DOI: https://doi.org/10.36948/ijfmr.2025.v07i01.35488
تاريخ النشر: 2025-01-19
تآزر الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي والبيانات الضخمة في المخاطر المالية: مراجعة للتطورات الحديثة
الملخص
تقدم هذه الورقة مراجعة شاملة لأحدث التطورات في الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي والبيانات الضخمة مع تطبيقات في المالية. عام 2025 هو عام الذكاء الاصطناعي الوكالي، مما يمثل تحولًا محوريًا في الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي (Gen AI) ودمجه مع البيانات الضخمة. تستكشف هذه الورقة التآزر بين Gen AI والبيانات الضخمة، لا سيما في إدارة المخاطر المالية، مقترحة استراتيجيات للتكامل الأعمق. من خلال الاستشهاد بأحدث الأوراق البيضاء والتركيز على التطورات خلال العامين الماضيين، نوسع نطاق البحث في هذا المجال التحويلي. تظهر التطورات الأخيرة في Gen AI، مثل GPT-4 وVAE-GANs وهياكل الذكاء الاصطناعي القابلة للتفسير، تحسينات كبيرة، بما في ذلك
1. المقدمة
تقدم هذه الورقة مراجعة شاملة لأحدث التطورات في البيانات الضخمة وGen AI، مع تركيز خاص على تطبيقاتها في إدارة المخاطر المالية. من خلال استكشاف الخلفية والسياق لهذه الابتكارات، نوضح كيف يمكن لقدراتها المشتركة تحسين تطوير النماذج واتخاذ القرار في المؤسسات المالية. علاوة على ذلك، تقدم هذه العمل رؤى قابلة للتنفيذ للجهات التنظيمية المالية والمشاركين في السوق، بهدف تعزيز الكفاءة العامة والمتانة للأنظمة المالية مع تقليل المخاطر.
محرك رئيسي لهذا الابتكار هو الفرصة للاستفادة من البنى التحتية الحالية بشكل أكثر فعالية. غالبًا ما تمتلك المنظمات موارد حاسوبية غير مستخدمة، مثل وحدات معالجة الرسوميات ومنصات البيانات الضخمة المعتمدة على Hadoop، والتي يمكن إعادة توظيفها لتطبيقات متكاملة من Gen AI والبيانات الضخمة. تؤكد هذه الورقة
على الحاجة إلى تعظيم استخدام هذه الموارد لتحقيق تقدم ذي مغزى في نمذجة المالية وتقييم المخاطر.
أهداف ونطاق هذه الورقة هي تحديد التآزر بين Gen AI والبيانات الضخمة، ومراجعة التطورات الأخيرة، واستكشاف آثارها على المخاطر المالية. من خلال التركيز على مخاطر السوق والائتمان، نبرز حالات استخدام محددة واستراتيجيات للتغلب على الحواجز، بما في ذلك غياب هياكل بايثون الكاملة العالمية التي تمكّن من التكامل السلس لهذه التقنيات.
في النهاية، تهدف هذه الورقة إلى دعم المؤسسات المالية والجهات التنظيمية والمحللين في تعزيز بنيتهم التحتية وسير العمل. مع اعتبار عام 2025 هو عام الذكاء الاصطناعي الوكالي، فإن هذا الاستكشاف هو في الوقت المناسب وضروري لتحقيق الإمكانات الكاملة لهذه التقنيات التحويلية في القطاع المالي.
2. البيانات الضخمة التقليدية التي تساعد الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي
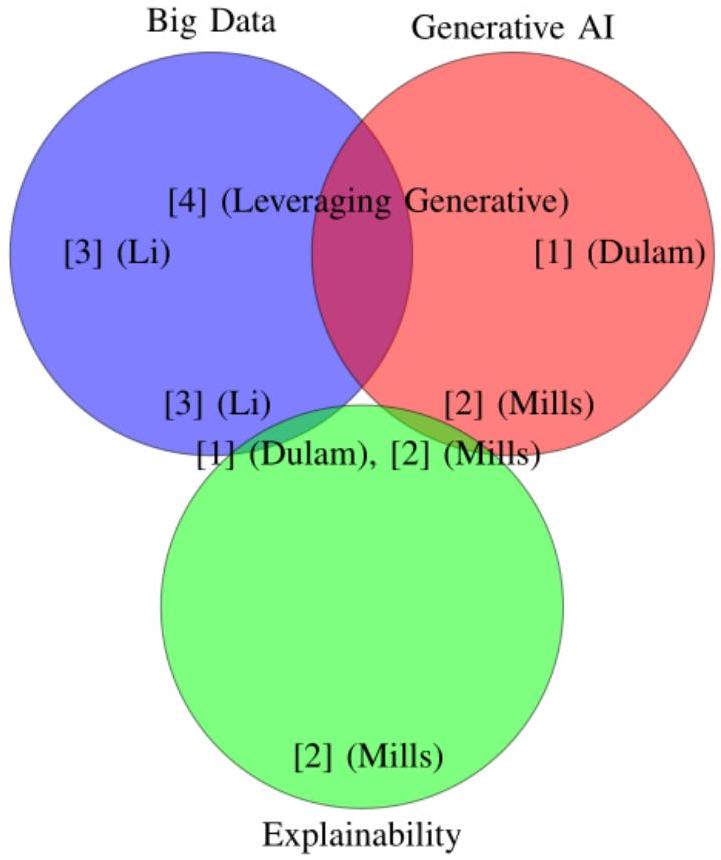
تستكشف دراسة واحدة [1] دور البيانات الضخمة في تحسين وظيفة GPT-4، لا سيما في هندسة البيانات. تظهر النتائج كيف تعزز مجموعات البيانات الكبيرة قدرة هذا النظام الذكي على توليد بيانات اصطناعية عالية الجودة، مما يحسن الدقة التنبؤية بنسبة
الحلول القابلة للتوسع. علاوة على ذلك، تمكّن هذه الأنظمة التوليدية المستضافة على السحابة من تحليل البيانات واتخاذ القرارات بشكل فعال داخل بيئات المؤسسات، مما يقلل التكاليف بشكل كبير ويزيد من أتمتة النظام. يمكن أن تقيم الدراسات المستقبلية التأثيرات الأوسع لمثل هذه البنى على ثقة المستخدم والتبني في المجالات الحرجة.
