DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46372-y
PMID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38485722
تاريخ النشر: 2024-03-14
الميمريستورز ذات التبديل فائق السرعة المستندة إلى المواد ثنائية الأبعاد
تاريخ القبول: 26 فبراير 2024
تاريخ النشر على الإنترنت: 14 مارس 2024
(D) تحقق من التحديثات
الملخص
تقدم القدرة على تقليل سمك المواد ثنائية الأبعاد (2D) إلى طبقة أحادية فرصة واعدة لتحقيق متغيرات سريعة وفعالة من حيث الطاقة. هنا، نبلغ عن متغير سريع للغاية تم تصنيعه باستخدام أوراق رقيقة ذرية من نيتريد البورون السداسي ثنائي الأبعاد، مما يظهر أسرع سرعة تبديل تم ملاحظتها (120 بيكو ثانية) بين المتغيرات ثنائية الأبعاد وطاقات تبديل منخفضة (2 بيكو جول). علاوة على ذلك، ندرس ديناميات التبديل لهذه المتغيرات باستخدام نبضات جهد فائقة القصر (
النتائج
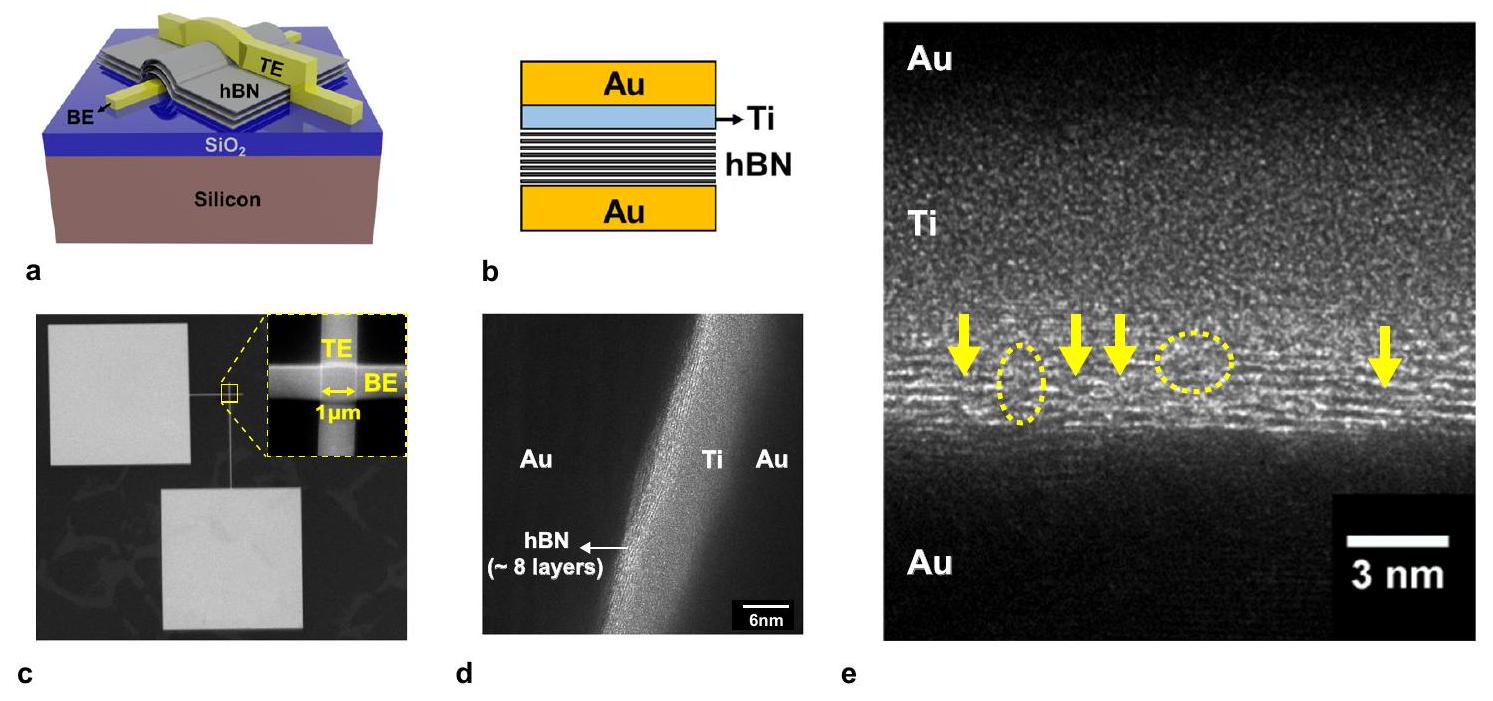
تصنيع الجهاز والأداء الكهربائي المستمر
