DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su16051790
تاريخ النشر: 2024-02-22
الابتكار المدعوم بالذكاء الاصطناعي في التحول الرقمي: الركائز الأساسية وتأثير الصناعة
تمت المراجعة: 17 فبراير 2024
تم القبول: 17 فبراير 2024
نُشر: 22 فبراير 2024
الملخص
تولد أنظمة التحول الرقمي حجمًا كبيرًا من البيانات، مما يخلق فرصًا للابتكار المحتمل، لا سيما تلك المدفوعة بالذكاء الاصطناعي. تركز هذه الدراسة على العلاقة المعقدة بين الذكاء الاصطناعي والابتكار كعناصر أساسية في إطار التحول الرقمي من أجل النمو المستدام والتميز التشغيلي. تقدم هذه الدراسة منظورًا شاملًا حول زراعة وأسس الابتكار المدعوم بالذكاء الاصطناعي، مع تسليط الضوء على دورها المحوري في إحداث ثورة في الصناعات، بما في ذلك الرعاية الصحية والتعليم والمالية والتصنيع والنقل والزراعة. تؤكد الدراسة على الأعمدة الرئيسية الضرورية لتعزيز الابتكار المدعوم بالذكاء الاصطناعي، بما في ذلك قياس أداء المراقبة لاستخدام قوة الحاضر، والتعلم المستمر والابتكار، وتحليل البيانات والرؤى، والتحليلات التنبؤية، وتطوير المنتجات المبتكرة. تستكشف هذه الدراسة كيف تعمل هذه الأعمدة كأساس للتقدمات الرائدة، مما يعزز الكفاءة، ويحسن عمليات اتخاذ القرار، ويعزز الإبداع داخل المنظمات. تستكشف هذه الدراسة أهمية التعلم المستمر، والتعاون بين التخصصات، والشراكات الصناعية في رعاية نظام بيئي مزدهر للابتكار المدعوم بالذكاء الاصطناعي. من خلال فهم واستغلال هذه العناصر الأساسية، يمكن للشركات التنقل في تعقيدات العصر الرقمي، وتعزيز الابتكار الذي لا يحسن العمليات فحسب، بل يعزز أيضًا التجربة الإنسانية الشاملة، مما يمهد الطريق لعصر جديد من التميز التكنولوجي والتقدم الاجتماعي.
1. المقدمة
يمكن أن يمكّن المؤسسات من أتمتة المهام الروتينية، وتعزيز الإنتاجية، وإعادة تصور نماذج الأعمال التقليدية. علاوة على ذلك، يمكن أن تقدم الابتكارات المدفوعة بالذكاء الاصطناعي تجارب مخصصة وسلسة للعملاء، مما يزيد من التفاعل والولاء. من خلال احتضان إمكانيات الذكاء الاصطناعي في رحلتهم نحو التحول الرقمي، تفتح المؤسسات عالماً من الاحتمالات غير المحدودة للنمو، والتنافسية، والنجاح على المدى الطويل في المشهد الرقمي المتطور باستمرار. وقد أدى ذلك إلى الابتكار المدفوع بالذكاء الاصطناعي في التحول الرقمي.
- التطور على مر الزمن: على عكس التقنيات الثابتة في الماضي، تتعلم أنظمة الذكاء الاصطناعي وتتكيف مع مرور الوقت. تتطلب هذه الطبيعة التطورية تحسينًا مستمرًا لهذه الأنظمة لضمان بقائها متوافقة مع أهدافها المقصودة والبيئة الخارجية المتغيرة باستمرار.
- بيتا الدائم: تصف عبارة “دائمًا في مرحلة البيتا” بشكل دقيق حالة أدوات وحلول الذكاء الاصطناعي. نظرًا لطبيعتها الديناميكية، فهي تخضع باستمرار للاختبار، وتتعلم من البيانات الجديدة، وتتطور. الابتكار في هذا المجال يعني احتضان هذه الحالة المستمرة من التغير والاستعداد لتعديل الاستراتيجيات والأنظمة وفقًا لذلك. إن تقارب الذكاء البشري مع الذكاء الاصطناعي يعيد تشكيل عالمنا بطرق عميقة، مما يبشر بعصر من التقدم غير المسبوق والفرص اللامحدودة. يمثل تقارب الذكاء البشري مع الذكاء الاصطناعي قفزة هائلة إلى الأمام للبشرية، مما ي usher في عصر يتميز بالتقدم غير المسبوق والفرص غير المحدودة. هذه التآزر بين الإبداع البشري والقوة الحاسوبية لأنظمة الذكاء الاصطناعي يحدث ثورة في جوانب مختلفة من حياتنا، ويحول الصناعات، ويشكل المستقبل بطرق عميقة.
تقدم هذه الدراسة الركائز الأساسية للابتكار المدعوم بالذكاء الاصطناعي في إطار عملية التحول الرقمي. تشمل هذه الركائز مراقبة الأداء، التعلم المستمر، تحليل البيانات، التحليل التنبؤي، وتطوير المنتجات المبتكرة. معًا، تشكل هذه الركائز الأساس الذي تُبنى عليه التقدمات الرائدة، مما يعزز الكفاءة، ويسهل عمليات اتخاذ القرار المستنير، ويغذي الإبداع داخل المنظمات.
تضمن هذه المقاربة الشاملة ليس فقط دفع التقدم التحويلي ولكن أيضًا ضمان النمو المستدام، مما يمكّن الشركات من البقاء مرنة وذات صلة في بيئة الأعمال المتغيرة باستمرار.
RQ1: كيف تساهم أعمدة الابتكار في الذكاء الاصطناعي في نجاح واستدامة جهود التحول الرقمي؟
RQ2: ما هي تداعيات الابتكار المدعوم بالذكاء الاصطناعي على التحول الصناعي المحدد والتقدم الاجتماعي العام؟
2. المواد والأساليب
- مراجعة الأدبيات: تبدأ هذه الجهود البحثية بمراجعة أدبية شاملة، حيث يتم إجراء فحص منهجي للمقالات الأكاديمية، والأوراق البحثية، والأطر النظرية للذكاء الاصطناعي، والابتكار، والتحول الرقمي، والنمو المستدام، والتميز التشغيلي. تعتبر هذه المراجعة الشاملة حجر الزاوية لفهم الحالة الحالية للخطاب الأكاديمي في هذه المجالات، مما يضع الأساس لتطوير إطار للابتكار المدعوم بالذكاء الاصطناعي يهدف إلى إحداث ثورة في الصناعات [12]. تتبع المراجعة الخطوات التالية:
- تعريف النطاق: تبدأ مراجعة الأدبيات بتعريف دقيق للنطاق، موضحة الموضوعات الرئيسية والمعايير ذات الصلة بالذكاء الاصطناعي، والابتكار، والتحول الرقمي، والنمو المستدام، والتميز التشغيلي. تضمن هذه الخطوة استكشافًا مركزًا وهادفًا لجسم المعرفة الموجود [13].
- منهجية المراجعة المنهجية: من خلال استخدام منهجية مراجعة منهجية، يتم البحث بدقة في قواعد البيانات الأكاديمية، ومستودعات الأبحاث، والمجلات ذات الصلة. تضمن هذه المقاربة الصارمة تضمين الأدبيات الشاملة والملائمة مع الحفاظ على عملية منظمة ومهيكلة [14].
- التصنيف الموضوعي: يتم تصنيف الأدبيات المحددة موضوعيًا، مما يسمح بتنظيم المعلومات بشكل منهجي. يساعد هذا التصنيف في تمييز الموضوعات الشائعة، والاتجاهات، والأنماط عبر مصادر متنوعة، مما يساهم في فهم شامل للموضوع [15].
- تحديد المفاهيم الرئيسية: يتم استخراج المفاهيم الرئيسية المتعلقة بالذكاء الاصطناعي، والابتكار، والتحول الرقمي، والنمو المستدام، والتميز التشغيلي من الأدبيات. تسهل هذه العملية تطوير أساس مفاهيمي لإطار الابتكار المدعوم بالذكاء الاصطناعي.
- التقييم النقدي: تخضع كل مصدر لتقييم نقدي لتقييم صرامته المنهجية، وموثوقيته، وملاءمته لأهداف البحث. يضمن هذا التحليل الدقيق تضمين أدبيات عالية الجودة، مما يساهم في قوة تطوير الإطار اللاحق [16].
- تركيب الأدبيات: تعتبر المعلومات المجمعة من مراجعة الأدبيات بمثابة الأساس الفكري لتصور إطار الابتكار المدعوم بالذكاء الاصطناعي. يتم دمج الرؤى، والنظريات، والنتائج التجريبية من الأدبيات لإبلاغ المراحل اللاحقة من البحث [17].
- تطوير الإطار المفاهيمي: يتم تطوير إطار مفاهيمي بناءً على مراجعة الأدبيات. يحدد هذا الإطار الأسس النظرية ويعرف المفاهيم الرئيسية، والعلاقات، والمتغيرات الضرورية لفهم كيفية إحداث الذكاء الاصطناعي ثورة في الصناعات من خلال الابتكار، والتحول الرقمي، والنمو المستدام، والتميز التشغيلي.
- دمج العنوان: يضع الإطار المفاهيمي الذي تم تطويره من خلال مراجعة الأدبيات الأساس للاستكشاف اللاحق لإطار الابتكار المدعوم بالذكاء الاصطناعي الذي يحدث ثورة في الصناعات. توجه الرؤى المجمعة تشكيل الحلول المبتكرة ضمن هذا الإطار المفاهيمي.
من خلال متابعة هذه الخطوات بدقة في مراجعة الأدبيات، نهدف إلى عدم فقط إنشاء فهم شامل للخطاب الأكاديمي الحالي ولكن أيضًا تمييز الفرص للمساهمة برؤى جديدة في العلاقة المعقدة بين الذكاء الاصطناعي، والابتكار، والتحول الرقمي، والنمو المستدام، والتميز التشغيلي.
- النهج المدفوع بالتجربة: تدمج هذه الدراسة توجهاً “مدفوعًا بالتجربة”، مستندة إلى المعرفة العملية المستمدة من المشاركة النشطة في مجال هندسة الأنظمة الصناعية. يتضمن ذلك تجارب مباشرة، وملاحظات، وتفاعلات مع الذكاء الاصطناعي والابتكار في سياقات العالم الحقيقي. يتم توثيق هذه التجارب وتحليلها لاستخراج رؤى قيمة تكمل وتثري المنظورات النظرية. تشير دمج نهج “مدفوع بالتجربة” في هذه الدراسة إلى تكامل متعمد للمعرفة العملية المكتسبة من خلال المشاركة النشطة في مجال هندسة الأنظمة الصناعية لتكملة وتثري المنظورات النظرية المتعلقة بالذكاء الاصطناعي والابتكار. يبرز هذا التوجه المنهجي التجارب المباشرة، والملاحظات المباشرة، والتفاعلات مع الذكاء الاصطناعي والابتكار ضمن سياقات العالم الحقيقي [18]. تتبع هذه الخطوات التالية:
- الانغماس في الميدان: ينغمس الباحثون بنشاط في البيئة التشغيلية لهندسة الأنظمة الصناعية من خلال الانخراط في تطبيقات الذكاء الاصطناعي والممارسات الابتكارية. يسمح هذا الانغماس بفهم مباشر للتحديات العملية، والفرص، والديناميكيات الكامنة في دمج الذكاء الاصطناعي والابتكار ضمن الإعدادات الصناعية [18].
- تقنيات جمع البيانات النوعية: يتم تعزيز النهج التجريبي من خلال الدمج الحكيم لأساليب جمع البيانات النوعية، وخاصة المقابلات والاستطلاعات. يتم تطبيق هذه الأساليب الدقيقة بشكل استراتيجي لاستنباط رؤى من محترفين بارزين في الصناعة، وممارسين، وأصحاب مصلحة يعملون في مجالات هندسة الأنظمة الصناعية، والذكاء الاصطناعي، والابتكار. تعتبر المقابلات التي تم إجراؤها وسيلة للحصول على وجهات نظر دقيقة، تدعم النتائج بأدلة قصصية، وتوفر سياقًا حقيقيًا لا يقدر بثمن. لا تؤكد البيانات النوعية فقط على المعرفة التجريبية، بل تساهم أيضًا في فهم شامل للتفاعل بين النظرية والممارسة.
- التحليل الملاحظاتي: من خلال الملاحظة الدقيقة، يقوم الباحثون بتحليل منهجي لتنفيذ الذكاء الاصطناعي والابتكار في السيناريوهات الواقعية. يتضمن ذلك توثيق كيفية تطبيق هذه التقنيات، وتحديد أنماط الاستخدام، واكتشاف الفروق الدقيقة في تأثيرها على العمليات الصناعية والنتائج.
- المشاركة العملية: يشارك فريق البحث بنشاط في الأنشطة العملية المتعلقة بالذكاء الاصطناعي والابتكار في هندسة الأنظمة الصناعية. قد يشمل ذلك حل المشكلات بشكل تعاوني، أو مشاريع تجريبية، أو المشاركة المباشرة في تطوير وتنفيذ الحلول التكنولوجية. يسهل هذا النهج العملي فهمًا أعمق للتداعيات العملية لهذه التقنيات.
- توثيق التجارب: يتم توثيق التجارب والرؤى والملاحظات بدقة بطريقة منهجية. يتضمن هذا التوثيق سجلات مفصلة للسيناريوهات المحددة، والتحديات التي تم مواجهتها، والحلول التي تم وضعها، والدروس المستفادة. تعتبر هذه السجلات الشاملة مجموعة بيانات قيمة للتحليل.
- تحليل الرؤى: تخضع التجارب الموثقة لتحليل دقيق، مع التركيز على استخراج الرؤى التي تكمل وتعزز المنظورات النظرية المستمدة من مراجعة الأدبيات. يتضمن هذا التحليل تحديد الأنماط، والنجاحات، والإخفاقات، والاتجاهات الناشئة في التطبيق العملي للذكاء الاصطناعي والابتكار ضمن السياقات الصناعية.
- تس contextualization للنتائج: يتم بعد ذلك وضع الرؤى المستمدة من النهج القائم على التجربة في سياق الإطار النظري الأوسع الذي تم تأسيسه سابقًا. تضمن هذه العملية أن المعرفة العملية المكتسبة تتماشى مع وتساهم في الفهم المفاهيمي المستمد من الأدبيات الأكاديمية، مما يخلق سردًا متماسكًا وشاملاً.
- تحقق من الافتراضات النظرية: من خلال نهج قائم على التجربة، تسعى هذه الدراسة إلى التحقق من الافتراضات والنظريات النظرية أو تحديها. تقدم الرؤى العملية المكتسبة منظورًا واقعيًا يعزز مصداقية وقابلية تطبيق نتائج البحث.
