DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40813-023-00352-8
PMID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38218966
تاريخ النشر: 2024-01-13
}
الملخص
الخلفية: تعتبر الانتفاخات السُرّية (UO) في الخنازير مصدر قلق من الناحية الرفاهية بسبب خطر القرحة والمضاعفات. تتطلب التشريعات الدنماركية أن يتم إيواء الخنازير التي تعاني من UOs أكبر في حظائر مريضة مع فرش ناعم، وقد لا تكون بعض خنازير UO مناسبة للنقل. بسبب ذلك، يتم قتل العديد من خنازير UO، مما يزيد من تكاليف إنتاج الخنازير. الانتشار الحقيقي لـ
الخلفية
يُشتبه في أن حالات UOs لها خلفية متعددة العوامل؛ حيث تم اقتراح كل من الخلفيات الوراثية والعدوى كفرضيات [4]، بالإضافة إلى أن التعامل مع الخنازير قد يكون له صلة (مثل كيفية رفع الخنازير الصغيرة).
الخنازير التي تعاني من UO تحتاج إلى إدارة إضافية؛ تتطلب التشريعات الدنماركية أن يتم حبس الخنازير التي تعاني من UO كبير في حظائر مخصصة للمرضى مع فرشة ناعمة، ويزداد خطر عدم صلاحية الخنازير المصابة بـ UO للنقل مقارنة بالخنازير التي لا تعاني من UO. يمكن الموافقة على نقل بعض الخنازير المصابة بـ UO إذا قدم طبيب البيطرة الخاص بالقطيع شهادة صلاحية للنقل وتم نقلها تحت ظروف خاصة، مما يزيد من التكاليف المرتبطة بالحفاظ على الخنازير المصابة بـ UO. لذلك، يتم إعدام نسبة عالية من الخنازير المصابة بـ UO، مما يساهم في زيادة معدل الوفيات، واقتصاد أضعف، واستدامة أقل لإنتاج الخنازير.
إن الانتشار الحقيقي لمرض UO في إنتاج الخنازير المكثف غير معروف. تشير الدراسات السابقة إلى انتشار متفاوت، وتكون المقارنات بين الدراسات صعبة لأن تعريفات UO تختلف بشكل كبير. قام سيرسي-برنال وغاردنر [4] بفحص 2958 خنزيرًا أسبوعيًا ووجدوا حدوثًا تراكميًا لـ
وجد يون وآخرون [7] حالات تتراوح بين 0.7 و
هدفت هذه الدراسة إلى الحصول على معرفة حول UOs في قطعان دنماركية مختلفة، وبناء أساس للمقارنة بين القطعان، وزيادة الفهم حول الحالة، والتي يمكن استخدامها في المستقبل لتوليد تدخلات وقائية جديدة. تم إجراء دراسة مقطعية مع ثلاثة أهداف:
النتائج
احتمالات أعلى
نقاش
| % |
|
الرضع | ||||
| جميع القطعان | قطيع بدون حظائر مريضة | قطيع مع أقلام مريضة | ||||
| ن قطيع | 30 | 30 | 23 | ٧ | ||
| N خنازير | 8052 | 19,684 | ١٤,٥١٥ | ٥١٦٩ | ||
| خنازير N UO | ٣٨٠ | 579 | ٤٧٣ | ١٠٦ | ||
| إجمالي UO | ٤.٢ | 2.9 | 3.2 | 2.1 | ||
| [كل] | [3.3-5.1] | [2.5-3.4] | [2.7-3.7] | [1.0-3.1] | ||
| الحد الأدنى – الحد الأقصى | 0.8-13.6 | 1.0-5.3 | 1.3-5.3 | 1.0-4.1 | ||
| يو | 63.6 | ٥٦.٩ | ٥٦.٨ | ٥٧.٥ | ||
| [كل] | [٥٦.٢-٧١.٠] | [51.3-62.6] | [51.2-62.4] | [٣٧.٣-٧٧.٧] | ||
| الحد الأدنى – الحد الأقصى | 25-100 | 25-92.9 | 25-84.6 | ٣٤.٨-٩٢.٩ | ||
| متوسط UO* | ٢٠.٧ | ٢٤.٢ | ٢٤.٩ | ٢٢ | ||
| [كل] | [14.9-26.6] | [20.0-28.4] | [20.4-29.4] | [8.9-35] | ||
| الحد الأدنى – الحد الأقصى | 0-50 | 0-42.9 | 0-41.67 | 0-42.9 | ||
| UO* كبير | 15.7 | 18.8 | 18.3 | ٢٠.٥ | ||
| [كل] | [10.7-20.6] | [14.1-23.6] | [13.5-23.1] | [3.5-37.6] | ||
| الحد الأدنى – الحد الأقصى | 0-40 | 0-43.8 | 0-43.75 | 0-42.9 | ||
نسبة إجمالي عدد UO
| جنس | الخنازير الصغيرة ن (%) | الرضع ن (%) | ||
| نعم UO | إجمالي الخنازير | نعم UO | إجمالي الخنازير | |
| ذكر | 153 (40.3) | 3976 (49.4) | 231 (39.9) | 677(3.4) |
| أنثى | 226 (59.5) | 3944 (49) | ٣٤٧ (٥٩.٩) | 645 (3.3) |
| غير متوفر | 1 (0.3) | ١٣٢ (١.٦) | 1 (0.2) | 18,362 (93.3) * |
| إجمالي | ٣٨٠ (١٠٠) | 8052 | 579 (100) | 19,684 |
غير متوفر
انتشار الملاحظة في عيّنتنا العشوائية. العديد من القطيع، بما في ذلك القطعان المشاركة في هذه الدراسة، تقوم بشكل روتيني بقتل الخنازير التي تعاني من UO. قد تؤدي المشاركة الطوعية في الدراسة إلى تفضيل القطعان الأكثر تأثراً بالانتفاخات أو تجعل القطعان التي تواجه مشاكل أكثر احتمالاً لرفض المشاركة، وهو تحيز آخر.