ذات المقاومة الأولية المنخفضة على حدود حبيبية أو عيوب بعرض عدة ذرات تم إدخالها على الأرجح أثناء عمليات التصنيع. تم التخلص من هذه الأجهزة المتسربة ولم تؤخذ في الاعتبار لمزيد من التحليل. يولد الجهد العالي المطبق على القطب Ti أثناء عملية التشكيل الخيط الموصل داخل المتغير. يظهر الشكل التكميلي 7.2 أن مقدار جهد التشكيل مرتبط مباشرة بالمقاومة الأولية للمتغير. وبالتالي، تتطلب الأجهزة ذات المقاومة الأولية الأعلى، المميزة بعيوب أقل، جهدًا أعلى لتأسيس الخيط الموصل. من الواضح أن هذا الاتجاه صحيح لجميع الأجهزة، بغض النظر عن مقطع الجهاز العرضي. لضمان أن المقاومة الأولية المقاسة والتبديل المقاوم اللاحق لم تتأثر بطبقة غير مقصودة
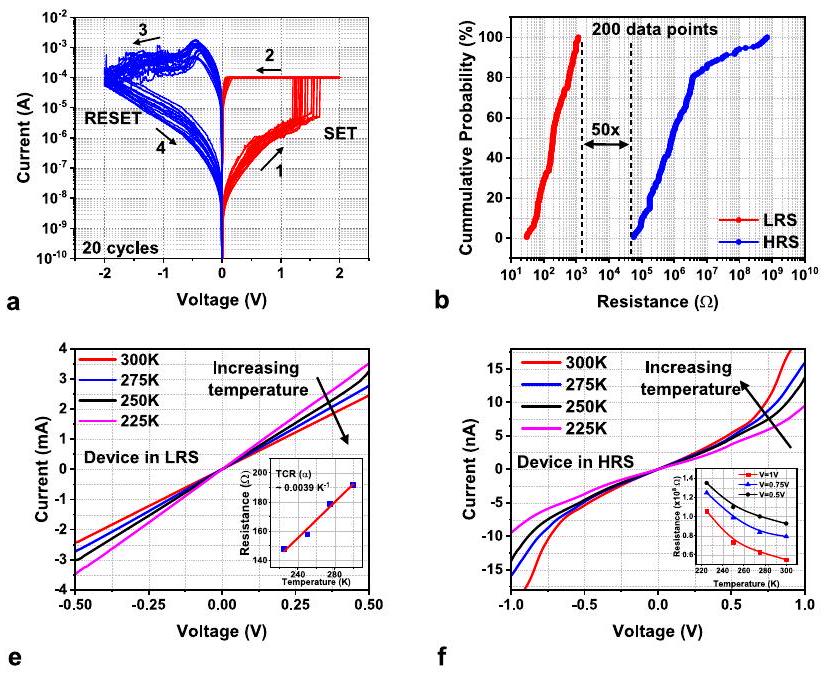

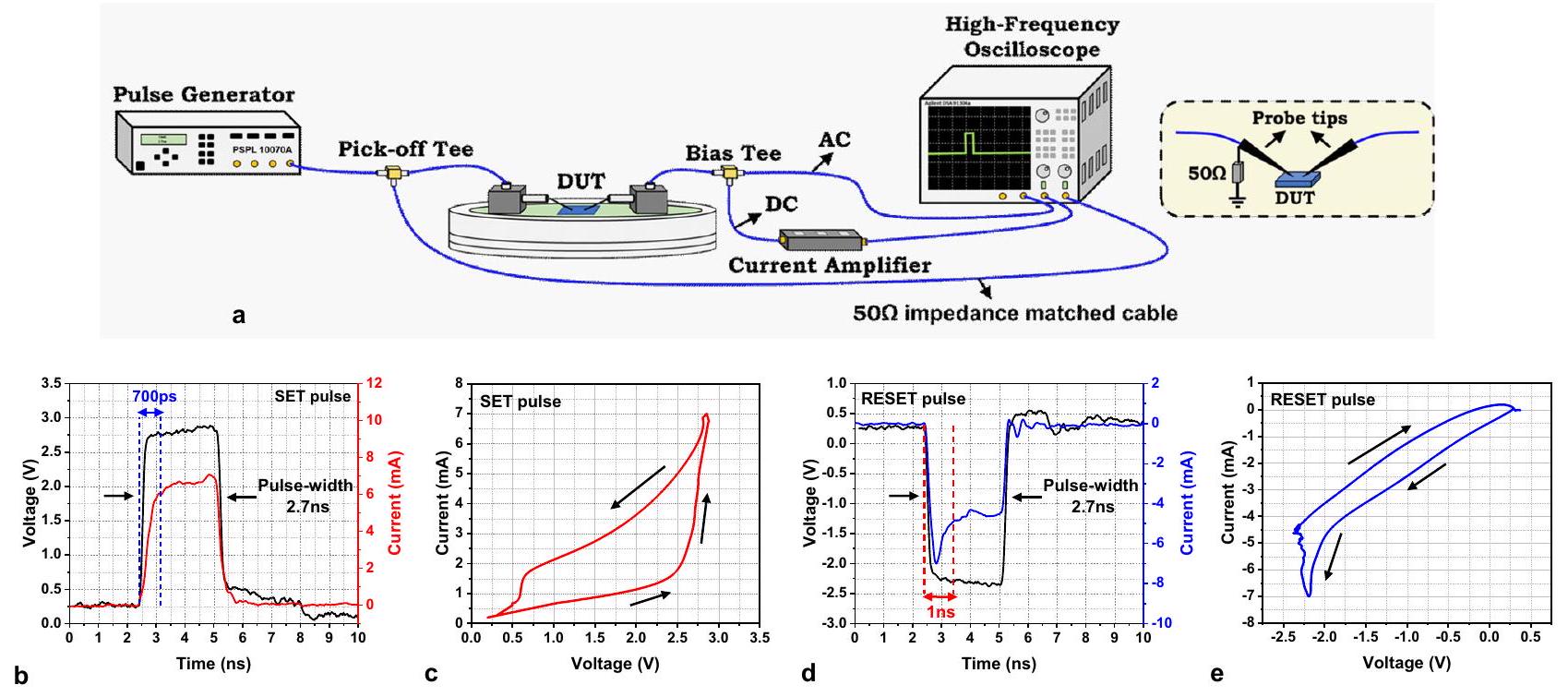
عمليات إجهاد جهد النبض
التحليل الإحصائي لديناميات التبديل
توليد/تبدد الطاقة، العيوب في الفيلم ثنائي الأبعاد، والواجهة مع الأقطاب. وبالتالي، تم استخدام التحليل الإحصائي لديناميات التبديل للحصول على رؤى حول آلية التبديل المقاوم. تم إجراء هذه الدراسة من خلال تطبيق نبضات جهد متطابقة (