- التكرار المستمر: النهج القائم على التجربة ليس ثابتًا بل تكراري. مع تقدم الدراسة، قد تؤدي التجارب والملاحظات المستمرة إلى تحسينات أو توسيعات في الإطار النظري، مما يخلق تفاعلًا ديناميكيًا بين الرؤى العملية والأسس النظرية.
3. التركيب والاستنتاج: تتضمن المرحلة النهائية تركيب النتائج المستخلصة من مراجعة الأدبيات، والنهج القائم على التجربة، وتحليل البيانات. تهدف هذه الدراسة إلى استخلاص استنتاجات ذات مغزى بشأن العلاقة بين الذكاء الاصطناعي والابتكار ضمن إطار التحول الرقمي، وتقديم رؤى حول كيفية مساهمة هذه العناصر في النمو المستدام والتميز التشغيلي. في مرحلة التركيب والاستنتاج، تجمع الدراسة بين خيوط متنوعة من المعلومات التي تم جمعها من مراجعة الأدبيات، والنهج القائم على التجربة، وتحليل البيانات.
4. أنظمة الذكاء الاصطناعي كمجموعة: في التنقل عبر المشهد المعقد للذكاء الاصطناعي، تصبح القدرة على تمييز وفهم الميزات المميزة لمختلف أنظمة الذكاء الاصطناعي أمرًا بالغ الأهمية. إن فهم هذه الفروق الدقيقة أمر حيوي لاستنباط رؤى حول تطبيقاتها المتنوعة والتأثير التحويلي الذي تمارسه في التطور الرقمي. ومع ذلك، من الجدير بالذكر أن تركيز هذا العمل المحدد يتجاوز الفحص المخصص لأي نظام ذكاء اصطناعي فردي. بدلاً من ذلك، يتبنى منظورًا أوسع يشمل جميع أدوات وأنظمة الذكاء الاصطناعي كمجموعة متكاملة. من خلال اعتماد هذا النهج الشامل، تهدف الدراسة إلى التقاط التآزر، والترابطات، والاتجاهات الشاملة التي تميز الديناميات التعاونية ضمن الطيف الأوسع لتقنيات الذكاء الاصطناعي. مع استمرار التحول الرقمي في إعادة تعريف الصناعات وإعادة تشكيل المشهد التكنولوجي، تسعى هذه الاستكشاف الشامل للذكاء الاصطناعي كمجموعة موحدة إلى تقديم رؤى حول الذكاء الجماعي الذي يدفع الابتكار، والأتمتة، والحدود المتوسعة باستمرار للذكاء الاصطناعي.
3. النتائج
3.1. تنمية عقلية مبتكرة للتحول الرقمي المدعوم بالذكاء الاصطناعي
(أ) احتضان ثقافة الفضول:
حلول تدفع التحول الرقمي. هذه الثقافة لا تؤدي فقط إلى التقدم التكنولوجي؛ بل تعزز عقلية تحول التحديات إلى فرص، والركود إلى تطور، والفضول إلى قوة دافعة تدفع الشركات نحو مستقبل حيث لا تقتصر إمكانيات الذكاء الاصطناعي على الخيال بل تتحقق أيضًا، مما يخلق عالمًا حيث لا تعرف الابتكارات حدودًا. إن احتضان ثقافة الفضول يتضمن التعلم المستمر. في مجال الذكاء الاصطناعي الذي يتطور بسرعة، من الضروري البقاء على اطلاع بأحدث التقنيات والخوارزميات والاتجاهات الصناعية. يعزز التعليم المستمر عقلية مفتوحة أمام إمكانيات وابتكارات جديدة. مع عقلية مبتكرة وتعلم مستمر، لا تنجو الشركات فقط في عصر التحول الرقمي المدعوم بالذكاء الاصطناعي، بل تزدهر أيضًا، مشكّلة مستقبلًا يتميز بالإبداع والعبقرية والسعي الدائم نحو التقدم.
(ب) تشجيع حل المشكلات الإبداعي:
(ج) التأكيد على تصميم يركز على المستخدم:
(د) تعزيز عقلية النمو:
عندما تحدث الإخفاقات، يسمح التطوير المرن للشركات بالتكيف بسرعة، مما يجعل التغييرات اللازمة وتحسين حلول الذكاء الاصطناعي بناءً على التعليقات الفورية. إن رؤية الفشل كجزء من العملية تبني المرونة داخل الفرق. الفرق المرنة تتعافى من النكسات، مستخدمة الفشل كدافع لاستكشاف طرق جديدة وحلول إبداعية. هذه المرونة ضرورية في التغلب على التحديات والسعي المستمر نحو الابتكار. يعلم الفشل القدرة على التكيف. الشركات التي تتعلم من الإخفاقات تكون أكثر استعدادًا للتكيف مع متطلبات السوق المتغيرة، والتقدم التكنولوجي، وتفضيلات المستخدمين. تضمن هذه القدرة على التكيف أن تظل حلول الذكاء الاصطناعي ذات صلة وفعالة في البيئات الديناميكية.
(هـ) تبني رؤية طويلة الأمد:
3.2. تطوير أعمدة الابتكار المدعوم بالذكاء الاصطناعي
(أ) مراقبة الرؤى الاستراتيجية:
تطورت بسرعة، خاصة في مجال الذكاء الاصطناعي. يتيح المراقبة في الوقت الحقيقي للشركات البقاء على اطلاع بأحدث التطورات. من خلال فهم أداء حلول الذكاء الاصطناعي الحالية، يمكن للشركات اتخاذ قرارات مستنيرة بشأن دمج تقنيات جديدة. قد يتضمن هذا الدمج اعتماد خوارزميات أكثر تعقيدًا، أو دمج تحسينات التعلم الآلي، أو الاستفادة من تطبيقات الذكاء الاصطناعي الجديدة التي تتماشى مع أهداف الأعمال. لا تُعلم المراقبة في الوقت الحقيقي الاستراتيجيات الداخلية فحسب، بل تسهل أيضًا التعاون الخارجي. من خلال مشاركة البيانات ذات الصلة مع الشركاء الاستراتيجيين أو المتعاونين في الصناعة، يمكن للشركات تشكيل مستقبل تطبيقات الذكاء الاصطناعي بشكل جماعي. يمكن أن تؤدي التعاونات إلى تطوير تقنيات رائدة أو إنشاء معايير صناعية، مما يضمن بقاء الشركات في طليعة الابتكار. توفر المراقبة في الوقت الحقيقي نقاط بيانات للتخطيط على المدى الطويل. من خلال تحليل بيانات الأداء التاريخية جنبًا إلى جنب مع الرؤى في الوقت الحقيقي، يمكن للشركات إنشاء خارطة طريق للمستقبل. توضح هذه الخارطة تطور تطبيقات الذكاء الاصطناعي، مما يضمن أن تكون لدى الشركات رؤية واضحة حول كيفية تطور تقنيتها مع مرور الوقت. تعتبر خارطة الطريق المحددة جيدًا ضرورية للابتكار المستدام والنمو الاستراتيجي.
(ب) التعلم المستمر والابتكار:
السلوكيات واستراتيجيات المنافسين. هذه الوعي أمر حاسم لاتخاذ القرارات الاستراتيجية والابتكار للبقاء على اطلاع بأحدث التطورات، مما يضمن أن تستفيد الشركات من أحدث أدوات الذكاء الاصطناعي ومنصات تحليل البيانات. حلقات التغذية الراجعة والتطوير التكراري: يتضمن التعلم المستمر جمع التغذية الراجعة من المستخدمين النهائيين. تضمن حلقة التغذية الراجعة التكرارية أن تكون الحلول المدعومة بالذكاء الاصطناعي موجهة نحو المستخدم وتتوافق مع تفضيلات المستخدم المتطورة. وهذا يمكّن من النمذجة السريعة والتطوير التكراري، مما يسمح للمنظمات بتنقيح تطبيقات الذكاء الاصطناعي بناءً على تجارب المستخدمين في العالم الحقيقي، وبالتالي تعزيز قابلية الاستخدام والوظائف. يؤدي ذلك إلى تحسين مستمر، والذي يمكن شرحه كما يلي. تحليل المشاعر: بالإضافة إلى مجرد جمع التغذية الراجعة، يمكن للأدوات المدفوعة بالذكاء الاصطناعي قياس المشاعر وراء تعليقات المستخدمين عبر المنصات، مثل وسائل التواصل الاجتماعي، ومواقع المراجعة، وقنوات دعم العملاء. يوفر ذلك للشركات رؤى دقيقة حول رضا المستخدم ومجالات التحسين. المنتجات التكيفية: من خلال دمج الذكاء الاصطناعي في المنتجات، يمكن أن تتكيف بشكل طبيعي بناءً على تغذية راجعة المستخدم. هذه القابلية للتكيف في الوقت الحقيقي لا تعزز تجربة المستخدم فحسب، بل تعزز أيضًا الثقة والولاء، حيث يشعر المستخدمون أن تغذيتهم الراجعة تشكل مباشرة المنتجات التي يستخدمونها. تحديد المشكلات بشكل استباقي: قبل أن تتصاعد المشكلات إلى مستويات حرجة أو عدم رضا واسع النطاق من المستخدمين، يمكن للذكاء الاصطناعي تحديد المشكلات الناشئة من خلال تحليل الأنماط في تغذية راجعة المستخدم. يعد هذا الكشف الاستباقي عن المشكلات ذا قيمة كبيرة للحفاظ على سمعة المنتج وضمان رضا المستخدم المستمر. التجريب والمخاطرة: إن إنشاء مختبرات الابتكار أو المساحات المخصصة للتجريب يشجع الفرق على استكشاف تطبيقات الذكاء الاصطناعي غير التقليدية. تعزز هذه البيئة الإبداع والمخاطرة. الفشل كتعلم يحتضن الفشل كخطوة نحو الابتكار. تتعلم المنظمات دروسًا قيمة من التجارب الفاشلة، مما يؤدي إلى حلول أكثر تنقيحًا وابتكارًا. تطوير مهارات القوى العاملة: التعلم المستمر لا يتعلق فقط بالتكنولوجيا. مع تطور الذكاء الاصطناعي، يحتاج المحترفون إلى تطوير مهاراتهم، مما يضمن أنهم يستطيعون الاستفادة من الأدوات الجديدة، وفهم الخوارزميات الجديدة، وتطبيق أفضل الممارسات في تنفيذ الذكاء الاصطناعي.
(ج) تحليلات البيانات والرؤى
التوقف عن العمل والخسائر المرتبطة به. في مجال الموارد البشرية، يمكن أن تكشف التحليلات عن أنماط تؤثر على دوران الموظفين، مما يمكّن من تشكيل استراتيجيات احتفاظ استباقية [46]. تخصيص تجارب العملاء: يساعد تحليل بيانات تفاعلات العملاء وسلوكهم الشركات على اكتساب رؤى حول تفضيلات العملاء. تتيح هذه المعرفة إنشاء تجارب مخصصة تعزز من تفاعل العملاء وولائهم. تمكّن تحليلات البيانات في الوقت الحقيقي الشركات المبتكرة من تخصيص تفاعلات العملاء بشكل فوري [47]. أدت المحتويات والعروض الديناميكية المستندة إلى سلوك العملاء في الوقت الحقيقي إلى معدلات تحويل أعلى ورضا العملاء. اتخاذ قرارات مستنيرة: توفر تحليلات البيانات رؤى موثوقة تستند إلى البيانات بدلاً من الاعتماد فقط على الحدس أو الملاحظة. يمكن للقادة اتخاذ قرارات استراتيجية مدعومة بأدلة ملموسة، مما يقلل من المخاطر المرتبطة باتخاذ القرارات المستندة إلى الحدس. تتيح تحليلات البيانات للشركات محاكاة سيناريوهات مختلفة. يمكن للمنظمات اتخاذ قرارات مستنيرة واختيار المسار الأكثر وعدًا من خلال تحليل النتائج المحتملة لاستراتيجيات مختلفة. على سبيل المثال، يمكن لشركة في قطاع التجارة الإلكترونية الاستفادة من تحليل البيانات لضبط تسعير المنتجات بشكل مثالي، متأثرة بمعايير مثل الطلب، تسعير المنافسين، واتجاهات سلوك العملاء [48]. التغذية الراجعة المستمرة والتحسين: تعالج تحليلات البيانات ملاحظات المستخدم من قنوات مختلفة. تكتسب الشركات رؤى قيمة حول مشاعر العملاء، مما يمكّن من تحسينات متكررة للمنتجات والخدمات. يمكن للشركات تحسين عروضها باستمرار من خلال تحليل ملاحظات المستخدم وبيانات الاستخدام. تضمن هذه الطريقة المرنة أن تظل المنتجات ذات صلة وتنافسية ومتوافقة مع احتياجات المستخدمين.
(د) التحليلات التنبؤية
- توقع سلوك العملاء: تصنف التحليلات التنبؤية العملاء إلى شرائح بناءً على سلوكهم وتفضيلاتهم. من خلال فهم احتياجات كل شريحة، يمكن للشركات تخصيص المنتجات والخدمات، مما يعزز رضا العملاء وولائهم. يتيح تحليل بيانات العملاء التاريخية للمنظمات توقع فقدان العملاء. من خلال تحديد العملاء المعرضين للخطر، يمكن للشركات تنفيذ استراتيجيات احتفاظ لتقليل معدلات فقدان العملاء.
- تحسين استراتيجيات التسويق: تقيم التحليلات التنبؤية الحملات التسويقية السابقة لتحديد ما نجح وما لم ينجح. تساعد الرؤى المستمدة في تحسين الحملات المستقبلية وضمان عائد أعلى على الاستثمار. من خلال تحليل تفاعلات العملاء والخصائص الديموغرافية، تعطي التحليلات التنبؤية درجات للعملاء المحتملين بناءً على احتمالية تحويلهم. يساعد ذلك فرق المبيعات في تركيز جهودهم على العملاء المحتملين ذوي الإمكانيات العالية، مما يحسن معدلات التحويل.
- توقع الطلب وإدارة المخزون: تحلل التحليلات التنبؤية بيانات المبيعات التاريخية واتجاهات السوق. يمكن للشركات توقع الطلب على المنتجات والخدمات بدقة من خلال تحسين مستويات المخزون وتقليل الفائض. من خلال توقع أنماط الطلب، تقوم المنظمات بتبسيط سلاسل التوريد الخاصة بها. تضمن الرؤى التنبؤية توافق الإمدادات مع الطلب، مما يقلل من تكاليف التخزين ويقلل من الفاقد.
