DOI: https://doi.org/10.54097/v160aa61
تاريخ النشر: 2024-03-26
نظام توصية بالأدوية يعتمد على معالجة اللغة الطبيعية لتحليل مشاعر المرضى
الملخص
معالجة اللغة الطبيعية (NLP) هي مجال متعدد التخصصات في علوم الحاسوب، والذكاء الاصطناعي، واللغويات، يركز على قدرة الحواسيب على فهم ومعالجة وتوليد ومحاكاة اللغة البشرية من أجل تحقيق القدرة على إجراء محادثات طبيعية مع البشر. المبادئ الأساسية لمعالجة اللغة الطبيعية تتواجد على مستويات متعددة، بما في ذلك اللغويات، وعلوم الحاسوب، والإحصاء. يتضمن ذلك دراسة بنية اللغة، والدلالات، والقواعد، والبراغماتية، بالإضافة إلى التحليل الإحصائي ونمذجة مجموعات البيانات الكبيرة. في عملية التنفيذ الفعلي، من الضروري معالجة اللغة الطبيعية على مستويات متعددة. بناءً على ذلك، قامت هذه الورقة بدمج التعلم العميق وتقنية معالجة اللغة الطبيعية لإجراء تحليل المشاعر على تعليقات المرضى، بهدف التوصية بالأدوية الأكثر ملاءمة للمرضى، وبالتالي تحقيق وصف دقيق للأدوية وتوصيات مخصصة.
1. المقدمة
في نفس الوقت، قامت العديد من الشركات المحلية أيضًا بتطبيق تقنية معالجة اللغة الطبيعية في خدمة العملاء الذكية، ومحركات البحث، وأنظمة التوصية وغيرها من السيناريوهات.
2. الأعمال ذات الصلة
2.1. تقنية معالجة اللغة الطبيعية (NLP)
2.2. تحليل عواطف اللغة الطبيعية
تشمل المبادئ الرئيسية لخوارزميات تحليل المشاعر ما يلي:
- طريقة التعلم الإحصائي: يمكن لخوارزمية تحليل العواطف المعتمدة على طريقة التعلم الإحصائي تحديد معلومات العواطف في النص من خلال تعلم مجموعة بيانات التدريب. تشمل هذه الخوارزميات باي البسيط، وآلات الدعم الشعاعي، وأشجار القرار، وما إلى ذلك.
- طريقة التعلم العميق: تتعلم خوارزمية تحليل العواطف المعتمدة على طريقة التعلم العميق معلومات العواطف في النص من خلال شبكة عصبية متعددة الطبقات. تشمل هذه الخوارزميات الشبكة العصبية التلافيفية، والشبكة العصبية التكرارية، وآلية الانتباه الذاتي، وما إلى ذلك.
2.3. معالجة اللغة الطبيعية والرعاية الصحية
- التعرف على الكلام
2. الوثائق السريرية
3. الترميز المدعوم بالحاسوب (CAC)
4. مطابقة التجارب السريرية
5. أبحاث التنقيب عن البيانات
6. الدردشة الآلية والكتبة الافتراضية
7. تحليل السبب الجذري
التحليلات التنبؤية على تقديم حلول لمشاكل الصحة الشائعة.
8. إدارة المراجعات وتحليل العواطف
3. المنهجية
3.1. خوارزمية تحليل المشاعر
- معالجة البيانات: يتم تنظيف النص المدخل، وإزالة الكلمات التوقف، ووضع علامات على أجزاء الكلام، واستخراج الكلمات وغيرها من المعالجة لاستخراج ميزات ذات مغزى.
- استخراج الميزات: يتم تحويل النص المعالج مسبقًا إلى تمثيل متجه لتسهيل فهم الكمبيوتر ومعالجته. يمكن تحقيق ذلك من خلال نموذج كيس الكلمات، TF-IDF، Word2Vec وما إلى ذلك.
- تدريب النموذج: وفقًا لمبدأ الخوارزمية المختارة، يتم إجراء تدريب النموذج على مجموعة بيانات التدريب. يمكن تحقيق ذلك من خلال طرق تحسين مثل الانحدار التدرجي والانحدار التدرجي العشوائي.
- تقييم النموذج: يتم تقييم مجموعات بيانات الاختبار لقياس أداء ودقة النموذج. يمكن تقييم ذلك من خلال مقاييس مثل الدقة، ومعدلات الاسترجاع، ودرجات F1، وما إلى ذلك.
