DOI: https://doi.org/10.58257/ijprems40411
تاريخ النشر: 2025-04-25
نظام منع حوادث السيارات المعتمد على إنترنت الأشياء
الملخص
يقدم هذا المشروع نظام كشف وتنبيه لحوادث السيارات في الوقت الحقيقي، باستخدام ESP32 كجهاز تحكم مركزي. يدمج النظام مستشعر اهتزاز/صدمة (SW-420 أو MPU6050) لاكتشاف الصدمات المفاجئة، مثل تلك التي تحدث في حادث سيارة أو دراجة. عند اكتشاف صدمة، يقوم النظام بتفعيل وحدة NEO-6MGPS لالتقاط إحداثيات الموقع الدقيقة. ثم يتم إرسال هذه الإحداثيات عبر الرسائل القصيرة باستخدام وحدة SIM800L GSM إلى جهات الاتصال الطارئة. يعمل هذا الحل بشكل مستقل عن الإنترنت، مما يجعله مثاليًا للمناطق ذات الاتصال الضعيف. النظام فعال من حيث التكلفة، موفر للطاقة، وقابل للتوسع بشكل كبير، مما يضمن تفعيل التنبيهات الطارئة بسرعة، مما يحسن من فرص الإنقاذ والمساعدة السريعة.
1. المقدمة
يركز هذا المشروع على تقديم حل فعال لهذه المشكلة من خلال نظام كشف حوادث تلقائي في الوقت الحقيقي. الفكرة الأساسية هي الاستفادة من متحكم ESP32 مع مجموعة متنوعة من المستشعرات والوحدات لاكتشاف حادث وإخطار جهات الاتصال الطارئة على الفور عبر الرسائل القصيرة. تم تصميم هذا النظام ليكون قويًا ومستقلاً عن الإنترنت، مما يجعله مثاليًا للاستخدام في المناطق النائية أو الريفية حيث قد يكون تغطية الشبكة الخلوية هي الخيار الوحيد للتواصل.
بالإضافة إلى معالجة المخاوف الأمنية الفورية، تم تصميم النظام ليكون منخفض التكلفة وموفر للطاقة، مما يجعله متاحًا لمجموعة واسعة من المستخدمين. تعزز قابلية توسيع النظام سهولة تطبيقه العملي، سواء للمركبات الفردية أو لإدارة الأسطول. الحل ذو قيمة خاصة في البلدان التي تتكرر فيها حوادث الطرق، حيث يمكن أن يحسن الوصول السريع إلى المساعدة الطارئة النتائج بشكل كبير. يهدف هذا النظام إلى سد الفجوة بين وقوع الحوادث والاستجابة الطارئة، مما يحسن السلامة على الطرق.
2. مراجعة الأدبيات
www.ijprems.com
editor@ijprems.com
المجلد 05، العدد 04، أبريل 2025، الصفحات: 2338-2341
7.001
وظائف لتشمل المشاة، وراكبي الدراجات، وغيرهم من مستخدمي الطرق.
ومع ذلك، فإن التحديات المختلفة تعيق التنفيذ الواسع النطاق لأنظمة منع الحوادث المعتمدة على إنترنت الأشياء. تثير المخاوف المتعلقة بالخصوصية المتعلقة بكميات كبيرة من البيانات الشخصية، بما في ذلك موقع المركبة وعادات القيادة، قضية ملحوظة. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يمكن أن تحدد الاتصال الموثوق، خاصة في المناطق الأقل كثافة سكانية أو المناطق ذات الوصول المحدود إلى الشبكة، فعالية هذه الأنظمة. الاعتماد على شبكات الاتصال السريعة مثل 5G أو غيرها من الشبكات عالية السرعة أمر ضروري لتبادل البيانات الفوري. علاوة على ذلك، فإن ضمان موثوقية أنظمة إنترنت الأشياء في الظروف الحرجة، مثل فشل النظام أو التنبيهات الكاذبة، لا يزال مصدر قلق رئيسي.