- تبسيط العمليات: في صناعات التصنيع والخدمات، تتوقع التحليلات التنبؤية فشل المعدات واحتياجات الصيانة. تقلل الصيانة الاستباقية من التوقف عن العمل، وتطيل عمر المعدات، وتعزز الكفاءة التشغيلية العامة. تحلل التحليلات التنبؤية أداء الموردين التاريخي وأنماط الطلب. يمكن للشركات تحسين سلاسل التوريد الخاصة بها من خلال ضمان التسليم في الوقت المناسب، وتقليل التكاليف، والحفاظ على مستويات مخزون فعالة.
- تخفيف المخاطر: يمكن استخدام التحليلات التنبؤية لتخفيف المخاطر من خلال تحديد التهديدات أو المشكلات المحتملة قبل أن تظهر. من خلال تحديد الأنماط والاتجاهات والشذوذ في البيانات التاريخية والبيانات في الوقت الحقيقي، يمكن للمنظمات اتخاذ قرارات استباقية لتخفيف المخاطر المحتملة. على سبيل المثال، في مجال الأمن السيبراني، يمكن أن تساعد التحليلات التنبؤية في تحديد التهديدات أو الهجمات المحتملة. في الرعاية الصحية، يمكن أن تساعد في التنبؤ بتفشي الأمراض.
- التحديات والاعتبارات: بينما تقدم التحليلات التنبؤية فوائد عديدة، من المهم مراعاة قيودها وتحدياتها. على سبيل المثال، تعتمد دقة التنبؤات بشكل كبير على جودة البيانات واكتمالها. لذلك، فإن تنظيف البيانات، والمعالجة المسبقة، وضمان الجودة هي خطوات حاسمة. علاوة على ذلك، قد لا تأخذ النماذج التنبؤية في الاعتبار التغيرات المفاجئة أو أحداث البجعة السوداء بالكامل؛ ومن ثم، هناك حاجة لمراجعة النماذج بانتظام وتنقيحها.
- التحيزات المحتملة في التحليلات التنبؤية: يمكن أن تؤدي خوارزميات الذكاء الاصطناعي، التي تعتمد على البيانات التاريخية، بشكل غير مقصود إلى استمرار التحيزات الموجودة. على سبيل المثال، إذا كانت البيانات تعكس ممارسات تمييزية سابقة أو تحيزات اجتماعية، فقد تنتج النماذج التنبؤية نتائج متحيزة. وهذا يثير القلق بشكل خاص في مجالات مثل التوظيف، والإقراض، وإنفاذ القانون، حيث يمكن أن تؤدي التنبؤات المتحيزة إلى نتائج غير عادلة أو تمييزية.
- الآثار الأخلاقية: يثير استخدام التحليلات التنبؤية أسئلة أخلاقية هامة، خاصة فيما يتعلق بالخصوصية والموافقة والشفافية. هناك خطر من إساءة استخدام التحليلات التنبؤية بطرق تنتهك خصوصية الأفراد أو استقلاليتهم، مثل المراقبة المتطفلة أو الشرطة التنبؤية.
- استراتيجيات للتخفيف من التحيزات: لمعالجة هذه التحيزات، من الضروري تنفيذ استراتيجيات مثل:
- تنويع مصادر البيانات: ضمان أن البيانات المستخدمة في تدريب النماذج التنبؤية تمثل مجموعات سكانية وسيناريوهات متنوعة.
- تدقيقات منتظمة: إجراء تدقيقات منتظمة لخوارزميات الذكاء الاصطناعي للتحقق من التحيزات وتصحيحها.
- الشفافية: الحفاظ على الشفافية بشأن كيفية بناء النماذج التنبؤية والبيانات التي تم تدريبها عليها، مما يسمح بالمساءلة.
- تعزيز ممارسات الذكاء الاصطناعي المسؤولة: يجب أن تكون ممارسات الذكاء الاصطناعي المسؤولة في صميم التحليلات التنبؤية. يشمل ذلك جمع البيانات بشكل أخلاقي، وضمان الحصول على موافقة مستنيرة عند استخدام البيانات الشخصية، وتنفيذ تدابير لحماية خصوصية البيانات. يجب على المنظمات أيضًا وضع إرشادات أخلاقية لاستخدام التحليلات التنبؤية، لضمان استخدام التكنولوجيا بطريقة تحترم حقوق الأفراد وتعزز العدالة.
- معالجة جودة البيانات واكتمالها: تعتمد دقة التنبؤات بشكل كبير على جودة البيانات واكتمالها. لذلك، فإن تنظيف البيانات، والمعالجة المسبقة، وضمان الجودة هي خطوات حاسمة. قد لا تأخذ النماذج التنبؤية في الاعتبار التغيرات المفاجئة أو أحداث ‘البجعة السوداء’ بشكل كامل، مما يستلزم مراجعة النماذج بانتظام وتنقيحها.
- التدريب المستمر على الأخلاقيات والتحيز: يجب على المنظمات الاستثمار في التدريب المستمر على الأخلاقيات وبرامج الوعي بالتحيز لفرقها، لضمان أن يكون أولئك الذين يقومون بتطوير ونشر النماذج التنبؤية على دراية بالقضايا الأخلاقية المحتملة ويمكنهم التخفيف من التحيزات.
باختصار، توفر التحليلات التنبؤية، على الرغم من تقديمها قدرات تحويلية للمنظمات، مسؤوليات كبيرة. إن معالجة التحيزات المحتملة والآثار الأخلاقية أمر حاسم لاستغلال القوة الكاملة للتحليلات التنبؤية بشكل مسؤول وفعال. من خلال دمج هذه الاستراتيجيات، يمكن للمنظمات تقليل المخاطر وتعزيز الثقة والمصداقية في مبادرات الذكاء الاصطناعي الخاصة بها.
(هـ) تطوير المنتجات المبتكرة
تحليل البيانات في الوقت الحقيقي: يمكن لخوارزميات الذكاء الاصطناعي معالجة كميات هائلة من بيانات المستخدمين في الوقت الحقيقي. قد تشمل هذه البيانات سلوكيات المستخدمين وتفضيلاتهم وتعليقاتهم التي تُعلم تعديلات المنتجات أو تحسينات الميزات التي تتناسب مع شرائح المستخدمين المختلفة. التخصيص التنبؤي: يمكن للذكاء الاصطناعي التنبؤ باحتياجات أو تفضيلات المستخدمين المستقبلية بناءً على سلوكياتهم السابقة. تضمن هذه القوة التنبؤية أن تتطور المنتجات بما يتماشى مع توقعات المستخدمين، حتى قبل أن تظهر. الحفاظ على الكفاءة: بينما يبدو أن التخصيص غالبًا ما يتطلب موارد كبيرة، تضمن أنظمة الذكاء الاصطناعي أن تخصيص المنتجات لتناسب تفضيلات الأفراد لا يضر بكفاءة أو قابلية توسيع عملية الإنتاج.
(ب) تصميم المنتجات المرتكز على العميل: تقوم الذكاء الاصطناعي بتحليل مجموعات بيانات ضخمة، مما يوفر رؤى حول تفضيلات العملاء وسلوكياتهم ونقاط الألم لديهم. تُعلم هذه المقاربة المعتمدة على البيانات تصميم المنتجات، مما يضمن أن العروض مصممة لتلبية احتياجات العملاء. يمكّن الذكاء الاصطناعي من إنشاء منتجات وخدمات مخصصة للغاية. من التوصيات المخصصة إلى تجارب المستخدم الفردية، تعزز التخصيص رضا العملاء وولائهم. لقد منح العصر الرقمي المستهلكين قوة غير مسبوقة. مع وجود خيارات لا حصر لها في متناول أيديهم، أصبحت توقعاتهم أعلى من أي وقت مضى. الإشباع الفوري: يتوقع المستهلك الرقمي استجابات فورية، سواء في توصيلات التجارة الإلكترونية، أو أداء التطبيقات، أو خدمة العملاء. المشاركة في التطوير: أصبحت المصادر الجماعية، واختبار النسخ التجريبية، وتطوير المنتجات المدفوع من المجتمع أكثر شيوعًا، مما يblur الخطوط الفاصلة بين المستهلكين والمبدعين. الطلب على التكامل الرقمي: مع انتشار الأجهزة الذكية.
تزداد الطلبات على المنتجات التي تتكامل بسلاسة في النظام الرقمي الأوسع.
(ج) التطوير الرشيق والتكرار: تسهل المنهجيات الرشيقة المدمجة مع أدوات مدعومة بالذكاء الاصطناعي النمذجة السريعة، والتجريب، والتطوير التكراري. يمكن للشركات بسرعة إنشاء واختبار نماذج المنتجات، وجمع ملاحظات المستخدمين، والتكرار على التصاميم. يسرع هذا النهج الرشيق من وقت الوصول إلى السوق ويضمن توافق المنتجات مع توقعات المستخدمين. توفر تحليلات مدعومة بالذكاء الاصطناعي رؤى في الوقت الحقيقي حول أداء المنتج. يمكن للمنظمات مراقبة سلوك المستخدمين وملاحظاتهم، مما يتيح تحسينات مستمرة لتعزيز قابلية الاستخدام، والوظائف، وتجربة المستخدم بشكل عام. مع انتشار الأدوات الرقمية والذكاء الاصطناعي، فإن منتجات المستقبل ليست مجرد أدوات ثابتة بل حلول قابلة للتكيف. يمكن تعلم المنتجات من سلوك المستخدمين. يمكن للمنتجات المجهزة بالذكاء الاصطناعي تحليل سلوك المستخدمين في الوقت الحقيقي، وتكييف الوظائف وفقًا للتفضيلات الفردية، وضمان تجربة مستخدم مخصصة [61]. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يمكن للمنتجات أن تتطور ذاتيًا. تقوم الحلول البرمجية الحديثة بتحديث نفسها بشكل متكرر لإصلاح الأخطاء، وتعزيز الأمان، أو تقديم ميزات جديدة، مما يضمن التوافق المستمر مع احتياجات المستخدمين والتقدم التكنولوجي [62].
(د) تحسينات المنتجات المدعومة بالذكاء الاصطناعي: يعزز دمج الذكاء الاصطناعي المنتجات بميزات ذكية مثل التحليلات التنبؤية، ومعالجة اللغة الطبيعية، ورؤية الكمبيوتر. تضيف هذه الميزات قيمة، مما يجعل المنتجات أكثر تنوعًا وكفاءة وسهولة في الاستخدام. يقوم الذكاء الاصطناعي بأتمتة المهام المتكررة داخل المنتجات، مما يزيد من الكفاءة ويسمح للمستخدمين بالتركيز على الأنشطة ذات القيمة الأعلى. لا توفر الأتمتة الوقت فحسب، بل تعزز أيضًا إنتاجية المستخدم.
4. المناقشة
4.1. الابتكارات المدعومة بالذكاء الاصطناعي: تحويل الصناعات المتنوعة
(أ) الرعاية الصحية:
(ب) التعلم الشخصي:
الاهتمامات والتفضيلات. نتيجة لذلك، يصبح الطلاب أكثر حماسًا للمشاركة بنشاط وفهم المادة بعمق. يساهم النهج المخصص في سد الفجوات في الفهم، مما يضمن أن يستوعب الطلاب المفاهيم بشكل كامل. تحسين نتائج التعلم: يترجم النهج الفردي للتعلم المخصص مباشرة إلى تحسين نتائج التعلم. يحصل الطلاب على الدعم الذي يحتاجونه بالضبط عندما يحتاجون إليه، مما يؤدي إلى أداء أكاديمي أفضل، وزيادة الثقة، وموقف إيجابي تجاه التعلم. تلبية الاحتياجات المتنوعة: يعترف التعلم المخصص ويستوعب الاحتياجات والقدرات المتنوعة للطلاب. يوفر دعمًا إضافيًا للمتعلمين الذين يواجهون صعوبات وتحديات للطلاب المتقدمين، مما يضمن أن يحصل كل طالب على تعليم مصمم وفقًا لمستواه.
(ج) المالية:
(1) الذكاء الاصطناعي في التداول المالي. تحليل البيانات في الوقت الحقيقي: تقوم الخوارزميات المدفوعة بالذكاء الاصطناعي بمعالجة كميات هائلة من بيانات السوق في الوقت الحقيقي. يشمل ذلك البيانات التاريخية، والأسعار الحالية للسوق، وأحجام التداول، ومؤشرات أخرى متنوعة. يعد تحليل هذه البيانات بسرعة أمرًا حيويًا لاتخاذ قرارات تداول مستنيرة. التعرف على الأنماط والاتجاهات: تتفوق خوارزميات الذكاء الاصطناعي في تحديد الأنماط والاتجاهات المعقدة داخل بيانات السوق. من خلال التعرف على هذه الأنماط، يمكن للخوارزميات توقع تحركات السوق، مما يمكّن من إجراء توقعات أكثر دقة حول الأداء المستقبلي للأسهم أو العملات أو السلع. تنفيذ الصفقات بشكل مثالي: تقوم خوارزميات الذكاء الاصطناعي بتنفيذ الصفقات في الأوقات المثلى بناءً على الأنماط والاتجاهات المحددة. تقوم بتقييم ظروف السوق وتنفيذ الصفقات بسرعة وكفاءة، مما يضمن إجراء المعاملات بأفضل الأسعار المتاحة. تعظم هذه التنفيذ الاستراتيجي الأرباح للمؤسسات المالية. ميزة السرعة والنطاق: تتجاوز قدرات معالجة الذكاء الاصطناعي بكثير القدرة البشرية. يمكنه تحليل البيانات، وتحديد الأنماط، وتنفيذ الصفقات بسرعات تقاس بالمللي ثانية. تمنح هذه المعالجة السريعة المؤسسات المالية ميزة كبيرة في التفاعل بسرعة مع تغييرات السوق، خاصة في بيئات التداول عالية التردد. الميزة التنافسية: توفر القدرة على معالجة كميات هائلة من البيانات وتنفيذ الصفقات بسرعة ميزة تنافسية للمؤسسات المالية. من خلال الاستفادة من تقنيات الذكاء الاصطناعي، يمكن للمؤسسات أن تظل في المقدمة في الأسواق المالية الديناميكية والسريعة، مما يمكنها من اتخاذ قرارات في أجزاء من الثانية قد تؤدي إلى أرباح كبيرة. التداول عالي التردد: يمكّن الذكاء الاصطناعي التداول عالي التردد، وهي استراتيجية يتم فيها تنفيذ الصفقات في غضون مللي ثانية لاستغلال حتى أدنى كفاءة في السوق. تتيح هذه الطريقة للمؤسسات الاستفادة من الفروق السعرية الصغيرة عبر صفقات متعددة، مما يؤدي إلى أرباح كبيرة على مر الزمن.