أكدت الدراسة توقعاتنا السابقة بوجود اختلافات بين القطيع ومستوى عام يقارب ثلاثة في المئة من UOs في الخنازير الصغيرة، كما أظهرت مستوى أعلى من UOs في الخنازير الصغيرة. خاصة في وحدة الولادة، كانت الانتشار متفاوتة بين القطعان. ومع ذلك، لا يمكننا تحديد ما الذي تسبب في هذه الاختلافات، ومن الممكن أن يكون التفسير هو اختلاف الفطام.
تتراوح الأعمار بين القطيع وبالتالي تكون السرة أكثر أو أقل شفاءً/ ملتهبة والتورمات المتزامنة. نعلم من دراسات أخرى أن الأورام قد تختفي/ تظهر مع نمو الخنازير [6، 9، 10] مما يؤثر على انتشارها الملحوظ.
| خنازير صغيرة جميع القطعان | الفطام | |||||
| جميع القطعان | قطيع بدون حظائر مريضة | قطيع مع حظائر مريضة | الخنازير في حظائر المرض | |||
| قابل للاختزال | ن قطيع | 30 | 30 | 23 | ٧ | ٧ |
| N خنازير | 8052 | ١٩٦٨٤ | ١٤,٥١٥ | ٥١٦٩ | 554 | |
| خنازير N UO | ٣٨٠ | 579 | 473 | ١٠٦ | ١٧٦ | |
| قرحات ن | ٤ | 69 | 60 | 9 | 30 | |
| نعم، % | ٣٢.٣ | 21 | ٢٠.٠ | ٢٤.٢ | 18.1 | |
| [كل] | [24.2-40.4] | [15.9-26.1] | [13.8-26.2] | [13.6-34.8] | [5.0-31.2] | |
| مين-ماكس | 0-70.6 | 0-50 | 0-50 | 11.1-42.9 | 6.2-47.1 | |
| جزئيًا، % | 10.7 | 13.3 | 13.4 | ١٣.٢ | 19.2 | |
| [كل] | [5.2-16.1] | [9.6-17.1] | [9.0-17.8] | [3.8-22.7] | [13.4-25.0] | |
| مين-ماكس | 0-50 | 0-35.7 | 0-35.7 | 0-28.6 | 12.5-29.4 | |
| لا، % | 57 | 65.7 | 66.7 | 62.6 | 62.7 | |
|
|
[٤٨.٠-٦٦.٠] | [60.0-71.7] | [60.2-73.2] | [٤٤.٦-٨٠.٦] | [٤٤.٨-٨٠.٧] | |
| مين-ماكس | 12.5-100 | 28.6-100 | 41.7-100 | ٢٨.٦-٨١.٨ | ٢٣.٥-٨١.٢ | |
| ملمس | ناعم، % | ٥٦.٥ | ٤٨ | ٤٦.٥ | 53.1 | ٥٦.٨ |
| [كل] | [٤٦.٣-٦٦.٦] | [٤١.٨-٥٤.٢] | [٤٠.٥-٥٢.٥] | [30.8-75.3] | [٣٦.٣-٧٧.٤] | |
| مين-ماكس | 0-100 | 9.1-85.7 | 9.1-66.7 | 18.2-85.7 | 25-87.5 | |
| خلط، % | 1.7 | 7.4 | 7.11 | 8.5 | 9.4 | |
| [كل] | [0.3-3.0] | [4.8-10.0] | [4.0-10.3] | [2.9-14.0] | [0-22.2] | |
| مين-ماكس | 0-13.3 | 0-27.3 | 0-27.3 | 0-14.3 | 0-37.5 | |
| صعب، % | ٤٠.٧ | ٤٣.٥ | ٤٥.١ | ٣٨.٥ | ٣٣.٨ | |
| [كل] | [30.4-51.0] | [٣٦.٦-٥٠.٥] | [٣٨.١-٥٢.١] | [14.1-62.8] | [15.9-51.8] | |
| مين-ماكس | 0-100 | 0-81.8 | ٢٢.٧-٨١.٨ | 0-72.7 | 11.8-66.7 | |
| غير متوفر، % | 1.2 | 1 | 1.3 | 0 | 0 | |
| [كل] | [0-2.9] | [0-2.3] | [0-3] | |||
| مين-ماكس | 0-25 | 0-16.7 | 0-16.7 | |||
| قرحة | نعم، % | 0.7 | 12.5 | 12.6 | 12.4 | 15.2 |
| [كل] | [0-1.5] | [7.9-17.2] | [8.4-16.8] | [0-30.9] | [7.1-23.4] | |
| مين-ماكس | 0-10.5 | 0-57.1 | 0-33.3 | 0-57.1 | 0-25 | |