نتطلع إلى الأمام، من المتوقع أن تعزز التطورات في الذكاء الاصطناعي (AI) وتعلم الآلة (ML) دقة وقدرات اتخاذ القرار لهذه الأنظمة. يمكن أن يمكّن الذكاء الاصطناعي المركبات من تحليل وفهم البيانات المعقدة بشكل أكثر فعالية، مما يحسن قدرتها على توقع وتجنب الحوادث. من المحتمل أيضًا أن تسرع تقدم المركبات المستقلة من دمج إنترنت الأشياء في النقل، حيث تعتمد السيارات ذاتية القيادة بشكل كبير على تقنيات إنترنت الأشياء للتنقل والسلامة. على الرغم من العقبات، تقدم أنظمة منع حوادث السيارات المعتمدة على إنترنت الأشياء إمكانيات كبيرة لزيادة سلامة الطرق، على الرغم من أنه يجب معالجة التحديات التقنية والتنظيمية والخصوصية من أجل نشرها على نطاق واسع.
3. المنهجية
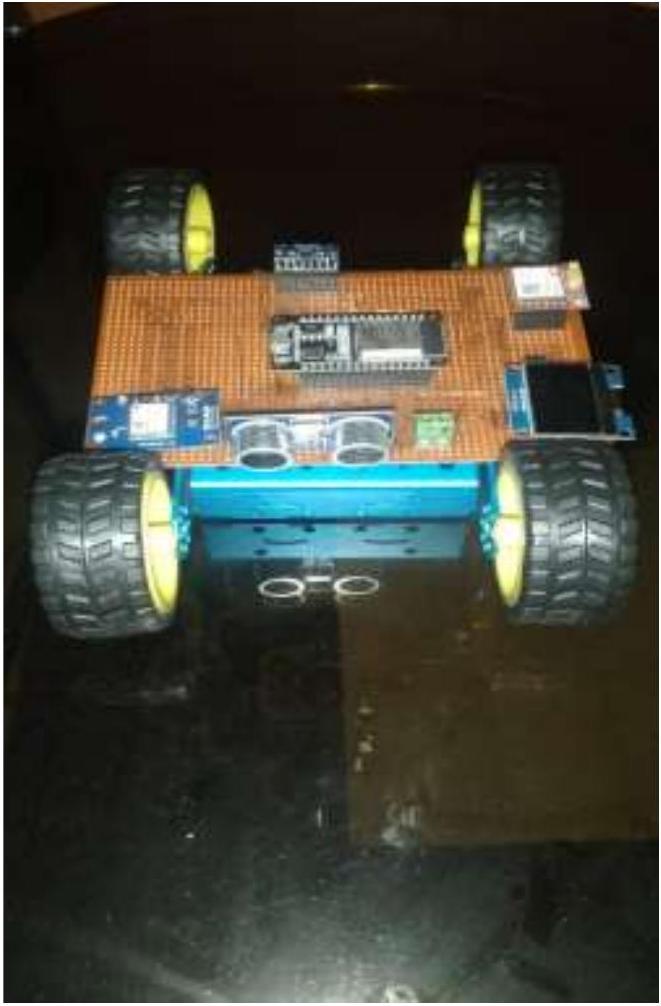
تصميم الدائرة: تصميم الاتصالات بين ESP32، مستشعر الاهتزاز، وحدة GPS، ووحدة GSM، مع ضمان توجيه الطاقة والإشارات بشكل صحيح.
تطوير البرمجيات: كتابة برنامج في بيئة Arduino IDE لاكتشاف الاهتزازات، وجلب إحداثيات GPS، وإرسال تنبيهات الرسائل القصيرة عبر وحدة GSM عند اكتشاف صدمة.
الاختبار: إجراء اختبارات في ظروف العالم الحقيقي لضمان قدرة النظام على اكتشاف الصدمات بشكل موثوق، والحصول على بيانات GPS دقيقة وإرسال تنبيهات الرسائل القصيرة دون تأخير.
تحسين: ضبط النظام لتحسين كفاءة الطاقة، وتقليل التنبيهات الكاذبة من مستشعر الاهتزاز، وتحسين موثوقية تسليم الرسائل القصيرة.