(2) كشف الاحتيال باستخدام الذكاء الاصطناعي. تحديد الأنماط والشذوذ: تقوم الأنظمة المدعومة بالذكاء الاصطناعي بتحليل كميات هائلة من البيانات المعاملاتية في الوقت الفعلي. من خلال مقارنة المعاملات الجارية بالبيانات التاريخية، تحدد هذه الأنظمة الأنماط المتوافقة مع المعاملات الشرعية والشذوذات التي تنحرف عن القاعدة. يمكن أن تثير الأنشطة غير العادية، مثل أنماط الإنفاق غير المعتادة أو المعاملات المتعددة من مواقع مختلفة في فترة زمنية قصيرة، علامات حمراء. التحليل في الوقت الفعلي: تقوم خوارزميات الذكاء الاصطناعي بإجراء هذا التحليل بسرعة وفي الوقت الفعلي. مع حدوث المعاملات، يستمر الذكاء الاصطناعي-
يقيمونها بشكل مستمر، مما يضمن الكشف الفوري عن السلوك المشبوه. التحليل في الوقت الحقيقي ضروري لمنع المعاملات الاحتيالية قبل إتمامها، مما يوفر نهجًا استباقيًا لمنع الاحتيال. التعرف على أنماط الاحتيال: يتم تدريب أنظمة الذكاء الاصطناعي على التعرف على أنماط الاحتيال المعروفة ويمكن أن تتطور لتحديد أنماط جديدة ناشئة. تتعلم خوارزميات التعلم الآلي من بيانات الاحتيال التاريخية، مما يمكنها من التكيف والتعرف على مخططات الاحتيال الجديدة مع تطورها. تضمن هذه القابلية للتكيف أن تظل آليات الكشف عن الاحتيال فعالة ضد تكتيكات الاحتيال المتطورة والمعقدة. الكشف والوقاية الفورية: من خلال تحديد الأنشطة المشبوهة بسرعة، يمكن للمؤسسات المالية اتخاذ إجراءات فورية لمنع المعاملات الاحتيالية. قد يتضمن ذلك حظر حساب مؤقتًا، أو وضع علامة على معاملة للمراجعة اليدوية، أو إبلاغ العميل لتأكيد شرعية المعاملة. تساعد التدخلات في الوقت المناسب على حماية أصول العملاء والمؤسسات. التحليل متعدد العوامل: تستخدم أنظمة الذكاء الاصطناعي التحليل متعدد العوامل، مع الأخذ في الاعتبار معايير مختلفة في وقت واحد. تشمل هذه العوامل مبلغ المعاملة، الموقع، الوقت، الجهاز المستخدم، وسلوك الإنفاق. من خلال تقييم عوامل متعددة، تعزز خوارزميات الذكاء الاصطناعي دقة الكشف عن الاحتيال، مما يقلل من الإيجابيات الكاذبة والسلبية. التعلم المستمر والتحسين: تتعلم أنظمة الكشف عن الاحتيال المدفوعة بالذكاء الاصطناعي باستمرار من البيانات الجديدة. مع معالجتها لمزيد من المعاملات ومواجهتها لمحاولات احتيال جديدة، تقوم بتحسين خوارزمياتها، مما يزيد من دقتها مع مرور الوقت. تضمن هذه العملية التعليمية التكرارية أن يصبح النظام أكثر كفاءة في تحديد الأنشطة الاحتيالية.
(د) الصيانة التنبؤية:
(هـ) تحسين مسارات النقل:
الطقس، تقلل أنظمة تحسين المسارات المدعومة بالذكاء الاصطناعي من وقت السفر وتقلل من استهلاك الوقود [81]. لا يعزز ذلك الكفاءة للسائقين الأفراد فحسب، بل يؤثر أيضًا بشكل إيجابي على البيئة من خلال تقليل الانبعاثات. يمكن معالجة ذلك على النحو التالي:
(و) الزراعة الدقيقة:
4.2. البحث المستقبلي
5. الاستنتاجات
مساهمات المؤلفين: التصور، أ.أ. وأ.م.ح.; الكتابة – إعداد المسودة الأصلية، أ.أ، أ.م.ح. و ك.ن.أ.-ك.; الكتابة – المراجعة والتحرير، أ.م.ح. وأ.أ.; الإشراف، ك.ن.أ.-ك. وأ.م.ح. جميع المؤلفين قرأوا ووافقوا على النسخة المنشورة من المخطوطة.
بيان الموافقة المستنيرة: غير قابل للتطبيق.
بيان توفر البيانات: لم يتم إنشاء بيانات جديدة في هذه الدراسة. أي بيانات أو معلومات استخدمت خلال الدراسة متاحة من المؤلف المراسل عند الطلب.
References
- Martínez-Peláez, R.; Ochoa-Brust, A.; Rivera, S.; Félix, V.G.; Ostos, R.; Brito, H.; Félix, R.A.; Mena, L.J. Role of digital transformation for achieving sustainability: Mediated role of stakeholders, key capabilities, and technology. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11221. [CrossRef]
- Espina-Romero, L.; Guerrero-Alcedo, J.; Goñi Avila, N.; Noroño Sánchez, J.G.; Gutiérrez Hurtado, H.; Quiñones Li, A. Industry 5.0: Tracking scientific activity on the most influential industries, associated topics, and future research agenda. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5554. [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Pan, X. Government attention, market competition and firm digital transformation. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9057. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, P.; Lin, Z. Artificial intelligence in education: A review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 75264-75278. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Singla, J.; Nkenyereye, L.; Jha, S.; Prashar, D.; Joshi, G.P.; El-Sappagh, S.; Islam, M.S.; Islam, S.M.R. Medical diagnostic systems using artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms: Principles and perspectives. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 228049-228069. [CrossRef]
- Al-Mushayt, O.S. Automating E-government services with artificial intelligence. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 146821-146829. [CrossRef]
- Gołąb-Andrzejak, E. AI-powered digital transformation: Tools, benefits and challenges for marketers-Case study of LPP. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 219, 397-404. [CrossRef]
- Candelon, F.; Reeves, M. (Eds.) The Rise of AI-Powered Companies; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG: Berlin, Germany, 2022.
- Fountaine, T.; McCarthy, B.; Saleh, T. Building the AI-powered organization. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2019, 97, 62-73.
- Mulder, J. The real world of digital transformation. In Modern Enterprise Architecture: Using DevSecOps and Cloud-Native in Large Enterprises; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2023; pp. 73-103.
- Jarrahi, M.H.; Askay, D.; Eshraghi, A.; Smith, P. Artificial intelligence and knowledge management: A partnership between human and AI. Bus. Horiz. 2023, 66, 87-99. [CrossRef]
- Snyder, H. Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 104, 333-339. [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.; Rialp Criado, A. The art of writing literature review: What do we know and what do we need to know? Int. Bus. Rev. 2020, 29, 101717. [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.S.; Kunz, R.; Kleijnen, J.; Antes, G. Five steps to conducting a systematic review. J. R. Soc. Med. 2003, 96, 118-121. [CrossRef]
- Patton, M.Q. Qualitative Research & Evaluation Methods: Integrating Theory and Practice; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014.
- Anney, V.N. Ensuring the quality of the findings of qualitative research: Looking at trustworthiness criteria. J. Emerg. Trends Educ. Res. Policy Stud. 2014, 5, 272-281.
- Schryen, G. Writing qualitative is literature reviews-Guidelines for synthesis interpretation, and guidance of research. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2015, 37, 12. [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, J.M.; Buckles, D.J. Participatory Action Research: Theory and Methods for Engaged Inquiry; Routledge: London, UK, 2019.
- Hammersley, M.; Atkinson, P. Ethnography: Principles in Practice; Routledge: London, UK, 2019.
- Tracy, S.J. Qualitative Research Methods: Collecting Evidence, Crafting Analysis, Communicating Impact; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019.
- Hennink, M.; Hutter, I.; Bailey, A. Qualitative Research Methods; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2020.
- Enholm, I.M.; Papagiannidis, E.; Mikalef, P.; Krogstie, J. Artificial intelligence and business value: A literature review. Inf. Syst. Front. 2022, 24, 1709-1734. [CrossRef]
- Evans, N.; Miklosik, A.; Bosua, R.; Qureshi, M.A. Digital business transformation: An experience-based holistic framework. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 121930-121939. [CrossRef]
- Du, M. Strategic thinking in artificial intelligence and expert: Problem-solving and creativity. PsyArXiv 2023. [CrossRef]
- Subramonyam, H.; Im, J.; Seifert, C.; Adar, E. Solving separation-of-concerns problems in collaborative design of human-AI systems through leaky abstractions. In Proceedings of the 2022 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 29 April-5 May 2022; pp. 1-21.
- Usmani, U.A.; Happonen, A.; Watada, J. Human-centered artificial intelligence: Designing for user empowerment and ethical considerations. In Proceedings of the 2023 5th International Congress on Human-Computer Interaction 2023, Optimization and Robotic Applications (HORA), Istanbul, Turkey, 8-10 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1-5.
- Troussas, C.; Krouska, A.; Koliarakis, A.; Sgouropoulou, C. Harnessing the power of user-centric artificial intelligence: Customized recommendations and personalization in hybrid recommender systems. Computers 2023, 12, 109. [CrossRef]
- Marshall, L. Invention to Innovation: How Scientists Can Drive Our Economy; CSIRO Publishing: Clayton, Australia, 2023.
- Panesar, G.S.; Venkatesh, D.; Rakhra, M.; Jairath, K.; Shabaz, M. Agile software and business development using artificial intelligence. Ann. Rom. Soc. Cell Biol. 2021, 25, 1851-1857.
- Rosário, A.T.; Dias, J.C. Sustainability and the digital transition: A literature review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4072. [CrossRef]
- Bharadiya, J.P. Driving business growth with artificial intelligence and business intelligence. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2022, 6, 28-44.
- Campbell, C.; Sands, S.; Ferraro, C.; Tsao, H.J.; Mavrommatis, A. From data to action: How marketers can leverage AI. Bus. Horiz. 2020, 63, 227-243. [CrossRef]
- Ambasht, A. Real-time data integration and analytics: Empowering data-driven decision-making. Int. J. Comput. Trends Technol. 2023, 71, 8-14. [CrossRef]
- Latif, H. Advancing data integrity in banking: AI/ML solutions and best practices. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2023, 7, 185-203.
- Bharadiya, J.P. Machine learning and AI in business intelligence: Trends and opportunities. Int. J. Comput. (IJC) 2023, 48, 123-134.
- van de Wetering, R.; de Weerd-Nederhof, P.; Bagheri, S.; Bons, R. Architecting agility: Unraveling the impact of AI capability on organizational change and competitive advantage. In International Symposium on Business Modeling and Software Design; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 203-213.
- Burström, T.; Parida, V.; Lahti, T.; Wincent, J. AI-enabled business-model innovation and transformation in industrial ecosystems: A framework, model and outline for further research. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 127, 85-95. [CrossRef]
- Neeley, T.; Leonardi, P. Developing a digital mindset. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2022, 100, 50-55.
- Garcia, N.; Roberts, H. The power of sentiment analysis in product feedback. Data Insight Mon. 2020, 10, 45-53.
- Jensen, M.; Peters, L. Real-time product refinement: The AI approach. Digit. Bus. Q. 2021, 3, 12-25.
- Torres, M.; Lee, E. Proactive issue detection in AI-driven products. Tech. Evolve Mag. 2022, 11, 16-25.
- Pradhan, I.P.; Saxena, P. Reskilling workforce for the artificial intelligence age: Challenges and the way forward. In The Adoption and Effect of Artificial Intelligence on Human Resources Management, Part B; Emerald Publishing Limited: Bradford, UK, 2023; pp. 181-197.
- Beer, D. Envisioning the power of data analytics. Inf. Commun. Soc. 2018, 21, 465-479. [CrossRef]
- Kibria, M.G.; Nguyen, K.; Villardi, G.P.; Zhao, O.; Ishizu, K.; Kojima, F. Big data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence in next-generation wireless networks. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 32328-32338. [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, I.; Moloney, K.G.; Ross, J.W.; Fonstad, N.O.; Beath, C.M.; Mocker, M. How big old companies navigate digital transformation. MIS Q. Exec. 2017, 16, 6.
- Davenport, T.H.; Guha, A.; Grewal, D.; Bressgott, T. How AI will change the future of marketing. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2020, 48, 24-42. [CrossRef]
- Braun, A.; Garriga, G. Consumer journey analytics in the context of data privacy and ethics. In Digital Marketplaces Unleashed; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 663-674.
- Bughin, J. Artificial Intelligence, the Next Digital Frontier? McKinsey Global Institute: New York, NY, USA, 2018.
- Rathore, B. Predictive metamorphosis: Unveiling the fusion of AI-powered analytics in digital marketing revolution. Int. J. Transcont. Discov. 2020, 7, 15-24.
- Chase, C.W. Consumption-Based Forecasting and Planning: Predicting Changing Demand Patterns in the New Digital Economy; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021.
- Fayyad, U.; Piatetsky-Shapiro, G.; Smyth, P. From data mining to knowledge discovery: An overview. In Advances in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining; American Association for Artificial Intelligence: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; pp. 1-36.
- Siegel, E. Predictive Analytics: The Power to Predict Who Will Click, Buy, Lie, or Die; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016.
- Hisrich, R.D.; Soltanifar, M. Unleashing the creativity of entrepreneurs with digital technologies. In Digital Entrepreneurship: Impact on Business and Society; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 23-49.
- Veryzer, R.W., Jr. Discontinuous innovation and the new product development process. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 1998, 15, 304-321. [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Verma, S.; Lim, W.M.; Kumar, S.; Donthu, N. Personalization in personalized marketing: Trends and ways forward. Psychol. Mark. 2022, 39, 1529-1562. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Davis, A.; Ward, S. Predictive customization: AI’s role in personalized product evolution. AI Strategy J. 2020, 5, 11-20.
- Rafieian, O.; Yoganarasimhan, H. AI and personalization. In Artificial Intelligence in Marketing; Emerald Publishing Limited: Bradford, UK, 2023; pp. 77-102.
- Rainsberger, L. The modern customer-The PHANTOM. In The Modern Customer-the PHANTOM: Customers on the Run: How Sales Must Respond to Radically New Buying Behavior; Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2023; pp. 35-74.
- Peters, J.; Lee, F. Crowdsourcing in product development. Collab. Innov. 2020, 7, 18-26.
- Nash, A.; Ryan, B. Interconnected systems and the demand for seamless products. Digit. Ecosyst. J. 2021, 6, 29-37.