| لا، % | 98.9 | 86.7 | 87.0 | 85.8 | 84.6 | |
| [كل] | [97.9-99.9] | [82.0-91.3] | [82.7-91.2] | [67.6-100] | [76.4-92.8] | |
| مين-ماكس | 89.5-100 | 42-100 | 66.7-100 | 42.9-100 | 75-100 | |
| غير متوفر، % | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.48 | 1.8 | 0.2 | |
| [كل] | [0-1.0] | [0.1-1.5] | [0-1.1] | [0-4.8] | [0-0.5] | |
| مين-ماكس | 0-8.3 | 0-7.1 | 0-5.1 | 0-7.1 | 0-1.1 | |
| حجم القرحة | صغير، % | * | ٢٢.٧ | ٢٣.٤ | 20 | ٣٣.٩ |
| [كل] | [8.3-37.1] | [7.8-39] | [0-75.5] | [0-78.2] | ||
| مين-ماكس | 0-100 | 0-100 | 0-100 | 0-100 | ||
| متوسط، % | * | 54.3 | ٥٩.٣ | ٣٥ | ٥٧ | |
| [كل] | [٣٧.٧-٧٠.٨] | [٤١.٨-٧٦.٨] | [0-95.5] | [15.5-98.5] | ||
| مين-ماكس | 0-100 | 0-100 | 0-100 | 0-100 | ||
| كبير، % | * | 19.2 | 12.5 | ٤٥ | ٣.٥ | |
| [كل] | [6.2-32.3] | [2.8-22] | [0-100] | [0-12.5] | ||
| مين-ماكس | 0-33.3 | 0-50 | 0-100 | 0-33.3 | ||
| غير متوفر، % | * | 3.8 | ٤.٨ | 0 | ٥.٦ | |
|
|
[0-8.2] | [0-10.4] | [0-19.8] | |||
| مين-ماكس | 0-33.3 | 0-33.3 | 0-33 | |||
| متغير | أحادي المتغير | متعدد المتغيرات | ||||
| مستوى | OR (فاصل الثقة 95%) | قيمة P | مستوى | OR (فاصل الثقة 95%) | قيمة P | |
| فئة الحجم UO | صغير | 1 | صغير | 1 | ||
| متوسط | 3.8 (2.1-7.2) | < 0.001 | وسيط | 3.8 (2.0-7.2) | < 0.001 | |
| كبير | 9.7 (5.6-17.7) | < 0.001 | كبير | 9.9 (5.6-18.4) | <0.001 | |
| قابلية الاختزال | نعم | 1 | نعم | 1 | ||
| جزئيًا | 2.7 (1.2-6.3) | 0.0143 | جزئي/ لا | 2.4 (1.2-5.2) | 0.017 | |
| لا | 1.9 (1-4.1) | 0.0628 | – | – | ||
| ملمس UO | ناعم | 1 | ناعم | 1 | ||
| مزيج | 2 (0.9-4.1 | 0.0826 | خلط/ صعب | 0.8 (0.3-1.7) | 0.087 | |
| صعب | 2.2 (1.4-3.6) | < 0.001 | – | – | ||
الاستنتاجات
احتمال آخر هو استكشاف استخدام حلول الذبح المتنقلة. معالجة الخنازير مباشرة في المزرعة ستجنبها ضغط النقل، وتقلل من عدد الخنازير المهدرة، مما يجعل إنتاج الخنازير أكثر استدامة وإنسانية.
طرق
تصميم الدراسة
حجم العينة
استنادًا إلى الأدبيات، تم تحديد انتشار الفتق المفترض (P) إلى
اختيار القطعان والخنازير
| فئة الفتق السري | فئة حجم القرحة | |||||
| صغير | متوسط | كبير | صغير | متوسط | كبير | |
| خنازير صغيرة | 4 سم |
|
|
2 سم |
|
|
| خنازير صغيرة |
|
|
|
|
|
|
الخنازير المسجلة بنفس رقم CHR، وأن تكون ضمن مسافة ثلاث ساعات بالسيارة من كوبنهاغن. ثانيًا، يجب أن تستخدم القطعان إما Danbred أو Danish Genetics وأن تحتفظ بالخنازير طوال فترة الحضانة. كان يجب أن تكون الخنازير هجينة بين Landrace/Yorkshire/Duroc.