أوقات (600 بيكوثانية إلى 2.5 نانوثانية – انظر الشكل التوضيحي 16 لمزيد من التفاصيل) كما هو موضح في الشكل 4 أ (تم حذف مخططات نبضات الجهد لزيادة الوضوح). توزيع أوقات التبديل (المستخرج من كل مخطط تيار) له قيمة متوسطة تبلغ 1.32 نانوثانية وانحراف معياري قدره 670 بيكوثانية (الشكل 4ب). من الجدير بالذكر،

عند واجهة Ti/hBN إطلاق أيونات التيتانيوم من القطب إلى طبقة التبديل hBN. الشكل 4د يقارن درجة الحرارة المتوسطة للواجهة لأجهزتنا و
دور تسخين جول في استقرار الشعيرات
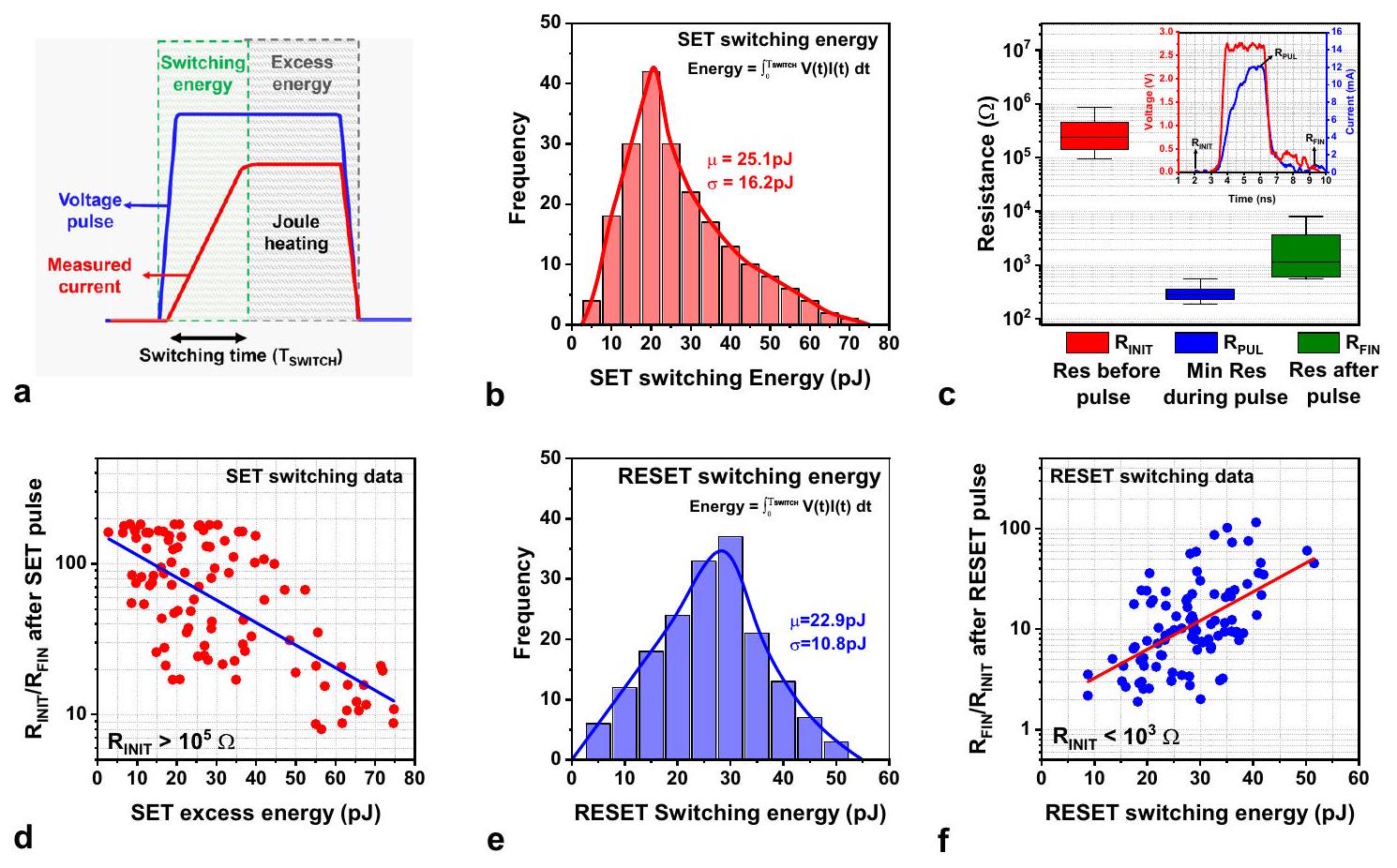
درجة حرارة مرتفعة (
ميمريستورات تبديل فائقة السرعة (
نقاش
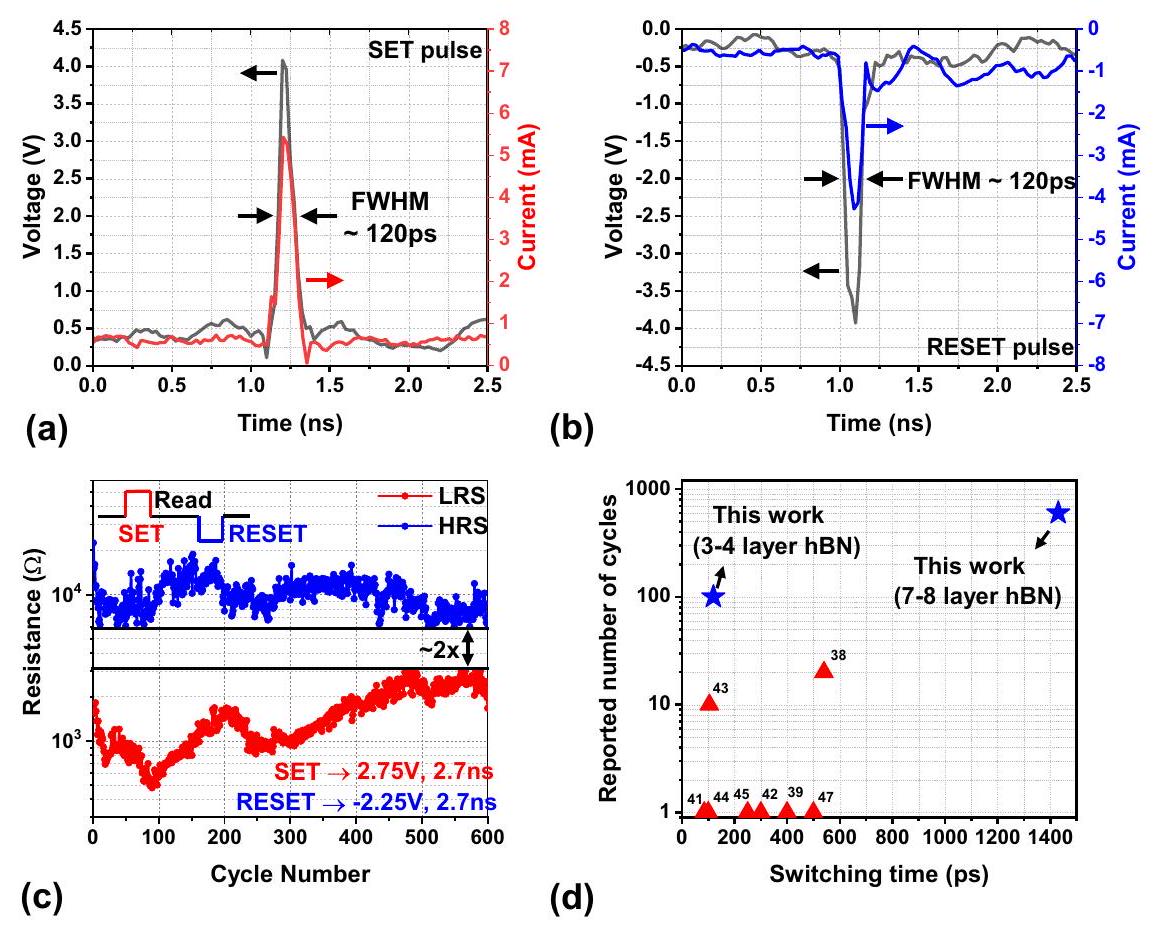
تظهر الجهاز 100 دورة متتالية من التبديل المتسق، وهو أعلى قدرة تحمل تم الإبلاغ عنها على الإطلاق باستخدام نبضات فائقة القصر. د رسم بياني يقارن أداء الأجهزة المقدمة في هذه المقالة مع ميمريستورات TMO و2D الأخرى.