- Liu, M.; Roberts, T. Adaptive solutions in modern product design. Tech Evol. Rev. 2020, 11, 54-63.
- Kapoor, R.; Singh, J. Self-evolving systems in digital products. Glob. Tech Rev. 2019, 10, 75-84.
- Dash, S.; Shakyawar, S.K.; Sharma, M.; Kaushik, S. Big data in healthcare: Management, analysis and future prospects. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 54. [CrossRef]
- Asha, P.; Srivani, P.; Ahmed, A.A.A.; Kolhe, A.; Nomani, M.Z.M. Artificial intelligence in medical imaging: An analysis of innovative technique and its future promise. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 56, 2236-2239. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Gupta, M.; Bhatt, S.; Tosun, A.S. Detecting anomalous user behavior in remote patient monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 22nd International Conference on Information Reuse and Integration for Data Science (IRI), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 10-12 August 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 33-40.
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Dong, T. A review of wearable technologies for elderly care that can accurately track indoor position, recognize physical activities and monitor vital signs in real-time. Sensors 2017, 17, 341. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahuja, A.S. The impact of artificial intelligence in medicine on the future role of the physician. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7702. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsin, S.N.; Gapizov, A.; Ekhator, C.; Ain, N.U.; Ahmad, S.; Khan, M.; Barker, C.; Hussain, M.; Malineni, J.; Ramadhan, A.; et al. The role of artificial intelligence in prediction, risk stratification, and personalized treatment planning for congenital heart diseases. Cureus 2023, 15, e44374. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Saleh, S.; Liu, Y. A review on artificial intelligence in education. Acad. J. Interdiscip. Stud. 2021, 10, 206-217. [CrossRef]
- Goodell, J.W.; Kumar, S.; Lim, W.M.; Pattnaik, D. Artificial intelligence and machine learning in finance: Identifying foundations, themes, and research clusters from bibliometric analysis. J. Behav. Exp. Financ. 2021, 32, 100577. [CrossRef]
- Abad-Segura, E.; González-Zamar, M.-D.; López-Meneses, E.; Vázquez-Cano, E. Financial technology: Review of trends, approaches, and management. Mathematics 2020, 8, 951. [CrossRef]
- Patra, S.; Mahfouz, M.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Magazzeni, D.; Veloso, M. FinRDDL: Can AI planning be used for quantitative finance problems? In Proceedings of the ICAPS 2023, Prague, Czech Republic, 8-13 July 2023.
- Bao, Y.; Hilary, G.; Ke, B. Artificial intelligence and fraud detection. In Innovative Technology at the Interface of Finance and Operations: Volume I; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 223-247.
- Kunduru, A.R. Artificial intelligence advantages in cloud Fintech application security. Cent. Asian J. Math. Theory Comput. Sci. 2023, 4, 48-53.
- Bhargavi, C.; Sravanthi, M. Significant role of digital technology in detecting banking frauds in India. Int. J. Adv. Multidisc. Res. Stud. 2023, 3, 1124-1127.
- Zhao, L.; Naktnasukanjn, N.; Mu, L.; Liu, H.; Pan, H. Fundamental quantitative investment theory and technical system based on multi-factor models. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 20th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Perth, Australia, 25-28 July 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 521-526.
- Lee, W.J.; Wu, H.; Yun, H.; Kim, H.; Jun, M.B.G.; Sutherland, J.W. Predictive maintenance of machine tool systems using artificial intelligence techniques applied to machine condition data. Procedia CIRP 2019, 80, 506-511. [CrossRef]
- Go, T.; Moe, T.; Hirotsugu, G.; Yuuichi, N. Machine learning applied to sensor data analysis. Yokogawa Tech. Rep. 2016, 59, 27-30.
- Karthik, T.S.; Kamala, B. Cloud-based AI approach for predictive maintenance and failure prevention. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2054, 012014. [CrossRef]
- Samadi-Parviznejad, P. Development of a mathematical model of preventive maintenance by increasing reliability and reducing cost. Appl. Innov. Ind. Manag. 2021, 1, 8-18.
- Abduljabbar, R.; Dia, H.; Liyanage, S.; Bagloee, S.A. Applications of artificial intelligence in transport: An overview. Sustainability 2019, 11, 189. [CrossRef]
- Broekman, A.; Gräbe, P.J.; Wynand, J. Real-time traffic quantization using a mini edge artificial intelligence platform. Transp. Eng. 2021, 4, 100068. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Ma, X.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Wang, L.; Cao, W.-L.; Li, J.-X.; Tong, J. A new form of deep learning in smart logistics with IoT environment. J. Supercomput. 2022, 78, 11873-11894. [CrossRef]
- Guerra, A.; Amini, E.; Elefteriadou, L. A Computationally-Efficient Algorithm to Enable Joint Optimization of Connected Automated Vehicles’ Trajectories and Signal Phasing and Timing in Coordinated Arterials. 2023. Available online: https: / / papers.ssrn.com/sol3/ papers.cfm?abstract_id=4411134 (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Joseph, R.B.; Lakshmi, M.B.; Suresh, S.; Sunder, R. Innovative analysis of precision farming techniques with artificial intelligence. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd International Conference on Innovative Mechanisms for Industry Applications (ICIMIA), Bangalore, India, 5-7 March 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 353-358.
- Agrawal, N.; Agrawal, H. Artificial Intelligence-Intelligent Inputs Revolutionizing Agriculture. 2021. Available online: https: //www.niti.gov.in/sites/default/files/2021-09/IntelligentInputsRevolutionisingAgriculture.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Otieno, M. An extensive survey of smart agriculture technologies: Current security posture. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2023, 18, 1207-1231. [CrossRef]
- Leong, Y.M.; Lim, E.H.; Subri, N.F.B.; Jalil, N.B.A. Transforming agriculture: Navigating the challenges and embracing the opportunities of artificial intelligence of things. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Agrosystem Engineering 2023, Technology & Applications (AGRETA), Shah Alam, Malaysia, 9 September 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 142-147.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su16051790
Publication Date: 2024-02-22
AI-Powered Innovation in Digital Transformation: Key Pillars and Industry Impact
Revised: 17 February 2024
Accepted: 17 February 2024
Published: 22 February 2024
Abstract
Digital transformation systems generate a substantial volume of data, creating opportunities for potential innovation, particularly those driven by artificial intelligence. This study focuses on the intricate relationship between artificial intelligence and innovation as foundational elements in the digital transformation framework for sustained growth and operational excellence. This study provides a holistic perspective on the cultivation and pillars of AI-powered innovation, highlighting their pivotal role in revolutionizing industries, including healthcare, education, finance, manufacturing, transportation, and agriculture. The work emphasizes the key pillars essential for fostering AI-powered innovation, including monitoring performance measurement to use the power of the present, continuous learning and innovation, data analytics and insights, predictive analytics, and innovative product development. This study investigates how these pillars serve as the foundation for groundbreaking advancements, driving efficiency, enhancing decision-making processes, and fostering creativity within organizations. This study explores the significance of continuous learning, interdisciplinary collaboration, and industry partnerships in nurturing a thriving AI-powered innovation ecosystem. By understanding and harnessing these fundamental elements, businesses can navigate the complexities of the digital age, fostering innovation that not only optimizes processes but also enhances the overall human experience, ushering in a new era of technological excellence and societal progress.
1. Introduction
empowers organizations to automate mundane tasks, enhance productivity, and reimagine traditional business models. Moreover, AI-driven innovation can deliver personalized and seamless experiences for customers, thus increasing engagement and loyalty. By embracing the potential of AI in their digital transformation journey, organizations open up a world of unlimited possibilities for growth, competitiveness, and long-term success in the ever-evolving digital landscape. This has led to AI-powered innovation in digital transformation [7].
- Evolution over time: Unlike the static technologies of the past, AI systems learn and adapt over time. This evolutionary nature necessitates constant refinement of these systems to ensure that they remain aligned with their intended objectives and the ever-changing external environment.
- Perpetual beta: The phrase “always in beta” aptly describes the state of AI tools and solutions [10]. Given their dynamic nature, they are perpetually undergoing testing, learning from new data, and evolving. Innovation, in this space, means embracing this continual state of flux and being prepared to adjust strategies and systems accordingly. The convergence of the human intellect with artificial intelligence [11] is reshaping our world in profound ways, heralding an era of unprecedented progress and boundless opportunities. The convergence of the human intellect with artificial intelligence represents a monumental leap forward for humanity, ushering in an era characterized by unparalleled advancement and limitless opportunities. This synergy between human creativity and the computational power of AI systems is revolutionizing various aspects of our lives, transforming industries, and shaping the future in profound ways.
This study presents the key pillars of AI-powered innovation in the digital transformation process framework. These pillars encompass performance monitoring, continuous learning, data analytics, predictive analytics, and innovative product development. Together, these pillars serve as the cornerstones upon which groundbreaking advancements are constructed, driving efficiency enhancements, facilitating informed decision-making processes, and nurturing creativity within organizations.
tion. This comprehensive approach not only propels transformative advancements but also ensures sustainable growth, enabling businesses to remain agile and relevant in the ever-changing business landscape.
RQ1: How do AI’s innovation pillars contribute to the success and sustainability of digital transformation efforts?
RQ2: What are the implications of AI-powered innovation for industry-specific transformation and overall societal progress?
2. Materials and Methods
- Literature review: The start of this research endeavor involves an exhaustive literature review, in which a methodical examination is conducted on academic articles, research papers, and theoretical frameworks of artificial intelligence, innovation, digital transformation, sustained growth, and operational excellence. This thorough review serves as the cornerstone for comprehending the current state of scholarly discourse in these domains, laying the groundwork for the development of a framework for AI-powered innovation aimed at revolutionizing industries [12]. The review follows the following steps:
- Scope definition: The literature review begins with a precise definition of the scope, elucidating the key themes and parameters relevant to AI, innovation, digital transformation, sustained growth, and operational excellence. This step ensures a focused and purposeful exploration of the existing body of knowledge [13].
- Systematic review methodology: Employing a systematic review methodology, academic databases, research repositories, and relevant journals are systematically searched and scrutinized. This rigorous approach ensures the inclusion of comprehensive and relevant literature while maintaining a structured and organized process [14].
- Thematic categorization: The identified literature is categorized thematically, allowing for the systematic organization of information. This categorization aids in discerning common themes, trends, and patterns across diverse sources, thus contributing to a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter [15].
- Identification of key concepts: Key concepts related to AI, innovation, digital transformation, sustained growth, and operational excellence are distilled from literature. This identification facilitates the development of a conceptual foundation for the framework for AI-powered innovation.
- Critical appraisal: Each source undergoes critical appraisal to evaluate its methodological rigor, reliability, and relevance to the research objectives. This discerning analysis ensures the inclusion of high-quality literature, which contributes to the robustness of the subsequent framework development [16].
- Synthesis of literature: The synthesized information from the literature review serves as the intellectual basis for conceptualizing the framework for AI-powered innovation. Insights, theories, and empirical findings from the literature are combined to inform the subsequent stages of the research [17].
- Conceptual framework development: A conceptual framework is developed based on the literature review. This framework delineates the theoretical underpinnings and defines key concepts, relationships, and variables essential to understanding how AI can revolutionize industries through innovation, digital transformation, sustained growth, and operational excellence.
- Title integration: The conceptual framework developed through the literature review lays the foundation for the subsequent exploration of an AI-powered innovation framework that revolutionizes industries. The synthesized insights guide the framing of innovative solutions within this conceptual framework.
By rigorously pursuing these steps in the literature review, we aim to not only establish a comprehensive understanding of the existing academic discourse but also discern opportunities for contributing novel insights to the intricate relationship between AI, innovation, digital transformation, sustained growth, and operational excellence.
- Experience-driven approach: This study integrates an “experience-driven” orientation, drawing on practical knowledge derived from active involvement in the field of industrial system engineering. This involves first-hand experiences, observations, and engagements with AI and innovation in real-world contexts. These experiences are documented and analyzed to extract valuable insights that complement and enrich the theoretical perspectives. The incorporation of an “experience-driven” approach in this study signifies a deliberate integration of practical knowledge acquired through active participation in the field of industrial system engineering to complement and enrich theoretical perspectives related to AI and innovation. This methodological orientation emphasizes first-hand experiences, direct observations, and engagements with AI and innovation within real-world contexts [18]. This follows the following steps:
- Field immersion: Researchers actively immerse themselves in the operational milieu of industrial system engineering by engaging in AI applications and innovative practices. This immersion allows for a first-hand understanding of the practical challenges, opportunities, and dynamics inherent in the integration of AI and innovation within industrial settings [18].
- Qualitative data collection techniques: The experiential approach is augmented through the judicious incorporation of qualitative data collection methodologies, specifically interviews and surveys. These rigorous methods are strategically applied to solicit insights from eminent industry professionals, practitioners, and stakeholders operating within the domains of industrial system engineering, AI, and innovation. The conducted interviews serve as a conduit for acquiring nuanced perspectives, substantiating findings with anecdotal evidence, and imparting an invaluable real-world context. Qualitative data not only validate experiential knowledge but also contribute to a holistic understanding of the interplay between theory and practice [19].
- Observational analysis: Through keen observation, researchers systematically analyze the implementation of AI and innovation in real-world scenarios. This involves documenting how these technologies are applied, identifying patterns of usage, and discerning the nuances of their impact on industrial processes and outcomes [20].
- Hands-on involvement: The research team actively participates in hands-on activities related to AI and innovation in industrial system engineering. This could include collaborative problem-solving, experimental projects, or direct involvement in the development and implementation of technological solutions. This hands-on approach facilitates a deeper understanding of the practical implications of these technologies.
- Documentation of experiences: Experiences, insights, and observations are meticulously documented in a systematic manner. This documentation includes detailed records of specific scenarios, challenges encountered, solutions devised, and lessons learned. This comprehensive record serves as a valuable dataset for analysis [21].
- Analysis for insights: The documented experiences are subjected to rigorous analysis, with a focus on extracting insights that complement and augment the theoretical perspectives derived from the literature review. This analytical process involves identifying patterns, successes, failures, and emerging trends in the practical application of AI and innovation within industrial contexts.
- Contextualization of findings: The insights derived from the experience-driven approach are then contextualized within the broader theoretical framework established earlier. This process ensures that the practical knowledge gained is aligned with and contributes to the conceptual understanding derived from academic literature, creating a cohesive and comprehensive narrative.
- Validation of theoretical assumptions: Through an experience-driven approach, this study seeks to validate or challenge theoretical assumptions and hypotheses. The practical insights obtained offer a real-world perspective that enhances the credibility and applicability of the research findings.