- تحسين النموذج: وفقًا لنتائج تقييم النموذج، يتم تحسين النموذج لتحسين الدقة والأداء. يمكن تحقيق ذلك من خلال ضبط المعلمات الفائقة، واختيار الميزات، ودمج النماذج وما إلى ذلك.
3.2. صيغة النموذج الرياضي لتحليل المشاعر
- بايزي البسيط
2. آلة الدعم الناقل
3.3. تصميم التجربة
اتبعت طرقًا منهجية منظمة تضمنت استكشاف البيانات، ومعالجة البيانات، وتطوير النموذج، وتقييم الاستنتاجات والقيود. في مرحلة استكشاف البيانات، تُستخدم تقنيات التصور والإحصاء للحصول على رؤى حول خصائص مجموعة البيانات. تساعد هذه العملية في معالجة البيانات وهندسة الميزات ذات الصلة للنموذج. لمعالجة القيود الموجودة في معالجة اللغة الطبيعية، نقدم نموذج التعلم الآلي LightGBM. خفف النموذج من التحيز المحتمل وحسن من الموثوقية من خلال دمج ميزات العد المفيدة.
3.4. تحليل بيانات الاستكشاف
| معرف فريد | اسم الدواء | الحالة | المراجعة | التقييم | التاريخ | عدد المفيدين | |
| 0 | 206461 | فالسارتان | خلل في البطين الأيسر | “ليس له آثار جانبية، أتناوله مع … | 9 | 2012-05-20 | 27 |
| 1 | 95260 | غوانفاسين | ADHD | “ابني في منتصف أسبوعه الرابع من … | 8 | 2010-04-27 | 192 |
| 2 | 92703 | ليبرل | وسيلة منع الحمل | “كنت أتناول وسيلة منع حمل فموية أخرى، … | 5 | 2009-12-14 | 17 |
| 3 | 138000 | أورثو إيفرا | وسيلة منع الحمل | “هذه هي المرة الأولى التي أستخدم فيها أي شكل من أشكال منع الحمل … | 8 | 2015-11-03 | 10 |
| 4 | 35696 | بويبرينورفين / نالوكسون | اعتماد الأفيون | “سبوكسيون غير حياتي تمامًا … | 9 | 2016-11-27 | 37 |
- اسم الدواء (فئوي): اسم الدواء
- الحالة (فئوي): اسم الحالة
- المراجعة (نص): مراجعة المريض
- التقييم (رقمي): تقييم المريض من 10 نجوم
- التاريخ (تاريخ): تاريخ إدخال المراجعة
- عدد المفيدين (رقمي): عدد المستخدمين الذين وجدوا المراجعة مفيدة
هيكل البيانات هو أن مريضًا يحمل معرفًا فريدًا يشتري دواءً يتناسب مع حالته ويكتب مراجعة وتقييمًا للدواء الذي اشتراه في التاريخ. بعد ذلك، إذا قرأ الآخرون تلك المراجعة ووجدوها مفيدة، فسوف ينقرون على عدد المفيدين، مما سيضيف 1 للمتغير.
3.5. تدريب نموذج مجموعة البيانات
كانت القيم الفريدة لاسم الدواء والحالة 3671 و917، على التوالي، بمتوسط حوالي 4 أدوية لكل حالة. قمنا بمزيد من التصور لأعلى 20 من حيث عدد الأدوية لكل حالة.
