DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-025-01294-7
تاريخ النشر: 2025-03-04
تعزيز صحة التربة وإنتاجية المحاصيل: دور بكتيريا حل الزنك في الزراعة المستدامة
© المؤلفون 2025
الملخص
الزنك ضروري للعديد من الوظائف الفسيولوجية للنباتات، بما في ذلك تنشيط الإنزيمات، وتخليق البروتينات، ومقاومة الضغوط. ومع ذلك، فإن ما يقرب من نصف الأراضي الزراعية في العالم تعاني من نقص الزنك، مما يؤثر سلبًا على إنتاجية المحاصيل وصحة الإنسان، خاصة في المناطق التي تعتمد على الأنظمة الغذائية النباتية. غالبًا ما تفشل طرق تكميل الزنك التقليدية، مثل الأسمدة الكيميائية، بسبب القيود البيئية والاقتصادية. تسلط هذه الدراسة الضوء على بكتيريا إذابة الزنك (ZSB) كبديل مستدام، قادرة على تحويل الزنك غير القابل للذوبان إلى أشكال حيوية متاحة من خلال آليات مثل إنتاج الأحماض العضوية، والتعقيد، ونشاط السايدروفور، مما يعزز امتصاص الزنك من قبل النباتات. تساهم هذه البكتيريا أيضًا في صحة التربة من خلال تحسين التنوع الميكروبي، ونشاط الإنزيمات، وبنية التربة، مما يعزز دورة المغذيات ويدعم نمو النباتات. تظهر الدراسات الميدانية أن تلقيح ZSB يزيد من غلة المحاصيل، ويحسن صحة النباتات، ويعزز الجودة الغذائية للمنتجات. يبرز دمج ZSB في تركيبات الأسمدة الحيوية دورها في الزراعة المستدامة من خلال تقليل الاعتماد على الأسمدة الكيميائية. تؤكد هذه الدراسة على الحاجة إلى أبحاث متقدمة في تقنيات الجيل التالي مثل الهندسة الجينومية، والتركيبات النانوية، والزراعة الدقيقة لتعزيز فعالية وتبني ZSB. على الرغم من وعدها، فإن التحديات مثل التخزين، وتباين الأداء الميداني، والعقبات التنظيمية تحد من التبني الواسع. في النهاية، يوفر استخدام ZSB مسارًا واعدًا لمعالجة التحديات العالمية لنقص الزنك، وصحة التربة، وأمن الغذاء، مما يساهم في ممارسات الزراعة المستدامة. يجب أن تركز الأبحاث المستقبلية على تحسين تركيبات ZSB، وتطوير سلالات قوية، ودمج ZSB مع الزراعة الدقيقة. وبالتالي، تستنتج هذه الدراسة أن الأسمدة الحيوية المعتمدة على ZSB تقدم حلاً قيمًا وصديقًا للبيئة لنقص الزنك، مما يعزز الزراعة المستدامة ويساهم في الأمن الغذائي العالمي وصحة التربة.
beheramaheswari97@gmail.com
غانغادار سيثي
gangadharsethig@gmail.com
كيشان كومار بيهيرا
kishanbehera777@gmail.com
رياز سايد
sayyedrz@gmail.com
فاراناسي أدارش
varanasiadarsh229@gmail.com
ب. س. سيبرا
bssipra@gmail.com
لاكشمي سينغ
lakshmisingh@ouat.ac.in
عبد الرحمن أ. العامرو
abdulrahman.alamro@outlook.com
2 قسم البيولوجيا الجزيئية والتكنولوجيا الحيوية، مركز جامعة أسام الزراعية، جورهات 785013، الهند
3 قسم العلوم البيولوجية والكيمياء، كلية الآداب والعلوم، جامعة نزوى، نزوى 616، سلطنة عمان
6 قسم علم النبات، كلية العلوم الأساسية والإنسانية، جامعة أوديشا للزراعة والتكنولوجيا، بوبانسوار 751003، الهند
مقدمة
الأسمدة الكيميائية إلى تدهور التربة وإزعاج الوجود الطبيعي للكائنات في الكمية المطلوبة من المغذيات في التربة مما يجعل التربة أقل خصوبة مع مرور الوقت. لقد استدعت هذه القيود استكشاف بدائل صديقة للبيئة ومستدامة لتعزيز توفر الزنك (Zn) في التربة الزراعية (حفيظ وآخرون 2013).
الزنك عنصر حيوي في تغذية النباتات
الأهمية البيولوجية للزنك
الزنك كعامل مساعد لوظائف الإنزيمات
تعتمد هذه الإنزيمات على الزنك من أجل استقرارها الهيكلي ووظيفتها التحفيزية. على سبيل المثال، الزنك هو مكون رئيسي للإنزيمات مثل الكربونيك أنهيدراز، الذي يلعب دورًا في تثبيت ثاني أكسيد الكربون خلال عملية التمثيل الضوئي، والسوبر أوكسيد ديسموتاز، الذي يعد ضروريًا لتسميم الأنواع التفاعلية من الأكسجين (ROS) وحماية النباتات من الإجهاد التأكسدي. كما أن الزنك ي stabilizes الهياكل البروتينية ويساهم في الطي الصحيح للبروتينات، مما يضمن أن التفاعلات الإنزيمية تسير بكفاءة (Barrameda-Medina et al. 2014; Hassan et al. 2020; Zlobin 2021; Ali et al. 2023a, b). توضح الجدول 1 قائمة الإنزيمات التي يعمل فيها الزنك كعامل مساعد.
الزنك في التعبير الجيني وتخليق البروتين
| إنزيم | الدور في نظام النبات | آثار نقص الزنك | مرجع |
| الكربونيك أنهيدراز | يسهل تثبيت ثاني أكسيد الكربون خلال عملية التمثيل الضوئي | كفاءة التمثيل الضوئي المنخفضة والنمو المتعثر | سينغ وآخرون 2019 |
| الكحول ديهيدروجيناز | مشارك في التنفس اللاهوائي والمسارات الأيضية | إنتاج الطاقة المتعطل في ظل ظروف نقص الأكسجين | ساكسانا وآخرون 2023 |
| سوبر أكسيد ديسموتاز | يخلص الجسم من الأنواع التفاعلية من الأكسجين (ROS) ويخفف من التوتر | زيادة الإجهاد التأكسدي وتلف الخلايا | سينغ وآخرون 2019 |
| بوليميراز RNA | أساسي لتخليق RNA والنسخ | اضطراب في تخليق البروتين ونمو ضعيف | زين وآخرون 2019 |
| بروتينات إصبع الزنك | تنظيم تعبير الجينات وارتباط الحمض النووي | تنظيم الجينات المعاق وعيوب التطور | مولك وآخرون 2023 |
| فوسفوليباز C | مشارك في مسارات نقل الإشارة | إشارات الإجهاد المخفضة والاستجابات التكيفية | ساغار وسينغ 2021 |
الزنك وعملية التمثيل الضوئي وإنتاج الكلوروفيل
Zn وتنظيم نمو النبات والتوازن الهرموني
الزنك ومرونة الإجهاد
نظام المناعة من خلال تمكين إنتاج البروتينات المتعلقة بتكوين الأمراض والمواد الثانوية التي تمنع غزو العوامل الممرضة (ما وآخرون 2017؛ نادراجاه 2020؛ هان وآخرون 2021؛ مولك وآخرون 2023).
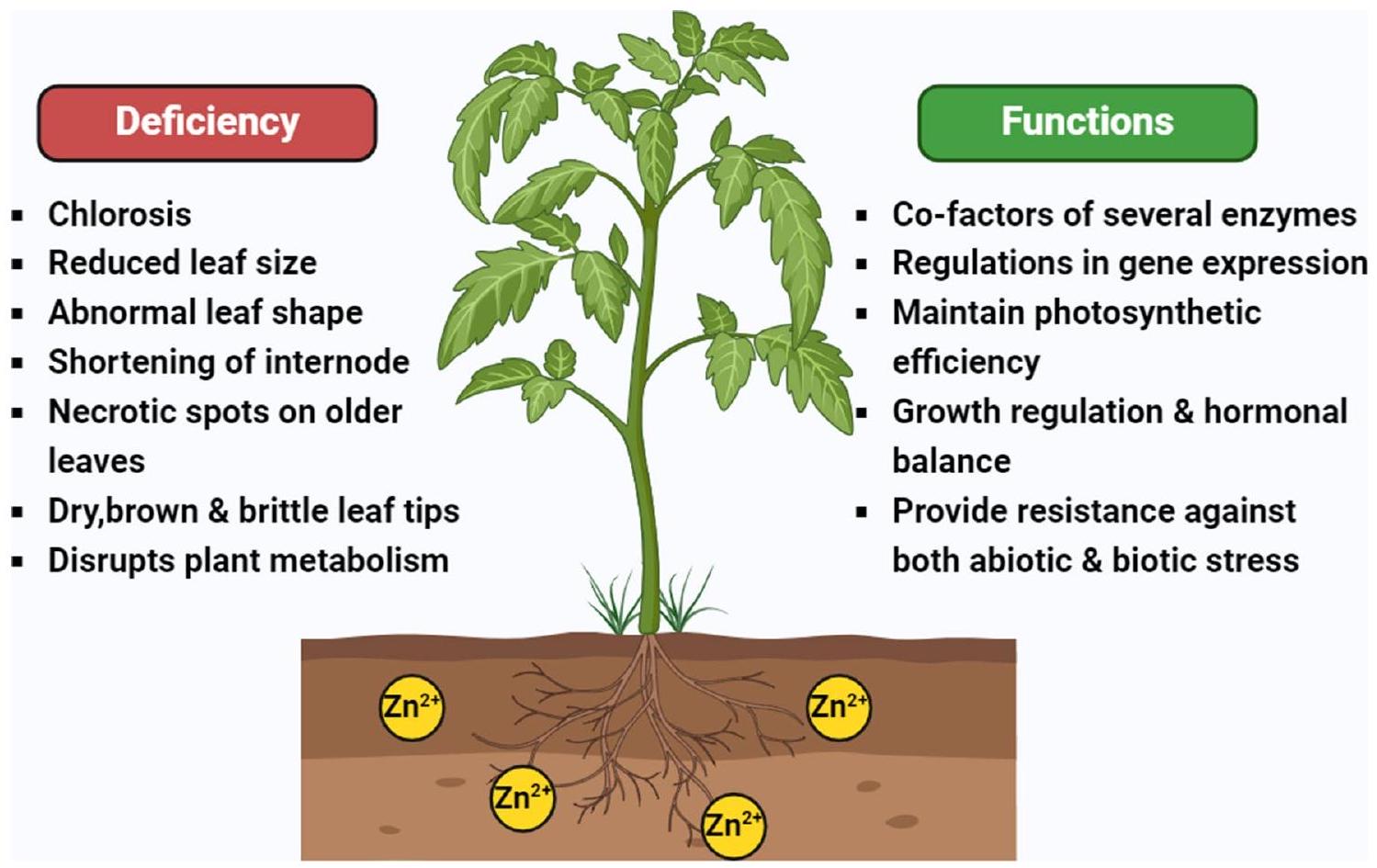
أعراض نقص الزنك
أقل فعالية في امتصاص الماء والمغذيات من التربة. يؤدي نقص الزنك إلى نقص في إنتاج الأوكسين، مما يؤدي إلى تقليل تكوين الجذور الجانبية وعدد شعيرات الجذور، مما يضعف قدرة النبات على دعم النمو الصحي فوق الأرض (هاجيساليه أوغلو 2020؛ زينغ وآخرون 2021؛ علي وآخرون 2021؛ خان وآخرون 2022).
توفر الزنك في التربة
درجة حموضة التربة
المادة العضوية
التي تساعد في إذابة الزنك من الأشكال المعدنية القليلة الذوبان (كاور وغارغ 2021).