- Continuous iteration: The experience-driven approach is not static but rather iterative. As the study progresses, ongoing experiences and observations may lead to refinements or expansions of the theoretical framework, creating a dynamic interplay between practical insights and theoretical foundations.
3. Synthesis and conclusion: The final phase involves synthesizing the findings from the literature review, the experience-driven approach, and the data analysis. This study aims to draw meaningful conclusions regarding the relationship between AI and innovation within the digital transformation framework, providing insights into how these elements contribute to sustained growth and operational excellence. In the synthesis and conclusion phase, the study brings together diverse strands of information gathered from the literature review, the experience-driven approach, and the data analysis.
4. AI systems a group: In navigating the intricate landscape of AI, the ability to discern and comprehend the distinct features of various AI systems becomes paramount. Understanding these nuances is crucial for unlocking insights into their diverse applications and the transformative impact they wield in digital evolution. However, it is noteworthy that the focus of this particular work extends beyond a dedicated examination of any singular AI system. Instead, it takes on the broader perspective of encompassing all AI tools and systems as an integrated collective. By adopting this holistic approach, the study aims to capture the synergies, interconnections, and overarching trends that characterize the collaborative dynamics within the broader spectrum of AI technologies. As digital transformation continues to redefine industries and reshape the technological landscape, this comprehensive exploration of AI as a unified group seeks to offer insights into the collective intelligence driving innovation, automation, and the ever-expanding boundaries of artificial intelligence.
3. Results
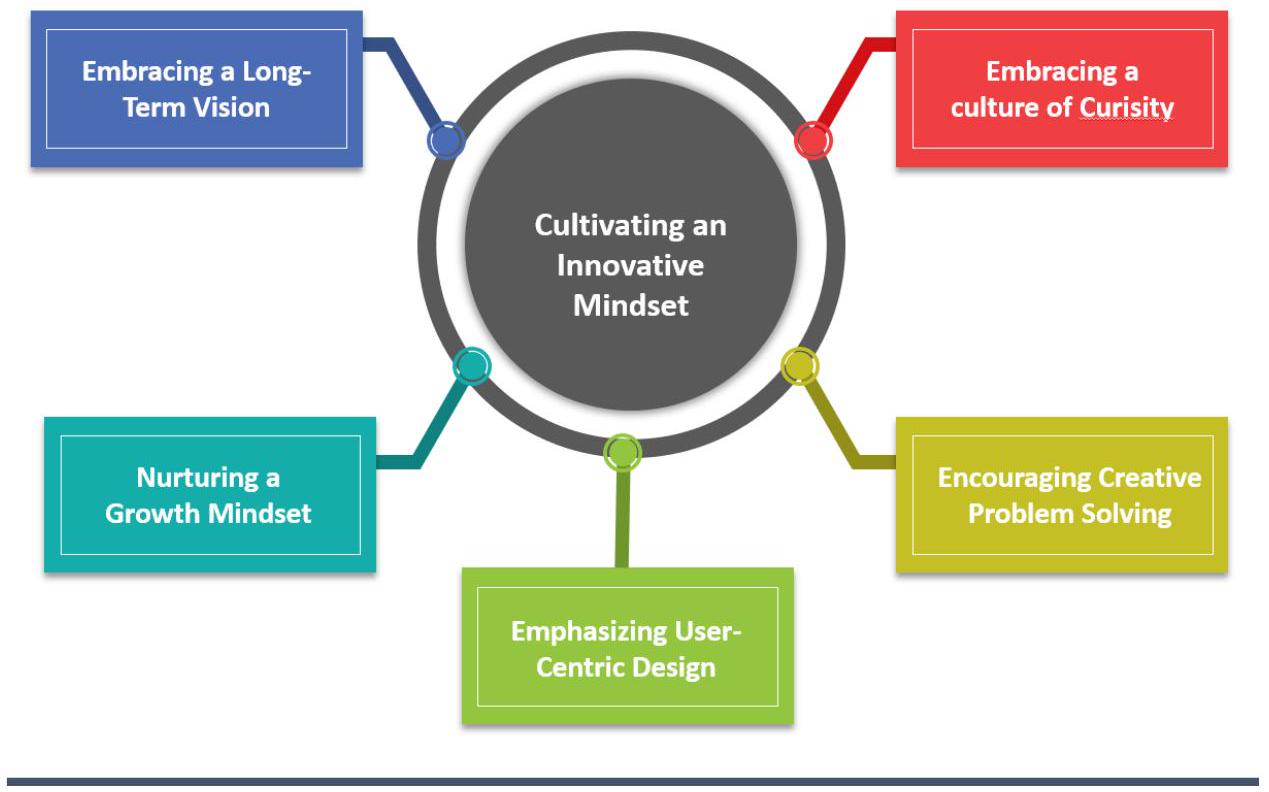
3.1. Cultivating an Innovative Mindset for AI-Powered Digital Transformation

(a) Embracing a Culture of Curiosity:
solutions that drive digital transformation. This culture does not just lead to technological advancements; it fosters a mindset that transforms challenges into opportunities, stagnation into evolution, and curiosity into a driving force that propels businesses into a future where the possibilities of AI are not just imagined but also realized, creating a world where innovation knows no bounds [23]. Embracing a culture of curiosity involves continuous learning. In the rapidly evolving field of AI, staying updated with the latest technologies, algorithms, and industry trends is essential. Continuous education fosters a mindset open to new possibilities and innovations. With an innovative mindset and continuous learning, businesses not only survive in the AI-powered DT age but also thrive, shaping a future that is defined by creativity, ingenuity, and a never-ending quest for progress.
(b) Encouraging Creative Problem-Solving:
(c) Emphasizing User-Centric Design:
(d) Nurturing a Growth Mindset:
mindset [29]. When failures occur, agile development allows businesses to pivot swiftly, making necessary changes and optimizing their AI solutions based on real-time feedback. Viewing failure as a part of the process builds resilience within teams. Resilient teams bounce back from setbacks, using failures as motivation to explore new avenues and creative solutions. This resilience is vital in overcoming challenges and persistently pursuing innovation. Failure teaches adaptability. Businesses that learn from failures are better equipped to adapt to changing market demands, technological advancements, and user preferences. This adaptability ensures that AI solutions remain relevant and effective in dynamic environments.
(e) Embracing a Long-term Vision:
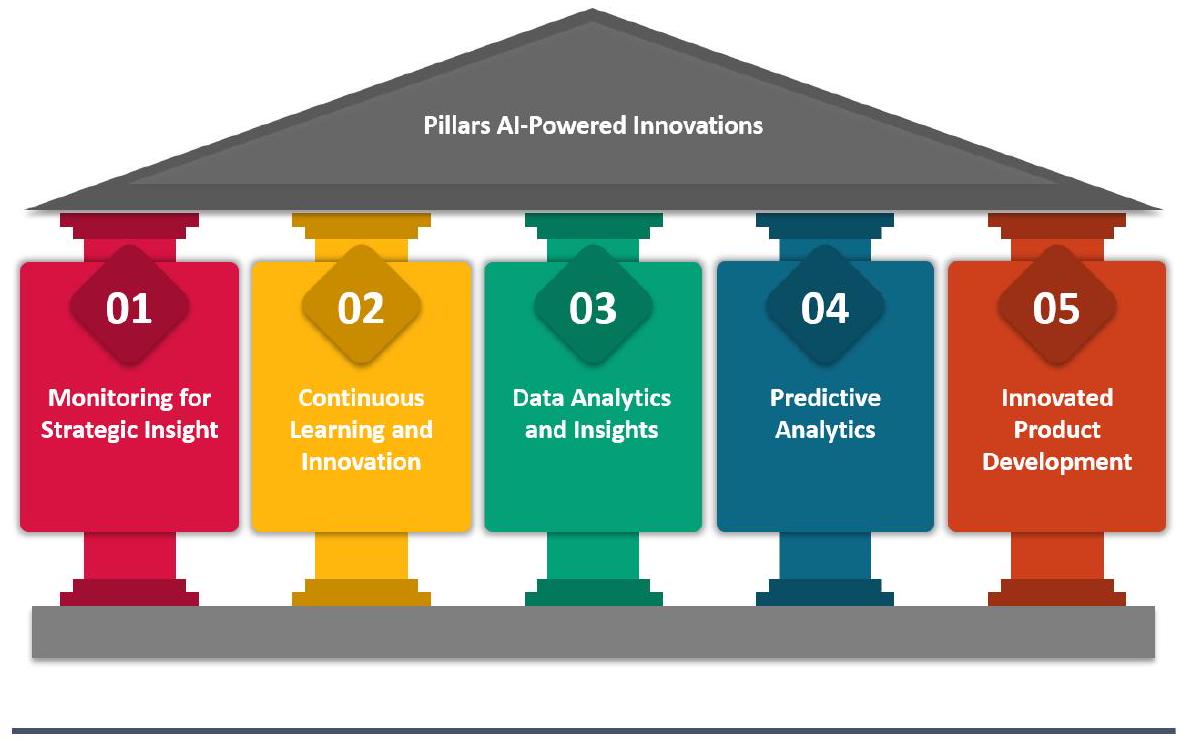
3.2. Development of the Pillars of AI-Powered Innovation

(a) Monitoring Strategic Insights:
evolved rapidly, especially in the field of artificial intelligence. Real-time monitoring allows businesses to stay abreast of the latest advancements. By understanding the performance of current AI solutions, businesses can make informed decisions about integrating new technologies. This integration might include adopting more sophisticated algorithms, incorporating machine learning enhancements, or leveraging novel AI applications that align with business objectives. Real-time monitoring not only informs internal strategies but also facilitates external collaboration. By sharing relevant data with strategic partners or industry collaborators, businesses can collectively shape the future of AI applications [37]. Collaborations can lead to the development of groundbreaking technologies or the creation of industry standards, ensuring that businesses remain at the forefront of innovation. Realtime monitoring provides data points for long-term planning. By analyzing historical performance data alongside real-time insights, businesses can create a roadmap for the future. This roadmap outlines the evolution of AI applications, ensuring that businesses have a clear vision of how their technology will develop over time. A well-defined roadmap is essential for sustained innovation and strategic growth.
(b) Continuous Learning and Innovation:
behaviors, and competitor strategies. This awareness is crucial for strategic decision-making and innovation to stay updated with the latest advancements, ensuring that businesses leverage the most cutting-edge AI tools and data analytics platforms. Feedback loops and iterative development: Continuous learning involves gathering feedback from end users. This iterative feedback loop ensures that AI-powered solutions are user-centric and align with evolving user preferences. This enables rapid prototyping and iterative development, allowing organizations to refine AI applications based on real-world user experiences, thereby enhancing usability and functionality. This leads to continuous enhancement, which can be explained as follows. Sentiment analysis: Beyond merely collecting feedback, AI-driven tools can gauge the sentiment behind user comments across platforms, such as social media, review sites, and customer support channels. This provides businesses with nuanced insights into user satisfaction and areas for enhancement [39]. Adaptive products: By integrating AI into products, they can inherently adapt based on user feedback. Such real-time adaptability not only enhances user experience but also fosters trust and loyalty, as users feel that their feedback directly shapes the products they use [40]. Proactive issue identification: Before issues escalate to critical levels or widespread user dissatisfaction, AI can pinpoint emerging problems by analyzing patterns in user feedback. Such proactive issue detection is invaluable for maintaining product reputation and ensuring continued user satisfaction [41]. Experimentation and risk-taking: Establishing innovation labs or dedicated spaces for experimentation encourages teams to explore unconventional AI applications. This environment fosters creativity and risk-taking. Failure as learning embraces failure as a stepping stone to innovation. Organizations learn valuable lessons from failed experiments, leading to more refined and innovative solutions. Upskilling the workforce: Continuous learning is not just about technology. As AI evolves, professionals need to upskill, ensuring that they can leverage new tools, understand novel algorithms, and apply best practices in AI implementation [42].
(c) Data Analytics and Insights
downtime and associated losses. In the HR realm, analytics can reveal patterns affecting employee turnover, enabling the formation of proactive retention strategies [46]. Personalizing customer experiences: Data analysis of customer interactions and behavior data helps businesses gain insights into customer preferences. This knowledge allows for the creation of personalized experiences that enhance customer engagement and loyalty. Real-time data analytics enable innovative businesses to personalize customer interactions on the fly [47]. Dynamic content and offers based on real-time customer behavior led to higher conversion rates and customer satisfaction. Informed decision-making: Data analytics provide reliable, data-driven insights rather than relying solely on intuition or observation. Leaders can make strategic decisions backed by concrete evidence, thereby reducing the risk associated with intuition-based decision-making. Data analytics allows businesses to simulate various scenarios. Organizations can make informed decisions and choose the most promising path forward by analyzing the potential outcomes of different strategies. For instance, a company in the e-commerce sector can harness data analysis to adjust product pricing optimally, influenced by parameters such as demand, competitor pricing, and customer behavior trends [48]. Continuous feedback and improvement: Data analytics process user feedback from various channels. Businesses gain valuable insights into customer sentiment, enabling iterative improvements to products and services. Businesses can continuously iterate their offerings by analyzing user feedback and usage data. This agile approach ensures that products remain relevant, competitive, and aligned with user needs.
(d) Predictive Analytics
- Anticipating customer behavior: Predictive analytics categorize customers into segments based on their behavior and preferences. By understanding each segment’s needs, businesses can tailor products and services, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. Analyzing historical customer data enables organizations to predict churn. By identifying customers at risk, businesses can implement retention strategies to reduce customer attrition rates.
- Optimizing marketing strategies: Predictive analytics evaluate past marketing campaigns to determine what worked and what did not. The insights derived help optimize future campaigns and ensure a higher return on investment. By analyzing customer interactions and demographics, predictive analytics assign scores to leads based on their likelihood of conversion. This aids sales teams in focusing their efforts on high-potential leads, thus improving conversion rates.
- Demand forecasting and inventory management: Predictive analytics analyze historical sales data and market trends. Businesses can accurately forecast the demand for products and services by optimizing inventory levels and reducing excess stock. By predicting demand patterns, organizations streamline their supply chains. Predictive insights ensure that supplies are aligned with demand, thereby reducing storage costs and minimizing waste.
- Streamlining operations: In the manufacturing and service industries, predictive analysis forecasts equipment failures and maintenance needs. Proactive maintenance reduces downtime, extends equipment life, and enhances overall operational efficiency. Predictive analytics analyze historical supplier performance and demand patterns. Businesses can optimize their supply chains by ensuring timely deliveries, minimizing costs, and maintaining efficient inventory levels.