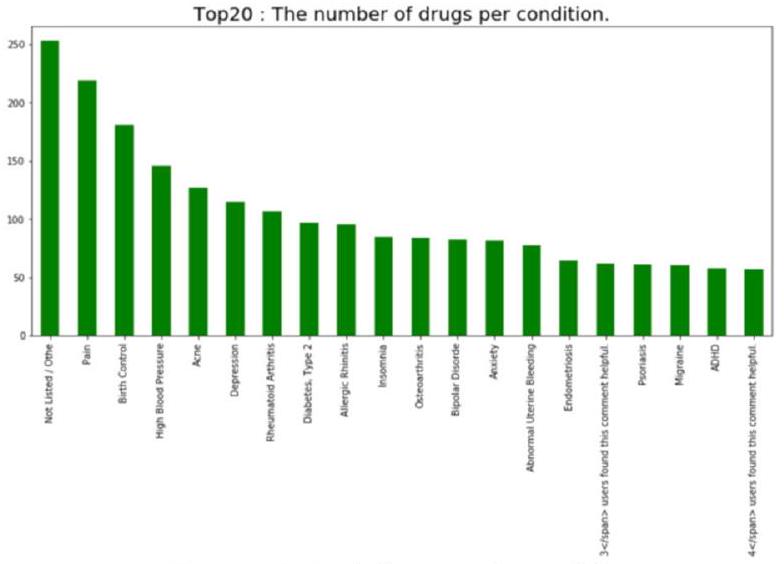
- بالنسبة لأولى ثماني حالات، عدد الأدوية
المطابقة لكل حالة حوالي 100. وهذا يشير إلى أن هناك المزيد من خيارات الأدوية لهذه الحالات الشائعة. - هناك بعض الاستثناءات في البيانات، على سبيل المثال، يحتوي حقل الحالة على ”
span> وجد المستخدمون هذه التعليق مفيدًا.”, مما قد يكون خطأ أثناء الزحف. نحتاج إلى إزالة هذه البيانات غير الطبيعية أثناء المعالجة المسبقة. - من خلال ملاحظة توزيع الأدوية لكل حالة، وُجد أن بعض الحالات تحتوي على دواء واحد فقط. بالنسبة لنظام الإحالة، فإن التوصية غير ممكنة في هذه الحالة، لذا سنحلل فقط الحالات التي تحتوي على ما لا يقل عن دواءين.
3.6. توليد سحابة الكلمات النصية العاطفية
3.7. النتائج التجريبية
تمثل المشاعر، والعلاقة بين التواريخ والتقييمات. في مرحلة معالجة البيانات، قمنا بمعالجة البيانات وفقًا للموضوع المحدد، مثل حذف حالة وجود دواء واحد فقط للتوصية. في عملية النمذجة، استخدمنا نموذج تعلم عميق مع n-gram، واستخدمنا أيضًا نموذج تعلم آلي يسمى Lightgbm للتغلب على قيود معالجة اللغة الطبيعية. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، نستخدم قواميس المشاعر لتحليل المشاعر للتغلب على قيود الحزم المكونة بناءً على بيانات الأفلام. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، نقوم بتطبيع usefulCount مع الشروط لتحسين الموثوقية. تتيح لنا هذه الخطوات حساب القيمة المتوقعة النهائية وتوصية الدواء المناسب لكل حالة بناءً على ترتيب تلك القيمة.
- عند استخدام قاموس المشاعر لتحليل المشاعر، تكون الموثوقية منخفضة عندما يكون عدد الكلمات الإيجابية والسلبية صغيرًا. على سبيل المثال، إذا كانت الكلمة الإيجابية 0 والكلمة السلبية 1، يتم تصنيفها على أنها عاطفة سلبية. [32] لذلك، إذا كان هناك أقل من 5 كلمات عاطفية، يمكننا استبعاد هذه الملاحظات.
- من أجل ضمان موثوقية القيمة المتوقعة، قمنا بتطبيع usefulCount وضربه في القيمة المتوقعة. ومع ذلك، مع زيادة العدد التراكمي لزوار الموقع، قد يميل usefulCount نحو المراجعات القديمة. لذلك، عند تطبيع usefulCount، يجب أن نأخذ في الاعتبار أيضًا عامل الوقت.
- إذا كانت العاطفة إيجابية، يجب أن تزداد الموثوقية في الاتجاه الإيجابي، وإذا كانت سلبية، يجب أن تزداد في الاتجاه السلبي. ومع ذلك، نحن ببساطة نستخدم usefulCount للموثوقية دون أخذ ذلك في الاعتبار. لذلك، يجب أن نأخذ في الاعتبار رمز usefulCount وفقًا لأنواع العواطف المختلفة، ونقوم بإجراء المعالجة المضاعفة المقابلة.
4. الخاتمة
- أهمية معالجة اللغة الطبيعية في الرعاية الصحية: تلعب تقنية معالجة اللغة الطبيعية دورًا حيويًا في جوانب مختلفة من الرعاية الصحية، بدءًا من التعرف على الكلام من أجل النسخ الفعال إلى مطابقة التجارب السريرية وتحليل المشاعر لتحسين رضا المرضى.