نوع التربة وملمسها
التفاعلات مع المغذيات الأخرى
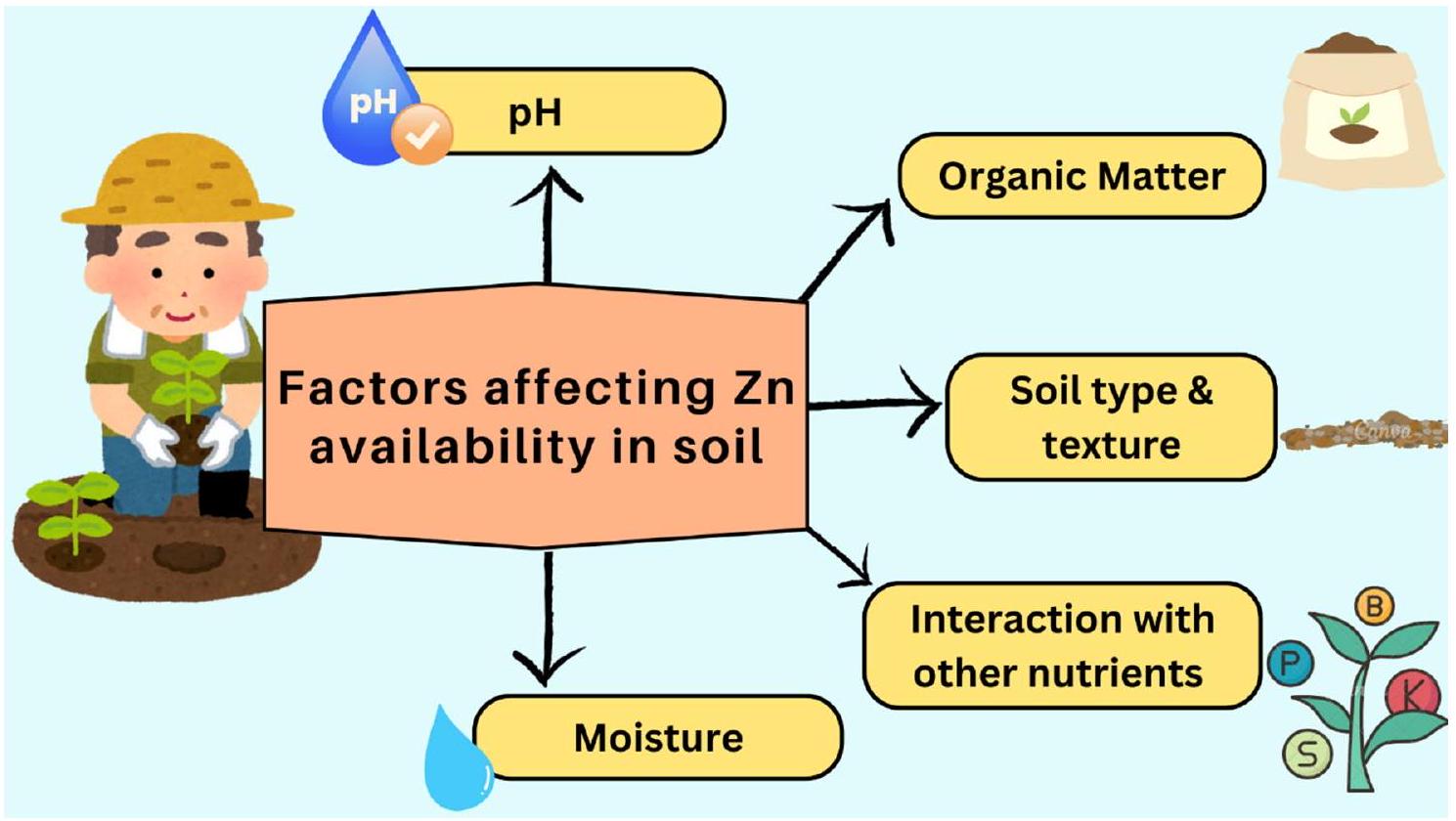
رطوبة التربة
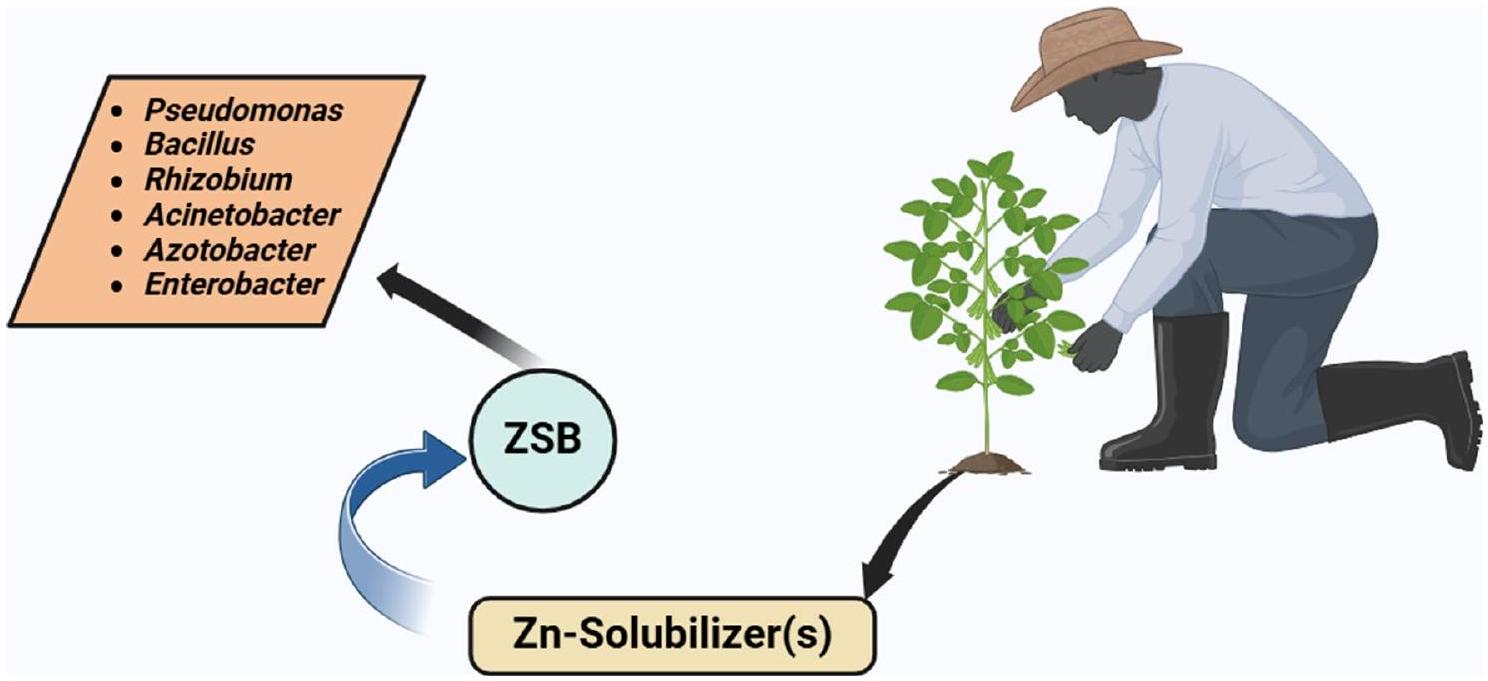
بكتيريا إذابة الزنك: بديل للزراعة المستدامة
الأنواع البكتيرية تستخدم آليات فريدة لإذابة الزنك، ودورها في الزراعة المستدامة يصبح ذا أهمية متزايدة. تم الإبلاغ عن أجناس بكتيرية أخرى مثل الأسيتيوباكتر، والأزوتوباكتر، والإنتيروباكتر كإذابة للزنك بشكل فعال (حسين وآخرون 2018؛ كومار وآخرون 2019؛ نيتو وآخرون 2020؛ سينغ وآخرون 2024). تستخدم كل من هذه البكتيريا مسارات كيميائية حيوية مختلفة لجعل الزنك متاحًا للنباتات، مما يعزز غالبًا خصوبة التربة العامة وتنوع الميكروبات في هذه العملية. الشكل 3 يمثل أنواع مختلفة من بكتيريا إذابة الزنك المستخدمة.
تحديد بكتيريا إذابة الزنك
آليات إذابة الزنك
إنتاج الأحماض العضوية
أنتجت حمض الستريك وحمض الجلوكونيك كواحد من الأحماض العضوية الرئيسية. إنها تخلق معقدات قابلة للذوبان مع الزنك تمكن من امتصاص المعدن بواسطة النباتات. على سبيل المثال، تنتج أنواع بكتيريا الزائفة والباسيلاس كميات كبيرة من هذه الأحماض وتلعب دورًا مهمًا في إذابة الزنك في التربة. بخلاف ذلك، تقوم بكتيريا إذابة الزنك أيضًا بإفراز أنواع مختلفة من الأحماض العضوية مثل حمض اللبنيك، وحمض الأكساليك، وحمض الأسيتيك، وما إلى ذلك. معًا، تقوم هذه الأحماض بخلب أيونات الزنك وتجعلها متاحة في منطقة الجذور (سينغ وآخرون 2018؛ كومawat وآخرون 2019؛ خالد وآخرون 2022؛ ياداف وآخرون 2022أ، ب).
خلب وتكوين أيونات الزنك
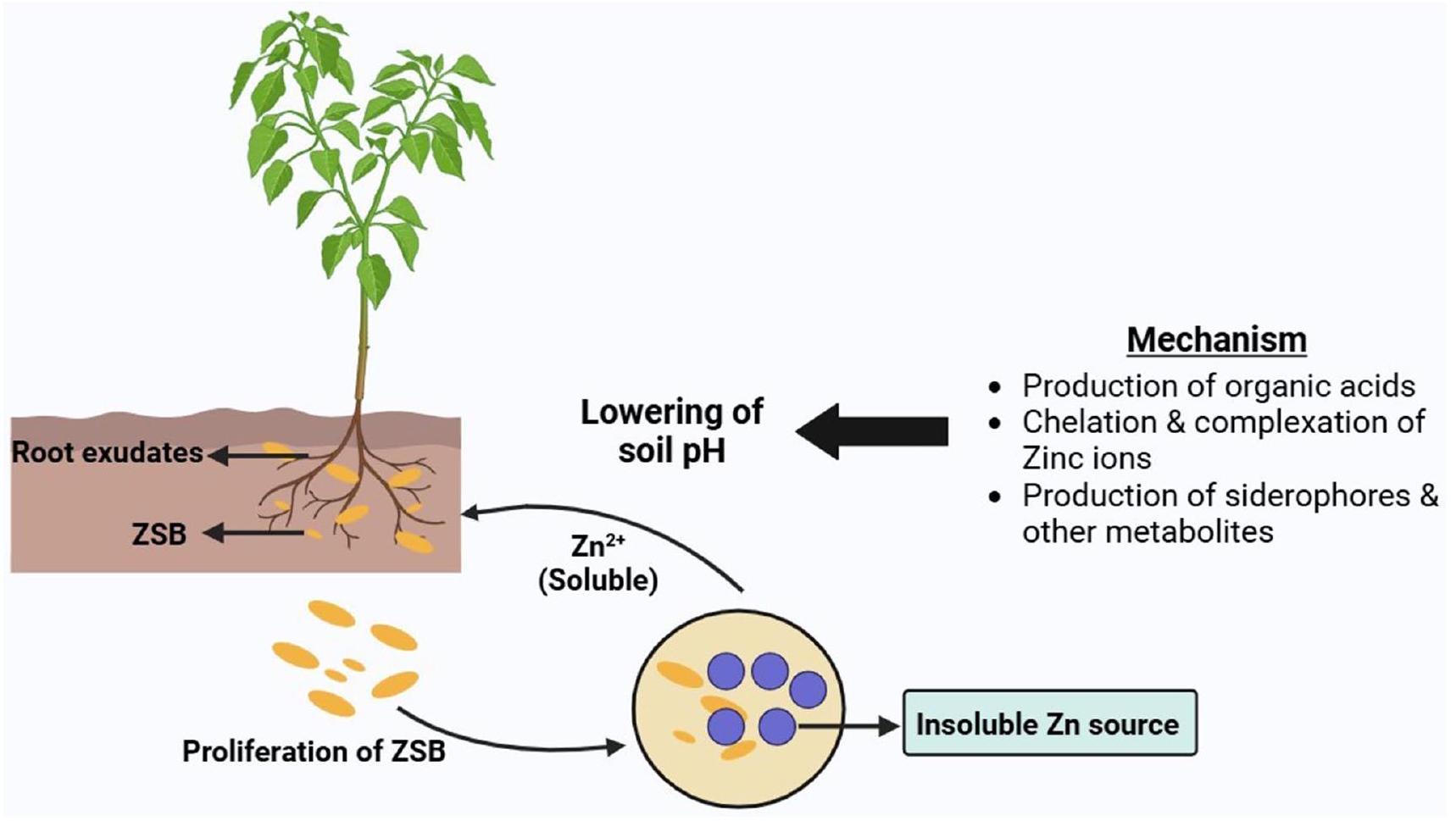
إنتاج السيدروفورات وغيرها من المستقلبات الميكروبية
أثر بكتيريا إذابة الزنك على صحة التربة
التفاعلات الميكروبية في منطقة الجذور
نشاط إنزيمات التربة
هيكل التربة والمواد العضوية
من خلال إنتاج إنزيمات تقوم بتفكيك المركبات العضوية المعقدة إلى جزيئات أبسط. تزيد هذه العملية من مستويات الدبال في التربة، مما يحسن قدرتها على الاحتفاظ بالرطوبة والمغذيات. كما تعمل المواد العضوية كخزان للمغذيات التي يمكن إطلاقها ببطء مع مرور الوقت، مما يدعم نمو النباتات على المدى الطويل. تعزز ZSB تجميع التربة من خلال إنتاج السكريات المتعددة خارج الخلوية (EPS) وأفلام حيوية أخرى تربط جزيئات التربة معًا. تعزز بنية التربة المحسنة، الناتجة عن نشاط ZSB، التهوية والصرف. تضمن التهوية المناسبة للتربة أن تتلقى جذور النباتات الأكسجين الكافي للتنفس، بينما يمنع الصرف المحسن تشبع التربة بالماء، مما قد يؤدي إلى أمراض الجذور وتقليل النشاط الميكروبي. تلعب ZSB، من خلال تعزيز تجميع التربة وتحلل المواد العضوية، دورًا حيويًا في الحفاظ على التوازن بين التهوية والصرف (Costerousse et al. 2018; Khan et al. 2019; Jalal et al. 2022; Barreto et al. 2024).