كانت عينة الدراسة هي الخنازير الصغيرة خلال أسبوع واحد قبل الفطام والخنازير المفطومة بين ثلاثة وثمانية أسابيع بعد الفطام. تم اختيار الخنازير على مستوى الحظيرة وتم إخضاع جميع الخنازير في الحظائر المختارة لفحص سريري. تم فحص كل
الفحص السريري
تم فحص الخنازير الصغيرة بواسطة فنيين مدربين الذين قاموا بتحسس منطقة البطن لجميع الخنازير. تم وضع علامة رذاذ على كل خنزير به شذوذ أو انتفاخ أو عدم يقين؛ ونتيجة لذلك، تم فحص الخنازير الصغيرة المشتبه بها فقط من قبل الطبيب البيطري وتم تسجيل الجنس. تم تثبيت الخنازير المعلّمة باستخدام لوحة تجميع ضد زاوية الحظيرة وتم فحصها وهي واقفة. واحد
التحليل الإحصائي
الشكر والتقدير
مساهمات المؤلفين
التمويل
توفر البيانات والمواد
الإعلانات
موافقة الأخلاقيات والموافقة على المشاركة
رقم AEIRB المعين: 2022-03-PNH-007A.
وافق جميع المزارعين الثلاثين على المشاركة في الدراسة.
الموافقة على النشر
المصالح المتنافسة
تم النشر عبر الإنترنت: 13 يناير 2024
References
- Straw B, Bates R, May G. Anatomical abnormalities in a group of finishing pigs: prevalence and pig performance. J Swine Health Prod. 2009;17:28-31.
- Andersen EO, Spangsberg R, Pedersen K, Barington K, Jensen HE. Umbilical Hernia and Differential Diagnoses in Slaughter Pigs | IVIS. Proceedings of the 23rd IPVS Congress, Cancun, Mexico. 2014. https://www.ivis.org/ library/ipvs/ipvs-biennial-international-congress-mexico-2014/umbilical-hernia-and-differential
- Schild SLA, Brandt P, Rousing T, Herskin MS. Does the presence of umbilical outpouchings affect the behaviour of pigs during the day of slaughter? Livest Sci. 2015;176:146-51.
- Searcy-Bernal R, Gardner IA. Effects of and factors associated with umbilical hernias in a swine herd. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1994;204:1660-4.
- The Danish Animal Welfare Council. Udtalelse af 2. december 2008 om svin med store_komplicerede navle-eller lyskebrok. 2008. https://detve tsund.dk/generelle-udtalelser/udtalelse/nyhed/udtalelse-af-2-december-2008-om-svin-med-storekomplicerede-navle-eller-lyskebrok
- Mattsson P, Johansson G, Mattsson B. Pigrapport nr 53 Januari 2013 SAMMANFATTNING. 2013 [cited 2021 Dec 10]. www.svenskapig.se
- Yun J, Olkkola S, Hänninen M-L, Oliviero C, Heinonen M. The effects of amoxicillin treatment of newborn piglets on the prevalence of hernias and abscesses, growth and ampicillin resistance of intestinal coliform bacteria in weaned pigs. PLoS One. 2017;12. www.zoonoosikeskus.fi
- Danish Crown DCV 18940 RD. Raised without antibiotics. [cited 2023 Aug 17]. https://www.danishcrown.com/en-gb/our-brands/pure-pork
- Hovmand-Hansen T, Nielsen SS, Jensen TB, Vestergaard K, Nielsen MBF, Jensen HE. Survival of pigs with different characteristics of umbilical outpouching in a prospective cohort study of Danish pigs. Prev Vet Med. 2021;191: 105343.
- Larsen I, Baekbo P, Nielsen JP. Umbilical Outpouchings in two Danish herds raising pigs with minimal use of antibiotics-Results from a field trial evaluating the efficacy of autogenous vaccines and iodine application. Prev Vet Med. 2023;214:105905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prevetmed. 2023.105905.
- Hovmand-Hansen T, Jensen TB, Vestergaard K, Nielsen MBF, Leifsson PS, Jensen HE. Early risk factors, development, disappearance and contents of umbilical outpouching in Danish pigs. Livest Sci. 2021;251: 104654.
- Petersen HH, Nielsen EO, Hassing AG, Ersbøll AK, Nielsen JP. Prevalence of clinical signs of disease in Danish finisher pigs. Vet Rec. 2008;162:377-82.
- Danish Agriculture and Food Council. STATISTICS 2022 Pigmeat. 2023. https://lf.dk/tal-og-analyser/statistik/svin/statistik-svin/statistik-gris-2022
- Houe H, Kjær Ersbøl A, Toft N. Introduction to veterinary epidemiology. 1st. ed. Frederiksberg C: Biofolia; 2004.
- Urbaniak GC, Plous S. Research Randomizer. 2013 [cited 2022 Jun 8]. https://randomizer.org/about/
- Posit Team PSP. R Studio: Integrated Development Environment for R. Boston, MA; 2023 [cited 2023 Jun 23]. http://www.posit.co/
- Wickham H, Averick M, Bryan J, Chang W, McGowan L, François R, et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J Open Source Softw. 2019;4:1686.
ملاحظة الناشر
هل أنت مستعد لتقديم بحثك؟ اختر BMC واستفد من:
- تقديم سريع ومريح عبر الإنترنت
- مراجعة دقيقة من قبل باحثين ذوي خبرة في مجالك
- نشر سريع عند القبول
- دعم لبيانات البحث، بما في ذلك أنواع البيانات الكبيرة والمعقدة
- الوصول المفتوح الذهبي الذي يعزز التعاون الأوسع وزيادة الاقتباسات
- أقصى رؤية لبحثك: أكثر من 100 مليون مشاهدة لموقع الويب سنويًا
في BMC، البحث دائمًا قيد التقدم.
