DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.3c14487
PMID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38531024
تاريخ النشر: 2024-03-26
امتصاص استثنائي عالي لحمض البيرفلوروأوكتانويك في الماء بواسطة إطار معدني عضوي قائم على الزركونيوم من خلال الامتزاز الكيميائي والفيزيائي التآزري
للاستشهاد بهذه النسخة:
امتصاص استثنائي لحمض البيرفلوروأوكتانويك في الماء بواسطة إطار معدني عضوي قائم على الزركونيوم من خلال الامتزاز الكيميائي والفيزيائي التآزري
اقرأ على الإنترنت
الملخص
حمض البيرفلوروأوكتانويك (PFOA) هو ملوث بيئي موجود في موارد المياه، والذي كعامل غريب ومسرطن، يشكل تهديدًا خطيرًا لصحة الإنسان. لذلك، فإن تطوير تقنيات لإزالته بكفاءة مطلوب بشدة. هنا، نعرض إطارًا معدنيًا عضويًا قائمًا على الزركونيوم (PCN-999) يمتلك
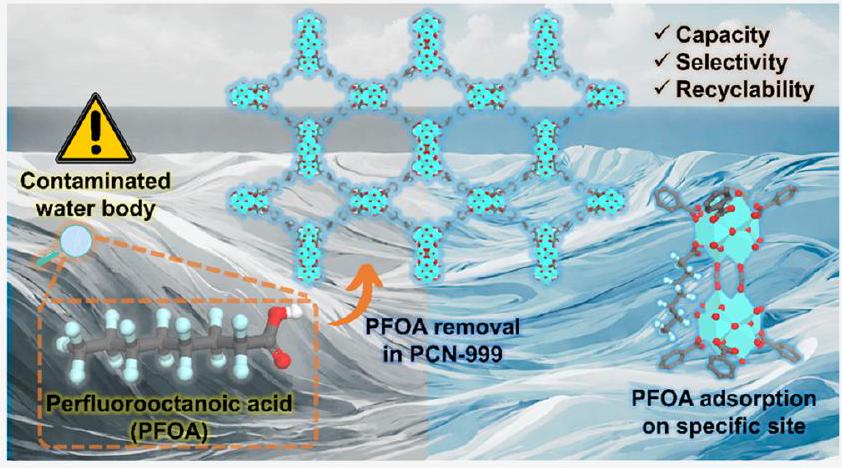 التفاعل بين PFOAs المنسقة والحرّة لعملية الامتزاز الفيزيائي، مما يعزز قدرة الامتزاز إلى مستوى غير مسبوق. تمثل نتائجنا خطوة كبيرة إلى الأمام في الفهم الأساسي لآلية إزالة PFOA المعتمدة على MOF، مما يمهد الطريق نحو التصميم العقلاني للمواد الماصة من الجيل التالي لإزالة المواد الفلورية المشبعة وغير المشبعة (PFAS).
التفاعل بين PFOAs المنسقة والحرّة لعملية الامتزاز الفيزيائي، مما يعزز قدرة الامتزاز إلى مستوى غير مسبوق. تمثل نتائجنا خطوة كبيرة إلى الأمام في الفهم الأساسي لآلية إزالة PFOA المعتمدة على MOF، مما يمهد الطريق نحو التصميم العقلاني للمواد الماصة من الجيل التالي لإزالة المواد الفلورية المشبعة وغير المشبعة (PFAS).
– المقدمة
تعتبر راتنجات التبادل من أحدث المواد الماصة لإزالة المواد الكيميائية PFAS.
تمت المراجعة: 11 مارس 2024
تم القبول: 12 مارس 2024
نُشر: 26 مارس 2024
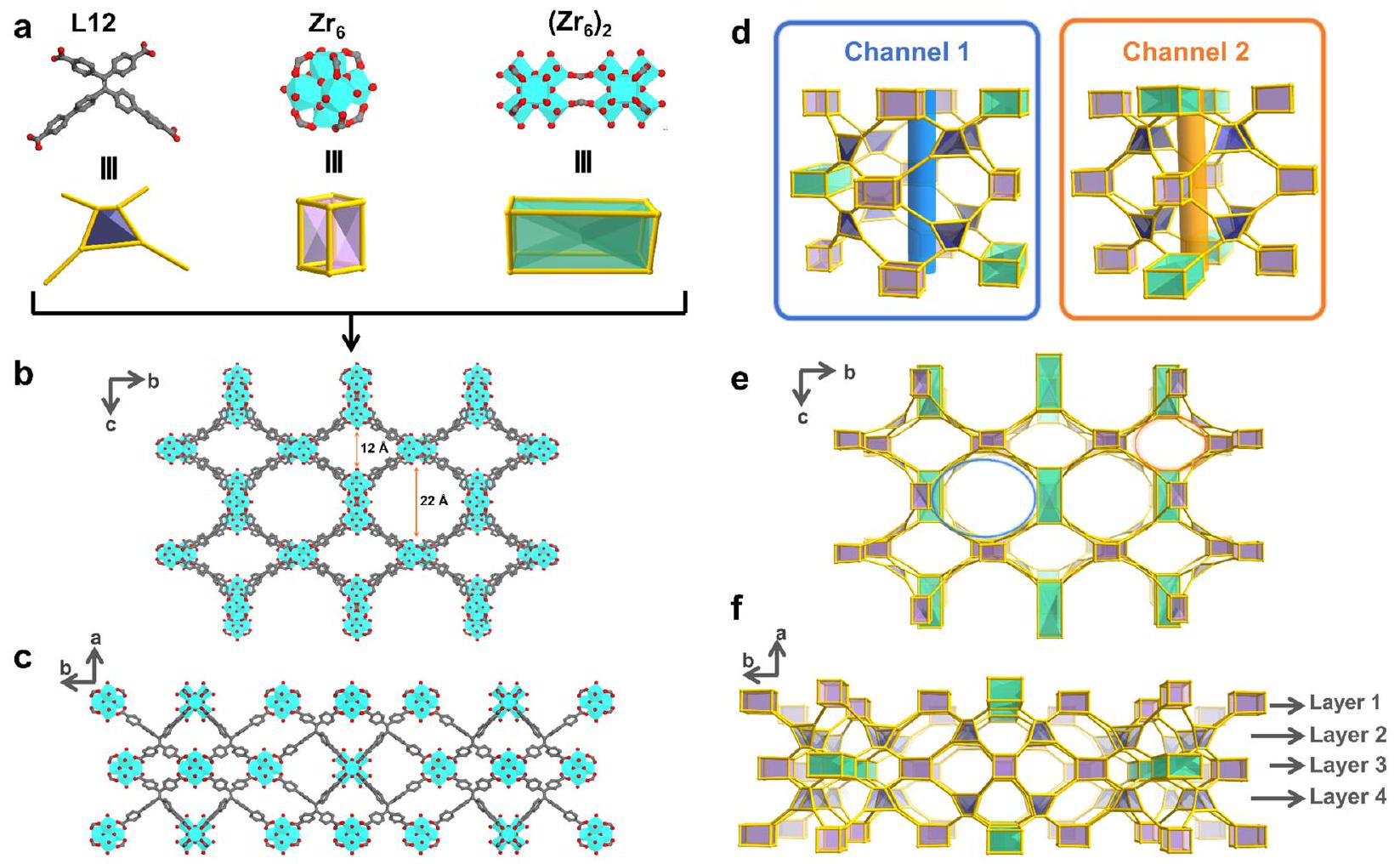