- التحديات والفرص: بينما تقدم معالجة اللغة الطبيعية فرصًا هائلة لتحسين تقديم الرعاية الصحية، فإنها تواجه أيضًا تحديات مثل انخفاض موثوقية تحليل المشاعر مع محدودية الكلمات العاطفية. ومع ذلك، يمكن معالجة هذه التحديات من خلال المعالجة المسبقة الدقيقة وتقنيات تحسين النموذج.
- النهج المنهجي: تضمنت المنهجية المستخدمة في هذه الدراسة استكشاف البيانات، والمعالجة المسبقة، وتطوير النموذج، والتقييم. تم استخدام تقنيات متقدمة مثل تحليل المشاعر باستخدام القواميس و n-grams، بالإضافة إلى نماذج التعلم الآلي مثل LightGBM، للتغلب على القيود وتحسين الموثوقية.
- نظام التوصية: تظهر النتائج التجريبية التطوير الناجح لنظام توصية الأدوية المصمم وفقًا لحالات المرضى الفردية. من خلال معالجة البيانات، والنمذجة باستخدام تقنيات التعلم العميق والتعلم الآلي، وتحليل المشاعر، يوصي النظام بشكل فعال بالأدوية المناسبة استنادًا إلى مراجعات المرضى.
- القيود والاتجاهات المستقبلية: على الرغم من نجاح نظام التوصيات، هناك قيود تتعلق بموثوقية تحليل المشاعر وتطبيع عدد الاستخدامات المفيد. يجب أن تركز الأبحاث المستقبلية على تحسين مقاييس الموثوقية وأخذ الجانب الزمني في تطبيع البيانات بعين الاعتبار.
شكر وتقدير
References
[2] Chen, Jianfeng, et al. “Implementation of an AI-Based MRD Evaluation and Prediction Model for Multiple Myeloma”. Frontiers in Computing and Intelligent Systems, vol. 6, no. 3, Jan. 2024, pp. 127-31, https://doi.org/10.54097/zJ4MnbWW.
[3] “Implementation of Computer Vision Technology Based on Artificial Intelligence for Medical Image Analysis”. International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology, vol. 1, no. 1, Dec. 2023, pp. 69-76, https://doi.org/10.62051/ijcsit.v1n1.10.
[4] Chen, Jianhang, et al. “One-stage object referring with gaze estimation.” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2022.
[5] Zhou, Y., Osman, A., Willms, M., Kunz, A., Philipp, S., Blatt, J., & Eul, S. (2023). Semantic Wireframe Detection.
[6] Cai, Guoqing et al. “A deep learning-based algorithm for crop Disease identification positioning using computer vision.” International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology (2023): n. pag.
[7] “Machine Learning Model Training and Practice: A Study on Constructing a Novel Drug Detection System”. International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology, vol. 1, no. 1, Dec. 2023, pp. 139-46, https://doi.org/10.62051/ijcsit.v1n1.19.
[8] “Unveiling the Future Navigating Next-Generation AI Frontiers and Innovations in Application”. International
[9] W. Sun, W. Wan, L. Pan, J. Xu, and Q. Zeng, “The Integration of Large-Scale Language Models Into Intelligent Adjudication: Justification Rules and Implementation Pathways”, Journal of Industrial Engineering & Applied Science, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 13-20, Feb. 2024.
[10] Zhou, Yanlin, et al. “Utilizing AI-Enhanced Multi-Omics Integration for Predictive Modeling of Disease Susceptibility in Functional Phenotypes.” Journal of Theory and Practice of Engineering Science 4.02 (2024): 45-51.
[11] Chen, J. (2022). The Reform of School Education and Teaching Under the “Double Reduction” Policy. Scientific and Social Research, 4(2), 42-45. (Feb 2022)
[12] Zhang, Y., Gono, R., & Jasiński, M. (2023). An Improvement in Dynamic Behavior of Single Phase PM Brushless DC Motor Using Deep Neural Network and Mixture of Experts. IEEE Access.
[13] Q. Cheng, M. Tian, L. Yang, J. Zheng, and D. Xin, “Enhancing High-Frequency Trading Strategies with Edge Computing and Deep Learning”, Journal of Industrial Engineering & Applied Science, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 32-38, Feb. 2024.
[14] Liang, Penghao, et al. “Enhancing Security in DevOps by Integrating Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning.” Journal of Theory and Practice of Engineering Science 4.02 (2024): 31-37.
[15] Zhang, Y., Abdullah, S., Ullah, I., & Ghani, F. (2024). A new approach to neural network via double hierarchy linguistic information: Application in robot selection. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 129, 107581.