- BMC
- *المراسلة:
ماري-لويز هانسن
mleh@sund.ku.dk
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40813-023-00352-8
PMID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38218966
Publication Date: 2024-01-13
}
Abstract
Background Umbilical outpouchings (UO) in pigs present a welfare concern because of ulceration risk and complications. Danish legislation requires pigs with larger UOs to be housed in sick pens with soft bedding, and some UO pigs might not be suited for transport. Because of this, many UO pigs are euthanized, adding to the costs of pig production. The true prevalence of
Background
UOs are suspected to have a multifactorial background; Both genetic as well as infectious backgrounds have been suggested as hypotheses [4], as well as the handling of pigs might be relevant (e.g. how the piglets are lifted).
Pigs with UO need extra management; Danish legislation requires pigs with large UO to be stabled in sick pens with soft bedding, and the risk of UO pigs being unfit for transport is increased compared to pigs without UO [5]. Some of the UO pigs can be approved for transport if the herd veterinarian provides them with a transport fitness certificate and they are transported under special conditions, which adds costs for keeping UO pigs. Therefore, a high proportion of UO pigs are euthanized, contributing to increased mortality, a poorer economy, and reduced sustainability for pig production.
The true prevalence of UO in intensive pig production is unknown. Earlier studies report varying prevalences and comparisons between studies are difficult because the definitions of UO vary considerably. Searcy-Bernal and Gardner [4] examined 2958 pigs weekly and found a cumulative incidence of
Yun et al. [7] found occurrences between 0.7 and
This study aimed to obtain knowledge about UOs in different Danish herds, build a foundation for benchmarking between herds, and add to an increasing understanding of the condition, which in the future can be used to generate new preventive interventions. A crosssectional study was performed with three objectives:
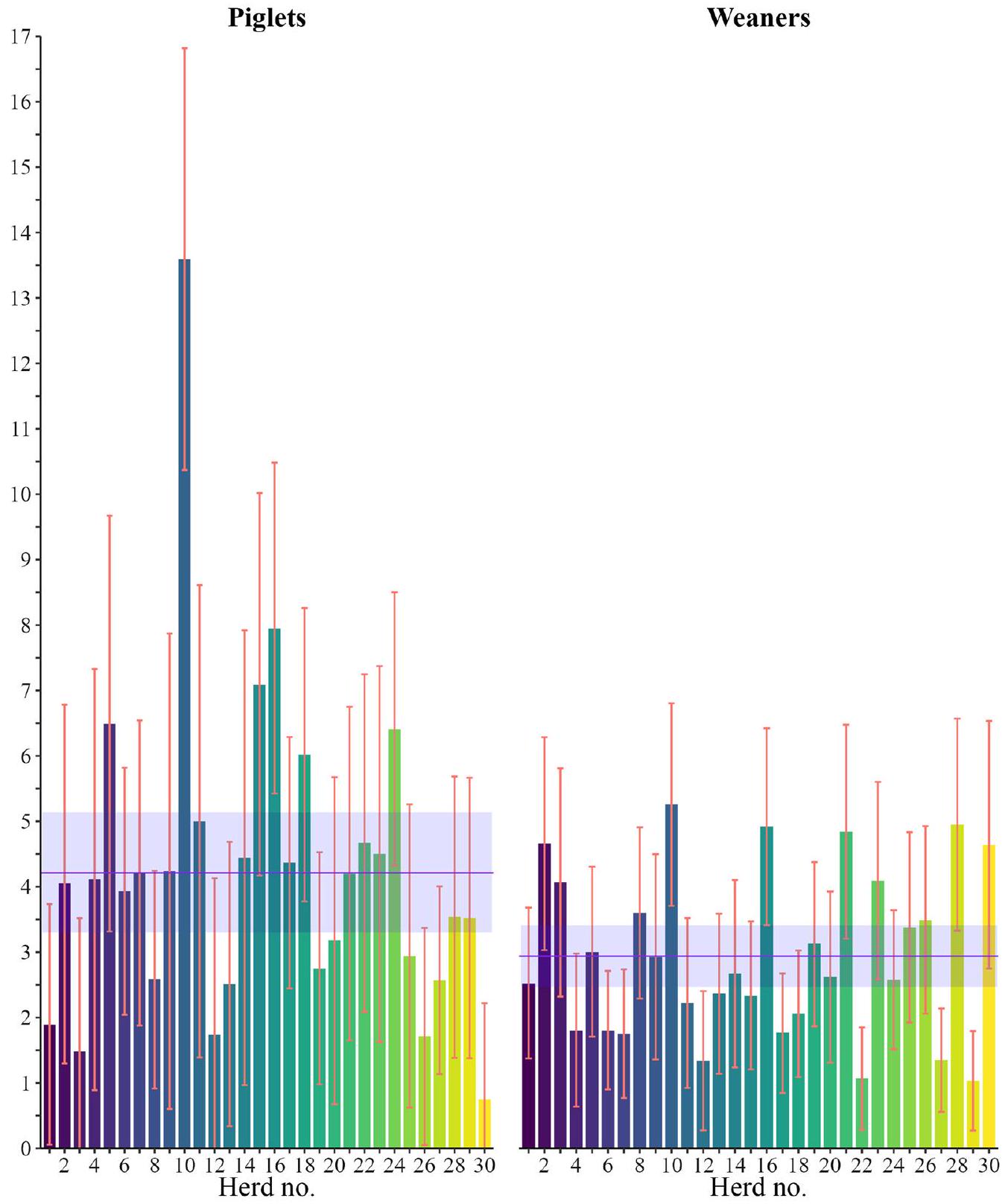
Results

higher odds (
Discussion
| % |
|
Weaners | ||||
| All herds | Herds without sick pens | Herds with sick pens | ||||
| N herds | 30 | 30 | 23 | 7 | ||
| N pigs | 8052 | 19,684 | 14,515 | 5169 | ||
| N UO pigs | 380 | 579 | 473 | 106 | ||
| Total UO | 4.2 | 2.9 | 3.2 | 2.1 | ||
| [Cl] | [3.3-5.1] | [2.5-3.4] | [2.7-3.7] | [1.0-3.1] | ||
| Min-max | 0.8-13.6 | 1.0-5.3 | 1.3-5.3 | 1.0-4.1 | ||
| Small UO* | 63.6 | 56.9 | 56.8 | 57.5 | ||
| [Cl] | [56.2-71.0] | [51.3-62.6] | [51.2-62.4] | [37.3-77.7] | ||
| Min-max | 25-100 | 25-92.9 | 25-84.6 | 34.8-92.9 | ||
| Medium UO* | 20.7 | 24.2 | 24.9 | 22 | ||
| [Cl] | [14.9-26.6] | [20.0-28.4] | [20.4-29.4] | [8.9-35] | ||