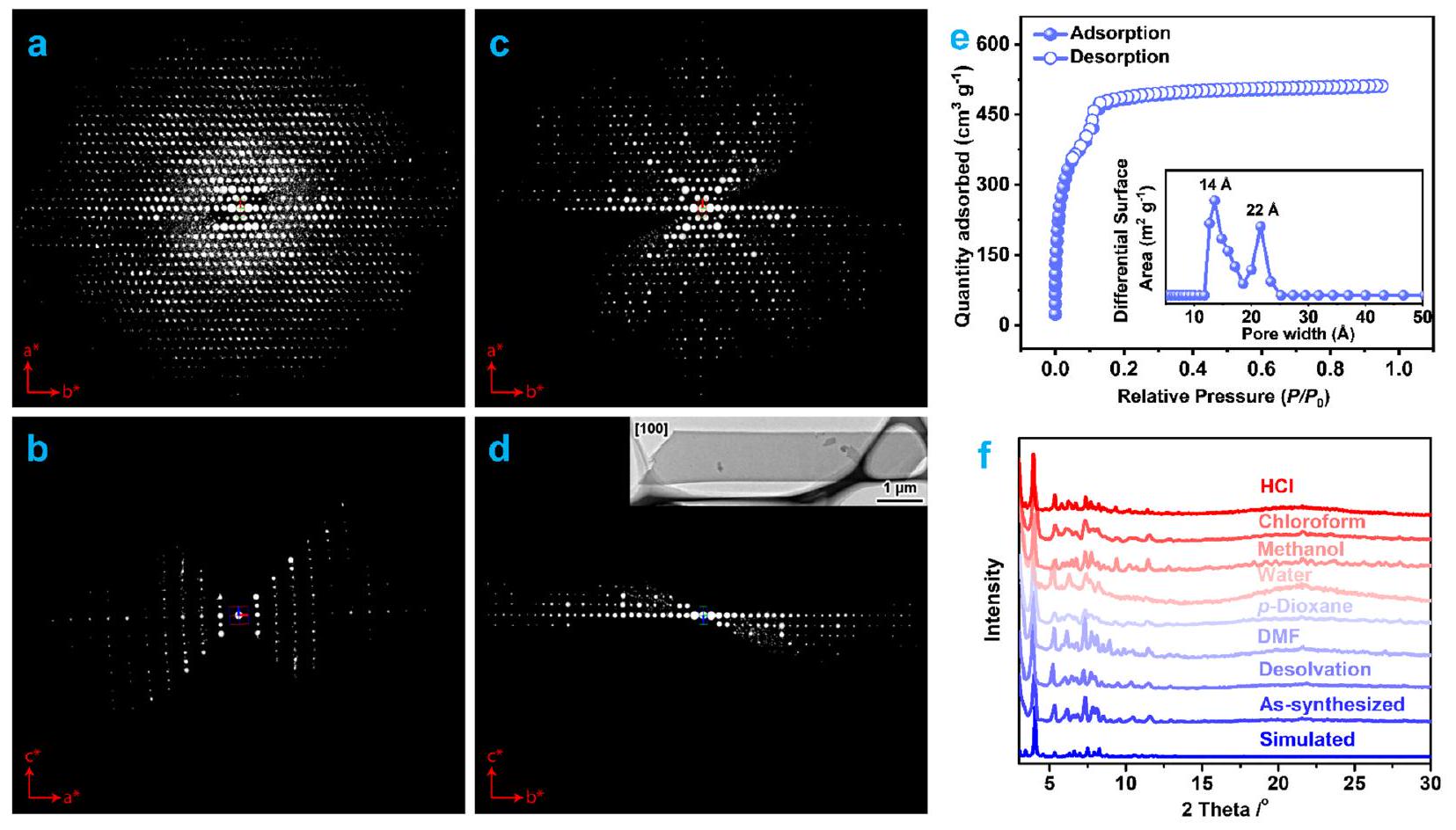
ترافق السعة مع كينتيك الامتصاص السريع، وعمر دورة طويل، وانتقائية عالية. كشفت التحليلات الهيكلية المفصلة، بما في ذلك حيود الأشعة السينية أحادية البلورة (SCXRD)، وطيف الأشعة تحت الحمراء بتحويل فورييه (FTIR)، واختبارات المسامية، والحسابات عن تنسيق مجموعة الكربوكسيلات من PFOA حصريًا مع
– النتائج والمناقشة
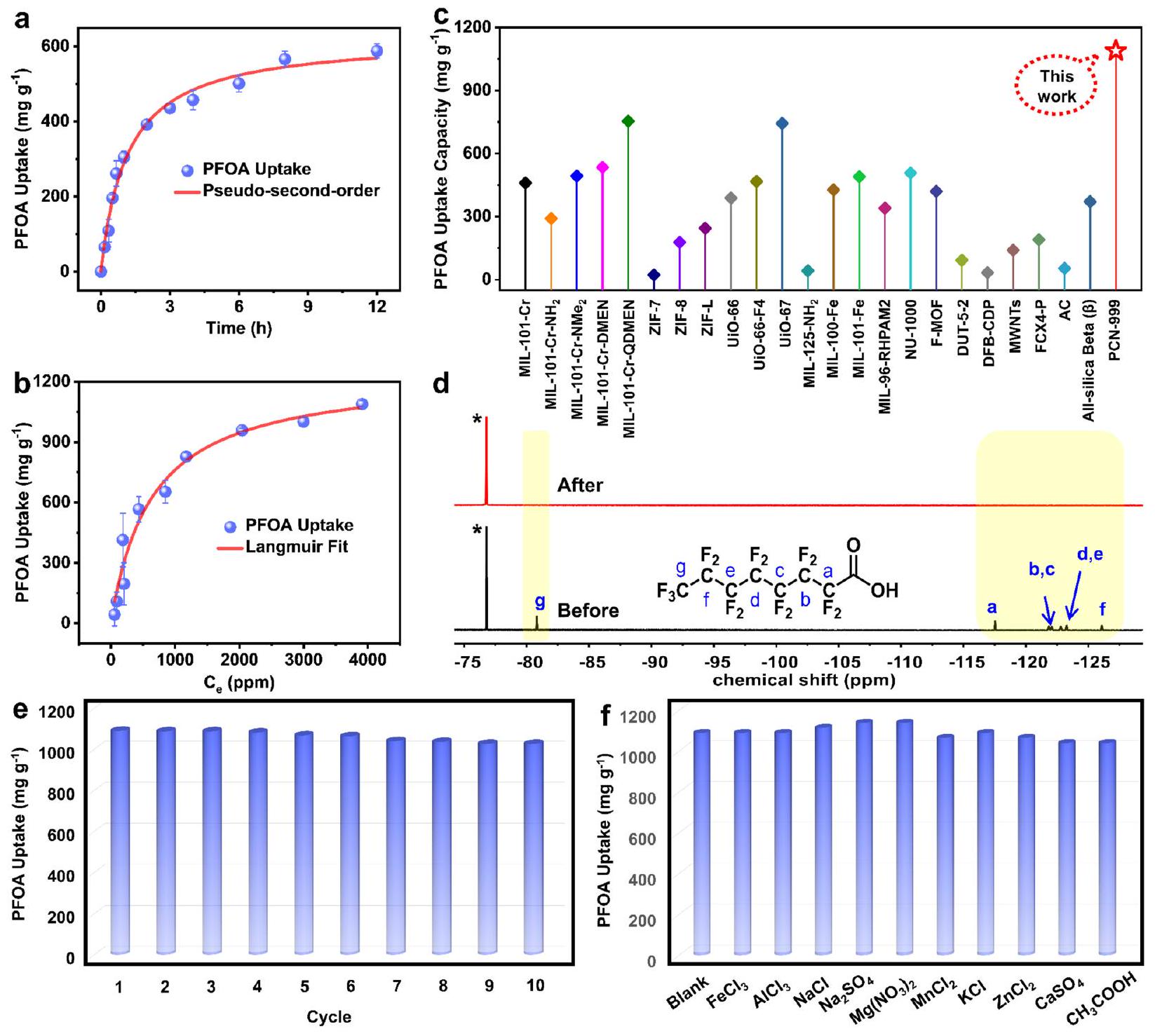
لقد شجعتنا الأداء المتميز على مزيد من التحقيق في حركيات عملية الامتزاز (الشكل S11). كما هو موضح في الشكل 3a، تظهر عملية الامتزاز حركيات سريعة حيث يتم الوصول إلى التوازن خلال 12 ساعة، مما يعطي ثابت سرعة امتزاز مرتفع.
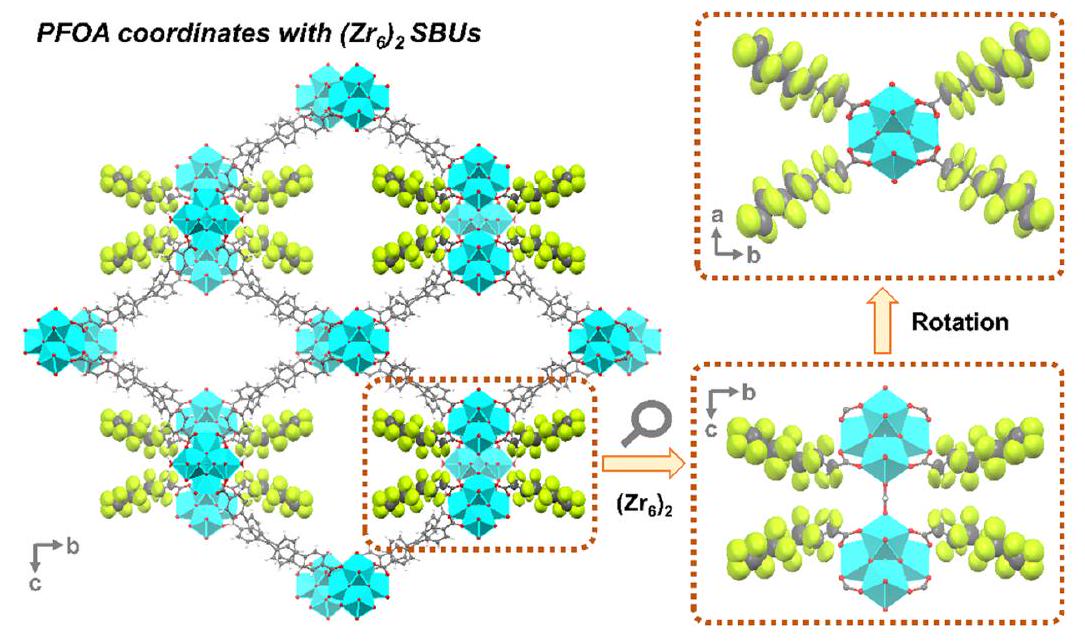
, فإن عدم وجود تفاعل بين سلاسل الكربون الفلورية الكارهة للماء الناتجة عن PFOA المنسقة والمجانية سيساهم في الانتقائية العالية.