[16] Ji, Huan, et al. “Utilizing Machine Learning for Precise Audience Targeting in Data Science and Targeted Advertising.” Academic Journal of Science and Technology 9.2 (2024): 215-220.
[17] Zhang, Chenwei, et al. “SegNet Network Architecture for Deep Learning Image Segmentation and Its Integrated Applications and Prospects.” Academic Journal of Science and Technology 9.2 (2024): 224-229.
[18] Wang, Yong, et al. “Autonomous Driving System Driven by Artificial Intelligence Perception Fusion.” Academic Journal of Science and Technology 9.2 (2024): 193-198.
[19] Qian, Wenpin, et al. “Clinical Medical Detection and Diagnosis Technology Based on the AlexNet Network Model.” Academic Journal of Science and Technology 9.2 (2024): 207-211.’
[20] Zhang, Y., & Zhang, H. (2023). Enhancing robot path planning through a twin-reinforced chimp optimization algorithm and evolutionary programming algorithm. IEEE Access.
[21] Zhang, Quan, et al. “Application of the AlphaFold2 Protein Prediction Algorithm Based on Artificial Intelligence.” Journal of Theory and Practice of Engineering Science 4.02 (2024): 5865.
[22] Wang, H., Bao, Q., Shui, Z., Li, L., & Ji, H. (2024). A Novel Approach to Credit Card Security with Generative Adversarial Networks and Security Assessment.
[23] Wu, Jiang, et al. “Case Study of Next-Generation Artificial Intelligence in Medical Image Diagnosis Based on Cloud Computing.” Journal of Theory and Practice of Engineering Science 4.02 (2024): 66-73
[24] Zhu, Mingwei, et al. “Enhancing Collaborative Machine Learning for Security and Privacy in Federated Learning.” Journal of Theory and Practice of Engineering Science 4.02 (2024): 74-82.
[25] Yang, Le, et al. “Research and Application of Visual Object Recognition System Based on Deep Learning and Neural Morphological Computation.” International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology 2.1 (2024): 1017.
[26] Qian, Jili, et al. “A Liver Cancer Question-Answering System Based on Next-Generation Intelligence and the Large Model Med-PaLM 2.” International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology 2.1 (2024): 28-35.
[27] Bao, Qiaozhi, et al. “Exploring ICU Mortality Risk Prediction and Interpretability Analysis Using Machine Learning.” (2024).
[28] Xiao, J., Chen, Y., Ou, Y., Yu, H., & Xiao, Y. (2024). Baichuan2-Sum: Instruction Finetune Baichuan2-7B Model for Dialogue Summarization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.15496.
[29] Huo, Shuning, et al. “Deep Learning Approaches for Improving Question Answering Systems in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Research.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.16038 (2024).
[30] Yu, Hanyi, et al. “Machine Learning-Based Vehicle Intention Trajectory Recognition and Prediction for Autonomous Driving.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.16036 (2024).
[31] Xiang, Yafei, et al. “Text Understanding and Generation Using Transformer Models for Intelligent E-commerce Recommendations.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.16035 (2024).
[32] Zhu, Mengran, et al. “Utilizing GANs for Fraud Detection: Model Training with Synthetic Transaction Data.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.09830 (2024).
[33] Gong, Yulu, et al. “Enhancing Cybersecurity Resilience in Finance with Deep Learning for Advanced Threat Detection.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.09820 (2024).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.54097/v160aa61
Publication Date: 2024-03-26
Medication Recommendation System Based on Natural Language Processing for Patient Emotion Analysis
Abstract
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is an interdisciplinary field of computer science, artificial intelligence, and linguistics that focuses on the ability of computers to understand, process, generate, and simulate human language in order to achieve the ability to have natural conversations with humans. The underlying principles of natural language processing are at multiple levels, including linguistics, computer science, and statistics. It involves the study of language structure, semantics, grammar and pragmatics, as well as the statistical analysis and modeling of large-scale corpora. In the process of concrete implementation, it is necessary to process natural language at multiple levels. Based on this, this paper combined deep learning and natural language processing technology to conduct sentiment analysis on patients’ comments, so as to recommend drugs that are more suitable for patients, thus achieving accurate drug prescribing and personalized recommendation.
1. Introduction
same time, many domestic companies have also applied natural language processing technology to intelligent customer service, search engines, recommendation systems and other scenarios.