التقنيات من الجيل التالي المستخدمة في ZSB
الأساليب الجينومية
كريسبر
الصيغ النانوية
المعلوماتية الحيوية والنماذج المدفوعة بالذكاء الاصطناعي
التجمعات الميكروبية متعددة الوظائف
الزراعة الدقيقة ودمج إنترنت الأشياء
أنظمة الصياغة والتوصيل المتقدمة
البكتيريا القابلة للذوبان في الزنك في إنتاجية المحاصيل
تعزيز جودتها الغذائية. وبالمثل، أظهرت نباتات الخيار الملقحة زيادة بنسبة 20% في إنتاج الثمار وتحسين محتوى المغذيات الدقيقة (توريخون وآخرون 2023؛ زانغ وآخرون 2023).
بكتيريا حلّ الزنك كمواد حيوية
تقنيات الصياغة
تركيبات سائلة
تركيبات المساحيق
| محصول | سلالة بكتيرية | أثر | مرجع | |||
| أرز | بوركولديريا؛ أسيتيتوباكتر | زيادة امتصاص الزنك | فيدا وآخرون (2014) | |||
| إنتروبكتر كلوكا | زيادة امتصاص الزنك | كريثيكا وآخرون (2016) | ||||
| رالستونيا بيكتي، الزائفة الزنجارية، كليبسيلا الرئوية وبوركولدرية سيباكيا | زيادة امتصاص الزنك | ميشرا وآخرون (2017) | ||||
| باسيلاس | نشاط الأيض المعزز | زيب وآخرون (2018) | ||||
|
زيادة إنتاج الحبوب |
|
||||
| قمح | سيرراتيا ليكويفاكسيانز FA-2، باكillus ثورنجينسيس FA-3، سيرراتيا مارسيانس FA-4 | تحسين في غلة الحبوب | عبيد الله وآخرون، (2015) | |||
| بانتوايا ديسبيرسا، ب. أغلوميرانس، بseudomonas فراجى، ريزوبيوم سب، وإي. كلواكاي | زيادة التوافر الحيوي للزنك | كامران وآخرون (2017) | ||||
| Trichoderma harzianum و Bacillus amyloliquefaciens | نمو النباتات المحسن | سينغ وآخرون (2021) | ||||
| باسيلاس spp. | تعزيز التخصيب الحيوي بالزنك | ياداف وآخرون (2022أ، ب) | ||||
| بنتويا نوع، كليبسيلا نوع، بريفباكتيريوم نوع، أسيتيبكتير نوع، ألكاليجينيس NCCP-650، سيتروباكتير نوع، إكسيغوباكتيريوم نوع، راوولتيلا نوع، وأسيتيبكتير نوع. | نمو النباتات المحسن | علي وآخرون (2023أ، ب) | ||||
| ذرة | باسيلاس سب. AZ6 | زيادة الكتلة الحيوية | حسين وآخرون (2015) | |||
| ب. أريابهاتا ز م 31، ب. سوبتيليس ز م 63 | زيادة امتصاص الزنك | ممتاز وآخرون (2020) | ||||
| سيرراتيا. نوع. | زيادة في فسيولوجيا النبات | جين وآخرون (2020) | ||||
| بوركولدرية سيباكيا وأسينتوباكتر باومانني | زيادة امتصاص الزنك | أوبادياي وآخرون (2021) | ||||
| أسيتيتوباكتر كالكواسيتيكوس، باكillus بروتيوتيكوس وستينوتروفوموناس بافاني | زيادة امتصاص الزنك | سلطان وآخرون (2023) | ||||
| العدس الأخضر | نيتسيريا، المكورات العنقودية، الإشريكية القولونية، وباسيلاس. | زيادة الكتلة الحيوية للنباتات | إقبال وآخرون (2010) | |||
| حمص | إنترobacter | تحسين جودة الحبوب | أولا وآخرون (2020) | |||
| أوكروبكتريم إنترميديوم، باينيباسيلاس بوليميكسا، باكترس سيريوس، ستينوتروفوموناس مالطوفيلي، ستربتوميس، وأرثروبكتير غلوبيفورمي | زيادة التوافر الحيوي للزنك | بتول وآخرون (2021) | ||||
| فول الصويا | الستربتوميس spp. | زيادة الكتلة الحيوية للنباتات | سوريشادكون وآخرون (2022) | |||
| البازلاء الحمامية | بسيودوموناس بليكوجلوسيسيدا SRI-156، بريفباكتيريوم أنتيكوم SRI-158 | زيادة في محصول الحبوب | غوبالاكريشنان وآخرون 2016 | |||
| طماطم | بكتيريا الزائفة spp. VBZ4 | زيادة عدد الثمار لكل نبات | كارنوال 2021أ، ب | |||
| عدس | رايزوبيوم spp. RL9 | تحسين الكتلة الحيوية وبروتين الحبوب | واني وآخرون 2008 |
تركيبات حبيبية
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يتعلمون بشكل جيد جداً عن رطوبة التربة ويحتفظون بالماء (ماسود وآخرون 2022).
مواد الحامل
تقنيات الطلاء
التكامل مع الأسمدة التقليدية
تعزيز كفاءة المغذيات
تقليل استخدام الأسمدة
توفير مغذيات متوازن
التوافق مع الأسمدة الحيوية الأخرى
durability (أحمد وآخرون 2021؛ ساراتامبال وآخرون 2022؛ محمود وآخرون 2024).
المزايا والقيود
ارتفاع القابلية والفعالية يمثل تحديًا للاعتماد العالمي على نطاق واسع.
وجهات نظر مستقبلية
الخاتمة
مفيد للنظم البيئية والتنوع البيولوجي، ويؤدي إلى ممارسات زراعية مرنة.
توفر البيانات لم يتم إنشاء أو تحليل أي مجموعات بيانات خلال الدراسة الحالية.
الإعلانات
مباشرة من صاحب حقوق الطبع والنشر. لعرض نسخة من هذه الرخصة، قم بزيارة http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
References
Ahmad I, Ahmad M, Hussain A, Jamil M (2021) Integrated use of phosphate-solubilizing Bacillus subtilis strain IA6 and zincsolubilizing Bacillus sp. strain IA16: a promising approach for improving cotton growth. Folia Microbiol 66(1):115-125
Ali MF, Ammar A, Bilal S, Ali U, Huma N, Adnan M (2021) Mitigating zinc deficiency in plants and soils through agronomic techniques: a review. J Environ Agric Sci 23(12):1-10
Ali MM, Gull S, Hu X, Hou Y, Chen F (2023a) Exogenously applied zinc improves sugar-acid profile of loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.) By regulating enzymatic activities and expression of their metabolism-related genes. Plant Physio Biochem 201:107829
Ali M, Ahmed I, Tariq H, Abbas S, Zia MH, Mumtaz A, Sharif M (2023b) Growth improvement of wheat (Triticum aestivum) and zinc biofortification using potent zinc-solubilizing bacteria. Front Plant Sci 14:1140454
Ambreetha S, Balachandar D (2019) Rhizobacteria-mediated root architectural improvement: a hidden potential for agricultural sustainability. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for agricultural sustainability: from theory to practices, 111-128
Arora PK, Tripathi S, Omar RA, Chauhan P, Sinhal VK, Singh A, Srivastava A, Garg SK, Singh VP (2024) Next-generation fertilizers: the impact of bionanofertilizers on sustainable agriculture. Microb Cell Fact 23(1):254
Assunção AG, Schat H, Aarts MG (2010) Regulation of the adaptation to zinc deficiency in plants. Plant Signal Behave 5(12):1553-1555
Badri DV, Weir TL, Van der Lelie D, Vivanco JM (2009) Rhizosphere chemical dialogues: plant-microbe interactions. Curr Opin Biotech 20(6):642-650
Barbosa BCF, Silva SC, de Oliveira RR, Chalfun A (2017) Zinc supply impacts on the relative expression of a metallothionein-like gene in Coffea arabica plants. Plant Soil 411:179-191
Barrameda-Medina Y, Montesinos-Pereira D, Romero L, Blasco B, Ruiz JM (2014) Role of GSH homeostasis under Zn toxicity in plants with different zn tolerance. Plant Sci 227:110-121
Barreto MSC, Elzinga EJ, Rouff AA, Siebecker MG, Sparks DL, Alleoni L, R F (2024) Zinc speciation in highly weathered tropical soils affected by large scale vegetable production. Sci Environ 916:170223
Batool S, Asghar HN, Shehzad MA, Yasin S, Sohaib M, Nawaz F, Akhtar G, Mubeen K, Zahir ZA, Uzair M (2021) Zinc-solubilizing bacteria-mediated enzymatic and physiological regulations confer zinc biofortification in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L). J Soil Sci Plant Nutri 21(3):2456-2471
Behera PR, Behera KK, Sethi G, Prabina BJ, Bai AT, Sipra BS, Adarsh V, Das S, Behera KC, Singh L, Mishra MK, Behera M (2024) Enhancing agricultural sustainability through Rhizomicrobiome: a review. J Basic Microbiol 64(11):e2400100
Bharti K, Pandey N, Shankhdhar D, Srivastava PC, Shankhdhar SC (2014) Effect of exogenous zinc supply on photosynthetic rate, chlorophyll content and some growth parameters in different wheat genotypes. Cereal Res Commun 42:589-600
Bhatt K, Maheshwari DK (2020) Zinc solubilizing bacteria (Bacillus megaterium) with multifarious plant growth promoting activities alleviates growth in Capsicum annuum L. 3 Biotech. 10(2): 36
Broeckling CD, Paschke MW, Vivanco JM, Manter D (2019) Rhizosphere ecology
Cherif-Silini H, Silini A, Chenari Bouket A, Alenezi FN, Luptakova L, Bouremani N, Nowakowska JA, Oszako T, Belbahri L (2021) Tailoring next generation plant growth promoting microorganisms as versatile tools beyond soil desalinization: a road map towards field application. Sustainability 13(8):4422
Choudhary S, Saharan BS, Gera R, Kumar S, Prasad M, Gupta A, Duhan JS (2024) Molecular characterization and validation of zinc solubilization potential of bacteria isolated from onion (Allium cepa L.) rhizosphere. Microbe 4:100145
Costerousse B, Schönholzer-Mauclaire L, Frossard E, Thonar C (2018) Identification of heterotrophic zinc mobilization processes among bacterial strains isolated from wheat rhizosphere (Triticum aestivum L). Appl Environ Microbiol 84(1):e01715-e01717
Das A, Singh SK, Kumar M, Kumar O (2019) Evaluation of different methods of zinc application on growth, yield and biofortification of zinc in rice (Oryza sativa L). J Indian Soc Soil Sci 67(1):92-102
Dhaliwal SS, Sharma V, Shukla AK, Kaur J, Verma V, Singh P, Singh H Abdel-Hafez Sayed SH, Gaber S, Ali A, Hossain R A (2021) Enrichment of zinc and iron micronutrients in lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) Through biofortification. Mol 26(24):7671
Garcia J, Kao-Kniffin J (2018) Microbial group dynamics in plant rhizospheres and their implications on nutrient cycling. Front Microbiol 9:1516
Gopalakrishnan S, Vadlamudi S, Samineni S, Sameer Kumar C (2016) Plant growth-promotion and biofortification of chickpea and pigeonpea through inoculation of biocontrol potential bacteria, isolated from organic soils. Springerplus 5:1-11
Hacisalihoglu G (2020) Zinc (zn): the last nutrient in the alphabet and shedding light on Zn efficiency for the future of crop production under suboptimal zn. Plants 9(11):1471
Hafeez BM, K Y, Khanif YM, Saleem M (2013) Role of zinc in plant nutrition-a review. Am J Exp Agric 3(2):374-391
Han G, Qiao Z, Li Y, Wang C, Wang B (2021) The roles of CCCH zinc-finger proteins in plant abiotic stress tolerance. Int J Mol Sci 22(15):8327
Haroon M, Khan ST, Malik A (2022) Zinc-solubilizing bacteria: an option to increase zinc uptake by plants. Microbial Biofertilizers and Micronutrient Availability: The Role of Zinc in Agriculture and Human Health, 207-238
Hashemnejad F, Barin M, Khezri M, Ghoosta Y, Hammer EC (2021) Isolation and identification of insoluble zinc-solubilising bacteria and evaluation of their ability to solubilise various zinc minerals. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21:2501-2509
Hassan MU, Aamer M, Umer Chattha M, Haiying T, Shahzad B, Barbanti L, Nawaz M, Rasheed A, Afzal A, Liu Y, Guoqin H (2020) The critical role of zinc in plants facing the drought stress. Agri 10(9):396
Hefferon K (2019) Biotechnological approaches for generating zincenriched crops to combat malnutrition. Nutr 11(2):253
Hussain A, Arshad M, Zahir ZA, Asghar M (2015) Prospects of zinc solubilizing bacteria for enhancing growth of maize. Pak J Agri Sci 52(4)
Hussain A, Zahir ZA, Asghar HN, Ahmad M, Jamil M, Naveed M, Zaman Akhtar, M F U (2018) Zinc solubilizing bacteria for zinc biofortification in cereals: a step toward sustainable nutritional security. Role of Rhizospheric Microbes in Soil: Volume 2: Nutrient Management and Crop Improvement, 203-227