| ورقة | النهج المقترح | النتائج الرئيسية | التطبيقات | الاتجاهات المستقبلية |
| [1] (دولام) | دور GPT-4 في تحسين هندسة البيانات للتطبيقات المالية من خلال توليد البيانات الاصطناعية. | تقليل وقت هندسة البيانات بنسبة 30%. تحسين الدقة التنبؤية بنسبة
|
توقعات السوق المالية، تحسين خطوط البيانات. | استكشاف تأثير GPT-4 على وقت التطوير عبر مهام هندسة البيانات المختلفة. |
| [2] (ميلز) | بنية معتمدة على السحابة لتحليلات البيانات الضخمة القابلة للتفسير باستخدام الذكاء الاصطناعي الذاتي الهيكلة. | تحقيق زيادة بنسبة 15% في ثقة المستخدم وتقليل التكاليف بنسبة 20% في الأنظمة على مستوى المؤسسات. | أنظمة ذكاء اصطناعي شفافة لاتخاذ القرار في المجالات الحرجة. | قياس ثقة المستخدم وقابلية تفسير النموذج عبر سير العمل المختلفة في المؤسسات. |
| [3] (لي) | التآزر بين البيانات الضخمة والذكاء الاصطناعي لتحسين الموثوقية في التحليلات التنبؤية. | أظهر الذكاء الاصطناعي المدرب على مجموعات بيانات كبيرة دقة تنبؤية أعلى بنسبة 40%. خطوط بيانات أسرع مع زيادة في الإنتاجية بنسبة 18%. | تحسين سير العمل، كشف الشذوذ، تصنيف البيانات. | استكشاف تكامل الذكاء الاصطناعي في أنظمة البيانات الضخمة المتنوعة وتأثيره على كشف الشذوذ. |
| [4] (شينزهو) | الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي الذي يستفيد من البيانات الضخمة لتجارة السوق المالية وإدارة البيانات. | تحسين دقة التوقعات بأكثر من 25%. استراتيجيات الاختبار الخلفي زادت من الربحية. | توليد بيانات السوق لاستراتيجيات تداول قوية وتوقعات. | تقييم فعالية طرق الاختبار الخلفي في سيناريوهات التداول الواقعية. |
3. التآزر بين البيانات الضخمة والذكاء الاصطناعي لتحسين التحليلات
3.1 الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي في توقعات السوق المالية
3.2 البنى التحتية السحابية والذكاء الاصطناعي القابل للتفسير
تدمج إحدى البنى المقترحة [2] الذكاء الاصطناعي القابل للهيكلة الذاتية مع تحليلات البيانات الضخمة لتعزيز قابلية تفسير النموذج. لا تحسن هذه الاستراتيجية الشفافية فحسب، بل تقلل أيضًا من التكاليف التشغيلية بنسبة
علاوة على ذلك، تمكّن هذه الأنظمة التوليدية المستضافة سحابيًا [2] من تحليل البيانات واتخاذ القرارات بكفاءة داخل بيئات المؤسسات، مما يقلل التكاليف بشكل كبير ويزيد من أتمتة النظام. يمكن أن تقيم الدراسات المستقبلية التأثيرات الأوسع لمثل هذه البنى على ثقة المستخدم والتبني في المجالات الحرجة.
3.3 التآزر بين البيانات الضخمة والذكاء الاصطناعي لتحسين التحليلات
تعزز قدرات الذكاء الاصطناعي في اكتشاف الشذوذ وتصنيف البيانات جودة البيانات، مما يمكّن من تنفيذ سير العمل بشكل أسرع. يمكن أن توسع الأبحاث المستقبلية من تحسين القرار باستخدام الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي في سير العمل، والتحقيق في قابليته للتوسع وفعاليته عبر سيناريوهات مؤسسية متنوعة [3].
3.4 الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي في توقعات السوق المالية
3.5 المواضيع المتقاطعة في الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي والبيانات الضخمة
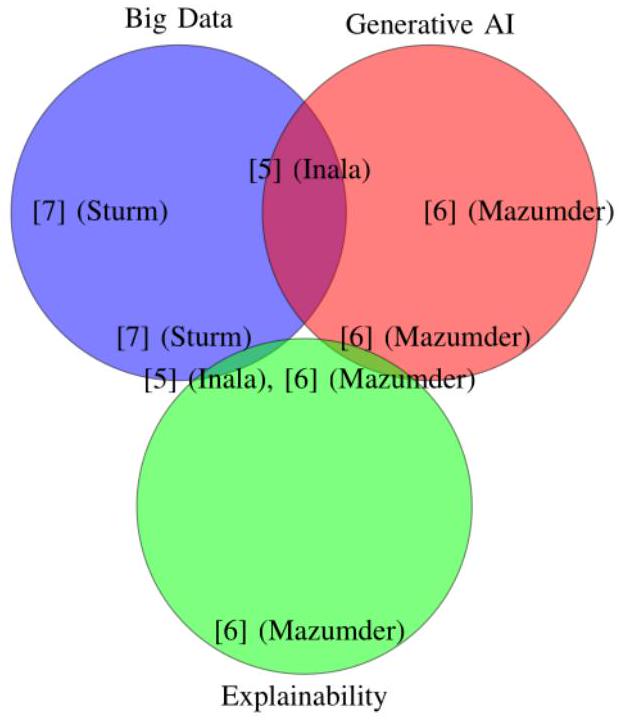
تستكشف دراسة أخرى دور الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي في تعزيز أدوات تصور البيانات الضخمة لاتخاذ القرارات التجارية [6]. تقلل التصورات المدفوعة بالذكاء الاصطناعي من وقت اتخاذ القرار بنسبة
| ورقة | النهج المقترح | النتائج الرئيسية | التطبيقات | الاتجاهات المستقبلية |
| [5] (إنالا) | الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي لاستكشاف البيانات التفاعلية وتحليل السوق المالية. | زيادة سرعة اتخاذ القرار بنسبة 50%. تحسين دقة توقعات اتجاه السوق بنسبة 20%. | الأسواق المالية، اختبار الفرضيات، رؤى أسرع. | تحديد تحسينات الإنتاجية للمحللين باستخدام أدوات الذكاء الاصطناعي. |
| [6] (مازومدر) | الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي في تصور البيانات الضخمة لتعزيز اتخاذ القرار واكتشاف الاحتيال. | تقليل وقت اتخاذ القرار بنسبة 20%. تحقيق تحسين بنسبة 25% في الرؤى التشغيلية. | اكتشاف الاحتيال، اتخاذ القرارات التجارية الدولية. | تقييم تأثير التصورات المدفوعة بالذكاء الاصطناعي على النتائج الاستراتيجية. |
| [7] (ستورم) | تحليلات البيانات الضخمة كمحرك للابتكار في استراتيجيات الأعمال. | شهدت 70% من الشركات تحسينات في دورات تطوير المنتجات بعد | تطوير المنتجات، استراتيجيات الابتكار. | استكشاف قطاعات إضافية حيث يمكن أن تدفع البيانات الضخمة الابتكار. |
| ورقة | النهج المقترح | النتائج الرئيسية | التطبيقات | الاتجاهات المستقبلية |
| [5] (إنالا) | الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي لاستكشاف البيانات التفاعلية وتحليل السوق المالية. | زيادة سرعة اتخاذ القرار بنسبة 50%. تحسين دقة توقعات اتجاه السوق بنسبة 20%. | الأسواق المالية، اختبار الفرضيات، رؤى أسرع. | تحديد تحسينات الإنتاجية للمحللين باستخدام أدوات الذكاء الاصطناعي. |
| دمج البيانات الضخمة. |
4. الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي وتعلم الآلة في إدارة المخاطر المالية
تعمل الأساليب المبتكرة لنمذجة المخاطر، بما في ذلك الشبكات التنافسية التوليدية (GANs) وتقنيات توليد أخرى، على تحسين منهجيات التنبؤ بالمخاطر. أظهرت تحسينات VaR المشفرة تحسينات ملحوظة في دقة تقارير المخاطر، مع تحسينات في التنبؤ تصل إلى
تمتد تطبيقات تعلم الآلة إلى ما هو أبعد من نمذجة VaR. يبرز إطار تنبؤ مقترح في دراسات سابقة [9] دمج تقنيات تعلم الآلة في تحسين دقة VaR، مما يوفر أدوات تتكيف مع الاتجاهات الديناميكية في السوق.