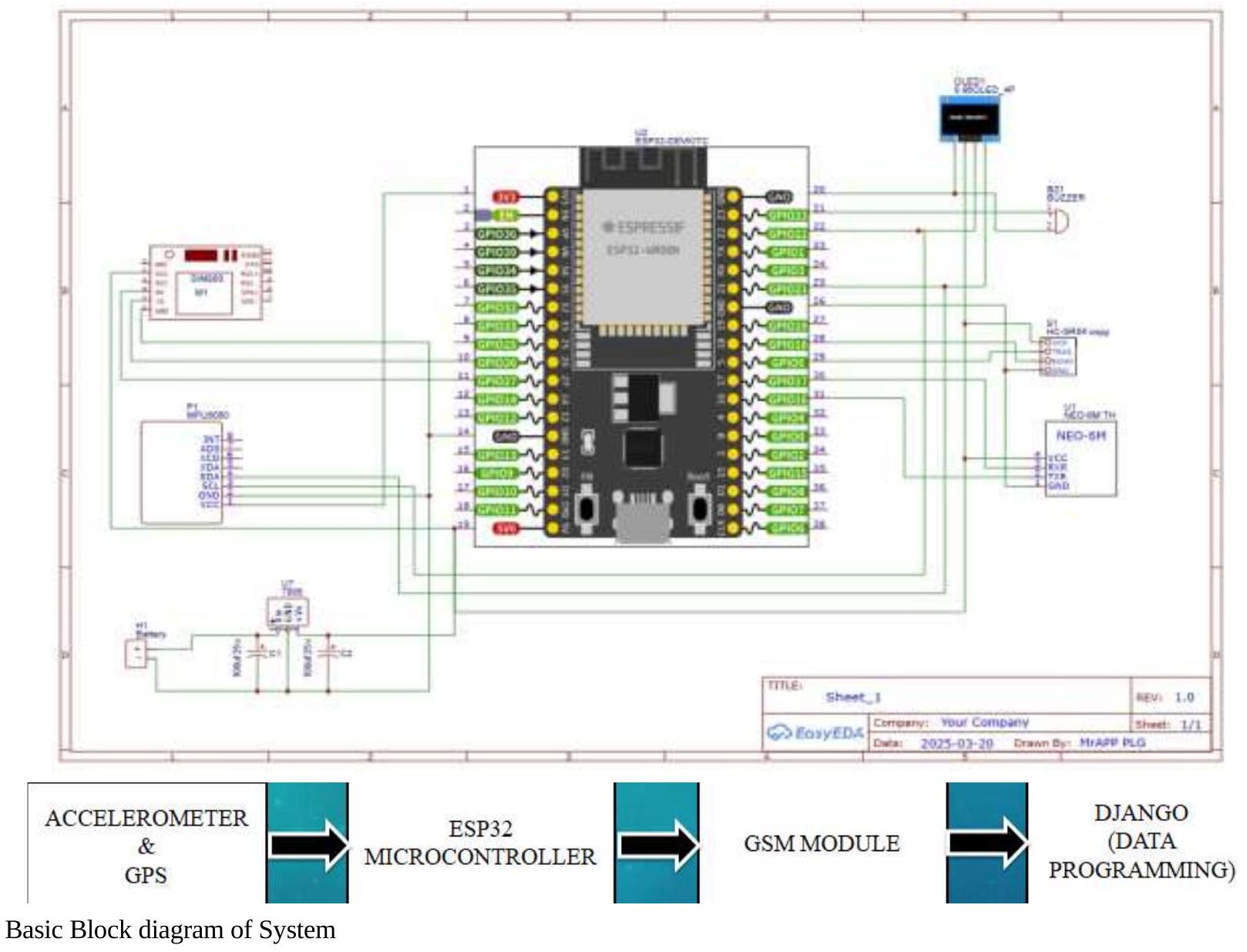
معامل المكونات
- وحدة GSM (SIM800L) (5V): لإرسال تنبيهات الرسائل القصيرة.
- متحكم ESP32 (5V): وحدة المعالجة الرئيسية.
- وحدة GPS (NEO-6M) (5V): لتتبع الموقع في الوقت الحقيقي.
- مستشعر الألتراساوند (HC-SR04) (5V): لقياس المسافة.
- مستشعر MPU6050 (3.3V): لاكتشاف التصادمات والميل.
- شاشة OLED (3.3V): لعرض البيانات في الوقت الحقيقي.
- صفارة (5V): لتوليد تنبيهات صوتية.
- المقاومات والمكثفات (5V): لتثبيت الإشارة وتحديد التيار.
- دايود (1N4007) (5V): لحماية التيار العكسي.