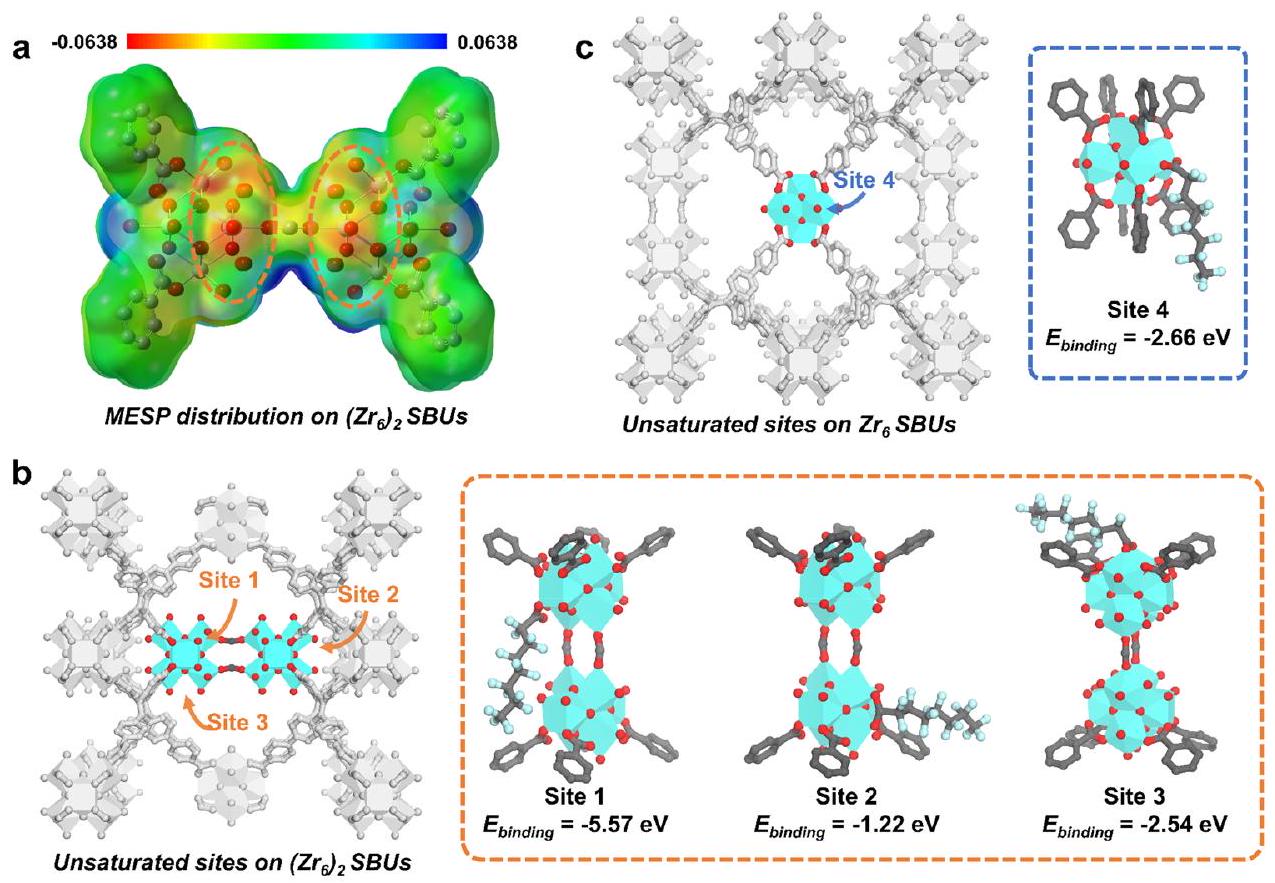
المجمعة GFN1-xtb لتحسين الهياكل النموذجية وحساب طاقة الارتباط، مما كشف أن الموقع 1 داخل (
– الاستنتاجات
بشكل معقد بثماني روابط، مما يؤدي إلى توليد عدة مواقع تنسيق مفتوحة. الميزات الهيكلية الدقيقة على المستوى الذري، جنبًا إلى جنب مع استقرارها الكيميائي والفيزيائي الاستثنائي، تمنح PCN-999 أداءً ملحوظًا في احتجاز PFOA، كما تم قياسه بسعة امتصاص قدرها
– المحتوى المرتبط
(s) المعلومات الداعمة
رموز الوصول
– معلومات المؤلف
المؤلفون المراسلون
Paolo Samorì – جامعة ستراسبورغ، CNRS، ISIS، 67000 ستراسبورغ، فرنسا؛ ©orcid.org/0000-0001-6256-8281؛ البريد الإلكتروني:samori@unistra.fr
Hong-Cai Zhou – قسم الكيمياء، جامعة تكساس A&M، كوليدج ستيشن، تكساس 77843، الولايات المتحدة؛ ©orcid.org/0000-0002-9029-3788؛ البريد الإلكتروني: zhou@chem.tamu.edu
المؤلفون
Shunqi Xu – جامعة ستراسبورغ، CNRS، ISIS، 67000 ستراسبورغ، فرنسا
Zongsu Han – قسم الكيمياء، جامعة تكساس A&M، كوليدج ستيشن، تكساس 77843، الولايات المتحدة
Kun-Yu Wang – قسم الكيمياء، جامعة تكساس A&M، كوليدج ستيشن، تكساس 77843، الولايات المتحدة
Zhehao Huang – قسم المواد والكيمياء البيئية، جامعة ستوكهولم، SE-106 91 ستوكهولم، السويد؛orcid.org/0000-0002-4575-7870
Joshua Rushlow – قسم الكيمياء، جامعة تكساس A&M، كوليدج ستيشن، تكساس 77843، الولايات المتحدة
معلومات الاتصال الكاملة متاحة على:
https://pubs.acs.org/10.1021/jacs.3c14487
مساهمات المؤلف
ملاحظات
– الشكر والتقدير
– REFERENCES
(2) Trang, B.; Li, Y.; Xue, X.-S.; Ateia, M.; Houk, K. N.; Dichtel, W. R. Low-temperature mineralization of perfluorocarboxylic acids. Science 2022, 377, 839-845.