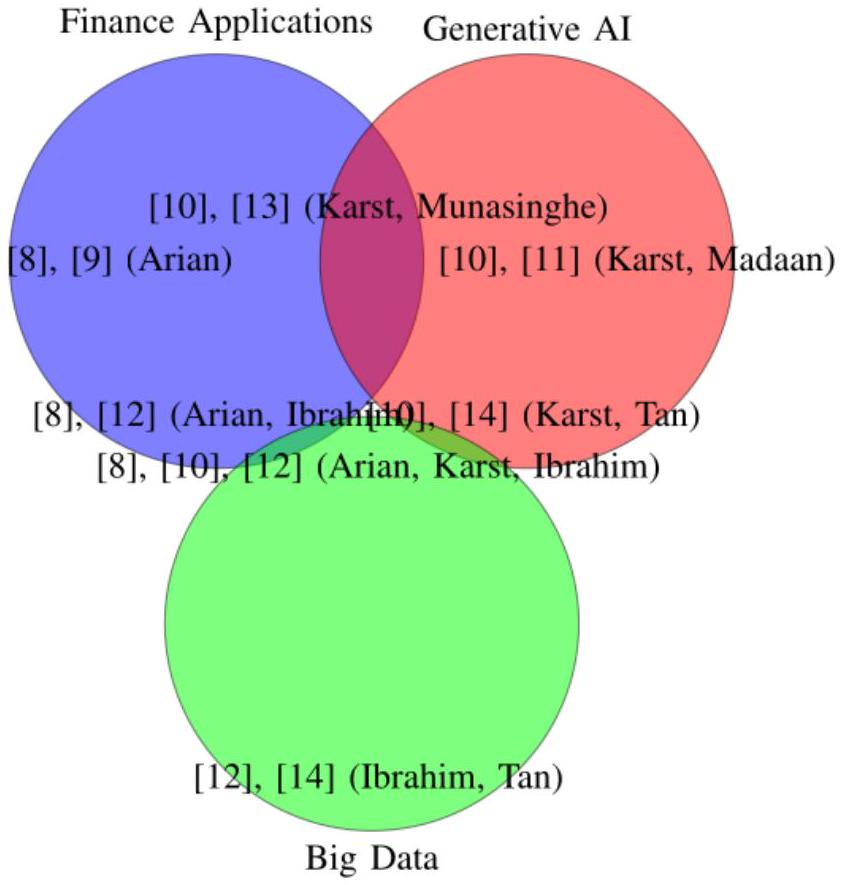
لقد استفاد القطاع المصرفي أيضًا بشكل كبير من ابتكارات الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي. يبرز استكشاف كارست لتوليد بيانات المعاملات المالية الاصطناعية كفاءة وموثوقية هذه الأدوات في تبسيط العمليات. تسلط الدراسة الضوء على كيفية تحسين المعايير والخوارزميات التوليدية لكل من اكتشاف الاحتيال وقابلية التوسع التشغيلية في المؤسسات المالية.
تطبيقات أوسع للذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي، كما ناقشها مادان وآخرون [11]، تبرز إمكانياته التحويلية عبر البنوك والخدمات المالية. من خلال أتمتة العمليات اليدوية، تعمل هذه التقنيات على تحسين الكفاءة التشغيلية بنسبة تصل إلى
لقد كانت دمج الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي وتعلم الآلة محورياً في تطوير استراتيجيات إدارة المخاطر المالية. يقترح أريان وآخرون [9] إطاراً تنبؤياً يستخدم تعلم الآلة لتعزيز دقة توقعات قيمة المخاطر (VaR). تثمر طريقتهم عن
تأتي مساهمة مهمة أخرى من أوديشكا مونا سينغه وآخرين [13]، الذين يطبقون الشبكات التوليدية التنافسية ثنائية الاتجاه (GANs) لتقدير قيمة المخاطر (VaR) في الأطراف المقابلة المركزية. تحقق هذه المنهجية تقليصًا بنسبة 20% في أخطاء التقدير، متفوقة على نماذج المخاطر التقليدية. علاوة على ذلك، فإنهم
تعزز هياكل GAN المخصصة مقاييس حساسية القيمة المعرضة للخطر من خلال
تتناول دراسة كارست [10] تطبيق الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي في القطاع المصرفي، مع التركيز على توليد بيانات معاملات مالية اصطناعية. تؤكد هذه الأبحاث على موثوقية وكفاءة الخوارزميات التوليدية في معالجة التحديات التشغيلية داخل المؤسسات المالية. تعزز هذه الأدوات من قدرات اكتشاف الاحتيال وتساهم في حلول قابلة للتوسع لإدارة الأنظمة المالية المعقدة.