2. Related Work
2.1. Natural language processing technology (NLP)
2.2. Natural language emotion analysis
The main principles of sentiment analysis algorithms include:
- Statistical learning method: Emotion analysis algorithm based on statistical learning method can identify emotion information in text by learning training data set. Such algorithms include naive Bayes, support vector machines, decision trees and so on.
- Deep learning method: Emotion analysis algorithm based on deep learning method learns emotion information in text through multi-layer neural network. Such algorithms include convolutional neural network, recurrent neural network, self-attention mechanism and so on.
2.3. NLP and Healthcare
- Speech recognition
2. Clinical documents
3. Computer Aided Coding (CAC)
4. Clinical trial matching
5. Data mining research
6. Ai chatbots and virtual scribes
7. Root cause analysis
predictive analytics to provide solutions to common health problems.
8. Review management and emotion analysis
3. Methodology
3.1. Emotion analysis algorithm
- Data preprocessing: The input text is cleaned, the words to stop, the partof speech tagging, the word extraction and other processing to extract meaningful features.
- Feature extraction: The preprocessed text is converted into a vector representation for easy computer understanding and processing. This can be achieved by means of bag of words model, TF-IDF, Word2Vec and so on.
- Model training: According to the selected algorithm principle, model training is carried out on the training data set. This can be achieved through optimization methods such as gradient descent and random gradient descent.
- Model evaluation: Test data sets are evaluated to measure the performance and accuracy of the model. This can be assessed by metrics such as accuracy, recall rates, F1 scores, etc.
- Model optimization: According to the model evaluation results, the model is optimized to improve the accuracy and performance. This can be achieved through hyperparameter adjustment, feature selection, model fusion and so on.
3.2. Emotion analysis mathematical model formula
- Naive Bayes
2. Support vector machine
3.3. Experimental design
methods followed a structured methodology that included data exploration, data preprocessing, model development, conclusion and limitation assessment. In the data exploration phase, visualization and statistical techniques are used to gain insight into the characteristics of the data set. This process helps to pre-process the data and engineer the relevant features for the model. To address the limitations inherent in natural language processing, we introduce the LightGBM machine learning model. The model mitigated potential bias and improved reliability by integrating useful counting features.
3.4. Exploration Data Analysis
| uniqueID | drugName | condition | review | rating | date | usefulCount | |
| 0 | 206461 | Valsartan | Left Ventricular Dysfunction | “It has no side effect, I take it in combinati… | 9 | 2012-05-20 | 27 |
| 1 | 95260 | Guanfacine | ADHD | “My son is halfway through his fourth week of … | 8 | 2010-04-27 | 192 |
| 2 | 92703 | Lybrel | Birth Control | “I used to take another oral contraceptive, wh… | 5 | 2009-12-14 | 17 |
| 3 | 138000 | Ortho Evra | Birth Control | “This is my first time using any form of birth… | 8 | 2015-11-03 | 10 |
| 4 | 35696 | Buprenorphine / naloxone | Opiate Dependence | “Suboxone has completely turned my life around… | 9 | 2016-11-27 | 37 |
- drugName (categorical): name of drug
- condition (categorical): name of condition
- review (text): patient review
- rating (numerical): 10 star patient rating
- date (date): date of review entry
- usefulCount (numerical): number of users who found review useful
The structure of the data is that a patient with a unique ID purchases a drug that meets his condition and writes a review and rating for the drug he/she purchased on the date. Afterwards, if the others read that review and find it helpful, they will click usefulCount, which will add 1 for the variable[28].
3.5. Data set model training
the unique values of drug name and condition were 3671 and 917, respectively, with an average of about 4 drugs for each condition. We further visualized the top 20 in terms of the number of drugs for each condition.

- For the first eight conditions, the number of drugs
corresponding to each condition is about 100 . This suggests that there are more drug options for these common conditions. - There are some exceptions in the data, for example, the condition field contains ”
span> users found this comment helpful.”, which may be an error during the crawl. We need to remove these abnormal data during preprocessing. - By observing the distribution of drugs for each condition, it was found that some conditions had only one drug. For the referral system, recommendation is not feasible in this case, so we will only analyze conditions with at least two drugs.