خصائص التبديل العابرة بما في ذلك التأثيرات الثانوية مثل تسخين جول. بشكل عام، تكشف هذه الدراسة عن الإمكانات الحقيقية لميمريستورات المواد ثنائية الأبعاد لتطبيقات الحوسبة عالية السرعة، والتخزين، وRF المستقبلية.
طرق
تحضير نيتريد البورون السداسي
نقل فيلم hBN
عملية النقل، تم طلاء رقائق النحاس مع أفلام hBN باستخدام تقنية الطلاء الدوراني بـ PMMA (بولي ميثيل ميثاكريلات) بسرعة 3000 دورة في الدقيقة لمدة دقيقة واحدة، تلاها خبز عند 180 درجة مئوية لمدة دقيقة واحدة. يوفر طبقة PMMA الدعم والحماية لأفلام hBN خلال عملية النقل. تم نقل أفلام hBN باستخدام
تصنيع جهاز الميمريستور
توصيف التيار المستمر الكهربائي
توصيف النبض الكهربائي
الخصائص الفيزيائية
توفر البيانات
References
- Talib, M. A., Majzoub, S., Nasir, Q. & Jamal, D. A systematic literature review on hardware implementation of artificial intelligence algorithms. J. Supercomput. 77, 1897-1938 (2021).
- Capra, M. et al. An updated survey of efficient hardware architectures for accelerating deep convolutional neural networks. Future Internet 12, 113 (2020).
- Stoica, I. et al. A Berkeley view of systems challenges for Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.05855 (2017).
- Pereira, F., Correia, R., Pinho, P., Lopes, S. I. & Carvalho, N. B. Challenges in resource-constrained IoT devices: energy and communication as critical success factors for future IoT deployment. Sensors 20, 6420 (2020).
- Fan, X. et al. Flexible and wearable power sources for next-generation wearable electronics. Batteries Supercaps 3, 1262-1274 (2020).
- Compagnoni, C. M. et al. Reviewing the evolution of the NAND flash technology. Proc. IEEE 105, 1609-1633 (2017).
- Hemink, G. & Goda, A. (eds) in Semiconductor Memories and Systems 119-158 (Woodhead publishing, 2022).
- Chua, L. Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 18, 507-519 (1971).
- Strukov, D. B., Snider, G. S., Stewart, D. R. & Williams, R. S. The missing memristor found. Nature 453, 80-83 (2008).
- Yang, J. J. et al. Memristive switching mechanism for metal/oxide/ metal nanodevices. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 429-433 (2008).
- Luo, Q. et al. 8-Layers 3D vertical RRAM with excellent scalability towards storage class memory applications. In: 2017 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) (ed Gendt, S. D.) 2-7 (IEEE, 2017).
- Luo, Q. et al. Demonstration of 3D vertical RRAM with ultra lowleakage, high-selectivity and self-compliance memory cells. In: 2015 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) (ed Suehle, J.) 10-12 (IEEE, 2015).
- Xu, X. et al. Fully CMOS compatible 3D vertical RRAM with selfaligned self-selective cell enabling sub- 5 nm scaling. In: 2016 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology (ed Philip Wong, H. S.) 1-2 (IEEE, 2016).
- lelmini, D. & Wong, H. S. P. In-memory computing with resistive switching devices. Nat. Electron. 1, 333-343 (2018).
- Yin, S., Sun, X., Yu, S. & Seo, J. S. High-throughput in-memory computing for binary deep neural networks with monolithically integrated RRAM and 90-nm CMOS. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 67, 4185-4192 (2020).
- Pedretti, G. & lelmini, D. In-memory computing with resistive memory circuits: status and outlook. Electronics 10, 1063 (2021).
- Yin, S. et al. Monolithically integrated RRAM-and CMOS-based inmemory computing optimizations for efficient deep learning. IEEE Micro 39, 54-63 (2019).
- Kim, M. et al. Zero-static power radio-frequency switches based on MoS2 atomristors. Nat. Commun. 9, 1-7 (2018).
- Kim, M. et al. Non-volatile RF and mm-wave switches based on monolayer hBN. In: 2019 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) (ed Datta, S.) 5-9 (IEEE, 2019).
- Kim, M., Pallecchi, E., Happy, H. & Akinwande, D. Single-Pole-Double-Throw RF switches based on monolayer
. In: 2021 Device Research Conference (DRC) (ed Chen, Z.) 1-2 (IEEE, 2021). - Wong, H. S. P. et al. Metal-oxide RRAM. Proc. IEEE 100, 1951-1970 (2012).
- Sawa, A. Resistive switching in transition metal oxides. Mater. Today 11, 28-36 (2008).
- Khan, R. et al. Oxide-based resistive switching-based devices: fabrication, influence parameters and applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 9, 15755-15788 (2021).
- Carlos, E., Branquinho, R., Martins, R., Kiazadeh, A. & Fortunato, E. Recent progress in solution-based metal oxide resistive switching devices. Adv. Mater. 33, 2004328 (2021).
- Jang, J., Pan, F., Braam, K. & Subramanian, V. Resistance switching characteristics of solid electrolyte chalcogenide Ag2Se nanoparticles for flexible nonvolatile memory applications. Adv. Mater. 24, 3573-3576 (2012).
- Pradel, A., Frolet, N., Ramonda, M., Piarristeguy, A. & Ribes, M. Bipolar resistance switching in chalcogenide materials. Phys. Status Solidi (a) 208, 2303-2308 (2011).
- Gao, S., Yi, X., Shang, J., Liu, G. & Li, R. W. Organic and hybrid resistive switching materials and devices. Chem. Soc. Rev. 48, 1531-1565 (2019).
- Yuan, L., Liu, S., Chen, W., Fan, F. & Liu, G. Organic memory and memristors: from mechanisms, materials to devices. Adv. Electron. Mater. 7, 2100432 (2021).