| Min-max | 0-50 | 0-42.9 | 0-41.67 | 0-42.9 | ||
| Large UO* | 15.7 | 18.8 | 18.3 | 20.5 | ||
| [Cl] | [10.7-20.6] | [14.1-23.6] | [13.5-23.1] | [3.5-37.6] | ||
| Min-max | 0-40 | 0-43.8 | 0-43.75 | 0-42.9 | ||
*Percentage of the total number of UO
| Sex | Piglets N (%) | Weaners N (%) | ||
| UO yes | Pigs total | UO yes | Pigs total | |
| Male | 153 (40.3) | 3976 (49.4) | 231 (39.9) | 677(3.4) |
| Female | 226 (59.5) | 3944 (49) | 347 (59.9) | 645 (3.3) |
| NA | 1 (0.3) | 132 (1.6) | 1 (0.2) | 18,362 (93.3) * |
| Total | 380 (100) | 8052 | 579 (100) | 19,684 |
NA: Not available
observed prevalence in our random sample. Many herds, including herds participating in this study, routinely euthanize pigs with UO. The study’s voluntary participation could favour herds more affected by outpouchings or make herds with problems more likely to decline to take part, which is another bias.
The study confirmed our prior expectation of differences between herds and a general level of approximately three percent UOs in the weaners, it also showed a higher level of UOs in the piglets. Especially in the farrowing unit, the prevalence varied between the herds. We cannot, however, tell what caused the differences, a possible explanation is different weaning
ages between the herds and as such more or less healed/ inflamed umbilici and concurrent swellings. We know from other studies that UOs might disappear/ appear as the pigs grow [6, 9, 10] thereby affecting the observed prevalence.
| Piglets All herds | Weaners | |||||
| All herds | Herds without sick pens | Herds with sick pens | Pigs in sick pens | |||
| Reducible | N herds | 30 | 30 | 23 | 7 | 7 |
| N pigs | 8052 | 19,684 | 14,515 | 5169 | 554 | |
| N UO pigs | 380 | 579 | 473 | 106 | 176 | |
| N ulcers | 4 | 69 | 60 | 9 | 30 | |
| Yes, % | 32.3 | 21 | 20.0 | 24.2 | 18.1 | |
| [Cl] | [24.2-40.4] | [15.9-26.1] | [13.8-26.2] | [13.6-34.8] | [5.0-31.2] | |
| Min-Max | 0-70.6 | 0-50 | 0-50 | 11.1-42.9 | 6.2-47.1 | |
| Partly, % | 10.7 | 13.3 | 13.4 | 13.2 | 19.2 | |
| [Cl] | [5.2-16.1] | [9.6-17.1] | [9.0-17.8] | [3.8-22.7] | [13.4-25.0] | |
| Min-Max | 0-50 | 0-35.7 | 0-35.7 | 0-28.6 | 12.5-29.4 | |
| No, % | 57 | 65.7 | 66.7 | 62.6 | 62.7 | |
|
|
[48.0-66.0] | [60.0-71.7] | [60.2-73.2] | [44.6-80.6] | [44.8-80.7] | |
| Min-Max | 12.5-100 | 28.6-100 | 41.7-100 | 28.6-81.8 | 23.5-81.2 | |
| Texture | Soft, % | 56.5 | 48 | 46.5 | 53.1 | 56.8 |
| [Cl] | [46.3-66.6] | [41.8-54.2] | [40.5-52.5] | [30.8-75.3] | [36.3-77.4] | |
| Min-Max | 0-100 | 9.1-85.7 | 9.1-66.7 | 18.2-85.7 | 25-87.5 | |
| Mix, % | 1.7 | 7.4 | 7.11 | 8.5 | 9.4 | |
| [Cl] | [0.3-3.0] | [4.8-10.0] | [4.0-10.3] | [2.9-14.0] | [0-22.2] | |
| Min-Max | 0-13.3 | 0-27.3 | 0-27.3 | 0-14.3 | 0-37.5 | |
| Hard, % | 40.7 | 43.5 | 45.1 | 38.5 | 33.8 | |
| [Cl] | [30.4-51.0] | [36.6-50.5] | [38.1-52.1] | [14.1-62.8] | [15.9-51.8] | |