3.6. Emotional text cloud word generation

3.7. Experimental result
represent emotions, and the relationship between dates and ratings. In the data preprocessing stage, we preprocessed the data according to the set topic, such as deleting the case of only one drug to recommend. In the modeling process, we used a deep learning model with n-gram, and also used a machine learning model called Lightgbm to overcome the limitations of natural language processing. In addition, we utilize sentiment dictionaries for sentiment analysis to overcome the limitations of packages formed based on movie data. In addition, we normalize usefulCount with conditions to improve reliability. These steps allow us to calculate the final predicted value and recommend the appropriate drug for each case based on the order of that value.
- When using the sentiment dictionary for sentiment analysis, the reliability is low when the number of positive and negative words is small. For example, if the positive word is 0 and the negative word is 1 , it is classified as a negative emotion. [32]Therefore, if there are fewer than 5 emotional words, we can rule out these observations.
- In order to ensure the reliability of the predicted value, we normalized usefulCount and multiplied it by the predicted value. However, as the cumulative number of site visitors increases, usefulCount may tilt toward older reviews. Therefore, when normalizing usefulCount, we should also consider the time factor.
- If the emotion is positive, reliability should increase in the positive direction, if it is negative, it should increase in the negative direction. However, we simply use usefulCount for reliability without taking this into account. Therefore, we should consider the symbol of usefulCount according to different emotion types, and carry out the corresponding multiplication processing.
4. Conclusion
- Significance of NLP in Healthcare: NLP technology plays a crucial role in various aspects of healthcare, ranging from speech recognition for efficient transcription to clinical trial matching and emotion analysis for improving patient satisfaction.
- Challenges and Opportunities[33-34]: While NLP presents immense opportunities for enhancing healthcare delivery, it also faces challenges such as low reliability in sentiment analysis with limited emotional words. However, these challenges can be addressed through careful preprocessing and model optimization techniques.
- Methodological Approach: The methodology employed in this study involved data exploration, preprocessing, model development, and evaluation. Advanced techniques like sentiment analysis using dictionaries and n-grams, as well as machine learning models like LightGBM, were utilized to overcome limitations and improve reliability.
- Recommendation System: The experimental results demonstrate the successful development of a drug recommendation system tailored to individual patient conditions. Through data preprocessing, modeling with deep learning and machine learning techniques, and sentiment analysis, the system effectively recommends suitable drugs based on patient reviews.
- Limitations and Future Directions: Despite the success of the recommendation system, there are limitations related to sentiment analysis reliability and normalization of usefulCount. Future research should focus on improving reliability metrics and considering the temporal aspect in data normalization.
Acknowledgment
References
[2] Chen, Jianfeng, et al. “Implementation of an AI-Based MRD Evaluation and Prediction Model for Multiple Myeloma”. Frontiers in Computing and Intelligent Systems, vol. 6, no. 3, Jan. 2024, pp. 127-31, https://doi.org/10.54097/zJ4MnbWW.
[3] “Implementation of Computer Vision Technology Based on Artificial Intelligence for Medical Image Analysis”. International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology, vol. 1, no. 1, Dec. 2023, pp. 69-76, https://doi.org/10.62051/ijcsit.v1n1.10.
[4] Chen, Jianhang, et al. “One-stage object referring with gaze estimation.” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2022.
[5] Zhou, Y., Osman, A., Willms, M., Kunz, A., Philipp, S., Blatt, J., & Eul, S. (2023). Semantic Wireframe Detection.
[6] Cai, Guoqing et al. “A deep learning-based algorithm for crop Disease identification positioning using computer vision.” International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology (2023): n. pag.
[7] “Machine Learning Model Training and Practice: A Study on Constructing a Novel Drug Detection System”. International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology, vol. 1, no. 1, Dec. 2023, pp. 139-46, https://doi.org/10.62051/ijcsit.v1n1.19.
[8] “Unveiling the Future Navigating Next-Generation AI Frontiers and Innovations in Application”. International
[9] W. Sun, W. Wan, L. Pan, J. Xu, and Q. Zeng, “The Integration of Large-Scale Language Models Into Intelligent Adjudication: Justification Rules and Implementation Pathways”, Journal of Industrial Engineering & Applied Science, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 13-20, Feb. 2024.
[10] Zhou, Yanlin, et al. “Utilizing AI-Enhanced Multi-Omics Integration for Predictive Modeling of Disease Susceptibility in Functional Phenotypes.” Journal of Theory and Practice of Engineering Science 4.02 (2024): 45-51.