- Park, S. P. et al. Analysis of the bipolar resistive switching behavior of a biocompatible glucose film for resistive random access memory. Adv. Mater. 30, 1800722 (2018).
- Yang, Y. et al. Electrochemical dynamics of nanoscale metallic inclusions in dielectrics. Nat. Commun. 5, 4232 (2014).
- Yang, Y. et al. Observation of conducting filament growth in nanoscale resistive memories. Nat. Commun. 3, 732 (2012).
- Qian, F. et al. A leaky integrate-and-fire neuron based on hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) monocrystalline memristor. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 69, 6049-6056 (2022).
- Clima, S. et al. First-principles thermodynamics and defect kinetics guidelines for engineering a tailored RRAM device. J. Appl. Phys. 119 (2016).
- Yu, S., Guan, X. & Wong, H.S.P. On the stochastic nature of resistive switching in metal oxide RRAM: physical modeling, Monte Carlo simulation, and experimental characterization. In: 2011 International Electron Devices Meeting (ed Ishimaru, K.) 17-3 (IEEE, 2011).
- Jain, P. et al. 13.2 A
embedded non-volatile ReRAM macro in 22nm FinFET technology with adaptive forming/ set/reset schemes yielding down to 0.5 V with sensing time of 5 ns at 0.7 V . In: 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference(ISSCC) (ed Spiegel, J. V. D.) 212-214 (IEEE, 2019). - Liu, T.Y. et al. A 130.7 mm 2 2-layer 32Gb ReRAM memory device in 24nm technology. In: 2013 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference Digest of Technical Papers (ed Nauta, B.) (San Francisco, CA, 2013).
- Chang, M. F. et al. 19.4 embedded 1 Mb ReRAM in 28 nm CMOS with 0.27-to-1V read using swing-sample-and-couple sense amplifier and self-boost-write-termination scheme. In: 2014 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference Digest of Technical Papers (ISSCC) (ed Stetzler, T.) 332-333 (IEEE, 2014).
- Chen, Z. et al. Ultrafast multilevel switching in Au/YIG/n-Si RRAM. Adv. Electron. Mater. 5, 1800418 (2019).
- Wang, C. et al. Ultrafast RESET analysis of HfOx-based RRAM by sub-nanosecond pulses. Adv. Electron. Mater. 3, 1700263 (2017).
- Shrestha, P. R. et al. Energy control paradigm for compliance-free reliable operation of RRAM. In: 2014 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium MY-10 (IEEE, 2014).
- Choi, B. J. et al. High-speed and low-energy nitride memristors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 26, 5290-5296 (2016).
- Lee, H. Y. et al. Evidence and solution of over-RESET problem for HfO x based resistive memory with sub-ns switching speed and high endurance. In: 2010 International Electron Devices Meeting (ed leong, M.) 19-7 (IEEE, 2010).
- Choi, B. J. et al. Electrical performance and scalability of Pt dispersed
nanometallic resistance switch. Nano letters 13, 3213-3217 (2013). - Torrezan, A. C., Strachan, J. P., Medeiros-Ribeiro, G. & Williams, R. S. Sub-nanosecond switching of a tantalum oxide memristor. Nanotechnology 22, 485203 (2011).
- Böttger, U. et al. Picosecond multilevel resistive switching in tantalum oxide thin films. Sci. Rep. 10, 1-9 (2020).
- Zhang, F. et al. An ultra-fast multi-level MoTe 2-based RRAM. In: 2018 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) (ed Takayanagi, M.) 22-27 (IEEE, 2018).
- Kim, M. et al. Monolayer molybdenum disulfide switches for 6 G communication systems. Nat. Electron. 5, 1-7 (2022).
- Chen, S. et al. Wafer-scale integration of two-dimensional materials in high-density memristive crossbar arrays for artificial neural networks. Nat. Electron. 3, 638-645 (2020).
- Zhu, K. et al. Graphene-boron nitride-graphene cross-point memristors with three stable resistive states. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 37999-38005 (2019).
- Zhuang, P. et al. Nonpolar resistive switching of multilayer-hBNbased memories. Adv. Electron. Mater. 6, 1900979 (2020).
- Fantini, A. et al. Intrinsic switching variability in HfO 2 RRAM. In: 2013 5th IEEE International Memory Workshop 30-33 (IEEE, 2013).
- Ambrogio, S. et al. Understanding switching variability and random telegraph noise in resistive RAM. In: 2013 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (ed Ghani, T.) 31-35 (IEEE, 2013)
- Guan, X., Yu, S. & Wong, H.S.P. On the switching parameter variation of metal-oxide RRAM-Part I: Physical modeling and simulation methodology. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 59, 172-1182 (2012).
- Shen, Y. et al. Variability and yield in h-BN-based memristive circuits: the role of each type of defect. Adv. Mater. 33, 2103656 (2021).
- Shi, Y. et al. Electronic synapses made of layered two-dimensional materials. Nat. Electron. 1, 458-465 (2018).
- Lim, E. W. & Ismail, R. Conduction mechanism of valence change resistive switching memory: a survey. Electronics 4, 586-613 (2015).
- Chakraborty, I., Panwar, N., Khanna, A. & Ganguly, U. Space Charge Limited Current with Self-heating in
based RRAM. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1605.08755 (2016). - Puglisi, F. M. et al. 2D h-BN based RRAM devices. In: 2016 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) (ed Fay, P.) 34-38 (IEEE, 2016).
- Zhu, K. et al. Hybrid 2D-CMOS microchips for memristive applications. Nature 618, 57-62 (2023).
- Yu, S. & Wong, H. S. P. Compact modeling of conducting-bridge random-access memory (CBRAM). IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 58, 1352-1360 (2011).
- Ielmini, D. Modeling the universal set/reset characteristics of bipolar RRAM by field-and temperature-driven filament growth. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 58, 4309-4317 (2011).
- Huang, P. et al. A physics-based compact model of metal-oxidebased RRAM DC and AC operations. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 60, 4090-4097 (2013).
- Ielmini, D., Nardi, F. & Cagli, C. Physical models of size-dependent nanofilament formation and rupture in NiO resistive switching memories. Nanotechnology 22, 254022 (2011).
- Jo, I. et al. Thermal conductivity and phonon transport in suspended few-layer hexagonal boron nitride. Nano Lett. 13, 550-554 (2013).