www.ijprems.com
editor@ijprems.com
العامل :
(مجلة محكمة من قبل الأقران)
المجلد 05، العدد 04، أبريل 2025، الصفحات : 2338-234
7.001


عرض واجهة الويب
4. الاستنتاج
5. المراجع
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58257/ijprems40411
Publication Date: 2025-04-25
IOT BASED CAR ACCIDENT PREVENTION SYSTEM
Abstract
This project presents a real-time accident detection and alert system, utilizing an ESP32 as the central controller. The system integrates a vibration/impact sensor (SW-420 or MPU6050) to detect sudden shocks, such as those experienced in a vehicle or bike accident. Upon detecting an impact, the system activates the NEO-6MGPS module to capture the exact location coordinates. These coordinates are then sent via SMS using the SIM800L GSM module to emergency contacts. This solution operates independently of the internet, making it ideal for areas with poor connectivity. The system is cost-effective, power-efficient, and highly scalable, ensuring that emergency alerts are triggered quickly, improving the chances of prompt rescue and assistance.
1. INTRODUCTION
This project focuses on providing an efficient solution to this problem through an automatic, real-time accident detection system. The core idea is to leverage an ESP32 microcontroller along with various sensors and modules to detect an accident and immediately notify emergency contacts via SMS. This system is designed to be robust and independent of the internet, making it ideal for use in remote or rural areas where cellular network coverage may be the only option for communication.
In addition to addressing the immediate safety concerns, the system is designed to be low-cost and power-efficient, making it accessible for a wide range of users. The easy scalability of the system further enhances its practical application, whether for individual vehicles or for fleet management.The solution is particularly valuable in countries where road accidents are frequent, and quick access to emergency help can drastically improve outcomes.This system aims to bridge the gap between accident occurrence and emergency response, improving safety on the roads.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
www.ijprems.com
editor@ijprems.com
Vol. 05, Issue 04, April 2025, pp : 2338-2341
7.001
functionalities to include pedestrians, cyclists, and other road users.
Nonetheless, various challenges hinder the widespread implementation of IoT-based accident prevention systems. Concerns surrounding privacy related to the vast amounts of personal data, including vehicle location and driving habits, present a notable issue. Additionally, dependable connectivity, particularly in less populated areas or regions with limited network access, can restrict the effectiveness of these systems. The reliance on strong 5G or other high-speed communication networks is essential for the immediate exchange of data. Furthermore, guaranteeing the dependability of IoT systems in critical circumstances, such as system failures or false alerts, remains a primary concern.
Looking forward, advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are anticipated to enhance the accuracy and decision-making abilities of these systems. AI could empower vehicles to analyze and understand complex data more effectively, improving their capacity to foresee and avert accidents. The advancement of autonomous vehicles is also likely to hasten the integration of IoT in transportation, as self-driving cars rely significantly on IoT technologies for navigation and safety. Despite the obstacles, IoT-based car accident prevention systems offer considerable potential for increasing road safety, although technical, regulatory, and privacy challenges must be addressed for their broad deployment.
3. METHODOLOGY
Circuit Design: Design the connections between the ESP32, vibration sensor, GPS module, and GSM module, ensuring proper power and signal routing.
Software Development: Write a program in the Arduino IDE to detect vibrations, fetch GPS coordinates, and send SMS alerts via the GSM module when an impact is detected.
Testing: Perform tests in real-world conditions to ensure the system can detect impacts reliably , acquire accurate GPS data and send SMS alerts without delays.
Optimization: Fine-tune the system for better power efficiency ,reduce false triggers from the vibration sensor, and improve the reliability of SMS delivery.

COMPONENT PARAMETER
- GSM Module (SIM800L) (5V) : For sending SMS alerts.
- ESP32 Microcontroller (5V) : Main processing unit.
- GPS Module (NEO-6M) (5V) : For real-time location tracking
- Ultrasonic Sensor (HC-SR04) (5V) : For distance measurement.
- MPU6050 Accelerometer (3.3V) : For detecting collisions and tilts.
- OLED Display (3.3V) : For displaying real-time data
- Buzzer (5V) : For generating audible alerts.
- Resistors and Capacitors (5V) : For signal stabilization and current limiting.
- Diode (1N4007) (5V) : For reverse current protection.




www.ijprems.com
editor@ijprems.com
Factor :
(Int Peer Reviewed Journal)
Vol. 05, Issue 04, April 2025, pp : 2338-234
7.001



