts and pyrite crystallization kinetics: Insights from the Yongxin gold deposit, northeast China. Ore Geol. Rev. 156, 105370 (2023).
- Zhao, Z. H. et al. Early Cretaceous gold mineralization in the Lesser Xing’an Range of NE China: The Yongxin example. Int. Geol. Rev. 61, 1522-1548 (2018).
Acknowledgements
Author contributions
Declarations
Competing interests
Additional information
Reprints and permissions information is available at www.nature.com/reprints.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
© The Author(s) 2025
College of Mining, Liaoning Technical University, Fuxin, Liaoning 123000, China. Liaoning Key Laboratory of Green Development of Mineral Resources, LNTU, Fuxin, Liaoning 123000, China. Heilongjiang Institute of Natural Resources Survey, Harbin, Heilongjiang 150036, China. email: zhaozhonghai@Intu.edu.cn