| Min-Max | 0-100 | 0-81.8 | 22.7-81.8 | 0-72.7 | 11.8-66.7 | |
| NA, % | 1.2 | 1 | 1.3 | 0 | 0 | |
| [Cl] | [0-2.9] | [0-2.3] | [0-3] | |||
| Min-Max | 0-25 | 0-16.7 | 0-16.7 | |||
| Ulcer | Yes, % | 0.7 | 12.5 | 12.6 | 12.4 | 15.2 |
| [Cl] | [0-1.5] | [7.9-17.2] | [8.4-16.8] | [0-30.9] | [7.1-23.4] | |
| Min-Max | 0-10.5 | 0-57.1 | 0-33.3 | 0-57.1 | 0-25 | |
| No, % | 98.9 | 86.7 | 87.0 | 85.8 | 84.6 | |
| [Cl] | [97.9-99.9] | [82.0-91.3] | [82.7-91.2] | [67.6-100] | [76.4-92.8] | |
| Min-Max | 89.5-100 | 42-100 | 66.7-100 | 42.9-100 | 75-100 | |
| NA, % | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.48 | 1.8 | 0.2 | |
| [Cl] | [0-1.0] | [0.1-1.5] | [0-1.1] | [0-4.8] | [0-0.5] | |
| Min-Max | 0-8.3 | 0-7.1 | 0-5.1 | 0-7.1 | 0-1.1 | |
| Ulcer size | Small, % | * | 22.7 | 23.4 | 20 | 33.9 |
| [Cl] | [8.3-37.1] | [7.8-39] | [0-75.5] | [0-78.2] | ||
| Min-Max | 0-100 | 0-100 | 0-100 | 0-100 | ||
| Medium, % | * | 54.3 | 59.3 | 35 | 57 | |
| [Cl] | [37.7-70.8] | [41.8-76.8] | [0-95.5] | [15.5-98.5] | ||
| Min-Max | 0-100 | 0-100 | 0-100 | 0-100 | ||
| Large, % | * | 19.2 | 12.5 | 45 | 3.5 | |
| [Cl] | [6.2-32.3] | [2.8-22] | [0-100] | [0-12.5] | ||
| Min-Max | 0-33.3 | 0-50 | 0-100 | 0-33.3 | ||
| NA, % | * | 3.8 | 4.8 | 0 | 5.6 | |
|
|
[0-8.2] | [0-10.4] | [0-19.8] | |||
| Min-Max | 0-33.3 | 0-33.3 | 0-33 | |||
| Variable | Univariable | Multivariable | ||||
| Level | OR(95% CI) | P value | Level | OR(95% CI) | P value | |
| Size category UO | Small | 1 | Small | 1 | ||
| Medium | 3.8 (2.1-7.2) | < 0.001 | Medium | 3.8 (2.0-7.2) | < 0.001 | |
| Large | 9.7 (5.6-17.7) | < 0.001 | Large | 9.9 (5.6-18.4) | <0.001 | |
| Reducibility | Yes | 1 | Yes | 1 | ||
| Partly | 2.7 (1.2-6.3) | 0.0143 | Partly/ no | 2.4 (1.2-5.2) | 0.017 | |
| No | 1.9 (1-4.1) | 0.0628 | – | – | ||
| Texture UO | Soft | 1 | Soft | 1 | ||
| Mix | 2 (0.9-4.1 | 0.0826 | Mix/ hard | 0.8 (0.3-1.7) | 0.087 | |
| Hard | 2.2 (1.4-3.6) | < 0.001 | – | – | ||
Conclusions
Another possibility is exploring the utilisation of mobile slaughter solutions. Processing the pigs directly at the farm would spare them the stress of transport, and minimize the number of wasted pigs, thereby making pig production more sustainable and humane.
Methods
Study design
Sample size
Based on the literature a presumed UO prevalence (P) was set to
Selection of herds and pigs
| Umbilical outpouching category | Ulcer size category | |||||
| Small | Medium | Large | Small | Medium | Large | |
| Piglets | 4 cm |
|
|
2 cm |
|
|
| Weaners |
|
|
|
|
|
|
pigs registered on the same CHR number, and being within a three-hour drive from Copenhagen. Secondly, herds should use either Danbred or Danish Genetics and keep pigs for the entire nursery period. Pigs had to be crossbreds between Landrace/ Yorkshire/Duroc.