Hussain A, Zahir ZA, Ditta A, Tahir MU, Ahmad M, Mumtaz MZ, Hayat K, Hussain S (2019) Production and implication of
bio-activated organic fertilizer enriched with zinc-solubilizing bacteria to boost up maize (Zea mays L.) production and biofortification under two cropping seasons. Agronomy 10(1):39
Hussain A, Zahir ZA, Asghar HN, Imran M, Ahmad M, Hussain S (2020) Integrating the potential of Bacillus sp. Az6 and organic waste for zinc oxide bio-activation to improve growth, yield and zinc content of maize grains. Pak J Agri Sci 57(1)
Iqbal U, Jamil N, Ali I, Hasnain S (2010) Effect of zinc-phosphatesolubilizing bacterial isolates on growth of Vigna radiata. Annals Microbiol 60:243-248
Islam MA, Hasan MM, Akter T, Islam SMS (2024) Development of Iron and Zinc Biofortified Rice Variety for Nutrition Improvement in Bangladesh. Food Sci Engi. 322-330
Jain D, Kour R, Bhojiya AA, Meena RH, Singh A, Mohanty SR, Rajpurohit D, Ameta KD (2020) Zinc tolerant plant growth promoting bacteria alleviates phytotoxic effects of zinc on maize through zinc immobilization. Sci Rep 10(1): 13865
Jalal A, Shah S, Teixeira Filho MCM, Khan A, Shah T, Ilyas M, Rosa PAL (2020) Agro-biofortification of zinc and iron in wheat grains. Gesunde Pflanzen 72(3):227-236
Jalal A, Galindo FS, Freitas LA, da Silva Oliveira CE, de Lima BH, Pereira ÍT, Ferraz GF, Silva de Souza J, Nunes, da Costa K, Nogueira TAR, Teixeira Filho, M C M (2022) Yield, zinc efficiencies and biofortification of wheat with zinc sulfate application in soil and foliar nanozinc fertilisation. Crop and Pasture Science
Kamran S, Shahid I, Baig DN, Rizwan M, Malik KA, Mehnaz S (2017) Contribution of zinc solubilizing bacteria in growth promotion and zinc content of wheat. Front Microbiol 8:2593
Karnwal A (2021a) Pseudomonas spp., a zinc-solubilizing vermicompost bacteria with plant growth-promoting activity moderates zinc biofortification in tomato. Int J Veg Sci 27(4):398-412
Karnwal A (2021b) Zinc solubilizing Pseudomonas spp. from vermicompost bestowed with multifaceted plant growth promoting properties and having prospective modulation of zinc biofortification in Abelmoschus esculentus L. J Plant Nutr 44(7):1023-1038
Kaur H, Garg N (2021) Zinc toxicity in plants: a review. Planta 253(6):129
Khalid S, Amanullah, Ahmed I (2022) Enhancing zinc biofortification of wheat through integration of zinc, compost, and zinc-solubilizing bacteria. Agri 12(7):968
Khan A, Singh J, Upadhayay VK, Singh AV, Shah S (2019) Microbial biofortification: a green technology through plant growth promoting microorganisms. Sustain. Green Technol. Environ. Management: 255-269
Khan ST, Malik A, Alwarthan A, Shaik MR (2022) The enormity of the zinc deficiency problem and available solutions; an overview. Arab J Chem 15(3):103668
Khani AG, Enayatizamir N, Norouzi Masir M (2019) Impact of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on different forms of soil potassium under wheat cultivation. Lett App Microbiol 68(6):514-521
Khatoon Z, Huang S, Farooq MA, Santoyo G, Rafique M, Javed S, Gul B (2022) Role of plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB) in abiotic stress management. Mitigation of Plant Abiotic Stress by Microorganisms, pp 257-272
Kour D, Rana KL, Yadav N, Yadav AN, Kumar A, Meena VS, Singh B, Chauhan VS, Dhaliwal HS, Saxena AK (2019) Rhizospheric microbiomes: biodiversity, mechanisms of plant growth promotion, and biotechnological applications for sustainable agriculture. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for agricultural sustainability: from theory to practices, 19-65
Krithika S, Balachandar D (2016) Expression of zinc transporter genes in rice as influenced by zinc-solubilizing Enterobacter cloacae strain ZSB14. Front. Plant Sci 7:446
Kumar A, Patel JS, Meena VS (2018) Rhizospheric microbes for sustainable agriculture: an overview. Role of Rhizospheric Microbes
in Soil: Volume 1: Stress Management and Agricultural Sustainability, 1-31
Kumar A, Dewangan S, Lawate P, Bahadur I, Prajapati S (2019) Zincsolubilizing bacteria: a boon for sustainable agriculture. Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria for Sustainable Stress Management: Volume 1: Rhizobacteria in Abiotic Stress Management, 139-155
Kumawat N, Kumar R, Khandkar UR, Yadav RK, Saurabh K, Mishra JS, Dotaniya ML, Hans H (2019) Silicon (Si)-and zinc (Zn)-solubilizing microorganisms: role in sustainable agriculture. Biofertilizers Sustainable Agric Environ, 109-135
Kushwaha P, Kashyap PL, Pandiyan K, Bhardwaj AK (2020) Zincsolubilizing microbes for sustainable crop production: current understanding, opportunities, and challenges. Phytobiomes: Curr Insights Future Vistas, 281-298
Ladohia S, Rana N, Srivastava P, Kumar R, Mehta S, Pareek B (2024) Use of zinc solubilizing biofertilizers for increasing the growth and yield of cereals: a review. J Appl Nat Sci 16(3)
Liu Z, Meng J, Sun Z, Su J, Luo X, Song J, Li P, Sun Y, Yu C, Peng X (2022) Zinc application after low temperature stress promoted rice tillers recovery: aspects of nutrient absorption and plant hormone regulation. Plant Sci 314:111104
Lora AM, Delgado A (2020) Factors determining zn availability and uptake by plants in soils developed under Mediterranean climate. Geoderma 376:114509
Ma D, Sun D, Wang C, Ding H, Qin H, Hou J, Huang X, Xie Y, Guo T (2017) Physiological responses and yield of wheat plants in zinc-mediated alleviation of drought stress. Front Plant Sci 8:860
Mahmood I, Sami A, Asad SA, Shah GA, Rana RM, Raja NI, Sher A, Mashwani ZR, Quyyum A, Iqbal J, Awan TH (2024) Zinc-Oxide-Nanoparticles in conjugation with Zn-Solubilizing Bacteria improve Zn Biofortification and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Wheat. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 24(3):5565-5585
Mahmud K, Makaju S, Ibrahim R, Missaoui A (2020) Current progress in nitrogen fixing plants and microbiome research. Plants 9(1):97
Majeed A, Muhammad Z, Ahmad H (2018) Plant growth promoting bacteria: role in soil improvement, abiotic and biotic stress management of crops. Plant Cell Rep 37(12):1599-1609
Makarenko N, Bondar V, Makarenko V, Symochko L (2020) Factors affecting mobility of zinc in soils of Ukraine. Internat J Ecosyst Ecol Sci 10(4)
Masood F, Ahmad S, Malik A (2022) Role of rhizobacterial bacilli in zinc solubilization. Microb Biofertilizers Micronutrient Availability: Role zinc Agric Hum Health, 361-377
Mhlongo MI, Piater LA, Madala NE, Labuschagne N, Dubery IA (2018) The chemistry of plant-microbe interactions in the rhizosphere and the potential for metabolomics to reveal signaling related to defense priming and induced systemic resistance. Front Plant Sci 9:112
Moulick D, Bhutia KL, Sarkar S, Roy A, Mishra UN, Pramanick B, Maitra S, Shankar T, Hazra S, Skalicky M, Brestic B, Barek V, Hossain A (2023) The intertwining of Zn-finger motifs and abiotic stress tolerance in plants: current status and future prospects. Front Plant Sci 13:1083960
Mumtaz MZ, Ahmad M, Jamil M, Hussain T (2017) Zinc solubilizing Bacillus spp. potential candidates for biofortification in maize. Microbiol Res 202:51-60
Nadarajah KK (2020) ROS homeostasis in abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Int J Mol Sci 21(15):5208
Natasha N, Shahid M, Bibi I, Iqbal J, Khalid S, Murtaza B, Bakhat HF, Farooq AB, U, Amjad M, Hammad HM, Niazi NK, Arshad M (2022) Zinc in soil-plant-human system: a data-analysis review. Sci Total Environ 808:152024
Nithyapriya S, Lalitha S, Sayyed RZ, Reddy MS, Dailin DJ, Enshasy HE, Suriani NL, Herlambang S (2021) Production, purification, and characterization of bacillibactin siderophore of Bacillus
subtilis and its application for improvement in plant growth and oil content in sesame. Sustain 13:5394
Nithyapriya S, Lalitha S, Devi SU, Perveen K, Alshaikh NA, Sayyed RZ, Mastinu A (2024) Purification and characterization of desferrioxamine B of Pseudomonas fluorescens and its application to improve oil content, nutrient uptake, and plant growth in peanuts. Microbiol Eco 87:60
Nitu R, Rajinder K, Sukhminderjit K (2020) Zinc solubilizing bacteria to augment soil fertility—A comprehensive review. Int J Agricult Sci Vet Med 8:38-44
Noulas C, Tziouvalekas M, Karyotis T (2018) Zinc in soils, water and food crops. J Trace Ele Med Bio 49:252-260
Obaid H, Shrestha RK, Liu D, Elsayed NS, Ni J, Ni C (2022) Biofortification of maize with zinc and its effect on human health. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 22(2):1792-1804
Ofori KF, Antoniello S, English MM, Aryee AN (2022) Improving nutrition through biofortification-A systematic review. Front Nutr 9:1043655
Othman NMI, Othman R, Zuan ATK, Shamsuddin AS, Zaman NBK, Sari NA, Panhwar QA (2022) Isolation, characterization, and identification of zinc-solubilizing bacteria (ZSB) from wetland rice fields in Peninsular Malaysia. Agri 12(11): 1823
Pan J, Huang X, Li Y, Li M, Yao N, Zhou Z, Li X (2017) Zinc protects against cadmium-induced toxicity by regulating oxidative stress, ions homeostasis and protein synthesis. Chemos 188:265-273
Panpatte DG, Jhala YK, Shelat HN, Vyas RV (2016) Nanoparticles: the next generation technology for sustainable agriculture. Microb Inoculants Sustainable Agricultural Productivity: 2: Funct Appl, 289-300
Paramesh V, Dhar S, Dass A, Kumar B, Kumar A, El-Ansary DO, Elansary HO (2020) Role of integrated nutrient management and agronomic fortification of zinc on yield, nutrient uptake and quality of wheat. Sustain 12(9):3513
Patel JN, Alam MS (2024) Impact of Foliar Fortification of Zinc and Iron on Nutrient Content and their uptake by Maize Crop. J Exp Agri Internat 46(7):973-982
Patel PR, Shaikh SS, Sayyed RZ (2018) Modified chrome azurol S method for detection and estimation of siderophores having affinity for metal ions other than iron Fe. Environ Sustain 1(1):81-87
Pii Y, Mimmo T, Tomasi N, Terzano R, Cesco S, Crecchio C (2015) Microbial interactions in the rhizosphere: beneficial influences of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on nutrient acquisition process. A review. Biol. Fert. Soils. 51: 403-415.