- Alam, M. T., Bresnehan, M. S., Robinson, J. A. & Haque, M. A. Thermal conductivity of ultra-thin chemical vapor deposited hexagonal boron nitride films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 104 (2014).
- Panzer, M. A. et al. Thermal properties of ultrathin hafnium oxide gate dielectric films. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 30, 1269-1271 (2009).
- Cappella, A. et al. High temperature thermal conductivity of amorphous
thin films grown by low temperature ALD. Adv. Eng. Mater. 15, 1046-1050 (2013). - Landon, C. D. et al. Thermal transport in tantalum oxide films for memristive applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 107 (2015).
- Kwon, D. H. et al. Atomic structure of conducting nanofilaments in TiO2 resistive switching memory. Nat. Nanotechnol. 5, 148-153 (2010).
- Tsuruoka, T., Hasegawa, T., Terabe, K. & Aono, M. Conductance quantization and synaptic behavior in a Ta2O5-based atomic switch. Nanotechnology 23, 435705 (2012).
- Lee, S., Sohn, J., Jiang, Z., Chen, H. Y. & Philip Wong, H. S. Metal oxide-resistive memory using graphene-edge electrodes. Nat. Commun. 6, 1-7 (2015).
- Zhuang, P., Ma, W., Liu, J., Cai, W. & Lin, W. Progressive RESET induced by Joule heating in hBN RRAMs. Appl. Phys. Lett. 118, 143101 (2021).
- Lanza, M. et al. Temperature of conductive nanofilaments in hexagonal boron nitride based memristors showing threshold resistive switching. Adv. Electron. Mater. 8, 2100580 (2022).
- Li, S. et al. Fully coupled multiphysics simulation of crosstalk effect in bipolar resistive random access memory. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 64, 3647-3653 (2017).
- Hsieh, C. C., Roy, A., Chang, Y. F., Shahrjerdi, D. & Banerjee, S. K. A sub-1-volt analog metal oxide memristive-based synaptic device with large conductance change for energy-efficient spike-based computing systems. Appl. Phys. Lett. 109, 223501 (2016).
شكر وتقدير
مساهمات المؤلفين
المصالح المتنافسة
معلومات إضافية
المواد التكميلية المتاحة على
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46372-y.
http://www.nature.com/reprints
(ج) المؤلفون 2024
مركز أبحاث الميكروإلكترونيات، جامعة تكساس في أوستن، أوستن، تكساس 78758، الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية. معهد بيرلا للتكنولوجيا، ميسرا، رانشي 835215، الهند. مختبرات HRL، ماليبو، كاليفورنيا 90265، الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية. معهد مواد تكساس، جامعة تكساس في أوستن، أوستن، تكساس 78712، الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية. حلول M2D، أوستن، تكساس 78758، الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية. البريد الإلكتروني: subrahmanya_teja@utexas.edu; royanupam@bitmesra.ac.in; banerjee@ece.utexas.edu
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46372-y
PMID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38485722
Publication Date: 2024-03-14
Ultra-fast switching memristors based on two-dimensional materials
Accepted: 26 February 2024
Published online: 14 March 2024
(D) Check for updates
Abstract
The ability to scale two-dimensional (2D) material thickness down to a single monolayer presents a promising opportunity to realize high-speed energyefficient memristors. Here, we report an ultra-fast memristor fabricated using atomically thin sheets of 2D hexagonal Boron Nitride, exhibiting the shortest observed switching speed ( 120 ps ) among 2D memristors and low switching energy (2pJ). Furthermore, we study the switching dynamics of these memristors using ultra-short (
Results
Device fabrication and DC electrical performance
devices with low initial resistance likely contain grain boundaries or multi-atom wide defects which were probably introduced during the fabrication processes. These leaky devices were discarded and not considered for further analysis. The high voltage sweep applied to the Ti electrode during the forming process generates the conductive filament inside the memristor. Supplementary Fig. 7.2 shows that the magnitude of the forming voltage is directly correlated to the initial resistance of the memristor. Consequently, devices with higher initial resistance, characterized by fewer defects, require a higher voltage to establish the conductive filament. Apparently, this trend holds true for all devices, irrespective of the device cross-section. To ensure that the measured initial resistance and subsequent resistive switching were not influenced by an unintentional



Pulse voltage stress operations
Statistical analysis of switching dynamics
energy generation/dissipation, defects in the 2D film, and the interface with the electrodes. Hence, statistical analysis of the switching dynamics was employed to gain insights into the resistive switching mechanism. This study was conducted by applying identical voltage pulses (
times ( 600 ps to 2.5 ns-see Supplementary Fig. 16 for details) as seen from Fig. 4 a (voltage pulses traces omitted for clarity). The distribution of switching times (extracted from each current trace) has a mean value of 1.32 ns and a standard deviation of 670 ps (Fig. 4b). Notably,


temperature at the Ti/hBN interface facilitates Ti ion release from the electrode into the hBN switching layer. Figure 4d compares the average interface temperature for our devices and
Role of Joule heating on filament stability

elevated temperature (
Ultra-fast (
Discussion

pulses. The device shows 100 consecutive cycles of consistent switching, which is the highest ever reported endurance using ultra-short pulses. d Plot benchmarking the performance of the devices presented in this article with other TMO and 2D material memristors.
transient switching characteristics including secondary effects such as Joule heating. Overall, this study unveils the true potential of 2D material memristors for future high-speed computing, storage, and RF applications.
Methods
Hexagonal boron nitride synthesis
hBN film transfer
transfer process, the copper foils with hBN films were spin-coated with PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate) at 3000 rpm for 1 min followed by baking at 180 C for 1 min . The PMMA layer provides support and protection to the hBN films during the transfer process. The hBN films were transferred using
Memristor device fabrication
Electrical DC characterization
Electrical pulse characterization
Physical characterization
Data availability
References
- Talib, M. A., Majzoub, S., Nasir, Q. & Jamal, D. A systematic literature review on hardware implementation of artificial intelligence algorithms. J. Supercomput. 77, 1897-1938 (2021).
- Capra, M. et al. An updated survey of efficient hardware architectures for accelerating deep convolutional neural networks. Future Internet 12, 113 (2020).
- Stoica, I. et al. A Berkeley view of systems challenges for Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.05855 (2017).
- Pereira, F., Correia, R., Pinho, P., Lopes, S. I. & Carvalho, N. B. Challenges in resource-constrained IoT devices: energy and communication as critical success factors for future IoT deployment. Sensors 20, 6420 (2020).