(3) Li, R.; Adarsh, N. N.; Lu, H.; Wriedt, M. Metal-organic frameworks as platforms for the removal of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances from contaminated waters. Matter 2022, 5, 3161-3193.
(4) Evich, M. G.; Davis, M. J. B.; McCord, J. P.; Acrey, B.; Awkerman, J. A.; Knappe, D. R. U.; Lindstrom, A. B.; Speth, T. F.; Tebes-Stevens, C.; Strynar, M. J.; Wang, Z.; Weber, E. J.; Henderson, W. M.; Washington, J. W. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment. Science 2022, 375, eabg9065.
(5) Duh-Leong, C.; Maffini, M. V.; Kassotis, C. D.; Vandenberg, L. N.; Trasande, L. The regulation of endocrine-disrupting chemicals to minimize their impact on health. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 600614.
(6) Ji, W.; Xiao, L.; Ling, Y.; Ching, C.; Matsumoto, M.; Bisbey, R. P.; Helbling, D. E.; Dichtel, W. R. Removal of GenX and Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances from Water by Amine-Functionalized Covalent Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1267712681.
(7) Chen, Z.; Lu, Y. L.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Cheng, P.; Yang, S.; Shi, W. Efficient Recognition and Removal of Persistent Organic Pollutants by a Bifunctional Molecular Material. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 260-267.
(8) Román Santiago, A.; Yin, S.; Elbert, J.; Lee, J.; Shukla, D.; Su, X. Imparting Selective Fluorophilic Interactions in Redox Copolymers for the Electrochemically Mediated Capture of Short-Chain Perfluoroalkyl Substances. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 9508-9519.
(9) Wen, Y.; Rentería-Gómez, Á.; Day, G. S.; Smith, M. F.; Yan, T. H.; Ozdemir, R. O. K.; Gutierrez, O.; Sharma, V. K.; Ma, X.; Zhou, H.-C. Integrated Photocatalytic Reduction and Oxidation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid by Metal-Organic Frameworks: Key Insights into the Degradation Mechanisms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 11840-11850.
(10) Fang, Y.; Meng, P.; Schaefer, C.; Knappe, D. R. U. Removal and destruction of perfluoroalkyl ether carboxylic acids (PFECAs) in an anion exchange resin and electrochemical oxidation treatment train. Water. Res. 2023, 230, 119522.
(11) Sinha, S.; Chaturvedi, A.; Gautam, R. K.; Jiang, J. J. Molecular Cu Electrocatalyst Escalates Ambient Perfluorooctanoic Acid Degradation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 27390-27396.
(12) Li, J.; Li, X.; Da, Y.; Yu, J.; Long, B.; Zhang, P.; Bakker, C.; McCarl, B. A.; Yuan, J. S.; Dai, S. Y. Sustainable environmental remediation via biomimetic multifunctional lignocellulosic nanoframework. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4368.
(13) Zhang, C.; Yan, K.; Fu, C.; Peng, H.; Hawker, C. J.; Whittaker, A. K. Biological Utility of Fluorinated Compounds: from Materials Design to Molecular Imaging, Therapeutics and Environmental Remediation. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 167-208.
(14) Liu, H.; Yao, Y.; Samori, P. Taming Multiscale Structural Complexity in Porous Skeletons: From Open Framework Materials to Micro/Nanoscaffold Architectures. Small Methods 2023, 7, e2300468.
(15) Feng, G.; Cheng, P.; Yan, W.; Boronat, M.; Li, X.; Su, J.-H.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Corma, A.; Xu, R.; Yu, J. Accelerated crystallization of zeolites via hydroxyl free radicals. Science 2016, 351, 1188-1191.
(16) McDonald, T. M.; Mason, J. A.; Kong, X.; Bloch, E. D.; Gygi, D.; Dani, A.; Crocellà, V.; Giordanino, F.; Odoh, S. O.; Drisdell, W. S.; Vlaisavljevich, B.; Dzubak, A. L.; Poloni, R.; Schnell, S. K.; Planas, N.; Lee, K.; Pascal, T.; Wan, L. F.; Prendergast, D.; Neaton, J. B.; Smit, B.; Kortright, J. B.; Gagliardi, L.; Bordiga, S.; Reimer, J. A.; Long, J. R. Cooperative insertion of
(17) Furukawa, H.; Cordova, K. E.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O. M. The chemistry and applications of metal-organic frameworks. Science 2013, 341, 1230444.
(18) Cui, Y.; Yue, Y.; Qian, G.; Chen, B. Luminescent functional metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1126-1162.
(19) Zhou, H.-C.; Long, J. R.; Yaghi, O. M. Introduction to metalorganic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 673-674.
(20) Chen, Z.; Kirlikovali, K. O.; Li, P.; Farha, O. K. Reticular Chemistry for Highly Porous Metal-Organic Frameworks: The Chemistry and Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 579-591.
(21) Champness, N. R. Porous materials: Lining up metal-organic frameworks. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 283-284.
(22) Dong, R.; Feng, X. Making large single crystals of 2D MOFs. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 122-123.
(23) Zhang, C.; Dong, J.; Zhang, P.; Sun, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, W.; Zou, X.; Chen, Y.; Shang, Q.; Feng, D.; Zhu, G. Unique fluorophilic pores engineering within porous aromatic frameworks for trace perfluorooctanoic acid removal. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwad191.
(24) Liu, X.; Zhu, C.; Yin, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Shui, F.; You, Z.; Shi, Z.; Li, B.; Bu, X.-H.; Nafady, A.; Ma, S. Installation of synergistic binding sites onto porous organic polymers for efficient removal of perfluorooctanoic acid. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2132.
(25) Wang, W.; Zhou, Z.; Shao, H.; Zhou, S.; Yu, G.; Deng, S. Cationic covalent organic framework for efficient removal of PFOA substitutes from aqueous solution. Chemical Engineering Journal 2021, 412, 127509.