تستكشف مadaan وآخرون [11] التطبيقات الأوسع للذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي، حيث يناقشون تأثيره عبر البنوك والخدمات المالية. تكشف الدراسة أن أدوات الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي يمكن أن تبسط العمليات المالية، مما يقلل من أوقات معالجة البيانات اليدوية بـ
4.1 اكتشاف القيم الشاذة وتوليد البيانات باستخدام التعلم الآلي
تظهر المزيد من الاستكشافات لهذه المنهجية تطبيقها في منصات البيانات الضخمة القابلة للتوسع. يحقق إبراهيم وآخرون [12] إنجازًا ملحوظًا
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يبرز إبراهيم وآخرون [12] فعالية هذه الأدوات في إعدادات عدم وجود أمثلة، محققين نتائج متسقة
| ورق | النهج المقترح | النتائج الرئيسية | التطبيقات | الاتجاهات المستقبلية |
| [8] (أريان) | تعلم الآلة لقياس مخاطر المحفظة باستخدام القيمة المعرضة للخطر المشفرة. | خفض هوامش الخطأ بنسبة 18٪؛ تحسين دقة توقع VaR بـ
|
إدارة المخاطر المالية. | استكشف حالات استخدام إضافية لنماذج قيمة المخاطر المشفرة. |
| [10] (كارس) | الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي لبيانات المعاملات المالية الاصطناعية. | تم تقليل وقت توليد البيانات بنسبة 40٪؛ وتم تحسين نماذج كشف الاحتيال. | خصوصية البيانات، كشف الاحتيال. | تقييم فعالية نماذج العالم الحقيقي في اكتشاف الاحتيال. |
| [12] (إبراهيم) | VAE-GAN للاكتشاف غير المراقب في حالة عدم وجود بيانات | تحسين دقة اكتشاف الشذوذ | كشف الشذوذ، كبير- | تقييم قابلية التوسع لـ VAE-GAN لـ |
المجلة الدولية للبحوث متعددة التخصصات (IJFMR)
- البريد الإلكتروني: editor@ijfmr.com
| ورق | النهج المقترح | النتائج الرئيسية | التطبيقات | الاتجاهات المستقبلية |
| [8] (أريان) | تعلم الآلة لقياس مخاطر المحفظة باستخدام القيمة المعرضة للخطر المشفرة. | خفض هوامش الخطأ بنسبة 18٪؛ تحسين دقة توقع VaR بـ
|
إدارة المخاطر المالية. | استكشف حالات استخدام إضافية لنماذج قيمة المخاطر المشفرة. |
| الكشف في مجموعات البيانات الكبيرة. | بنسبة 18%؛ حقق موثوقية كشف بنسبة 95%. | منصات بيانات النطاق. | نشر على مستوى الصناعة. | |
| [13] (مونا سينغه) | شبكة الخصومة التوليدية ثنائية الاتجاه لتقدير القيمة المعرضة للمخاطر. | خفضت أخطاء التقدير بنسبة 20٪؛ حسنت مقاييس الحساسية بـ
|
المقاصد المركزية، الاستقرار المالي. | قارن الأداء مع طرق تقدير القيمة المعرضة للخطر التقليدية. |
| [14] (تان) | DPTVAE لتوليد بيانات ائتمانية صناعية تحافظ على الخصوصية. | خفض انتهاكات خصوصية البيانات بنسبة 30٪؛ تعزيز أمان البيانات. | أنظمة الائتمان المالي. | قياس تأثير تبادل البيانات في البيئات بين المؤسسات. |
4.2 الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي وهندسة البيانات
في [15]، يبرز دُهوني التآزر بين الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي والبيانات، مشددًا على أهمية مجموعات البيانات الكبيرة في تدريب النماذج القوية. يناقش الإمكانيات التي يمتلكها الذكاء الاصطناعي لإحداث ثورة في هندسة البيانات والتحليلات. إذا قمنا بتقدير استنادًا إلى أبحاث دُهوني، فإن تطبيق الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي يزيد من كفاءة معالجة البيانات بأكثر من
4.3 جودة البيانات وتحليلها
التطوير. يمكن أن تقيس الأعمال المستقبلية تقليل وقت التحليل وتحسين أداء النموذج الذي تسهله Ydata-Profiling.
5 تطبيقات قائمة على GPT في المالية
في [20]، يقارن شاركي وتريليفن بين BERT و GPT في المهام المالية. يحقق GPT
5.1 تقييم أداء النماذج التوليدية الشائعة (GPT، GPT-4، GANs، القيمة المعرضة للخطر المشفرة)
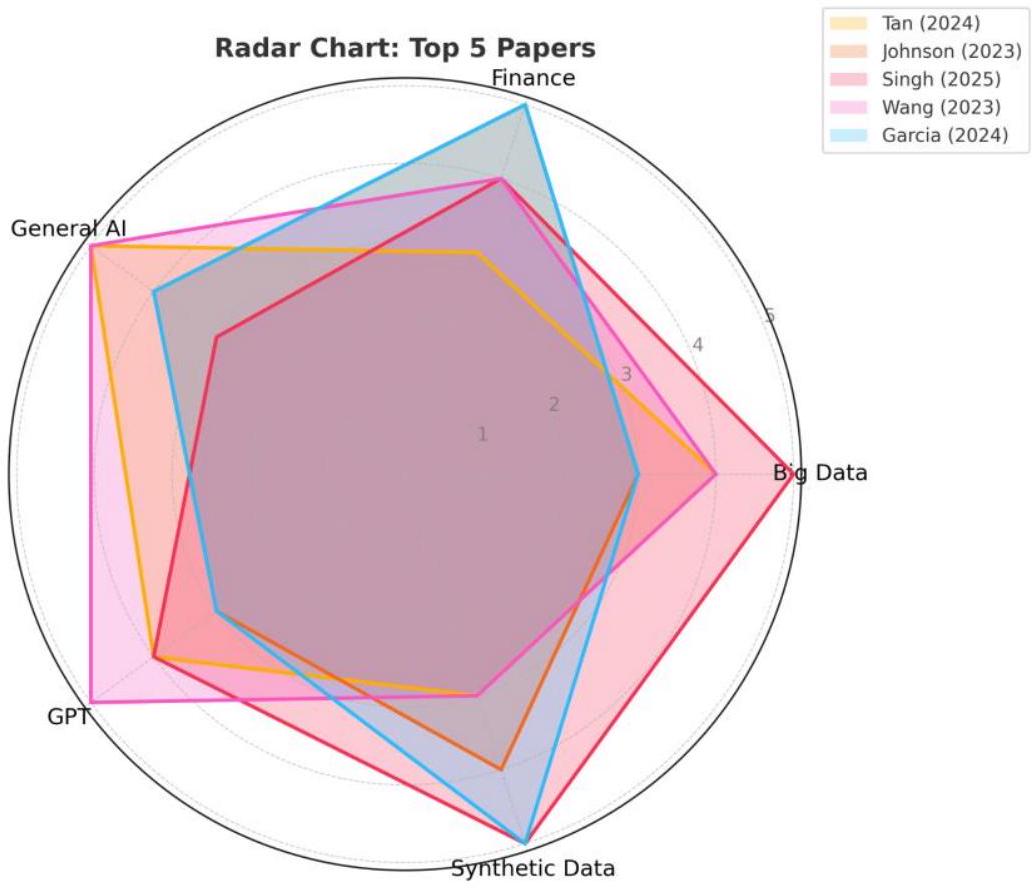
5.2 حلول قابلة للتوسع وأتمتة في أنظمة بيانات المؤسسات الكبيرة
في [22]، يناقش فارما وآخرون إعادة تصور إدارة بيانات المؤسسات باستخدام الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي. من خلال أتمتة تنظيف البيانات، والتحويل، والمهام الأخرى، يقدم الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي إمكانية تحقيق وفورات كبيرة في التكاليف وتحسين جودة البيانات داخل المؤسسات. يمكن أن تركز الأبحاث المستقبلية على قياس هذه التخفيضات في التكاليف والتحسين في دقة البيانات التي تم تحقيقها من خلال إدارة البيانات المدفوعة بالذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي. في هذا الصدد، نقترح استخدام القدرات الكامنة وغير المستخدمة للذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي في تتبع سجلات تشغيل البيانات الضخمة.