Prasad K, Khare A, Rawat P (2021) Microbial Functions Improve Agricultural Soil Health, Quality Productivity and Environmental sustainability for future generation. Gulf J Mol Biol 1(1):24-37
Rani N, Chauhan A, Kaur S, Solanki MK, Tripathi M, Jain D, Singh S, Upadhyay SK, Kaur G (2023) Molecular mechanistic of Znsolubilizing bacteria for agronomic eminence: recent updates and futuristic development. J Plant Growth Regul. 1-15
Rudani K, Vishal P, Kalavati P (2018) The importance of zinc in plant growth-A review. Int Res J Nat Appl Sci 5(2):38-48
Sabagh ELA, Islam MS, Hossain A, Iqbal MA, Mubeen M, Waleed M, Reginato M, Battaglia M, Ahmed S, Rehman A, Arif M, Athar HR, Ratnasekera DP, Danish S, Raza MA, Rajendran K, Mushtaq M, Skalicky M, Brestic M, Soufan W, Fahad S, Pandey S, Kamran M, Datta R, Abdelhamid MT (2022) Phytohormones as growth regulators during abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Front Agron 4:765068
Saboor A, Muhammad AA, Hussain S, El Enshasy HE, Hussain S, Ahmed N, Gafur A, Sayyed RZ, Shah F, Danish S, Datta S R (2021) Zinc nutrition and arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis effects on maize (Zea mays L.) growth and productivity. Saudi J Biol Sci 28(11):6339-6351
Sarathambal C, Dinesh R, Srinivasan V, Sheeja TE, Jeeva V, Manzoor M (2022) Changes in bacterial diversity and composition in response to co-inoculation of arbuscular mycorrhizae and zincsolubilizing bacteria in turmeric rhizosphere. Curr Microbiol 79:1-9
Saxena V, Bharti MK, Kumar P, Singh J, Patel VB (2023) Effect of zinc uptake on alcohol dehydrogenase, protein and mineral contents of hydroponically grown chickpea (Cicer arietinum). J Plant Nutr 46(6):867-876
Schmidt H, Nunan N, Höck A, Eickhorst T, Kaiser C, Woebken D, Raynaud X (2018) Recognizing patterns: spatial analysis of observed microbial colonization on root surfaces. Front Environ Sci 6:61
Sehrawat A, Sindhu SS (2024) Zinc-solubilizing microorganisms: contributions in nutrient availability and implications for Crop Productivity in Sustainable Agriculture. Plant Holobiome Engineering for Climate-Smart Agriculture. Springer Nature Singapore, Singapore, pp 183-213
Sindhu SS, Sharma R, Sindhu S, Phour M (2019) Plant nutrient management through inoculation of zinc-solubilizing bacteria for sustainable agriculture. Biofertilizers Sustainable Agric Environ, 173-201
Singh D, Geat N, Rajawat MVS, Prasanna R, Kar A, Singh AM, Saxena AK (2018) Prospecting endophytes from different Fe or Zn accumulating wheat genotypes for their influence as inoculants on plant growth, yield, and micronutrient content. Annals Microbiol 68:815-833
Singh P, Shukla AK, Behera SK, Tiwari PK (2019) Zinc application enhances superoxide dismutase and carbonic anhydrase activities in zinc-efficient and zinc-inefficient wheat genotypes. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 19(3):477-487
Singh K, Batra R, Sharma S, Saripalli G, Gautam T, Singh R, Pal S, Malik P, Kumar M, Jan I, Singh S, Kumar D, Pundir S, Chaturvedi D, Verma A, Rani A, Kumar A, Sharma H, Chaudhary J, Kumar K, Kumar S, Singh VK, Singh VP, Kumar S, Kumar R, Gaurav SS, Sharma S, Sharma PK, Balyan HS, Gupta PK (2021) WheatQTLdb: a QTL database for wheat. Mol Genet Genomics 296(5):1051-1056
Singh J, Singh AV, Upadhayay VK, Khan A, Chandra R (2022) Prolific contribution of Pseudomonas protegens in Zn biofortification of wheat by modulating multifaceted physiological response under saline and non-saline conditions. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 38(12):227
Singh S, Chhabra R, Sharma A, Bisht A (2024) Harnessing the power of zinc-solubilizing Bacteria: a Catalyst for a sustainable agrosystem. Bacteria 3(1):15-29
Srithaworn M, Jaroenthanyakorn J, Tangjitjaroenkun J, Suriyachadkun C, Chunhachart O (2023) Zinc solubilizing bacteria and their potential as bioinoculant for growth promotion of green soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) PeerJ. 11:e15128
Suganya A, Saravanan A, Manivannan N (2020) Role of zinc nutrition for increasing zinc availability, uptake, yield, and quality of maize (Zea mays L.) grains: an overview. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 51(15):2001-2021
Sultan A, Youssef HIA (2023) Biofertilizer effect of some zinc dissolving bacteria free and encapsulated on Zea mays growth. Archives Microbiol 205(5):202
Suriyachadkun C, Chunhachart O, Srithaworn M, Tangchitcharoenkhul R, Tangjitjareonkun J (2022) Zinc-solubilizing Streptomyces spp. as bioinoculants for promoting the growth of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill). J Microbiol Biotechnol 32(11):1435
Torrejón BP, Cáceres A, Sánchez M, Sainz L, Guzmán M, BermúdezPerez FJ, Ramírez-Rodríguez GB, Delgado-López JM (2023)
Ullah A, Heng S, Munis MFH, Fahad S, Yang X (2015) Phytoremediation of heavy metals assisted by plant growth promoting (PGP) bacteria: a review. Environ Exper Bot 117:28-40
Ullah A, Farooq M, Nadeem F, Rehman A, Hussain M, Nawaz A, Naveed M (2020) Zinc application in combination with zinc solubilizing Enterobacter sp. MN17 improved productivity, profitability, zinc efficiency, and quality of desi chickpea. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20(4):2133-2144
Upadhayay VK, Singh AV, Khan A (2022a) Cross talk between zincsolubilizing bacteria and plants: a short tale of bacterial-assisted zinc biofortification. Front Soil Sci 1:788170
Upadhayay VK, Singh AV, Khan A, Sharma A (2022b) Contemplating the role of zinc-solubilizing bacteria in crop biofortification: an approach for sustainable bioeconomy. Front Agron 4:903321
Upadhayay VK, Singh AV, Khan A, Singh J, Pareek N, Raghav A (2022c) FE-SEM/EDX based zinc mobilization analysis of Burkholderia cepacia and Pantoea rodasii and their functional annotation in crop productivity, soil quality, and zinc biofortification of paddy. Front Microbiol 13:852192
Upadhyay H, Gangola S, Sharma A, Singh A, Maithani D, Joshi S (2021) Contribution of zinc solubilizing bacterial isolates on enhanced zinc uptake and growth promotion of maize (Zea mays L). Folia Microbiol 66:543-553
Walitang D, Samaddar S, Roy Choudhury A, Chatterjee P, Ahmed S, Sa T (2019) Diversity and plant growth-promoting potential of bacterial endophytes in rice. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): prospects for sustainable agriculture, 3-17
Wani PA, Khan MS, Zaidi A (2008) Effect of metal-tolerant plant growth-promoting Rhizobium on the performance of pea grown in metal-amended soil. Archives Environ Cont Toxic 55:33-42
Wani SH, Gaikwad K, Razzaq A, Samantara K, Kumar M, Govindan V (2022) Improving zinc and iron biofortification in wheat through genomics approaches. Mol Biol Rep 49(8):8007-8023
Yadav RC, Sharma SK, Varma A, Rajawat MVS, Khan MS, Sharma PK, Malviya D, Singh UB, Rai JP, Saxena AK (2022a) Modulation in biofertilization and biofortification of wheat crop by inoculation of zinc-solubilizing rhizobacteria. Front Plant Sci 13:777771
Yadav VK, Yadav RC, Choudhary P, Sharma SK, Bhagat N (2022b) Mitigation of drought stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by
inoculation of drought tolerant Bacillus paramycoides DT-85 and Bacillus paranthracis DT-97. J Appl Biol Biotechnol 10:59-69
Yadav RC, Sharma SK, Varma A, Singh UB, Kumar A, Bhupenchandra I, Rai JP, Sharma PK, Singh HV (2023) Zinc-solubilizing Bacillus spp. in conjunction with chemical fertilizers enhance growth, yield, nutrient content, and zinc biofortification in wheat crop. Front Microbiol 14:1210938
Yasmin R, Hussain S, Rasool MH, Siddique MH, Muzammil S (2021) Isolation, characterization of Zn solubilizing bacterium (Pseudomonas Protegens RY2) and its contribution in growth of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L) as deciphered by improved growth parameters and zn content. Dose-response 19(3):15593258211036791
Younas N, Fatima I, Ahmad IA, Ayyaz MK (2023) Alleviation of zinc deficiency in plants and humans through an effective technique; biofortification: a detailed review. Acta Ecol Sin 43(3):419-425
Zeb H, Hussain A, Naveed M, Ditta A, Ahmad S, Jamshaid MU, Ahmad HT, Hussain MB, Aziz R, Haider MS (2018) Compost enriched with ZnO and Zn -solubilising bacteria improves yield and Zn -fortification in flooded rice. Italian J Agron 13(4):310-316
Zeng H, Zhang X, Ding M, Zhang X, Zhu Y (2019) Transcriptome profiles of soybean leaves and roots in response to zinc deficiency. Physiol Planta 167(3):330-351
Zeng H, Wu H, Yan F, Yi K, Zhu Y (2021) Molecular regulation of zinc deficiency responses in plants. J Plant Physiol 261:153419
Zhang J, Wang S, Song S, Xu F, Pan Y, Wang H (2019) Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses reveal new insight into chlorophyll synthesis and chloroplast structure of maize leaves under zinc deficiency stress. J Proteom 199:123-134
Zhang L, Zuluaga MYA, Pii Y, Barone A, Amaducci S, Miras-Moreno B, Martinelli E, Bellotti G, Trevisan M, Puglisi E, Lucini L (2023) A Pseudomonas Plant Growth promoting Rhizobacterium and Arbuscular Mycorrhiza differentially modulate the growth, photosynthetic performance, nutrients allocation, and stress response mechanisms triggered by a mild zinc and cadmium stress in tomato. Plant Sci 337:111873
Zlobin IE (2021) Current understanding of plant zinc homeostasis regulation mechanisms. Plant Physiol Biochem 162:327-335
Zlobin IE, Pashkovskiy PP, Kartashov AV, Nosov AV, Fomenkov AA, Kuznetsov VV (2020) The relationship between cellular zn status and regulation of Zn homeostasis genes in plant cells. Environ Exp Bot 176:104104
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-025-01294-7
Publication Date: 2025-03-04
Enhancing soil health and crop productivity: the role of zincsolubilizing bacteria in sustainable agriculture
© The Author(s) 2025
Abstract
Zinc is essential for various plant physiological functions, including enzyme activation, protein synthesis, and stress resistance. However, nearly half of the world’s arable soils are zinc-deficient, adversely affecting crop productivity and human health, especially in regions reliant on plant-based diets. Traditional zinc supplementation methods, such as chemical fertilizers, often fall short due to environmental and economic limitations. This study highlights Zinc solubilizing bacteria (ZSB) as a sustainable alternative, capable of converting insoluble zinc into bioavailable forms through mechanisms like organic acid production, chelation, and siderophore activity, thus enhancing plant zinc uptake. These bacteria also contribute to soil health by improving microbial diversity, enzyme activity, and soil structure, promoting nutrient cycling and supporting plant growth. Field studies demonstrate that ZSB inoculation increases crop yields, enhances plant health, and improves the nutritional quality of produce. The integration of ZSB into biofertilizer formulations further highlights their role in sustainable agriculture by reducing dependence on chemical fertilizers. This study emphasizes the need for advanced research into next-generation technologies like genomic engineering, nano-formulations, and precision agriculture to enhance the efficacy and adoption of ZSB. Despite their promise, challenges such as storage, field performance variability, and regulatory hurdles limit widespread adoption. Ultimately, the use of ZSB offers a promising pathway to address global challenges of zinc deficiency, soil health, and food security, contributing to sustainable agricultural practices. Future research should focus on optimizing ZSB formulations, developing robust strains, and integrating ZSB with precision agriculture. Hence this study concludes that ZSB-based biofertilizers offer a valuable, eco-friendly solution to zinc deficiency, promoting sustainable agriculture and contributing to global food security and soil health.
beheramaheswari97@gmail.com
Gangadhar Sethi
gangadharsethig@gmail.com
Kishan Kumar Behera
kishanbehera777@gmail.com
Riyaz Sayyed
sayyedrz@gmail.com
Varanasi Adarsh
varanasiadarsh229@gmail.com
B. S. Sipra
bssipra@gmail.com
Lakshmi Singh
lakshmisingh@ouat.ac.in
Addulrahman A. Alamro
abdulrahman.alamro@outlook.com
2 Department of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, DBTAssam Agricultural University Centre, Jorhat 785013, India
3 Department of Biological Sciences and Chemistry, College of Arts and Science, University of Nizwa, Nizwa 616, Sultanate of Oman
6 Department of Botany, College of Basic Science and Humanities, Odisha University of Agriculture & Technology, Bhubaneswar 751003, India
Introduction
chemical fertilizers can cause soil degradation and disturb the natural presence of organisms in the required amount of nutrients in the soil causing soil to be less fertile with time. These constraints have necessitated the exploration of ecofriendly and sustainable substitutes for bolstering zinc (Zn) bioavailability in farm soils (Hafeez et al. 2013).