(26) Li, R.; Alomari, S.; Islamoglu, T.; Farha, O. K.; Fernando, S.; Thagard, S. M.; Holsen, T. M.; Wriedt, M. Systematic Study on the Removal of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances from Contaminated Groundwater Using Metal-Organic Frameworks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 15162-15171.
(27) Li, R.; Alomari, S.; Stanton, R.; Wasson, M. C.; Islamoglu, T.; Farha, O. K.; Holsen, T. M.; Thagard, S. M.; Trivedi, D. J.; Wriedt, M. Efficient Removal of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances from Water
with Zirconium-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 3276-3285.
(28) Liu, K.; Zhang, S.; Hu, X.; Zhang, K.; Roy, A.; Yu, G. Understanding the Adsorption of PFOA on MIL-101(Cr)-Based Anionic-Exchange Metal-Organic Frameworks: Comparing DFT Calculations with Aqueous Sorption Experiments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8657-8665.
(29) Han, W.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Leng, F.; Xie, C.; Jiang, H. L. Endowing Porphyrinic Metal-Organic Frameworks with High Stability by a Linker Desymmetrization Strategy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 9665-9671.
(30) Lv, X. L.; Feng, L.; Xie, L. H.; He, T.; Wu, W.; Wang, K. Y.; Si, G.; Wang, B.; Li, J. R.; Zhou, H. C. Linker Desymmetrization: Access to a Series of Rare-Earth Tetracarboxylate Frameworks with EightConnected Hexanuclear Nodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 27842791.
(31) Wang, B.; Wang, P.; Xie, L. H.; Lin, R. B.; Lv, J.; Li, J. R.; Chen, B. A stable zirconium based metal-organic framework for specific recognition of representative polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin molecules. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3861.
(32) Ding, M.; Cai, X.; Jiang, H. L. Improving MOF stability: approaches and applications. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 10209-10230.
(33) Medishetty, R.; Nemec, L.; Nalla, V.; Henke, S.; Samoc, M.; Reuter, K.; Fischer, R. A. Multi-Photon Absorption in Metal-Organic Frameworks. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14743-14748.
(34) Qiao, G. Y.; Yuan, S.; Pang, J.; Rao, H.; Lollar, C. T.; Dang, D.; Qin, J. S.; Zhou, H. C.; Yu, J. Functionalization of Zirconium-Based Metal-Organic Layers with Tailored Pore Environments for Heterogeneous Catalysis. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 1822418228.
(35) Zhou, P.; Yue, L.; Wang, X.; Fan, L.; Chen, D.-L.; He, Y. Improving Ethane/Ethylene Separation Performance of Isoreticular Metal-Organic Frameworks via Substituent Engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 54059-54068.
(36) Wang, X.; Yue, L.; Zhou, P.; Fan, L.; He, Y. LanthanideOrganic Frameworks Featuring Three-Dimensional Inorganic Connectivity for Multipurpose Hydrocarbon Separation. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 17249-17257.
(37) Yang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Ji, W.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X. Insights to perfluorooctanoic acid adsorption micro-mechanism over Fe-based metal organic frameworks: Combining computational calculation with response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122686.
(38) Xiao, L.; Ling, Y.; Alsbaiee, A.; Li, C.; Helbling, D. E.; Dichtel, W. R. beta-Cyclodextrin Polymer Network Sequesters Perfluorooctanoic Acid at Environmentally Relevant Concentrations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 7689-7692.
(39) Van den Bergh, M.; Krajnc, A.; Voorspoels, S.; Tavares, S. R.; Mullens, S.; Beurroies, I.; Maurin, G.; Mali, G.; De Vos, D. E. Highly Selective Removal of Perfluorinated Contaminants by Adsorption on All-Silica Zeolite Beta. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 14086-14090.
(40) Hadjiivanov, K. I.; Panayotov, D. A.; Mihaylov, M. Y.; Ivanova, E. Z.; Chakarova, K. K.; Andonova, S. M.; Drenchev, N. L. Power of Infrared and Raman Spectroscopies to Characterize Metal-Organic Frameworks and Investigate Their Interaction with Guest Molecules. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1286-1424.
(41) Shi, Y.; Mu, H.; You, J.; Han, C.; Cheng, H.; Wang, J.; Hu, H.; Ren, H. Confined water-encapsulated activated carbon for capturing short-chain perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances from drinking water. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2023, 120, e2219179120.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.3c14487
PMID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38531024
Publication Date: 2024-03-26
Exceptionally High Perfluorooctanoic Acid Uptake in Water by a Zirconium-Based Metal-Organic Framework through Synergistic Chemical and Physical Adsorption
To cite this version:
Exceptionally High Perfluorooctanoic Acid Uptake in Water by a Zirconium-Based Metal-Organic Framework through Synergistic Chemical and Physical Adsorption
Read Online
Abstract
Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) is an environmental contaminant ubiquitous in water resources, which as a xenobiotic and carcinogenic agent, severely endangers human health. The development of techniques for its efficient removal is therefore highly sought after. Herein, we demonstrate an unprecedented zirconium-based MOF (PCN-999) possessing
 interaction between coordinated and free PFOAs for physical adsorption, boosting the adsorption capacity to an unparalleled high standard. Our findings represent a major step forward in the fundamental understanding of the MOF-based PFOA removal mechanism, paving the way toward the rational design of nextgeneration adsorbents for per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) removal.
interaction between coordinated and free PFOAs for physical adsorption, boosting the adsorption capacity to an unparalleled high standard. Our findings represent a major step forward in the fundamental understanding of the MOF-based PFOA removal mechanism, paving the way toward the rational design of nextgeneration adsorbents for per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) removal.
– INTRODUCTION
exchange resin are the state-of-the-art adsorbents for PFAS removal.
Revised: March 11, 2024
Accepted: March 12, 2024
Published: March 26, 2024

capacity is accompanied by rapid adsorption kinetics, long cycle life, and high selectivity. Detailed structural analyses, including single-crystal X-ray diffraction (SCXRD), Fouriertransform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, porosity tests, and computations revealed the coordination of the carboxylate group of PFOA exclusively with the
– RESULTS AND DISCUSSION


outstanding performance encouraged us to further investigate the kinetics of the adsorption process (Figure S11). As shown in Figure 3a, the adsorption process exhibits fast kinetics with the equilibrium being reached within 12 h , which gives a high adsorption rate constant

performance toward PFBS, indicating the preference of the MOF toward carboxylate-based PFASs.