5.3 النمذجة الكمية للمخاطر في المالية (GANs، VaR المشفر، GPT)
[13] تسليط الضوء على
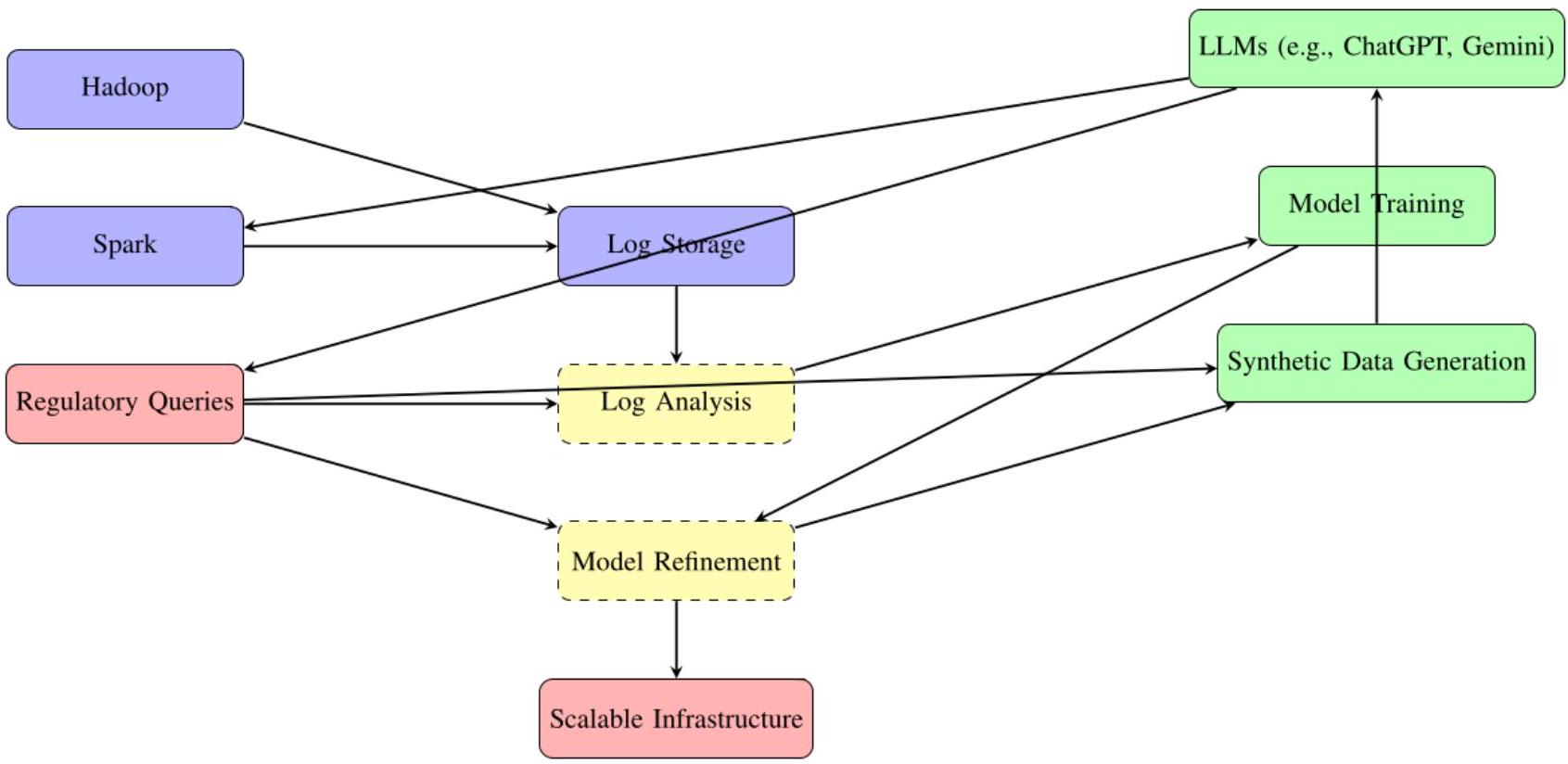
5.4 ابتكارات البيانات الاصطناعية
مثال آخر على الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي في المالية يظهر في [10]، حيث يقدم كارست وآخرون معايير وخوارزميات لبيانات المعاملات المالية الاصطناعية باستخدام الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي. يمكن أن يساعد توليد البيانات الاصطناعية في معالجة مخاوف خصوصية البيانات وقد يحسن أداء نماذج كشف الاحتيال. يمكن أن تقيم الأعمال المستقبلية فعالية هذه النماذج في كشف الاحتيال في العالم الحقيقي مع الحفاظ على خصوصية البيانات. [10] يقدم دراسة متعمقة لتطبيقات الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي في البنوك، مع التركيز بشكل خاص على المعايير والخوارزميات لتوليد بيانات المعاملات المالية الاصطناعية. تظهر الأبحاث أن الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي يمكن أن يقلل من وقت توليد البيانات بنسبة تصل إلى
| سنة | مرجع | التركيز الرئيسي | المساهمة/الأثر الرئيسي |
| ٢٠٢٢ | [3] | تفاعل البيانات الضخمة والذكاء الاصطناعي، مع التركيز على تحسين الدقة في التنبؤ | يحدد زيادة بنسبة 40% في دقة التنبؤ مع دمج الذكاء الاصطناعي في البيانات الضخمة. |
| ٢٠٢٣ | [6] | تصوير البيانات الضخمة من أجل اتخاذ القرارات التجارية، مع التركيز على تحسين سرعة اتخاذ القرارات الدولية | تحسين اتخاذ القرارات في الأعمال الدولية مع تقليص زمن القرار بنسبة 20%. |
| 2024 | [21] | الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي في تحليلات البيانات الذكية، يعزز اكتشاف الشذوذ وزيادة البيانات | أثر الذكاء الاصطناعي على تعزيز البيانات واكتشاف الشذوذ في الرعاية الصحية والبنوك مع تحسين بنسبة 40%. |
| 2024 | [22] | إدارة بيانات المؤسسات باستخدام الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي، مع التركيز على أتمتة سير العمل | يقلل من وقت معالجة البيانات بنسبة 30% باستخدام الذكاء الاصطناعي في سير عمل بيانات المؤسسات. |
| ٢٠٢٤ | [15] | التآزر بين الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي والبيانات الضخمة، مع التركيز على تكامل بيانات نماذج الذكاء الاصطناعي | يبرز أن 80% من بيانات نماذج الذكاء الاصطناعي تأتي من مصادر البيانات الضخمة، مما يحسن من أداء النموذج. |
| 2024 | [1] | جي بي تي-4 في هندسة البيانات، استكشاف استخدام نماذج جي بي تي في تحسين خطوط بيانات. | يحسن دقة التنبؤ بـ
|
| 2024 | [2] | الذكاء الاصطناعي القابل للتفسير في الأنظمة السحابية، لضمان موثوقية توقعات الذكاء الاصطناعي | يزيد من ثقة المستخدمين في الذكاء الاصطناعي بنسبة 15% من خلال نماذج الذكاء الاصطناعي القابلة للتفسير المستندة إلى السحابة. |