Zinc a vital component in Plant Nutrition
Biological importance of zinc
Zinc as cofactor for enzymes’ functions
production. These enzymes depend on zinc for their structural stability and catalytic function. For example, zinc is a key component of enzymes such as carbonic anhydrase, which plays a role in carbon dioxide fixation during photosynthesis, and superoxide dismutase, which is essential for detoxifying reactive oxygen species (ROS) and protecting plants from oxidative stress. Zinc also stabilizes protein structures and contributes to the proper folding of proteins, ensuring that enzymatic reactions proceed efficiently (Barrameda-Medina et al. 2014; Hassan et al. 2020; Zlobin 2021; Ali et al. 2023a, b). Table 1 depicts the list of enzymes where Zn serve as a cofactor.
Zn in Gene expression and protein synthesis

| Enzyme | Role in plant system | Effects of Zn deficiency | Reference |
| Carbonic anhydrase | Facilitates carbon dioxide fixation during photosynthesis | Reduced photosynthetic efficiency and stunted growth | Singh et al. 2019 |
| Alcohol dehydrogenase | Involved in anaerobic respiration and metabolic pathways | Impaired energy production under low oxygen conditions | Saxena et al. 2023 |
| Superoxide dismutase | Detoxifies reactive oxygen species (ROS) and mitigates stress | Increased oxidative stress and cell damage | Singh et al. 2019 |
| RNA polymerase | Essential for RNA synthesis and transcription | Disrupted protein synthesis and poor growth | Zeng et al. 2019 |
| Zinc finger proteins | Regulate gene expression and DNA binding | Impaired gene regulation and developmental abnormalities | Moulick et al. 2023 |
| Phospholipase C | Involved in signal transduction pathways | Reduced stress signaling and adaptive responses | Sagar and Singh 2021 |
Zn and photosynthesis and chlorophyll production
Zn and plant growth regulation and hormonal balance
Zn and stress resilience
immune system by enabling the production of pathogene-sis-related proteins and secondary metabolites that prevent pathogen invasion (Ma et al. 2017; Nadarajah 2020; Han et al. 2021; Moulick et al. 2023).
Symptoms of zinc deficiency
less effective at absorbing water and nutrients from the soil. A lack of adequate auxin production due to zinc deficiency leads to reduced lateral root formation and fewer root hairs, compromising the plant’s ability to support healthy growth above ground (Hacisalihoglu 2020; Zeng et al. 2021; Ali et al. 2021; Khan et al. 2022).
Zinc availability in soils
Soil pH
Organic matter
which assists in solubilizing zinc from sparingly soluble in mineral form (Kaur and Garg 2021).
Soil type and texture
Interactions with other nutrients

Soil moisture
Zinc solubilizing bacteria: an alternative to sustainable agriculture
bacterial species uses unique mechanisms to solubilize zinc, and their role in sustainable agriculture is becoming increasingly significant. Other bacterial genera like Acinetobacter, Azotobacter, and Enterobacter have been reported to solubilize zinc effectively (Hussain et al. 2018; Kumar et al. 2019; Nitu et al. 2020; Singh et al. 2024). Each of these bacteria employs various biochemical pathways to make zinc available to plants, often enhancing overall soil fertility and microbial diversity in the process. Figure 3 represents different ZSBs used.
Identification of ZSB

Mechanisms of Zn solubilization
Production of organic acids
produced citric acid and gluconic acids as one of the major organic acids. They create soluble complexes with zinc that enable uptake of the metal by plants. For example, Pseudomonas and Bacillus species produce a large amount of these acids and play an important role in zinc solubilization in the soil. Apart from that, zinc-solubilizing bacteria also secrete various types of organic acids such as lactic acid, oxalic acid, acetic acid, etc. Together, these acids chelate zinc ions and make them available in the rhizosphere (Singh et al. 2018; Kumawat et al. 2019; Khalid et al., 2022; Yadav et al. 2022a, b).
Chelation and complexation of zinc ions

Production of Siderophores and other Microbial metabolites
Impact of zinc-solubilizing bacteria on soil health
Microbial interactions in the rhizosphere
Soil enzyme activity
Soil structure and Organic Matter
matter by producing enzymes that break down complex organic compounds into simpler molecules. This process increases the levels of humus in the soil, which improves its ability to retain moisture and nutrients. Organic matter also serves as a reservoir of nutrients that can be released slowly over time, supporting long-term plant growth. ZSB enhances soil aggregation through the production of extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) and other biofilms that bind soil particles together. Improved soil structure, resulting from ZSB activity, enhances aeration and drainage. Proper soil aeration ensures that plant roots receive adequate oxygen for respiration, while improved drainage prevents waterlogging, which can lead to root diseases and reduced microbial activity. ZSB, by promoting soil aggregation and organic matter decomposition, plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance between aeration and drainage (Costerousse et al. 2018; Khan et al. 2019; Jalal et al. 2022; Barreto et al. 2024).
Next generation technologies used for ZSB
Genomic approaches
CRISPR
Nano-formulations
Bioinformatics and AI-driven models
Multi-functional microbial consortia
Precision agriculture and IoT integration
Advanced formulation and delivery systems
Zinc-solubilizing bacteria in crop productivity
enhancing their nutritional quality. Similarly, inoculated cucumber plants demonstrated a 20% increase in fruit yield and improved micronutrient content (Torrejón et al. 2023; Zhang et al. 2023).
Zinc-solubilizing bacteria as bioinoculants
Formulation techniques
Liquid formulations
Powder formulations
| Crop | Bacterial Strain | Effect | Reference | |||
| Rice | Burkholderia; Acinetobacter | Enhanced Zn uptake | Vaid et al. (2014) | |||
| Enterobacter cloacae | Enhanced Zn uptake | Krithika et al. (2016) | ||||
| Ralstonia picketti, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Burkholderia cepacian | Enhanced Zn uptake | Mishra et al. (2017) | ||||
| Bacillus sp. | Enhanced metabolic activity | Zeb et al. (2018) | ||||
|
Enhanced grain yield |
|
||||
| Wheat | Serratia liquefaciens FA-2, Bacillus thuringiensis FA-3, Serratia marcescens FA-4 | Improvement in grain yield | Abaid-Ullah et al., (2015) | |||
| Pantoea dispersa, P. agglomerans, Pseudomonas fragi, Rhizobium sp., and E. cloacae | Increased bioavailability of Zn | Kamran et al. (2017) | ||||
| Trichoderma harzianum and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens | Enhanced plant growth | Singh et al. (2021) | ||||
| Bacillus spp. | Enhanced Zn biofortification | Yadav et al. (2022a, b) | ||||
| Pantoea sp., Klebsiella sp., Brevibacterium sp., Acinetobacter sp., Alcaligenes sp. NCCP-650, Citrobacter sp., Exiguobacterium sp., Raoultella sp., and Acinetobacter sp. | Enhanced plant growth | Ali et al. (2023a, b) | ||||
| Maize | Bacillus sp. AZ6 | Increased biomass | Hussain et al. (2015) | |||
| B. aryabhattai ZM31, B. subtilis ZM63 | Enhanced Zn uptake | Mumtaz et al. (2020) | ||||
| Serratia. sp. | Increased plant physiology | Jain et al. (2020) | ||||
| Burkholderia cepacian and Acinetobacter baumannii | Enhanced Zn uptake | Upadhyay et al. (2021) | ||||
| Acinetobacter calcoaceticus, Bacillus proteolyticus and Stenotrophomonas pavanii | Enhanced Zn uptake | Sultan et al. (2023) | ||||
| Green gram | Neisseria, Staphylococcus cocci, Escherichia coli, and Bacillus sp. | Increased plant biomass | Iqbal et al. (2010) | |||
| Chickpea | Enterobacter sp. | Improved grain quality | Ullah et al. (2020) | |||
| Ochrobactrum intermedium, Paenibacillus polymyxa, Bacillus cereus, Stenotrophomonas maltophili, Streptomyces, and Arthrobacter globiformi | Increased bioavailability of Zn | Batool et al. (2021) | ||||
| Soybean | Streptomyces spp. | Increased plant biomass | Suriyachadkun et al. (2022) | |||
| Pigeonpea | Pseudomonas plecoglossicida SRI-156, Brevibacterium antiquum SRI-158 | Improved grain yield | Gopalakrishnan et al. 2016 | |||
| Tomato | Pseudomonas spp. VBZ4 | Increased number of fruits per plant | Karnwal 2021a, b | |||
| Lentil | Rhizobium spp. RL9 | Improvement of biomass and grain protein | Wani et al. 2008 |
Granular formulations
systems. Besides this, they learn very well on soil moisture and preserve up water (Masood et al. 2022).
Carrier materials
Coating technologies
Integration with traditional fertilizers
Enhancing nutrient efficiency
Reduction in fertilizer Use
Balanced nutrient supply
Compatibility with other biofertilizers
sustainability (Ahmad et al. 2021; Sarathambal et al. 2022; Mahmood et al. 2024).
Advantages, and limitations
high viability and efficacy is still a challenge for large-scale global adoption.
Future perspectives
Conclusion
beneficial to ecosystems and biodiversity, and leads to resilient farming practices.