- Fan, X. et al. Flexible and wearable power sources for next-generation wearable electronics. Batteries Supercaps 3, 1262-1274 (2020).
- Compagnoni, C. M. et al. Reviewing the evolution of the NAND flash technology. Proc. IEEE 105, 1609-1633 (2017).
- Hemink, G. & Goda, A. (eds) in Semiconductor Memories and Systems 119-158 (Woodhead publishing, 2022).
- Chua, L. Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 18, 507-519 (1971).
- Strukov, D. B., Snider, G. S., Stewart, D. R. & Williams, R. S. The missing memristor found. Nature 453, 80-83 (2008).
- Yang, J. J. et al. Memristive switching mechanism for metal/oxide/ metal nanodevices. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 429-433 (2008).
- Luo, Q. et al. 8-Layers 3D vertical RRAM with excellent scalability towards storage class memory applications. In: 2017 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) (ed Gendt, S. D.) 2-7 (IEEE, 2017).
- Luo, Q. et al. Demonstration of 3D vertical RRAM with ultra lowleakage, high-selectivity and self-compliance memory cells. In: 2015 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) (ed Suehle, J.) 10-12 (IEEE, 2015).
- Xu, X. et al. Fully CMOS compatible 3D vertical RRAM with selfaligned self-selective cell enabling sub- 5 nm scaling. In: 2016 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology (ed Philip Wong, H. S.) 1-2 (IEEE, 2016).
- lelmini, D. & Wong, H. S. P. In-memory computing with resistive switching devices. Nat. Electron. 1, 333-343 (2018).
- Yin, S., Sun, X., Yu, S. & Seo, J. S. High-throughput in-memory computing for binary deep neural networks with monolithically integrated RRAM and 90-nm CMOS. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 67, 4185-4192 (2020).
- Pedretti, G. & lelmini, D. In-memory computing with resistive memory circuits: status and outlook. Electronics 10, 1063 (2021).
- Yin, S. et al. Monolithically integrated RRAM-and CMOS-based inmemory computing optimizations for efficient deep learning. IEEE Micro 39, 54-63 (2019).
- Kim, M. et al. Zero-static power radio-frequency switches based on MoS2 atomristors. Nat. Commun. 9, 1-7 (2018).
- Kim, M. et al. Non-volatile RF and mm-wave switches based on monolayer hBN. In: 2019 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) (ed Datta, S.) 5-9 (IEEE, 2019).
- Kim, M., Pallecchi, E., Happy, H. & Akinwande, D. Single-Pole-Double-Throw RF switches based on monolayer
. In: 2021 Device Research Conference (DRC) (ed Chen, Z.) 1-2 (IEEE, 2021). - Wong, H. S. P. et al. Metal-oxide RRAM. Proc. IEEE 100, 1951-1970 (2012).
- Sawa, A. Resistive switching in transition metal oxides. Mater. Today 11, 28-36 (2008).
- Khan, R. et al. Oxide-based resistive switching-based devices: fabrication, influence parameters and applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 9, 15755-15788 (2021).
- Carlos, E., Branquinho, R., Martins, R., Kiazadeh, A. & Fortunato, E. Recent progress in solution-based metal oxide resistive switching devices. Adv. Mater. 33, 2004328 (2021).
- Jang, J., Pan, F., Braam, K. & Subramanian, V. Resistance switching characteristics of solid electrolyte chalcogenide Ag2Se nanoparticles for flexible nonvolatile memory applications. Adv. Mater. 24, 3573-3576 (2012).
- Pradel, A., Frolet, N., Ramonda, M., Piarristeguy, A. & Ribes, M. Bipolar resistance switching in chalcogenide materials. Phys. Status Solidi (a) 208, 2303-2308 (2011).
- Gao, S., Yi, X., Shang, J., Liu, G. & Li, R. W. Organic and hybrid resistive switching materials and devices. Chem. Soc. Rev. 48, 1531-1565 (2019).
- Yuan, L., Liu, S., Chen, W., Fan, F. & Liu, G. Organic memory and memristors: from mechanisms, materials to devices. Adv. Electron. Mater. 7, 2100432 (2021).
- Park, S. P. et al. Analysis of the bipolar resistive switching behavior of a biocompatible glucose film for resistive random access memory. Adv. Mater. 30, 1800722 (2018).
- Yang, Y. et al. Electrochemical dynamics of nanoscale metallic inclusions in dielectrics. Nat. Commun. 5, 4232 (2014).
- Yang, Y. et al. Observation of conducting filament growth in nanoscale resistive memories. Nat. Commun. 3, 732 (2012).
- Qian, F. et al. A leaky integrate-and-fire neuron based on hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) monocrystalline memristor. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 69, 6049-6056 (2022).
- Clima, S. et al. First-principles thermodynamics and defect kinetics guidelines for engineering a tailored RRAM device. J. Appl. Phys. 119 (2016).
- Yu, S., Guan, X. & Wong, H.S.P. On the stochastic nature of resistive switching in metal oxide RRAM: physical modeling, Monte Carlo simulation, and experimental characterization. In: 2011 International Electron Devices Meeting (ed Ishimaru, K.) 17-3 (IEEE, 2011).
- Jain, P. et al. 13.2 A
embedded non-volatile ReRAM macro in 22nm FinFET technology with adaptive forming/ set/reset schemes yielding down to 0.5 V with sensing time of 5 ns at 0.7 V . In: 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference(ISSCC) (ed Spiegel, J. V. D.) 212-214 (IEEE, 2019). - Liu, T.Y. et al. A 130.7 mm 2 2-layer 32Gb ReRAM memory device in 24nm technology. In: 2013 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference Digest of Technical Papers (ed Nauta, B.) (San Francisco, CA, 2013).
- Chang, M. F. et al. 19.4 embedded 1 Mb ReRAM in 28 nm CMOS with 0.27-to-1V read using swing-sample-and-couple sense amplifier and self-boost-write-termination scheme. In: 2014 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference Digest of Technical Papers (ISSCC) (ed Stetzler, T.) 332-333 (IEEE, 2014).
- Chen, Z. et al. Ultrafast multilevel switching in Au/YIG/n-Si RRAM. Adv. Electron. Mater. 5, 1800418 (2019).
- Wang, C. et al. Ultrafast RESET analysis of HfOx-based RRAM by sub-nanosecond pulses. Adv. Electron. Mater. 3, 1700263 (2017).
- Shrestha, P. R. et al. Energy control paradigm for compliance-free reliable operation of RRAM. In: 2014 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium MY-10 (IEEE, 2014).