| 2024 | [5] | الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي في تحليل البيانات، يعزز اتخاذ القرار في التحليلات | تحسن الذكاء الاصطناعي سرعة اتخاذ القرار بنسبة 50%، مما يتيح اتخاذ قرارات تجارية أسرع. |
| 2024 | [4] | الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي في توقعات السوق المالية، تحسين دقة التنبؤ بالسوق | يعزز دقة التنبؤ بالسوق بنسبة 25% مع التنبؤات المدفوعة بالذكاء الاصطناعي في الأسواق المالية. |
| السنة | المرجع | التركيز الرئيسي | المساهمة/الأثر الرئيسي |
| 2022 | [3] | تفاعل البيانات الضخمة والذكاء الاصطناعي، مع التركيز على تحسين الدقة في التنبؤ | يحدد زيادة بنسبة 40% في دقة التنبؤ مع دمج الذكاء الاصطناعي في البيانات الضخمة. |
6. مقترحات للعمل المستقبلي
استنادًا إلى هذه الأسس، يمكن أن تركز الأعمال المستقبلية على تعزيز التآزر بين البيانات الضخمة وGen AI، لا سيما في تطبيقات مخاطر السوق والائتمان. يشمل ذلك تطوير أطر مبتكرة تعمل على تحسين استخدامهما المشترك لتعزيز دقة التنبؤ والموثوقية في إدارة المخاطر المالية.
اتجاه بحثي آخر محتمل يتضمن تصنيف وتقييم تطبيقات Gen AI في المجالات الرئيسية للمالية. يتطلب ذلك تحليلًا منهجيًا لإمكاناتها، وتحديد تحديات التنفيذ، ومقارنة أدائها في سيناريوهات مختلفة. يمثل دمج نماذج اللغة الكبيرة المتاحة للجمهور (LLMs) مثل ChatGPT وGemini مع البنى التحتية للبيانات الضخمة فرصة لتقييم استجابتها وقدرتها على التكيف مع المهام المالية المعقدة المدفوعة بالبيانات. يمكن أن تستكشف الدراسات المستقبلية أيضًا كيفية دمج الاستفسارات التنظيمية في خطوط تحليل البيانات الضخمة، باستخدام واجهات Gen AI لتعزيز عمليات اتخاذ القرار.
نقترح مزيدًا من التحقيق في أطر توليد السيناريوهات، مع الاستفادة بشكل خاص من MapReduce للتعامل مع الاستفسارات المخصصة وتوليد رؤى قابلة للتنفيذ. سيتضمن ذلك رسم استفسارات النظام المولدة إلى تعديلات نموذج الخلفية وتنقيح توليد البيانات الاصطناعية باستخدام الرؤى المستمدة من مجموعات البيانات العامة. يمكن أن يوسع هذا البحث من التطبيق العملي لهذه التقنيات في الامتثال التنظيمي ونمذجة السيناريوهات المالية.
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، فإن استكشاف الطاقة الحاسوبية غير المستخدمة خلال ساعات الذروة المنخفضة يقدم اتجاهًا عمليًا للعمل المستقبلي. على سبيل المثال، يمكن استخدام أنظمة Gen AI غير المستخدمة لتدريب النماذج باستخدام السجلات من منصات البيانات الضخمة، وتحديد وتصحيح الأخطاء والتناقضات في هذه العملية. بالمثل، يمكن أن تعمل أنظمة البيانات الضخمة على تحسين الموارد غير المستخدمة لتوليد مجموعات بيانات اصطناعية أو معالجة البيانات مسبقًا، بينما يقوم Gen AI بتدريب وتنقيح النماذج للمهام اللاحقة. من خلال إنشاء إطار متبادل – حيث تظل أنظمة Hadoop أو أنظمة موزعة أخرى نشطة جنبًا إلى جنب مع Gen AI – يمكننا ضمان استخدام الموارد الحاسوبية بشكل أقصى، حتى خلال فترات الطلب المنخفض.