Data availability No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Declarations
directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
References
Ahmad I, Ahmad M, Hussain A, Jamil M (2021) Integrated use of phosphate-solubilizing Bacillus subtilis strain IA6 and zincsolubilizing Bacillus sp. strain IA16: a promising approach for improving cotton growth. Folia Microbiol 66(1):115-125
Ali MF, Ammar A, Bilal S, Ali U, Huma N, Adnan M (2021) Mitigating zinc deficiency in plants and soils through agronomic techniques: a review. J Environ Agric Sci 23(12):1-10
Ali MM, Gull S, Hu X, Hou Y, Chen F (2023a) Exogenously applied zinc improves sugar-acid profile of loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.) By regulating enzymatic activities and expression of their metabolism-related genes. Plant Physio Biochem 201:107829
Ali M, Ahmed I, Tariq H, Abbas S, Zia MH, Mumtaz A, Sharif M (2023b) Growth improvement of wheat (Triticum aestivum) and zinc biofortification using potent zinc-solubilizing bacteria. Front Plant Sci 14:1140454
Ambreetha S, Balachandar D (2019) Rhizobacteria-mediated root architectural improvement: a hidden potential for agricultural sustainability. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for agricultural sustainability: from theory to practices, 111-128
Arora PK, Tripathi S, Omar RA, Chauhan P, Sinhal VK, Singh A, Srivastava A, Garg SK, Singh VP (2024) Next-generation fertilizers: the impact of bionanofertilizers on sustainable agriculture. Microb Cell Fact 23(1):254
Assunção AG, Schat H, Aarts MG (2010) Regulation of the adaptation to zinc deficiency in plants. Plant Signal Behave 5(12):1553-1555
Badri DV, Weir TL, Van der Lelie D, Vivanco JM (2009) Rhizosphere chemical dialogues: plant-microbe interactions. Curr Opin Biotech 20(6):642-650
Barbosa BCF, Silva SC, de Oliveira RR, Chalfun A (2017) Zinc supply impacts on the relative expression of a metallothionein-like gene in Coffea arabica plants. Plant Soil 411:179-191
Barrameda-Medina Y, Montesinos-Pereira D, Romero L, Blasco B, Ruiz JM (2014) Role of GSH homeostasis under Zn toxicity in plants with different zn tolerance. Plant Sci 227:110-121
Barreto MSC, Elzinga EJ, Rouff AA, Siebecker MG, Sparks DL, Alleoni L, R F (2024) Zinc speciation in highly weathered tropical soils affected by large scale vegetable production. Sci Environ 916:170223
Batool S, Asghar HN, Shehzad MA, Yasin S, Sohaib M, Nawaz F, Akhtar G, Mubeen K, Zahir ZA, Uzair M (2021) Zinc-solubilizing bacteria-mediated enzymatic and physiological regulations confer zinc biofortification in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L). J Soil Sci Plant Nutri 21(3):2456-2471
Behera PR, Behera KK, Sethi G, Prabina BJ, Bai AT, Sipra BS, Adarsh V, Das S, Behera KC, Singh L, Mishra MK, Behera M (2024) Enhancing agricultural sustainability through Rhizomicrobiome: a review. J Basic Microbiol 64(11):e2400100
Bharti K, Pandey N, Shankhdhar D, Srivastava PC, Shankhdhar SC (2014) Effect of exogenous zinc supply on photosynthetic rate, chlorophyll content and some growth parameters in different wheat genotypes. Cereal Res Commun 42:589-600
Bhatt K, Maheshwari DK (2020) Zinc solubilizing bacteria (Bacillus megaterium) with multifarious plant growth promoting activities alleviates growth in Capsicum annuum L. 3 Biotech. 10(2): 36
Broeckling CD, Paschke MW, Vivanco JM, Manter D (2019) Rhizosphere ecology
Cherif-Silini H, Silini A, Chenari Bouket A, Alenezi FN, Luptakova L, Bouremani N, Nowakowska JA, Oszako T, Belbahri L (2021) Tailoring next generation plant growth promoting microorganisms as versatile tools beyond soil desalinization: a road map towards field application. Sustainability 13(8):4422
Choudhary S, Saharan BS, Gera R, Kumar S, Prasad M, Gupta A, Duhan JS (2024) Molecular characterization and validation of zinc solubilization potential of bacteria isolated from onion (Allium cepa L.) rhizosphere. Microbe 4:100145
Costerousse B, Schönholzer-Mauclaire L, Frossard E, Thonar C (2018) Identification of heterotrophic zinc mobilization processes among bacterial strains isolated from wheat rhizosphere (Triticum aestivum L). Appl Environ Microbiol 84(1):e01715-e01717
Das A, Singh SK, Kumar M, Kumar O (2019) Evaluation of different methods of zinc application on growth, yield and biofortification of zinc in rice (Oryza sativa L). J Indian Soc Soil Sci 67(1):92-102
Dhaliwal SS, Sharma V, Shukla AK, Kaur J, Verma V, Singh P, Singh H Abdel-Hafez Sayed SH, Gaber S, Ali A, Hossain R A (2021) Enrichment of zinc and iron micronutrients in lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) Through biofortification. Mol 26(24):7671
Garcia J, Kao-Kniffin J (2018) Microbial group dynamics in plant rhizospheres and their implications on nutrient cycling. Front Microbiol 9:1516
Gopalakrishnan S, Vadlamudi S, Samineni S, Sameer Kumar C (2016) Plant growth-promotion and biofortification of chickpea and pigeonpea through inoculation of biocontrol potential bacteria, isolated from organic soils. Springerplus 5:1-11
Hacisalihoglu G (2020) Zinc (zn): the last nutrient in the alphabet and shedding light on Zn efficiency for the future of crop production under suboptimal zn. Plants 9(11):1471
Hafeez BM, K Y, Khanif YM, Saleem M (2013) Role of zinc in plant nutrition-a review. Am J Exp Agric 3(2):374-391
Han G, Qiao Z, Li Y, Wang C, Wang B (2021) The roles of CCCH zinc-finger proteins in plant abiotic stress tolerance. Int J Mol Sci 22(15):8327
Haroon M, Khan ST, Malik A (2022) Zinc-solubilizing bacteria: an option to increase zinc uptake by plants. Microbial Biofertilizers and Micronutrient Availability: The Role of Zinc in Agriculture and Human Health, 207-238
Hashemnejad F, Barin M, Khezri M, Ghoosta Y, Hammer EC (2021) Isolation and identification of insoluble zinc-solubilising bacteria and evaluation of their ability to solubilise various zinc minerals. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21:2501-2509
Hassan MU, Aamer M, Umer Chattha M, Haiying T, Shahzad B, Barbanti L, Nawaz M, Rasheed A, Afzal A, Liu Y, Guoqin H (2020) The critical role of zinc in plants facing the drought stress. Agri 10(9):396
Hefferon K (2019) Biotechnological approaches for generating zincenriched crops to combat malnutrition. Nutr 11(2):253
Hussain A, Arshad M, Zahir ZA, Asghar M (2015) Prospects of zinc solubilizing bacteria for enhancing growth of maize. Pak J Agri Sci 52(4)
Hussain A, Zahir ZA, Asghar HN, Ahmad M, Jamil M, Naveed M, Zaman Akhtar, M F U (2018) Zinc solubilizing bacteria for zinc biofortification in cereals: a step toward sustainable nutritional security. Role of Rhizospheric Microbes in Soil: Volume 2: Nutrient Management and Crop Improvement, 203-227
Hussain A, Zahir ZA, Ditta A, Tahir MU, Ahmad M, Mumtaz MZ, Hayat K, Hussain S (2019) Production and implication of
bio-activated organic fertilizer enriched with zinc-solubilizing bacteria to boost up maize (Zea mays L.) production and biofortification under two cropping seasons. Agronomy 10(1):39
Hussain A, Zahir ZA, Asghar HN, Imran M, Ahmad M, Hussain S (2020) Integrating the potential of Bacillus sp. Az6 and organic waste for zinc oxide bio-activation to improve growth, yield and zinc content of maize grains. Pak J Agri Sci 57(1)
Iqbal U, Jamil N, Ali I, Hasnain S (2010) Effect of zinc-phosphatesolubilizing bacterial isolates on growth of Vigna radiata. Annals Microbiol 60:243-248
Islam MA, Hasan MM, Akter T, Islam SMS (2024) Development of Iron and Zinc Biofortified Rice Variety for Nutrition Improvement in Bangladesh. Food Sci Engi. 322-330
Jain D, Kour R, Bhojiya AA, Meena RH, Singh A, Mohanty SR, Rajpurohit D, Ameta KD (2020) Zinc tolerant plant growth promoting bacteria alleviates phytotoxic effects of zinc on maize through zinc immobilization. Sci Rep 10(1): 13865
Jalal A, Shah S, Teixeira Filho MCM, Khan A, Shah T, Ilyas M, Rosa PAL (2020) Agro-biofortification of zinc and iron in wheat grains. Gesunde Pflanzen 72(3):227-236
Jalal A, Galindo FS, Freitas LA, da Silva Oliveira CE, de Lima BH, Pereira ÍT, Ferraz GF, Silva de Souza J, Nunes, da Costa K, Nogueira TAR, Teixeira Filho, M C M (2022) Yield, zinc efficiencies and biofortification of wheat with zinc sulfate application in soil and foliar nanozinc fertilisation. Crop and Pasture Science
Kamran S, Shahid I, Baig DN, Rizwan M, Malik KA, Mehnaz S (2017) Contribution of zinc solubilizing bacteria in growth promotion and zinc content of wheat. Front Microbiol 8:2593
Karnwal A (2021a) Pseudomonas spp., a zinc-solubilizing vermicompost bacteria with plant growth-promoting activity moderates zinc biofortification in tomato. Int J Veg Sci 27(4):398-412
Karnwal A (2021b) Zinc solubilizing Pseudomonas spp. from vermicompost bestowed with multifaceted plant growth promoting properties and having prospective modulation of zinc biofortification in Abelmoschus esculentus L. J Plant Nutr 44(7):1023-1038
Kaur H, Garg N (2021) Zinc toxicity in plants: a review. Planta 253(6):129
Khalid S, Amanullah, Ahmed I (2022) Enhancing zinc biofortification of wheat through integration of zinc, compost, and zinc-solubilizing bacteria. Agri 12(7):968
Khan A, Singh J, Upadhayay VK, Singh AV, Shah S (2019) Microbial biofortification: a green technology through plant growth promoting microorganisms. Sustain. Green Technol. Environ. Management: 255-269
Khan ST, Malik A, Alwarthan A, Shaik MR (2022) The enormity of the zinc deficiency problem and available solutions; an overview. Arab J Chem 15(3):103668
Khani AG, Enayatizamir N, Norouzi Masir M (2019) Impact of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on different forms of soil potassium under wheat cultivation. Lett App Microbiol 68(6):514-521
Khatoon Z, Huang S, Farooq MA, Santoyo G, Rafique M, Javed S, Gul B (2022) Role of plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB) in abiotic stress management. Mitigation of Plant Abiotic Stress by Microorganisms, pp 257-272
Kour D, Rana KL, Yadav N, Yadav AN, Kumar A, Meena VS, Singh B, Chauhan VS, Dhaliwal HS, Saxena AK (2019) Rhizospheric microbiomes: biodiversity, mechanisms of plant growth promotion, and biotechnological applications for sustainable agriculture. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for agricultural sustainability: from theory to practices, 19-65
Krithika S, Balachandar D (2016) Expression of zinc transporter genes in rice as influenced by zinc-solubilizing Enterobacter cloacae strain ZSB14. Front. Plant Sci 7:446
Kumar A, Patel JS, Meena VS (2018) Rhizospheric microbes for sustainable agriculture: an overview. Role of Rhizospheric Microbes
in Soil: Volume 1: Stress Management and Agricultural Sustainability, 1-31
Kumar A, Dewangan S, Lawate P, Bahadur I, Prajapati S (2019) Zincsolubilizing bacteria: a boon for sustainable agriculture. Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria for Sustainable Stress Management: Volume 1: Rhizobacteria in Abiotic Stress Management, 139-155
Kumawat N, Kumar R, Khandkar UR, Yadav RK, Saurabh K, Mishra JS, Dotaniya ML, Hans H (2019) Silicon (Si)-and zinc (Zn)-solubilizing microorganisms: role in sustainable agriculture. Biofertilizers Sustainable Agric Environ, 109-135
Kushwaha P, Kashyap PL, Pandiyan K, Bhardwaj AK (2020) Zincsolubilizing microbes for sustainable crop production: current understanding, opportunities, and challenges. Phytobiomes: Curr Insights Future Vistas, 281-298
Ladohia S, Rana N, Srivastava P, Kumar R, Mehta S, Pareek B (2024) Use of zinc solubilizing biofertilizers for increasing the growth and yield of cereals: a review. J Appl Nat Sci 16(3)
Liu Z, Meng J, Sun Z, Su J, Luo X, Song J, Li P, Sun Y, Yu C, Peng X (2022) Zinc application after low temperature stress promoted rice tillers recovery: aspects of nutrient absorption and plant hormone regulation. Plant Sci 314:111104
Lora AM, Delgado A (2020) Factors determining zn availability and uptake by plants in soils developed under Mediterranean climate. Geoderma 376:114509
Ma D, Sun D, Wang C, Ding H, Qin H, Hou J, Huang X, Xie Y, Guo T (2017) Physiological responses and yield of wheat plants in zinc-mediated alleviation of drought stress. Front Plant Sci 8:860
Mahmood I, Sami A, Asad SA, Shah GA, Rana RM, Raja NI, Sher A, Mashwani ZR, Quyyum A, Iqbal J, Awan TH (2024) Zinc-Oxide-Nanoparticles in conjugation with Zn-Solubilizing Bacteria improve Zn Biofortification and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Wheat. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 24(3):5565-5585
Mahmud K, Makaju S, Ibrahim R, Missaoui A (2020) Current progress in nitrogen fixing plants and microbiome research. Plants 9(1):97
Majeed A, Muhammad Z, Ahmad H (2018) Plant growth promoting bacteria: role in soil improvement, abiotic and biotic stress management of crops. Plant Cell Rep 37(12):1599-1609
Makarenko N, Bondar V, Makarenko V, Symochko L (2020) Factors affecting mobility of zinc in soils of Ukraine. Internat J Ecosyst Ecol Sci 10(4)
Masood F, Ahmad S, Malik A (2022) Role of rhizobacterial bacilli in zinc solubilization. Microb Biofertilizers Micronutrient Availability: Role zinc Agric Hum Health, 361-377
Mhlongo MI, Piater LA, Madala NE, Labuschagne N, Dubery IA (2018) The chemistry of plant-microbe interactions in the rhizosphere and the potential for metabolomics to reveal signaling related to defense priming and induced systemic resistance. Front Plant Sci 9:112
Moulick D, Bhutia KL, Sarkar S, Roy A, Mishra UN, Pramanick B, Maitra S, Shankar T, Hazra S, Skalicky M, Brestic B, Barek V, Hossain A (2023) The intertwining of Zn-finger motifs and abiotic stress tolerance in plants: current status and future prospects. Front Plant Sci 13:1083960
Mumtaz MZ, Ahmad M, Jamil M, Hussain T (2017) Zinc solubilizing Bacillus spp. potential candidates for biofortification in maize. Microbiol Res 202:51-60
Nadarajah KK (2020) ROS homeostasis in abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Int J Mol Sci 21(15):5208
Natasha N, Shahid M, Bibi I, Iqbal J, Khalid S, Murtaza B, Bakhat HF, Farooq AB, U, Amjad M, Hammad HM, Niazi NK, Arshad M (2022) Zinc in soil-plant-human system: a data-analysis review. Sci Total Environ 808:152024
Nithyapriya S, Lalitha S, Sayyed RZ, Reddy MS, Dailin DJ, Enshasy HE, Suriani NL, Herlambang S (2021) Production, purification, and characterization of bacillibactin siderophore of Bacillus
subtilis and its application for improvement in plant growth and oil content in sesame. Sustain 13:5394
Nithyapriya S, Lalitha S, Devi SU, Perveen K, Alshaikh NA, Sayyed RZ, Mastinu A (2024) Purification and characterization of desferrioxamine B of Pseudomonas fluorescens and its application to improve oil content, nutrient uptake, and plant growth in peanuts. Microbiol Eco 87:60
Nitu R, Rajinder K, Sukhminderjit K (2020) Zinc solubilizing bacteria to augment soil fertility—A comprehensive review. Int J Agricult Sci Vet Med 8:38-44
Noulas C, Tziouvalekas M, Karyotis T (2018) Zinc in soils, water and food crops. J Trace Ele Med Bio 49:252-260
Obaid H, Shrestha RK, Liu D, Elsayed NS, Ni J, Ni C (2022) Biofortification of maize with zinc and its effect on human health. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 22(2):1792-1804
Ofori KF, Antoniello S, English MM, Aryee AN (2022) Improving nutrition through biofortification-A systematic review. Front Nutr 9:1043655
Othman NMI, Othman R, Zuan ATK, Shamsuddin AS, Zaman NBK, Sari NA, Panhwar QA (2022) Isolation, characterization, and identification of zinc-solubilizing bacteria (ZSB) from wetland rice fields in Peninsular Malaysia. Agri 12(11): 1823
Pan J, Huang X, Li Y, Li M, Yao N, Zhou Z, Li X (2017) Zinc protects against cadmium-induced toxicity by regulating oxidative stress, ions homeostasis and protein synthesis. Chemos 188:265-273
Panpatte DG, Jhala YK, Shelat HN, Vyas RV (2016) Nanoparticles: the next generation technology for sustainable agriculture. Microb Inoculants Sustainable Agricultural Productivity: 2: Funct Appl, 289-300
Paramesh V, Dhar S, Dass A, Kumar B, Kumar A, El-Ansary DO, Elansary HO (2020) Role of integrated nutrient management and agronomic fortification of zinc on yield, nutrient uptake and quality of wheat. Sustain 12(9):3513
Patel JN, Alam MS (2024) Impact of Foliar Fortification of Zinc and Iron on Nutrient Content and their uptake by Maize Crop. J Exp Agri Internat 46(7):973-982
Patel PR, Shaikh SS, Sayyed RZ (2018) Modified chrome azurol S method for detection and estimation of siderophores having affinity for metal ions other than iron Fe. Environ Sustain 1(1):81-87
Pii Y, Mimmo T, Tomasi N, Terzano R, Cesco S, Crecchio C (2015) Microbial interactions in the rhizosphere: beneficial influences of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on nutrient acquisition process. A review. Biol. Fert. Soils. 51: 403-415.