- Risk mitigation: Predictive analytics can be used for risk mitigation by identifying potential threats or issues before they materialize. By identifying patterns, trends, and anomalies in historical and real-time data, organizations can make proactive decisions to mitigate potential risks. For instance, in cybersecurity, predictive analytics can help identify potential threats or attacks. In healthcare, it can help predict disease outbreaks [51].
- Challenges and considerations: While predictive analytics offers numerous benefits, it is important to consider its limitations and challenges. For instance, the accuracy of predictions heavily depends on the quality and completeness of the data. Therefore, data cleaning, pre-processing, and quality assurance are crucial steps. Moreover, predictive models might not fully account for abrupt changes or black swan events; hence, regular model review and refinement are needed [52].
- Potential biases in predictive analytics: AI algorithms, which are dependent on historical data, can inadvertently perpetuate existing biases. For instance, if the data reflect past discriminatory practices or societal biases, the predictive models may produce biased outcomes. This is particularly concerning in areas such as hiring, lending, and law enforcement, where biased predictions could lead to unfair or prejudicial outcomes.
- Ethical implications: The use of predictive analytics raises significant ethical questions, particularly regarding privacy, consent, and transparency. There is a risk of misuse of predictive analytics in ways that infringe on individual privacy or autonomy, such as through intrusive surveillance or predictive policing.
- Strategies to mitigate biases: To address these biases, it is crucial to implement strategies such as:
- Diversifying data sources: Ensuring that the data used to train predictive models is representative of diverse populations and scenarios.
- Regular audits: Conduct regular audits of AI algorithms to check for and correct biases.
- Transparency: Maintain transparency about how predictive models are built and the data on which they are trained, allowing for accountability.
- Promoting responsible AI practices: Responsible AI practices should be at the core of predictive analytics. This includes ethical data collection, ensuring informed consent where personal data is used, and implementing data privacy safeguards. Organizations should also establish ethical guidelines for the use of predictive analytics, ensuring that the technology is used in a manner that respects individual rights and promotes fairness.
- Addressing data quality and completeness: The accuracy of predictions heavily depends on the quality and completeness of the data. Therefore, data cleaning, pre-processing, and quality assurance are crucial steps. Predictive models might not fully account for abrupt changes or ‘black swan’ events, necessitating regular model review and refinement.
- Continuous ethical and bias training: Organizations should invest in continuous ethical training and bias awareness programs for their teams, ensuring that those developing and deploying predictive models are aware of and can mitigate potential ethical issues and biases.
In summary, predictive analytics, while offering transformative capabilities for organizations, comes with significant responsibilities. Addressing potential biases and ethical implications is critical for harnessing the full power of predictive analytics responsibly and effectively. By incorporating these strategies, organizations can mitigate risks and foster trust and credibility in their AI initiatives.
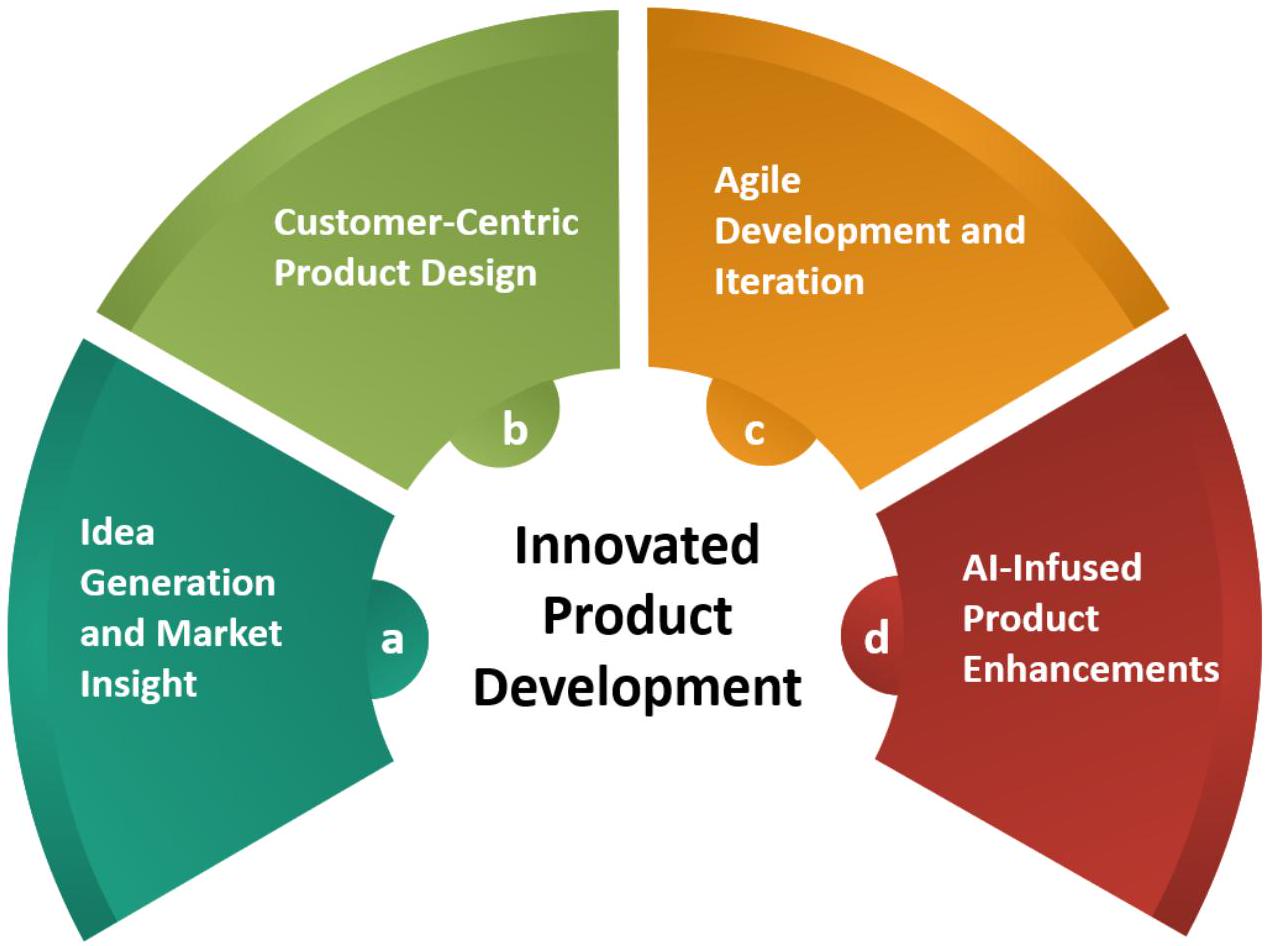
(e) Innovative Product Development

Real-time data analysis: AI algorithms can process vast amounts of user data in real time. These data may include user behaviors, preferences, and feedback that inform product modifications or feature enhancements that resonate with distinct user segments [55]. Predictive customization: AI can forecast future user needs or preferences based on past behaviors. This predictive power ensures that products evolve in alignment with user expectations, even pre-empting them [56]. Maintaining efficiency: While personalization often sounds resource-intensive, AI systems ensure that tailoring products to individual preferences does not compromise the efficiency or scalability of the production process [57].
(b) Customer-centric product design: AI analyzes vast datasets, offering insights into customer preferences, behaviors, and pain points. This data-driven approach informs product design, ensuring that offerings are tailored to meet customer needs. AI enables the creation of highly personalized products and services. From customized recommendations to individualized user experiences, personalization enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty. The digital era has given consumers unprecedented power. With myriad options available at their fingertips, their expectations are higher than ever. Immediate gratification: The digital consumer expects instantaneous responses, whether in e-commerce deliveries, app performance, or customer service [58]. Participation in development: Crowdsourcing, beta testing, and community-driven product development have become more prevalent, blurring the lines between consumers and creators [59]. Demand for digital integration: With the proliferation of smart devices
and interconnected systems, there is a growing demand for products that seamlessly integrate into the broader digital ecosystem [60].
(c) Agile development and iteration: Agile methodologies combined with AI-powered tools facilitate rapid prototyping, experimentation, and iterative development. Businesses can quickly create and test product prototypes, gather user feedback, and iterate on designs. This agile approach accelerates time-to-market and ensures that products align with user expectations. AI-powered analytics provide real-time insights into product performance. Organizations can monitor user behavior and feedback, making continuous improvements to enhance usability, functionality, and overall user experience. As digital tools and AI become ubiquitous, the products of the future are not just static tools but adaptive solutions. Products can be learned from user behavior. Products equipped with AI can analyze user behavior in real time, adapt functionalities to individual preferences, and ensure a personalized user experience [61]. In addition, the products can self-evolve. Modern software solutions frequently update themselves to fix bugs, enhance security, or introduce new features, ensuring constant alignment with user needs and technological advancements [62].
(d) AI-infused product enhancements: AI integration enhances products with intelligent features such as predictive analytics, natural language processing, and computer vision. These features add value, making products more versatile, efficient, and userfriendly. AI automates repetitive tasks within products, increasing efficiency and allowing users to focus on higher-value activities. Automation not only saves time but also enhances user productivity.
4. Discussion
4.1. AI-Innovations: Transforming Diverse Industries
(a) Healthcare:
(b) Personalized Learning:
interests and preferences. As a result, students are more motivated to participate actively and understand the material in-depth. The tailored approach bridges gaps in understanding, ensuring that students grasp concepts thoroughly. Improved Learning outcomes: The individualized approach to personalized learning directly translates into improved learning outcomes. Students receive the support they need precisely when they need it, leading to better academic performance, confidence, and a positive attitude toward learning. Catering to diverse needs: Personalized learning acknowledges and accommodates the diverse needs and abilities of students. It provides additional support for struggling learners and challenges for advanced students, ensuring that every student receives an education tailored to their level.
(c) Finance:
(1) AI in financial trading. Real-time data analysis: AI-driven algorithms process vast amounts of real-time market data. This includes historical data, current market prices, trading volumes, and various other indicators. Analyzing this data swiftly is crucial for making informed trading decisions [35]. Pattern and trend recognition: AI algorithms excel at identifying complex patterns and trends within market data. By recognizing these patterns, algorithms can anticipate market movements, enabling more accurate predictions about the future performance of stocks, currencies, or commodities [35,71]. Optimal trade execution: AI algorithms execute trades at optimal times based on the identified patterns and trends. They assess market conditions and execute trades swiftly and efficiently, ensuring that transactions are made at the most advantageous prices. This strategic execution maximizes profits for financial institutions [72]. Speed and scale advantage: AI processing capabilities far exceed human capacity. It can analyze data, identify patterns, and execute trades at speeds measured in milliseconds. This rapid processing gives financial institutions a significant advantage in promptly reacting to market changes, especially in high-frequency trading environments. Competitive edge: The ability to process vast amounts of data and execute trades swiftly provides financial institutions with a competitive edge. By leveraging AI technologies, institutions can stay ahead in dynamic and fast-paced financial markets, making split-second decisions that can result in substantial profits. High-frequency trading: AI enables high-frequency trading, a strategy in which trades are executed within milliseconds to exploit even the slightest market inefficiencies. This approach allows institutions to capitalize on small price differentials across multiple trades, leading to significant profits over time.
(2) Fraud detection with AI. Pattern and anomaly identification: AI-powered systems analyze vast amounts of transactional data in real time. By comparing ongoing transactions with historical data, these systems identify patterns consistent with legitimate transactions and anomalies that deviate from the norm. Unusual activities, such as atypical spending patterns or multiple transactions from different locations in a short time, can raise red flags [73]. Real-time analysis: AI algorithms perform this analysis swiftly and in real time. As transactions occur, AI continu-
ously evaluates them, ensuring the immediate detection of suspicious behavior. Real-time analysis is essential for preventing fraudulent transactions before they are completed, providing a proactive approach to fraud prevention [74]. Fraud pattern recognition: AI systems are trained to recognize known fraud patterns and can evolve to identify new, emerging patterns. Machine learning algorithms learn from historical fraud data, enabling them to adapt and recognize novel fraud schemes as they develop. This adaptability ensures that fraud detection mechanisms remain effective against evolving and sophisticated fraud tactics [75]. Prompt detection and prevention: By promptly identifying suspicious activities, financial institutions can take immediate action to prevent fraudulent transactions. This might involve temporarily blocking an account, flagging a transaction for manual review, or notifying the customer to confirm the legitimacy of the transaction. Timely intervention helps protect both customers’ and institutions’ assets. Multi-factor analysis: AI systems employ multi-factor analysis, considering various parameters simultaneously. These factors include transaction amount, location, time, device used, and spending behavior. By assessing multiple factors, AI algorithms enhance the accuracy of fraud detection, thereby reducing false positives and negatives [76]. Continuous learning and improvement: AI-driven fraud detection systems continuously learn from new data. As they process more transactions and encounter new fraud attempts, they refine their algorithms, improving their accuracy over time. This iterative learning process ensures that the system becomes increasingly proficient in identifying fraudulent activities.
(d) Predictive Maintenance:
(e) Transportation Route Optimization:
weather, AI-powered route optimization systems minimize travel time and reduce fuel consumption [81]. This not only enhances efficiency for individual drivers but also positively impacts the environment by reducing emissions. This can be processed as follows:
(f) Precision Farming:
4.2. Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions: Conceptualization, A.A. and A.M.H.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A., A.M.H. and K.N.A.-K.; writing-review and editing, A.M.H. and A.A.; supervision, K.N.A.-K. and A.M.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Informed Consent Statement: Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement: No new data were created in this study. Any data or information used during the study are available from the corresponding author by request.
References
- Martínez-Peláez, R.; Ochoa-Brust, A.; Rivera, S.; Félix, V.G.; Ostos, R.; Brito, H.; Félix, R.A.; Mena, L.J. Role of digital transformation for achieving sustainability: Mediated role of stakeholders, key capabilities, and technology. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11221. [CrossRef]
- Espina-Romero, L.; Guerrero-Alcedo, J.; Goñi Avila, N.; Noroño Sánchez, J.G.; Gutiérrez Hurtado, H.; Quiñones Li, A. Industry 5.0: Tracking scientific activity on the most influential industries, associated topics, and future research agenda. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5554. [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Pan, X. Government attention, market competition and firm digital transformation. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9057. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, P.; Lin, Z. Artificial intelligence in education: A review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 75264-75278. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Singla, J.; Nkenyereye, L.; Jha, S.; Prashar, D.; Joshi, G.P.; El-Sappagh, S.; Islam, M.S.; Islam, S.M.R. Medical diagnostic systems using artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms: Principles and perspectives. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 228049-228069. [CrossRef]
- Al-Mushayt, O.S. Automating E-government services with artificial intelligence. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 146821-146829. [CrossRef]
- Gołąb-Andrzejak, E. AI-powered digital transformation: Tools, benefits and challenges for marketers-Case study of LPP. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 219, 397-404. [CrossRef]
- Candelon, F.; Reeves, M. (Eds.) The Rise of AI-Powered Companies; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG: Berlin, Germany, 2022.