- Choi, B. J. et al. High-speed and low-energy nitride memristors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 26, 5290-5296 (2016).
- Lee, H. Y. et al. Evidence and solution of over-RESET problem for HfO x based resistive memory with sub-ns switching speed and high endurance. In: 2010 International Electron Devices Meeting (ed leong, M.) 19-7 (IEEE, 2010).
- Choi, B. J. et al. Electrical performance and scalability of Pt dispersed
nanometallic resistance switch. Nano letters 13, 3213-3217 (2013). - Torrezan, A. C., Strachan, J. P., Medeiros-Ribeiro, G. & Williams, R. S. Sub-nanosecond switching of a tantalum oxide memristor. Nanotechnology 22, 485203 (2011).
- Böttger, U. et al. Picosecond multilevel resistive switching in tantalum oxide thin films. Sci. Rep. 10, 1-9 (2020).
- Zhang, F. et al. An ultra-fast multi-level MoTe 2-based RRAM. In: 2018 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) (ed Takayanagi, M.) 22-27 (IEEE, 2018).
- Kim, M. et al. Monolayer molybdenum disulfide switches for 6 G communication systems. Nat. Electron. 5, 1-7 (2022).
- Chen, S. et al. Wafer-scale integration of two-dimensional materials in high-density memristive crossbar arrays for artificial neural networks. Nat. Electron. 3, 638-645 (2020).
- Zhu, K. et al. Graphene-boron nitride-graphene cross-point memristors with three stable resistive states. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 37999-38005 (2019).
- Zhuang, P. et al. Nonpolar resistive switching of multilayer-hBNbased memories. Adv. Electron. Mater. 6, 1900979 (2020).
- Fantini, A. et al. Intrinsic switching variability in HfO 2 RRAM. In: 2013 5th IEEE International Memory Workshop 30-33 (IEEE, 2013).
- Ambrogio, S. et al. Understanding switching variability and random telegraph noise in resistive RAM. In: 2013 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (ed Ghani, T.) 31-35 (IEEE, 2013)
- Guan, X., Yu, S. & Wong, H.S.P. On the switching parameter variation of metal-oxide RRAM-Part I: Physical modeling and simulation methodology. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 59, 172-1182 (2012).
- Shen, Y. et al. Variability and yield in h-BN-based memristive circuits: the role of each type of defect. Adv. Mater. 33, 2103656 (2021).
- Shi, Y. et al. Electronic synapses made of layered two-dimensional materials. Nat. Electron. 1, 458-465 (2018).
- Lim, E. W. & Ismail, R. Conduction mechanism of valence change resistive switching memory: a survey. Electronics 4, 586-613 (2015).
- Chakraborty, I., Panwar, N., Khanna, A. & Ganguly, U. Space Charge Limited Current with Self-heating in
based RRAM. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1605.08755 (2016). - Puglisi, F. M. et al. 2D h-BN based RRAM devices. In: 2016 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) (ed Fay, P.) 34-38 (IEEE, 2016).
- Zhu, K. et al. Hybrid 2D-CMOS microchips for memristive applications. Nature 618, 57-62 (2023).
- Yu, S. & Wong, H. S. P. Compact modeling of conducting-bridge random-access memory (CBRAM). IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 58, 1352-1360 (2011).
- Ielmini, D. Modeling the universal set/reset characteristics of bipolar RRAM by field-and temperature-driven filament growth. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 58, 4309-4317 (2011).
- Huang, P. et al. A physics-based compact model of metal-oxidebased RRAM DC and AC operations. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 60, 4090-4097 (2013).
- Ielmini, D., Nardi, F. & Cagli, C. Physical models of size-dependent nanofilament formation and rupture in NiO resistive switching memories. Nanotechnology 22, 254022 (2011).
- Jo, I. et al. Thermal conductivity and phonon transport in suspended few-layer hexagonal boron nitride. Nano Lett. 13, 550-554 (2013).
- Alam, M. T., Bresnehan, M. S., Robinson, J. A. & Haque, M. A. Thermal conductivity of ultra-thin chemical vapor deposited hexagonal boron nitride films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 104 (2014).
- Panzer, M. A. et al. Thermal properties of ultrathin hafnium oxide gate dielectric films. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 30, 1269-1271 (2009).
- Cappella, A. et al. High temperature thermal conductivity of amorphous
thin films grown by low temperature ALD. Adv. Eng. Mater. 15, 1046-1050 (2013). - Landon, C. D. et al. Thermal transport in tantalum oxide films for memristive applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 107 (2015).
- Kwon, D. H. et al. Atomic structure of conducting nanofilaments in TiO2 resistive switching memory. Nat. Nanotechnol. 5, 148-153 (2010).
- Tsuruoka, T., Hasegawa, T., Terabe, K. & Aono, M. Conductance quantization and synaptic behavior in a Ta2O5-based atomic switch. Nanotechnology 23, 435705 (2012).
- Lee, S., Sohn, J., Jiang, Z., Chen, H. Y. & Philip Wong, H. S. Metal oxide-resistive memory using graphene-edge electrodes. Nat. Commun. 6, 1-7 (2015).
- Zhuang, P., Ma, W., Liu, J., Cai, W. & Lin, W. Progressive RESET induced by Joule heating in hBN RRAMs. Appl. Phys. Lett. 118, 143101 (2021).
- Lanza, M. et al. Temperature of conductive nanofilaments in hexagonal boron nitride based memristors showing threshold resistive switching. Adv. Electron. Mater. 8, 2100580 (2022).
- Li, S. et al. Fully coupled multiphysics simulation of crosstalk effect in bipolar resistive random access memory. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 64, 3647-3653 (2017).
- Hsieh, C. C., Roy, A., Chang, Y. F., Shahrjerdi, D. & Banerjee, S. K. A sub-1-volt analog metal oxide memristive-based synaptic device with large conductance change for energy-efficient spike-based computing systems. Appl. Phys. Lett. 109, 223501 (2016).
Acknowledgements
Author contributions
Competing interests
Additional information
supplementary material available at
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46372-y.
http://www.nature.com/reprints
(c) The Author(s) 2024
Microelectronics Research Center, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX 78758, USA. Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra, Ranchi 835215, India. HRL Laboratories, Malibu, CA 90265, USA. Texas Materials Institute, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX 78712, USA. M2D solutions, Austin, TX 78758, USA. e-mail: subrahmanya_teja@utexas.edu; royanupam@bitmesra.ac.in; banerjee@ece.utexas.edu