The study population was piglets within one week before weaning and weaned pigs between three and eight weeks after weaning. Pigs were selected at pen level and all pigs in selected pens were subjected to clinical examination. Every
Clinical examination
The weaners were screened by trained technicians who palpated the abdominal area of all pigs. Every pig with an abnormality, bulge, or uncertainty was spray-marked by the technicians; as a result, only weaners with suspected outpouchings were examined by the vet and had sex recorded. Marked pigs were fixated with a herding board against a corner of the pen and examined standing. One
Statistical analysis
Acknowledgements
Author contributions
Funding
Availability of data and materials
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Assigned AEIRB Number: 2022-03-PNH-007A.
All 30 farmers consented to participate in the study.
Consent for publication
Competing interests
Published online: 13 January 2024
References
- Straw B, Bates R, May G. Anatomical abnormalities in a group of finishing pigs: prevalence and pig performance. J Swine Health Prod. 2009;17:28-31.
- Andersen EO, Spangsberg R, Pedersen K, Barington K, Jensen HE. Umbilical Hernia and Differential Diagnoses in Slaughter Pigs | IVIS. Proceedings of the 23rd IPVS Congress, Cancun, Mexico. 2014. https://www.ivis.org/ library/ipvs/ipvs-biennial-international-congress-mexico-2014/umbilical-hernia-and-differential
- Schild SLA, Brandt P, Rousing T, Herskin MS. Does the presence of umbilical outpouchings affect the behaviour of pigs during the day of slaughter? Livest Sci. 2015;176:146-51.
- Searcy-Bernal R, Gardner IA. Effects of and factors associated with umbilical hernias in a swine herd. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1994;204:1660-4.
- The Danish Animal Welfare Council. Udtalelse af 2. december 2008 om svin med store_komplicerede navle-eller lyskebrok. 2008. https://detve tsund.dk/generelle-udtalelser/udtalelse/nyhed/udtalelse-af-2-december-2008-om-svin-med-storekomplicerede-navle-eller-lyskebrok
- Mattsson P, Johansson G, Mattsson B. Pigrapport nr 53 Januari 2013 SAMMANFATTNING. 2013 [cited 2021 Dec 10]. www.svenskapig.se
- Yun J, Olkkola S, Hänninen M-L, Oliviero C, Heinonen M. The effects of amoxicillin treatment of newborn piglets on the prevalence of hernias and abscesses, growth and ampicillin resistance of intestinal coliform bacteria in weaned pigs. PLoS One. 2017;12. www.zoonoosikeskus.fi
- Danish Crown DCV 18940 RD. Raised without antibiotics. [cited 2023 Aug 17]. https://www.danishcrown.com/en-gb/our-brands/pure-pork
- Hovmand-Hansen T, Nielsen SS, Jensen TB, Vestergaard K, Nielsen MBF, Jensen HE. Survival of pigs with different characteristics of umbilical outpouching in a prospective cohort study of Danish pigs. Prev Vet Med. 2021;191: 105343.
- Larsen I, Baekbo P, Nielsen JP. Umbilical Outpouchings in two Danish herds raising pigs with minimal use of antibiotics-Results from a field trial evaluating the efficacy of autogenous vaccines and iodine application. Prev Vet Med. 2023;214:105905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prevetmed. 2023.105905.
- Hovmand-Hansen T, Jensen TB, Vestergaard K, Nielsen MBF, Leifsson PS, Jensen HE. Early risk factors, development, disappearance and contents of umbilical outpouching in Danish pigs. Livest Sci. 2021;251: 104654.
- Petersen HH, Nielsen EO, Hassing AG, Ersbøll AK, Nielsen JP. Prevalence of clinical signs of disease in Danish finisher pigs. Vet Rec. 2008;162:377-82.
- Danish Agriculture and Food Council. STATISTICS 2022 Pigmeat. 2023. https://lf.dk/tal-og-analyser/statistik/svin/statistik-svin/statistik-gris-2022
- Houe H, Kjær Ersbøl A, Toft N. Introduction to veterinary epidemiology. 1st. ed. Frederiksberg C: Biofolia; 2004.
- Urbaniak GC, Plous S. Research Randomizer. 2013 [cited 2022 Jun 8]. https://randomizer.org/about/
- Posit Team PSP. R Studio: Integrated Development Environment for R. Boston, MA; 2023 [cited 2023 Jun 23]. http://www.posit.co/
- Wickham H, Averick M, Bryan J, Chang W, McGowan L, François R, et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J Open Source Softw. 2019;4:1686.
Publisher’s Note
Ready to submit your research? Choose BMC and benefit from:
- fast, convenient online submission
- thorough peer review by experienced researchers in your field
- rapid publication on acceptance
- support for research data, including large and complex data types
- gold Open Access which fosters wider collaboration and increased citations
- maximum visibility for your research: over 100 M website views per year
At BMC, research is always in progress.
- BMC
- *Correspondence:
Marie-Louise Hansen
mleh@sund.ku.dk