- Fountaine, T.; McCarthy, B.; Saleh, T. Building the AI-powered organization. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2019, 97, 62-73.
- Mulder, J. The real world of digital transformation. In Modern Enterprise Architecture: Using DevSecOps and Cloud-Native in Large Enterprises; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2023; pp. 73-103.
- Jarrahi, M.H.; Askay, D.; Eshraghi, A.; Smith, P. Artificial intelligence and knowledge management: A partnership between human and AI. Bus. Horiz. 2023, 66, 87-99. [CrossRef]
- Snyder, H. Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 104, 333-339. [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.; Rialp Criado, A. The art of writing literature review: What do we know and what do we need to know? Int. Bus. Rev. 2020, 29, 101717. [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.S.; Kunz, R.; Kleijnen, J.; Antes, G. Five steps to conducting a systematic review. J. R. Soc. Med. 2003, 96, 118-121. [CrossRef]
- Patton, M.Q. Qualitative Research & Evaluation Methods: Integrating Theory and Practice; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014.
- Anney, V.N. Ensuring the quality of the findings of qualitative research: Looking at trustworthiness criteria. J. Emerg. Trends Educ. Res. Policy Stud. 2014, 5, 272-281.
- Schryen, G. Writing qualitative is literature reviews-Guidelines for synthesis interpretation, and guidance of research. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2015, 37, 12. [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, J.M.; Buckles, D.J. Participatory Action Research: Theory and Methods for Engaged Inquiry; Routledge: London, UK, 2019.
- Hammersley, M.; Atkinson, P. Ethnography: Principles in Practice; Routledge: London, UK, 2019.
- Tracy, S.J. Qualitative Research Methods: Collecting Evidence, Crafting Analysis, Communicating Impact; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019.
- Hennink, M.; Hutter, I.; Bailey, A. Qualitative Research Methods; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2020.
- Enholm, I.M.; Papagiannidis, E.; Mikalef, P.; Krogstie, J. Artificial intelligence and business value: A literature review. Inf. Syst. Front. 2022, 24, 1709-1734. [CrossRef]
- Evans, N.; Miklosik, A.; Bosua, R.; Qureshi, M.A. Digital business transformation: An experience-based holistic framework. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 121930-121939. [CrossRef]
- Du, M. Strategic thinking in artificial intelligence and expert: Problem-solving and creativity. PsyArXiv 2023. [CrossRef]
- Subramonyam, H.; Im, J.; Seifert, C.; Adar, E. Solving separation-of-concerns problems in collaborative design of human-AI systems through leaky abstractions. In Proceedings of the 2022 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 29 April-5 May 2022; pp. 1-21.
- Usmani, U.A.; Happonen, A.; Watada, J. Human-centered artificial intelligence: Designing for user empowerment and ethical considerations. In Proceedings of the 2023 5th International Congress on Human-Computer Interaction 2023, Optimization and Robotic Applications (HORA), Istanbul, Turkey, 8-10 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1-5.
- Troussas, C.; Krouska, A.; Koliarakis, A.; Sgouropoulou, C. Harnessing the power of user-centric artificial intelligence: Customized recommendations and personalization in hybrid recommender systems. Computers 2023, 12, 109. [CrossRef]
- Marshall, L. Invention to Innovation: How Scientists Can Drive Our Economy; CSIRO Publishing: Clayton, Australia, 2023.
- Panesar, G.S.; Venkatesh, D.; Rakhra, M.; Jairath, K.; Shabaz, M. Agile software and business development using artificial intelligence. Ann. Rom. Soc. Cell Biol. 2021, 25, 1851-1857.
- Rosário, A.T.; Dias, J.C. Sustainability and the digital transition: A literature review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4072. [CrossRef]
- Bharadiya, J.P. Driving business growth with artificial intelligence and business intelligence. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2022, 6, 28-44.
- Campbell, C.; Sands, S.; Ferraro, C.; Tsao, H.J.; Mavrommatis, A. From data to action: How marketers can leverage AI. Bus. Horiz. 2020, 63, 227-243. [CrossRef]
- Ambasht, A. Real-time data integration and analytics: Empowering data-driven decision-making. Int. J. Comput. Trends Technol. 2023, 71, 8-14. [CrossRef]
- Latif, H. Advancing data integrity in banking: AI/ML solutions and best practices. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2023, 7, 185-203.
- Bharadiya, J.P. Machine learning and AI in business intelligence: Trends and opportunities. Int. J. Comput. (IJC) 2023, 48, 123-134.
- van de Wetering, R.; de Weerd-Nederhof, P.; Bagheri, S.; Bons, R. Architecting agility: Unraveling the impact of AI capability on organizational change and competitive advantage. In International Symposium on Business Modeling and Software Design; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 203-213.
- Burström, T.; Parida, V.; Lahti, T.; Wincent, J. AI-enabled business-model innovation and transformation in industrial ecosystems: A framework, model and outline for further research. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 127, 85-95. [CrossRef]
- Neeley, T.; Leonardi, P. Developing a digital mindset. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2022, 100, 50-55.
- Garcia, N.; Roberts, H. The power of sentiment analysis in product feedback. Data Insight Mon. 2020, 10, 45-53.
- Jensen, M.; Peters, L. Real-time product refinement: The AI approach. Digit. Bus. Q. 2021, 3, 12-25.
- Torres, M.; Lee, E. Proactive issue detection in AI-driven products. Tech. Evolve Mag. 2022, 11, 16-25.
- Pradhan, I.P.; Saxena, P. Reskilling workforce for the artificial intelligence age: Challenges and the way forward. In The Adoption and Effect of Artificial Intelligence on Human Resources Management, Part B; Emerald Publishing Limited: Bradford, UK, 2023; pp. 181-197.
- Beer, D. Envisioning the power of data analytics. Inf. Commun. Soc. 2018, 21, 465-479. [CrossRef]
- Kibria, M.G.; Nguyen, K.; Villardi, G.P.; Zhao, O.; Ishizu, K.; Kojima, F. Big data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence in next-generation wireless networks. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 32328-32338. [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, I.; Moloney, K.G.; Ross, J.W.; Fonstad, N.O.; Beath, C.M.; Mocker, M. How big old companies navigate digital transformation. MIS Q. Exec. 2017, 16, 6.
- Davenport, T.H.; Guha, A.; Grewal, D.; Bressgott, T. How AI will change the future of marketing. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2020, 48, 24-42. [CrossRef]
- Braun, A.; Garriga, G. Consumer journey analytics in the context of data privacy and ethics. In Digital Marketplaces Unleashed; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 663-674.
- Bughin, J. Artificial Intelligence, the Next Digital Frontier? McKinsey Global Institute: New York, NY, USA, 2018.
- Rathore, B. Predictive metamorphosis: Unveiling the fusion of AI-powered analytics in digital marketing revolution. Int. J. Transcont. Discov. 2020, 7, 15-24.
- Chase, C.W. Consumption-Based Forecasting and Planning: Predicting Changing Demand Patterns in the New Digital Economy; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021.
- Fayyad, U.; Piatetsky-Shapiro, G.; Smyth, P. From data mining to knowledge discovery: An overview. In Advances in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining; American Association for Artificial Intelligence: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; pp. 1-36.
- Siegel, E. Predictive Analytics: The Power to Predict Who Will Click, Buy, Lie, or Die; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016.
- Hisrich, R.D.; Soltanifar, M. Unleashing the creativity of entrepreneurs with digital technologies. In Digital Entrepreneurship: Impact on Business and Society; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 23-49.
- Veryzer, R.W., Jr. Discontinuous innovation and the new product development process. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 1998, 15, 304-321. [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Verma, S.; Lim, W.M.; Kumar, S.; Donthu, N. Personalization in personalized marketing: Trends and ways forward. Psychol. Mark. 2022, 39, 1529-1562. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Davis, A.; Ward, S. Predictive customization: AI’s role in personalized product evolution. AI Strategy J. 2020, 5, 11-20.
- Rafieian, O.; Yoganarasimhan, H. AI and personalization. In Artificial Intelligence in Marketing; Emerald Publishing Limited: Bradford, UK, 2023; pp. 77-102.
- Rainsberger, L. The modern customer-The PHANTOM. In The Modern Customer-the PHANTOM: Customers on the Run: How Sales Must Respond to Radically New Buying Behavior; Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2023; pp. 35-74.
- Peters, J.; Lee, F. Crowdsourcing in product development. Collab. Innov. 2020, 7, 18-26.
- Nash, A.; Ryan, B. Interconnected systems and the demand for seamless products. Digit. Ecosyst. J. 2021, 6, 29-37.
- Liu, M.; Roberts, T. Adaptive solutions in modern product design. Tech Evol. Rev. 2020, 11, 54-63.
- Kapoor, R.; Singh, J. Self-evolving systems in digital products. Glob. Tech Rev. 2019, 10, 75-84.
- Dash, S.; Shakyawar, S.K.; Sharma, M.; Kaushik, S. Big data in healthcare: Management, analysis and future prospects. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 54. [CrossRef]
- Asha, P.; Srivani, P.; Ahmed, A.A.A.; Kolhe, A.; Nomani, M.Z.M. Artificial intelligence in medical imaging: An analysis of innovative technique and its future promise. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 56, 2236-2239. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Gupta, M.; Bhatt, S.; Tosun, A.S. Detecting anomalous user behavior in remote patient monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 22nd International Conference on Information Reuse and Integration for Data Science (IRI), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 10-12 August 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 33-40.
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Dong, T. A review of wearable technologies for elderly care that can accurately track indoor position, recognize physical activities and monitor vital signs in real-time. Sensors 2017, 17, 341. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahuja, A.S. The impact of artificial intelligence in medicine on the future role of the physician. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7702. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsin, S.N.; Gapizov, A.; Ekhator, C.; Ain, N.U.; Ahmad, S.; Khan, M.; Barker, C.; Hussain, M.; Malineni, J.; Ramadhan, A.; et al. The role of artificial intelligence in prediction, risk stratification, and personalized treatment planning for congenital heart diseases. Cureus 2023, 15, e44374. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Saleh, S.; Liu, Y. A review on artificial intelligence in education. Acad. J. Interdiscip. Stud. 2021, 10, 206-217. [CrossRef]
- Goodell, J.W.; Kumar, S.; Lim, W.M.; Pattnaik, D. Artificial intelligence and machine learning in finance: Identifying foundations, themes, and research clusters from bibliometric analysis. J. Behav. Exp. Financ. 2021, 32, 100577. [CrossRef]
- Abad-Segura, E.; González-Zamar, M.-D.; López-Meneses, E.; Vázquez-Cano, E. Financial technology: Review of trends, approaches, and management. Mathematics 2020, 8, 951. [CrossRef]
- Patra, S.; Mahfouz, M.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Magazzeni, D.; Veloso, M. FinRDDL: Can AI planning be used for quantitative finance problems? In Proceedings of the ICAPS 2023, Prague, Czech Republic, 8-13 July 2023.
- Bao, Y.; Hilary, G.; Ke, B. Artificial intelligence and fraud detection. In Innovative Technology at the Interface of Finance and Operations: Volume I; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 223-247.
- Kunduru, A.R. Artificial intelligence advantages in cloud Fintech application security. Cent. Asian J. Math. Theory Comput. Sci. 2023, 4, 48-53.
- Bhargavi, C.; Sravanthi, M. Significant role of digital technology in detecting banking frauds in India. Int. J. Adv. Multidisc. Res. Stud. 2023, 3, 1124-1127.
- Zhao, L.; Naktnasukanjn, N.; Mu, L.; Liu, H.; Pan, H. Fundamental quantitative investment theory and technical system based on multi-factor models. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 20th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Perth, Australia, 25-28 July 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 521-526.
- Lee, W.J.; Wu, H.; Yun, H.; Kim, H.; Jun, M.B.G.; Sutherland, J.W. Predictive maintenance of machine tool systems using artificial intelligence techniques applied to machine condition data. Procedia CIRP 2019, 80, 506-511. [CrossRef]
- Go, T.; Moe, T.; Hirotsugu, G.; Yuuichi, N. Machine learning applied to sensor data analysis. Yokogawa Tech. Rep. 2016, 59, 27-30.
- Karthik, T.S.; Kamala, B. Cloud-based AI approach for predictive maintenance and failure prevention. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2054, 012014. [CrossRef]
- Samadi-Parviznejad, P. Development of a mathematical model of preventive maintenance by increasing reliability and reducing cost. Appl. Innov. Ind. Manag. 2021, 1, 8-18.
- Abduljabbar, R.; Dia, H.; Liyanage, S.; Bagloee, S.A. Applications of artificial intelligence in transport: An overview. Sustainability 2019, 11, 189. [CrossRef]
- Broekman, A.; Gräbe, P.J.; Wynand, J. Real-time traffic quantization using a mini edge artificial intelligence platform. Transp. Eng. 2021, 4, 100068. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Ma, X.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Wang, L.; Cao, W.-L.; Li, J.-X.; Tong, J. A new form of deep learning in smart logistics with IoT environment. J. Supercomput. 2022, 78, 11873-11894. [CrossRef]
- Guerra, A.; Amini, E.; Elefteriadou, L. A Computationally-Efficient Algorithm to Enable Joint Optimization of Connected Automated Vehicles’ Trajectories and Signal Phasing and Timing in Coordinated Arterials. 2023. Available online: https: / / papers.ssrn.com/sol3/ papers.cfm?abstract_id=4411134 (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Joseph, R.B.; Lakshmi, M.B.; Suresh, S.; Sunder, R. Innovative analysis of precision farming techniques with artificial intelligence. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd International Conference on Innovative Mechanisms for Industry Applications (ICIMIA), Bangalore, India, 5-7 March 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 353-358.
- Agrawal, N.; Agrawal, H. Artificial Intelligence-Intelligent Inputs Revolutionizing Agriculture. 2021. Available online: https: //www.niti.gov.in/sites/default/files/2021-09/IntelligentInputsRevolutionisingAgriculture.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Otieno, M. An extensive survey of smart agriculture technologies: Current security posture. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2023, 18, 1207-1231. [CrossRef]
- Leong, Y.M.; Lim, E.H.; Subri, N.F.B.; Jalil, N.B.A. Transforming agriculture: Navigating the challenges and embracing the opportunities of artificial intelligence of things. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Agrosystem Engineering 2023, Technology & Applications (AGRETA), Shah Alam, Malaysia, 9 September 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 142-147.