combined GFN1-xtb method was applied to optimize the model structures and calculate the binding energy, which revealed that site 1 within the (
– CONCLUSIONS
intricately connected to eight ligands, resulting in the generation of multiple open coordination sites. The atomically precise structural features, coupled with its exceptional chemical and physical stability, endow PCN-999 with a remarkable PFOA adsorption performance, as quantified by an uptake capacity of
– ASSOCIATED CONTENT
(s) Supporting Information
Accession Codes
– AUTHOR INFORMATION
Corresponding Authors
Paolo Samorì – Université de Strasbourg, CNRS, ISIS, 67000 Strasbourg, France; © orcid.org/0000-0001-6256-8281; Email: samori@unistra.fr
Hong-Cai Zhou – Department of Chemistry, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas 77843, United States; © orcid.org/0000-0002-9029-3788; Email: zhou@ chem.tamu.edu
Authors
Shunqi Xu – Université de Strasbourg, CNRS, ISIS, 67000 Strasbourg, France
Zongsu Han – Department of Chemistry, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas 77843, United States
Kun-Yu Wang – Department of Chemistry, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas 77843, United States
Zhehao Huang – Department of Materials and Environmental Chemistry, Stockholm University, SE-106 91 Stockholm, Sweden; orcid.org/0000-0002-4575-7870
Joshua Rushlow – Department of Chemistry, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas 77843, United States
Complete contact information is available at:
https://pubs.acs.org/10.1021/jacs.3c14487
Author Contributions
Notes
– ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
– REFERENCES
(2) Trang, B.; Li, Y.; Xue, X.-S.; Ateia, M.; Houk, K. N.; Dichtel, W. R. Low-temperature mineralization of perfluorocarboxylic acids. Science 2022, 377, 839-845.
(3) Li, R.; Adarsh, N. N.; Lu, H.; Wriedt, M. Metal-organic frameworks as platforms for the removal of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances from contaminated waters. Matter 2022, 5, 3161-3193.
(4) Evich, M. G.; Davis, M. J. B.; McCord, J. P.; Acrey, B.; Awkerman, J. A.; Knappe, D. R. U.; Lindstrom, A. B.; Speth, T. F.; Tebes-Stevens, C.; Strynar, M. J.; Wang, Z.; Weber, E. J.; Henderson, W. M.; Washington, J. W. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment. Science 2022, 375, eabg9065.
(5) Duh-Leong, C.; Maffini, M. V.; Kassotis, C. D.; Vandenberg, L. N.; Trasande, L. The regulation of endocrine-disrupting chemicals to minimize their impact on health. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 600614.
(6) Ji, W.; Xiao, L.; Ling, Y.; Ching, C.; Matsumoto, M.; Bisbey, R. P.; Helbling, D. E.; Dichtel, W. R. Removal of GenX and Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances from Water by Amine-Functionalized Covalent Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1267712681.
(7) Chen, Z.; Lu, Y. L.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Cheng, P.; Yang, S.; Shi, W. Efficient Recognition and Removal of Persistent Organic Pollutants by a Bifunctional Molecular Material. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 260-267.
(8) Román Santiago, A.; Yin, S.; Elbert, J.; Lee, J.; Shukla, D.; Su, X. Imparting Selective Fluorophilic Interactions in Redox Copolymers for the Electrochemically Mediated Capture of Short-Chain Perfluoroalkyl Substances. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 9508-9519.
(9) Wen, Y.; Rentería-Gómez, Á.; Day, G. S.; Smith, M. F.; Yan, T. H.; Ozdemir, R. O. K.; Gutierrez, O.; Sharma, V. K.; Ma, X.; Zhou, H.-C. Integrated Photocatalytic Reduction and Oxidation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid by Metal-Organic Frameworks: Key Insights into the Degradation Mechanisms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 11840-11850.
(10) Fang, Y.; Meng, P.; Schaefer, C.; Knappe, D. R. U. Removal and destruction of perfluoroalkyl ether carboxylic acids (PFECAs) in an anion exchange resin and electrochemical oxidation treatment train. Water. Res. 2023, 230, 119522.
(11) Sinha, S.; Chaturvedi, A.; Gautam, R. K.; Jiang, J. J. Molecular Cu Electrocatalyst Escalates Ambient Perfluorooctanoic Acid Degradation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 27390-27396.
(12) Li, J.; Li, X.; Da, Y.; Yu, J.; Long, B.; Zhang, P.; Bakker, C.; McCarl, B. A.; Yuan, J. S.; Dai, S. Y. Sustainable environmental remediation via biomimetic multifunctional lignocellulosic nanoframework. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4368.
(13) Zhang, C.; Yan, K.; Fu, C.; Peng, H.; Hawker, C. J.; Whittaker, A. K. Biological Utility of Fluorinated Compounds: from Materials Design to Molecular Imaging, Therapeutics and Environmental Remediation. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 167-208.
(14) Liu, H.; Yao, Y.; Samori, P. Taming Multiscale Structural Complexity in Porous Skeletons: From Open Framework Materials to Micro/Nanoscaffold Architectures. Small Methods 2023, 7, e2300468.
(15) Feng, G.; Cheng, P.; Yan, W.; Boronat, M.; Li, X.; Su, J.-H.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Corma, A.; Xu, R.; Yu, J. Accelerated crystallization of zeolites via hydroxyl free radicals. Science 2016, 351, 1188-1191.
(16) McDonald, T. M.; Mason, J. A.; Kong, X.; Bloch, E. D.; Gygi, D.; Dani, A.; Crocellà, V.; Giordanino, F.; Odoh, S. O.; Drisdell, W. S.; Vlaisavljevich, B.; Dzubak, A. L.; Poloni, R.; Schnell, S. K.; Planas, N.; Lee, K.; Pascal, T.; Wan, L. F.; Prendergast, D.; Neaton, J. B.; Smit, B.; Kortright, J. B.; Gagliardi, L.; Bordiga, S.; Reimer, J. A.; Long, J. R. Cooperative insertion of
(17) Furukawa, H.; Cordova, K. E.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O. M. The chemistry and applications of metal-organic frameworks. Science 2013, 341, 1230444.