Prasad K, Khare A, Rawat P (2021) Microbial Functions Improve Agricultural Soil Health, Quality Productivity and Environmental sustainability for future generation. Gulf J Mol Biol 1(1):24-37
Rani N, Chauhan A, Kaur S, Solanki MK, Tripathi M, Jain D, Singh S, Upadhyay SK, Kaur G (2023) Molecular mechanistic of Znsolubilizing bacteria for agronomic eminence: recent updates and futuristic development. J Plant Growth Regul. 1-15
Rudani K, Vishal P, Kalavati P (2018) The importance of zinc in plant growth-A review. Int Res J Nat Appl Sci 5(2):38-48
Sabagh ELA, Islam MS, Hossain A, Iqbal MA, Mubeen M, Waleed M, Reginato M, Battaglia M, Ahmed S, Rehman A, Arif M, Athar HR, Ratnasekera DP, Danish S, Raza MA, Rajendran K, Mushtaq M, Skalicky M, Brestic M, Soufan W, Fahad S, Pandey S, Kamran M, Datta R, Abdelhamid MT (2022) Phytohormones as growth regulators during abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Front Agron 4:765068
Saboor A, Muhammad AA, Hussain S, El Enshasy HE, Hussain S, Ahmed N, Gafur A, Sayyed RZ, Shah F, Danish S, Datta S R (2021) Zinc nutrition and arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis effects on maize (Zea mays L.) growth and productivity. Saudi J Biol Sci 28(11):6339-6351
Sarathambal C, Dinesh R, Srinivasan V, Sheeja TE, Jeeva V, Manzoor M (2022) Changes in bacterial diversity and composition in response to co-inoculation of arbuscular mycorrhizae and zincsolubilizing bacteria in turmeric rhizosphere. Curr Microbiol 79:1-9
Saxena V, Bharti MK, Kumar P, Singh J, Patel VB (2023) Effect of zinc uptake on alcohol dehydrogenase, protein and mineral contents of hydroponically grown chickpea (Cicer arietinum). J Plant Nutr 46(6):867-876
Schmidt H, Nunan N, Höck A, Eickhorst T, Kaiser C, Woebken D, Raynaud X (2018) Recognizing patterns: spatial analysis of observed microbial colonization on root surfaces. Front Environ Sci 6:61
Sehrawat A, Sindhu SS (2024) Zinc-solubilizing microorganisms: contributions in nutrient availability and implications for Crop Productivity in Sustainable Agriculture. Plant Holobiome Engineering for Climate-Smart Agriculture. Springer Nature Singapore, Singapore, pp 183-213
Sindhu SS, Sharma R, Sindhu S, Phour M (2019) Plant nutrient management through inoculation of zinc-solubilizing bacteria for sustainable agriculture. Biofertilizers Sustainable Agric Environ, 173-201
Singh D, Geat N, Rajawat MVS, Prasanna R, Kar A, Singh AM, Saxena AK (2018) Prospecting endophytes from different Fe or Zn accumulating wheat genotypes for their influence as inoculants on plant growth, yield, and micronutrient content. Annals Microbiol 68:815-833
Singh P, Shukla AK, Behera SK, Tiwari PK (2019) Zinc application enhances superoxide dismutase and carbonic anhydrase activities in zinc-efficient and zinc-inefficient wheat genotypes. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 19(3):477-487
Singh K, Batra R, Sharma S, Saripalli G, Gautam T, Singh R, Pal S, Malik P, Kumar M, Jan I, Singh S, Kumar D, Pundir S, Chaturvedi D, Verma A, Rani A, Kumar A, Sharma H, Chaudhary J, Kumar K, Kumar S, Singh VK, Singh VP, Kumar S, Kumar R, Gaurav SS, Sharma S, Sharma PK, Balyan HS, Gupta PK (2021) WheatQTLdb: a QTL database for wheat. Mol Genet Genomics 296(5):1051-1056
Singh J, Singh AV, Upadhayay VK, Khan A, Chandra R (2022) Prolific contribution of Pseudomonas protegens in Zn biofortification of wheat by modulating multifaceted physiological response under saline and non-saline conditions. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 38(12):227
Singh S, Chhabra R, Sharma A, Bisht A (2024) Harnessing the power of zinc-solubilizing Bacteria: a Catalyst for a sustainable agrosystem. Bacteria 3(1):15-29
Srithaworn M, Jaroenthanyakorn J, Tangjitjaroenkun J, Suriyachadkun C, Chunhachart O (2023) Zinc solubilizing bacteria and their potential as bioinoculant for growth promotion of green soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) PeerJ. 11:e15128
Suganya A, Saravanan A, Manivannan N (2020) Role of zinc nutrition for increasing zinc availability, uptake, yield, and quality of maize (Zea mays L.) grains: an overview. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 51(15):2001-2021
Sultan A, Youssef HIA (2023) Biofertilizer effect of some zinc dissolving bacteria free and encapsulated on Zea mays growth. Archives Microbiol 205(5):202
Suriyachadkun C, Chunhachart O, Srithaworn M, Tangchitcharoenkhul R, Tangjitjareonkun J (2022) Zinc-solubilizing Streptomyces spp. as bioinoculants for promoting the growth of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill). J Microbiol Biotechnol 32(11):1435
Torrejón BP, Cáceres A, Sánchez M, Sainz L, Guzmán M, BermúdezPerez FJ, Ramírez-Rodríguez GB, Delgado-López JM (2023)
Ullah A, Heng S, Munis MFH, Fahad S, Yang X (2015) Phytoremediation of heavy metals assisted by plant growth promoting (PGP) bacteria: a review. Environ Exper Bot 117:28-40
Ullah A, Farooq M, Nadeem F, Rehman A, Hussain M, Nawaz A, Naveed M (2020) Zinc application in combination with zinc solubilizing Enterobacter sp. MN17 improved productivity, profitability, zinc efficiency, and quality of desi chickpea. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20(4):2133-2144
Upadhayay VK, Singh AV, Khan A (2022a) Cross talk between zincsolubilizing bacteria and plants: a short tale of bacterial-assisted zinc biofortification. Front Soil Sci 1:788170
Upadhayay VK, Singh AV, Khan A, Sharma A (2022b) Contemplating the role of zinc-solubilizing bacteria in crop biofortification: an approach for sustainable bioeconomy. Front Agron 4:903321
Upadhayay VK, Singh AV, Khan A, Singh J, Pareek N, Raghav A (2022c) FE-SEM/EDX based zinc mobilization analysis of Burkholderia cepacia and Pantoea rodasii and their functional annotation in crop productivity, soil quality, and zinc biofortification of paddy. Front Microbiol 13:852192
Upadhyay H, Gangola S, Sharma A, Singh A, Maithani D, Joshi S (2021) Contribution of zinc solubilizing bacterial isolates on enhanced zinc uptake and growth promotion of maize (Zea mays L). Folia Microbiol 66:543-553
Walitang D, Samaddar S, Roy Choudhury A, Chatterjee P, Ahmed S, Sa T (2019) Diversity and plant growth-promoting potential of bacterial endophytes in rice. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): prospects for sustainable agriculture, 3-17
Wani PA, Khan MS, Zaidi A (2008) Effect of metal-tolerant plant growth-promoting Rhizobium on the performance of pea grown in metal-amended soil. Archives Environ Cont Toxic 55:33-42
Wani SH, Gaikwad K, Razzaq A, Samantara K, Kumar M, Govindan V (2022) Improving zinc and iron biofortification in wheat through genomics approaches. Mol Biol Rep 49(8):8007-8023
Yadav RC, Sharma SK, Varma A, Rajawat MVS, Khan MS, Sharma PK, Malviya D, Singh UB, Rai JP, Saxena AK (2022a) Modulation in biofertilization and biofortification of wheat crop by inoculation of zinc-solubilizing rhizobacteria. Front Plant Sci 13:777771
Yadav VK, Yadav RC, Choudhary P, Sharma SK, Bhagat N (2022b) Mitigation of drought stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by
inoculation of drought tolerant Bacillus paramycoides DT-85 and Bacillus paranthracis DT-97. J Appl Biol Biotechnol 10:59-69
Yadav RC, Sharma SK, Varma A, Singh UB, Kumar A, Bhupenchandra I, Rai JP, Sharma PK, Singh HV (2023) Zinc-solubilizing Bacillus spp. in conjunction with chemical fertilizers enhance growth, yield, nutrient content, and zinc biofortification in wheat crop. Front Microbiol 14:1210938
Yasmin R, Hussain S, Rasool MH, Siddique MH, Muzammil S (2021) Isolation, characterization of Zn solubilizing bacterium (Pseudomonas Protegens RY2) and its contribution in growth of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L) as deciphered by improved growth parameters and zn content. Dose-response 19(3):15593258211036791
Younas N, Fatima I, Ahmad IA, Ayyaz MK (2023) Alleviation of zinc deficiency in plants and humans through an effective technique; biofortification: a detailed review. Acta Ecol Sin 43(3):419-425
Zeb H, Hussain A, Naveed M, Ditta A, Ahmad S, Jamshaid MU, Ahmad HT, Hussain MB, Aziz R, Haider MS (2018) Compost enriched with ZnO and Zn -solubilising bacteria improves yield and Zn -fortification in flooded rice. Italian J Agron 13(4):310-316
Zeng H, Zhang X, Ding M, Zhang X, Zhu Y (2019) Transcriptome profiles of soybean leaves and roots in response to zinc deficiency. Physiol Planta 167(3):330-351
Zeng H, Wu H, Yan F, Yi K, Zhu Y (2021) Molecular regulation of zinc deficiency responses in plants. J Plant Physiol 261:153419
Zhang J, Wang S, Song S, Xu F, Pan Y, Wang H (2019) Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses reveal new insight into chlorophyll synthesis and chloroplast structure of maize leaves under zinc deficiency stress. J Proteom 199:123-134
Zhang L, Zuluaga MYA, Pii Y, Barone A, Amaducci S, Miras-Moreno B, Martinelli E, Bellotti G, Trevisan M, Puglisi E, Lucini L (2023) A Pseudomonas Plant Growth promoting Rhizobacterium and Arbuscular Mycorrhiza differentially modulate the growth, photosynthetic performance, nutrients allocation, and stress response mechanisms triggered by a mild zinc and cadmium stress in tomato. Plant Sci 337:111873
Zlobin IE (2021) Current understanding of plant zinc homeostasis regulation mechanisms. Plant Physiol Biochem 162:327-335
Zlobin IE, Pashkovskiy PP, Kartashov AV, Nosov AV, Fomenkov AA, Kuznetsov VV (2020) The relationship between cellular zn status and regulation of Zn homeostasis genes in plant cells. Environ Exp Bot 176:104104