يمكن أن تتضمن نهجًا محددًا لتعزيز هذا التآزر تطبيق أطر MapReduce على واجهات نماذج اللغة الكبيرة (LLM)، مما يمكّن من التعامل الفعال مع المهام الموزعة. على سبيل المثال، عندما لا تقوم أنظمة Gen AI بمعالجة استفسارات المستخدم، يمكن أن تركز على تدريب النماذج من السجلات وإعادة-
تشغيل النماذج لتحديد وتصحيح المشكلات. ستساعد هذه العملية التكرارية في الحفاظ على دقة عالية وتقليل الأخطاء النظامية في كل من تطبيقات البيانات الضخمة والذكاء الاصطناعي.
أخيرًا، يجب أن تهدف الأعمال المستقبلية إلى تطوير أطر شاملة تعظم التآزر بين Gen AI والبيانات الضخمة، مما يضمن حلولًا فعالة وقابلة للتوسع وفعالة لإدارة المخاطر المالية. من خلال معالجة التحديات المتعلقة بالكفاءة الحاسوبية، والتوافق التنظيمي، وقابلية التكيف مع البيانات، يمكن للباحثين فتح الإمكانات التحويلية الكاملة لهذه التقنيات للقطاع المالي.
الخاتمة
تظهر التطبيقات في الأسواق المالية، مثل تحسين توقعات السوق، واكتشاف الاحتيال، وتقييم الائتمان، فائدة الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي في التعامل مع مجموعات البيانات المعقدة وتقليل أوقات المعالجة. تؤكد الابتكارات في أدوات مثل DPTVAE وVAE-GAN على قدرة الذكاء الاصطناعي على توليد بيانات موثوقة مع معالجة مخاوف الخصوصية واكتشاف الشذوذ.
يجب أن تستكشف الأبحاث المستقبلية التأثيرات المحددة لهذه التقنيات على التطبيقات الواقعية، مثل تقييم فعاليتها في ظروف السوق المتنوعة وقابليتها للتوسع في بيئات المؤسسات. مع استمرار تطور الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي والبيانات الضخمة، يعد تآزرهما بإعادة تعريف الكفاءة والابتكار عبر الصناعات، مما يبشر بعصر جديد من الحلول المدفوعة بالبيانات.
References
List of References
- N. Dulam, V. Gosukonda, and M. Ankam, “GPT-4 and Beyond: The Role of Generative AI in Data Engineering,” Journal of Bioinformatics and Artificial Intelligence, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 227-249, Feb. 2024.
- N. Mills et al., “A cloud-based architecture for explainable Big Data analytics using self-structuring Artificial Intelligence,” Discover Artificial Intelligence, vol. 4, no. 1, p. 33, May 2024, doi:
. - J. Li, Z. Ye, and C. Zhang, “Study on the interaction between big data and artificial intelligence,” Systems Research and Behavioral Science, vol. 39, no. 3, pp. 641-648, 2022, doi: 10.1002/sres.2878.
- “Leveraging Generative Artificial Intelligence for Financial Market Trading Data Management and Prediction Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Information.” https://woodyinternational.com/index.php/jaii/article/view/34.
- J. P. Inala et al., “Data Analysis in the Era of Generative AI.” arXiv, Sep. 2024. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2409.18475.
- M. Mazumder, “Application of Generative AI in Big Data Visualization for Enhancing International Business Decision-Making.” http://www.theseus.fi/handle/10024/816732, 2023.
- A. T. Sturm, “Data-driven innovation : Is big data the new source of business ideas?” Thesis, Technische Universität Wien, 2023. doi: 10.34726/hss.2023.116444.
- H. Arian, M. Moghimi, E. Tabatabaei, and S. Zamani, “Encoded Value-at-Risk: A machine learning approach for portfolio risk measurement,” Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, vol. 202, pp. 500-525, Dec. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.matcom.2022.07.015.
- H. Arian, M. Moghimi, E. Tabatabaei, and S. Zamani, “Encoded Value-at-Risk: A Predictive Machine for Financial Risk Management.” arXiv, Nov. 2020. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2011.06742.
- F. S. Karst, S.-Y. Chong, A. A. Antenor, E. Lin, M. M. Li, and J. M. Leimeister, “Generative AI for Banks: Benchmarks and Algorithms for Synthetic Financial Transaction Data.” arXiv, Dec. 2024. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2412.14730.
- G. Madaan, S. K. Asthana, and J. Kaur, “Generative AI: Applications, Models, Challenges, Opportunities, and Future Directions,” in Generative AI and Implications for Ethics, Security, and Data Management, IGI Global Scientific Publishing, 2024, pp. 88-121. doi: 10.4018/979-8-3693-8557-9.ch004.
- B. I. Ibrahim, D. C. Nicolae, A. Khan, S. I. Ali, and A. Khattak, “VAE-GAN Based Zero-shot Outlier Detection,” in Proceedings of the 2020 4th International Symposium on Computer Science and Intelligent Control, in ISCSIC 2020. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Feb. 2021, pp. 1-5. doi: 10.1145/3440084.3441180.
- S. Udeshika Munasinghe, R. Rafeh, and S. Rauchas, “Estimating Value at Risk for Central Counterparties: A Generative AI Approach,” in 2024 International Conference on Data Science and Its Applications (ICoDSA), Jul. 2024, pp. 305-310. doi: 10.1109/ICoDSA62899.2024.10652178.
- Y. Tan, H. Zhu, J. Wu, and H. Chai, “DPTVAE: Data-driven prior-based tabular variational autoencoder for credit data synthesizing,” Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 241, p. 122071, May 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.122071.
- P. Dhoni, “Exploring the Synergy between Generative AI, Data and Analytics in the Modern Age.”
- F. Clemente, G. M. Ribeiro, A. Quemy, M. S. Santos, R. C. Pereira, and A. Barros, “Ydata-profiling: Accelerating data-centric AI with high-quality data,” Neurocomputing, vol. 554, p. 126585, Oct. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2023.126585.
- G. Babaei and P. Giudici, “GPT classifications, with application to credit lending,” Machine Learning with Applications, vol. 16, p. 100534, Jun. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.mlwa.2024.100534.
- M. Sanz-Guerrero and J. Arroyo, “Credit Risk Meets Large Language Models: Building a Risk Indicator from Loan Descriptions in P2P Lending.” arXiv, Aug. 2024. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2401.16458.