(18) Cui, Y.; Yue, Y.; Qian, G.; Chen, B. Luminescent functional metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1126-1162.
(19) Zhou, H.-C.; Long, J. R.; Yaghi, O. M. Introduction to metalorganic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 673-674.
(20) Chen, Z.; Kirlikovali, K. O.; Li, P.; Farha, O. K. Reticular Chemistry for Highly Porous Metal-Organic Frameworks: The Chemistry and Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 579-591.
(21) Champness, N. R. Porous materials: Lining up metal-organic frameworks. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 283-284.
(22) Dong, R.; Feng, X. Making large single crystals of 2D MOFs. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 122-123.
(23) Zhang, C.; Dong, J.; Zhang, P.; Sun, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, W.; Zou, X.; Chen, Y.; Shang, Q.; Feng, D.; Zhu, G. Unique fluorophilic pores engineering within porous aromatic frameworks for trace perfluorooctanoic acid removal. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwad191.
(24) Liu, X.; Zhu, C.; Yin, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Shui, F.; You, Z.; Shi, Z.; Li, B.; Bu, X.-H.; Nafady, A.; Ma, S. Installation of synergistic binding sites onto porous organic polymers for efficient removal of perfluorooctanoic acid. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2132.
(25) Wang, W.; Zhou, Z.; Shao, H.; Zhou, S.; Yu, G.; Deng, S. Cationic covalent organic framework for efficient removal of PFOA substitutes from aqueous solution. Chemical Engineering Journal 2021, 412, 127509.
(26) Li, R.; Alomari, S.; Islamoglu, T.; Farha, O. K.; Fernando, S.; Thagard, S. M.; Holsen, T. M.; Wriedt, M. Systematic Study on the Removal of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances from Contaminated Groundwater Using Metal-Organic Frameworks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 15162-15171.
(27) Li, R.; Alomari, S.; Stanton, R.; Wasson, M. C.; Islamoglu, T.; Farha, O. K.; Holsen, T. M.; Thagard, S. M.; Trivedi, D. J.; Wriedt, M. Efficient Removal of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances from Water
with Zirconium-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 3276-3285.
(28) Liu, K.; Zhang, S.; Hu, X.; Zhang, K.; Roy, A.; Yu, G. Understanding the Adsorption of PFOA on MIL-101(Cr)-Based Anionic-Exchange Metal-Organic Frameworks: Comparing DFT Calculations with Aqueous Sorption Experiments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8657-8665.
(29) Han, W.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Leng, F.; Xie, C.; Jiang, H. L. Endowing Porphyrinic Metal-Organic Frameworks with High Stability by a Linker Desymmetrization Strategy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 9665-9671.
(30) Lv, X. L.; Feng, L.; Xie, L. H.; He, T.; Wu, W.; Wang, K. Y.; Si, G.; Wang, B.; Li, J. R.; Zhou, H. C. Linker Desymmetrization: Access to a Series of Rare-Earth Tetracarboxylate Frameworks with EightConnected Hexanuclear Nodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 27842791.
(31) Wang, B.; Wang, P.; Xie, L. H.; Lin, R. B.; Lv, J.; Li, J. R.; Chen, B. A stable zirconium based metal-organic framework for specific recognition of representative polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin molecules. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3861.
(32) Ding, M.; Cai, X.; Jiang, H. L. Improving MOF stability: approaches and applications. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 10209-10230.
(33) Medishetty, R.; Nemec, L.; Nalla, V.; Henke, S.; Samoc, M.; Reuter, K.; Fischer, R. A. Multi-Photon Absorption in Metal-Organic Frameworks. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14743-14748.
(34) Qiao, G. Y.; Yuan, S.; Pang, J.; Rao, H.; Lollar, C. T.; Dang, D.; Qin, J. S.; Zhou, H. C.; Yu, J. Functionalization of Zirconium-Based Metal-Organic Layers with Tailored Pore Environments for Heterogeneous Catalysis. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 1822418228.
(35) Zhou, P.; Yue, L.; Wang, X.; Fan, L.; Chen, D.-L.; He, Y. Improving Ethane/Ethylene Separation Performance of Isoreticular Metal-Organic Frameworks via Substituent Engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 54059-54068.
(36) Wang, X.; Yue, L.; Zhou, P.; Fan, L.; He, Y. LanthanideOrganic Frameworks Featuring Three-Dimensional Inorganic Connectivity for Multipurpose Hydrocarbon Separation. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 17249-17257.
(37) Yang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Ji, W.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X. Insights to perfluorooctanoic acid adsorption micro-mechanism over Fe-based metal organic frameworks: Combining computational calculation with response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122686.
(38) Xiao, L.; Ling, Y.; Alsbaiee, A.; Li, C.; Helbling, D. E.; Dichtel, W. R. beta-Cyclodextrin Polymer Network Sequesters Perfluorooctanoic Acid at Environmentally Relevant Concentrations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 7689-7692.
(39) Van den Bergh, M.; Krajnc, A.; Voorspoels, S.; Tavares, S. R.; Mullens, S.; Beurroies, I.; Maurin, G.; Mali, G.; De Vos, D. E. Highly Selective Removal of Perfluorinated Contaminants by Adsorption on All-Silica Zeolite Beta. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 14086-14090.
(40) Hadjiivanov, K. I.; Panayotov, D. A.; Mihaylov, M. Y.; Ivanova, E. Z.; Chakarova, K. K.; Andonova, S. M.; Drenchev, N. L. Power of Infrared and Raman Spectroscopies to Characterize Metal-Organic Frameworks and Investigate Their Interaction with Guest Molecules. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1286-1424.
(41) Shi, Y.; Mu, H.; You, J.; Han, C.; Cheng, H.; Wang, J.; Hu, H.; Ren, H. Confined water-encapsulated activated carbon for capturing short-chain perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances from drinking water. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2023, 120, e2219179120.