[11] Chen, J. (2022). The Reform of School Education and Teaching Under the “Double Reduction” Policy. Scientific and Social Research, 4(2), 42-45. (Feb 2022)
[12] Zhang, Y., Gono, R., & Jasiński, M. (2023). An Improvement in Dynamic Behavior of Single Phase PM Brushless DC Motor Using Deep Neural Network and Mixture of Experts. IEEE Access.
[13] Q. Cheng, M. Tian, L. Yang, J. Zheng, and D. Xin, “Enhancing High-Frequency Trading Strategies with Edge Computing and Deep Learning”, Journal of Industrial Engineering & Applied Science, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 32-38, Feb. 2024.
[14] Liang, Penghao, et al. “Enhancing Security in DevOps by Integrating Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning.” Journal of Theory and Practice of Engineering Science 4.02 (2024): 31-37.
[15] Zhang, Y., Abdullah, S., Ullah, I., & Ghani, F. (2024). A new approach to neural network via double hierarchy linguistic information: Application in robot selection. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 129, 107581.
[16] Ji, Huan, et al. “Utilizing Machine Learning for Precise Audience Targeting in Data Science and Targeted Advertising.” Academic Journal of Science and Technology 9.2 (2024): 215-220.
[17] Zhang, Chenwei, et al. “SegNet Network Architecture for Deep Learning Image Segmentation and Its Integrated Applications and Prospects.” Academic Journal of Science and Technology 9.2 (2024): 224-229.
[18] Wang, Yong, et al. “Autonomous Driving System Driven by Artificial Intelligence Perception Fusion.” Academic Journal of Science and Technology 9.2 (2024): 193-198.
[19] Qian, Wenpin, et al. “Clinical Medical Detection and Diagnosis Technology Based on the AlexNet Network Model.” Academic Journal of Science and Technology 9.2 (2024): 207-211.’
[20] Zhang, Y., & Zhang, H. (2023). Enhancing robot path planning through a twin-reinforced chimp optimization algorithm and evolutionary programming algorithm. IEEE Access.
[21] Zhang, Quan, et al. “Application of the AlphaFold2 Protein Prediction Algorithm Based on Artificial Intelligence.” Journal of Theory and Practice of Engineering Science 4.02 (2024): 5865.
[22] Wang, H., Bao, Q., Shui, Z., Li, L., & Ji, H. (2024). A Novel Approach to Credit Card Security with Generative Adversarial Networks and Security Assessment.
[23] Wu, Jiang, et al. “Case Study of Next-Generation Artificial Intelligence in Medical Image Diagnosis Based on Cloud Computing.” Journal of Theory and Practice of Engineering Science 4.02 (2024): 66-73
[24] Zhu, Mingwei, et al. “Enhancing Collaborative Machine Learning for Security and Privacy in Federated Learning.” Journal of Theory and Practice of Engineering Science 4.02 (2024): 74-82.
[25] Yang, Le, et al. “Research and Application of Visual Object Recognition System Based on Deep Learning and Neural Morphological Computation.” International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology 2.1 (2024): 1017.
[26] Qian, Jili, et al. “A Liver Cancer Question-Answering System Based on Next-Generation Intelligence and the Large Model Med-PaLM 2.” International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology 2.1 (2024): 28-35.
[27] Bao, Qiaozhi, et al. “Exploring ICU Mortality Risk Prediction and Interpretability Analysis Using Machine Learning.” (2024).
[28] Xiao, J., Chen, Y., Ou, Y., Yu, H., & Xiao, Y. (2024). Baichuan2-Sum: Instruction Finetune Baichuan2-7B Model for Dialogue Summarization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.15496.
[29] Huo, Shuning, et al. “Deep Learning Approaches for Improving Question Answering Systems in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Research.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.16038 (2024).
[30] Yu, Hanyi, et al. “Machine Learning-Based Vehicle Intention Trajectory Recognition and Prediction for Autonomous Driving.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.16036 (2024).
[31] Xiang, Yafei, et al. “Text Understanding and Generation Using Transformer Models for Intelligent E-commerce Recommendations.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.16035 (2024).
[32] Zhu, Mengran, et al. “Utilizing GANs for Fraud Detection: Model Training with Synthetic Transaction Data.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.09830 (2024).
[33] Gong, Yulu, et al. “Enhancing Cybersecurity Resilience in Finance with Deep Learning for Advanced Threat Detection.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.09820 (2024).