- Y. Wang, J. Zhao, and Y. Lawryshyn, “GPT-Signal: Generative AI for Semi-automated Feature Engineering in the Alpha Research Process.” arXiv, Oct. 2024. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2410.18448.
- E. Sharkey and P. Treleaven, “BERT vs GPT for financial engineering.” arXiv, Apr. 2024. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2405.12990.
- S. Balakrishna, V. K. Solanki, and R. G. Crespo, “Generative AI for Smart Data Analytics,” in Generative AI: Current Trends and Applications, K. Raza, N. Ahmad, and D. Singh, Eds., Singapore: Springer Nature, 2024, pp. 67-85. doi: 10.1007/978-981-97-8460-8_4.
- S. Varma, S. Shivam, B. Ray, and S. Biswas, “Reimagining Enterprise Data Management using Generative Artificial Intelligence,” in 2024 11th IEEE Swiss Conference on Data Science (SDS), May 2024, pp. 107-114. doi: 10.1109/SDS60720.2024.00023.
- Email: editor@ijfmr.com
- “Synthetic Data for Financial Anomaly Detection: AI-Driven Approaches to Simulate Rare Events and Improve Model Robustness Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research and Applications.” https://aimlstudies.co.uk/index.php/jaira/article/view/221.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36948/ijfmr.2025.v07i01.35488
Publication Date: 2025-01-19
The Synergy of Generative AI and Big Data for Financial Risk: Review of Recent Developments
Abstract
This paper presents a comprehensive review of the latest development in Generative AI and Big Data with application in Finance. 2025 is the year of Agentic AI, marking a pivotal shift in generative AI (Gen AI) and its integration with big data. This paper explores the synergies between Gen AI and big data, particularly in financial risk management, proposing strategies for deeper integration. By citing the latest white papers and focusing on developments over the past two years, we expand the scope of research in this transformative domain. Recent advancements in Gen AI, such as GPT-4, VAE-GANs, and explainable AI architectures, demonstrate significant improvements, including
1. Introduction
This paper provides a comprehensive review of the latest developments in Big Data and Gen AI, with a specific focus on their applications in financial risk management. By exploring the background and context of these innovations, we demonstrate how their combined capabilities can improve model development and decision-making in financial institutions. Furthermore, this work offers actionable insights for financial regulators and market participants, aiming to enhance the overall efficiency and robustness of financial systems while mitigating risks.
A key driver of this innovation is the opportunity to leverage existing infrastructures more effectively. Organizations often possess idle computational resources, such as GPUs and Hadoop-based Big Data platforms, which can be repurposed for integrated applications of Gen AI and Big Data. This paper
emphasizes the need to maximize the utilization of these resources to achieve meaningful advancements in financial modeling and risk assessment.
The objectives and scope of this paper are to identify the synergies between Gen AI and Big Data, review recent developments, and explore their implications for financial risk. By focusing on market and credit risk, we highlight specific use cases and strategies to overcome barriers, including the absence of universal Python full-stack architectures that enable seamless integration of these technologies.
Ultimately, this paper is intended to support financial institutions, regulators, and analysts in enhancing their infrastructure and workflows. As 2025 is heralded as the year of Agentic AI, this exploration is both timely and essential for realizing the full potential of these transformative technologies in the financial sector.
2. Traditional Big Data aiding Generative AI
One study [1] explores the role of Big Data in optimizing GPT-4’s functionality, particularly in data engineering. The findings demonstrate how large datasets enhance the ability of this AI system to generate high-quality synthetic data, improving predictive accuracy by

scalable solutions. Furthermore, these cloud-hosted generative systems enable efficient data analysis and decision-making within enterprise environments, significantly lowering costs and increasing system automation. Future studies could evaluate the broader impacts of such architectures on user trust and adoption in critical domains.
| Paper | Proposed Approach | Key Findings | Applications | Future Directions |
| [1] (Dulam) | Role of GPT-4 in enhancing data engineering for financial applications by generating synthetic data. | Reduced data engineering time by 30%. Improved predictive accuracy by
|
Financial market prediction, data pipeline optimization. | Investigate GPT4’s impact on development time across various data engineering tasks. |
| [2] (Mills) | Cloud-based architecture for explainable big data analytics using selfstructuring AI. | Achieved 15% increase in user trust and 20% cost reductions in enterprise-level systems. | Transparent AI systems for decision-making in critical domains. | Measure user trust and model interpretability across various enterprise workflows. |
| [3] (Li) | Synergy between big data and AI for improved reliability in predictive analytics. | AI-trained on large datasets showed 40% more accurate forecasting. Faster data pipelines with 18% increased throughput. | Optimized workflows, anomaly detection, data classification. | Explore AI integration in diverse big data systems and its impact on anomaly detection. |
| [4] (Xinzhu) | Generative AI leveraging big data for financial market trading and data management. | Improved forecasting accuracy by over 25%. Backtesting strategies enhanced profitability. | Market data generation for robust trading strategies and predictions. | Evaluate effectiveness of backtesting methods in realworld trading scenarios. |
3. Synergy between Big Data and AI for Improved Analytics

3.1 Generative AI in Financial Market Prediction
3.2 Cloud-based Architectures and Explainable AI
One proposed architecture [2] integrates self-structuring AI with Big Data analytics to enhance model interpretability. This strategy not only improves transparency but also reduces operational costs by
Furthermore, these cloud-hosted generative systems [2] enable efficient data analysis and decision-making within enterprise environments, significantly lowering costs and increasing system automation. Future studies could evaluate the broader impacts of such architectures on user trust and adoption in critical domains.
3.3 Synergy between Big Data and AI for Improved Analytics
profiling. AI’s capabilities in anomaly detection and data classification further enhance data quality, enabling faster workflow execution. Future research could expand on decision optimization using Generative AI in workflows, investigating its scalability and effectiveness across diverse enterprise scenarios [3].

3.4 Generative AI in Financial Market Prediction
3.5 Cross-Cutting Topics in Generative AI and Big Data
Another study explores the role of generative AI in enhancing big data visualization tools for business decision-making [6]. AI-driven visualizations reduce decision-making time by

| Paper | Proposed Approach | Key Findings | Applications | Future Directions |
| [5] (Inala) | Generative AI for interactive data exploration and financial market analysis. | Increased decision-making speed by 50%. Improved market trend prediction accuracy by 20%. | Financial markets, hypothesis testing, faster insights. | Quantify productivity improvements for analysts using AI tools. |
| [6] (Mazumder) | Generative AI in big data visualization to enhance decisionmaking and fraud detection. | Reduced decisionmaking time by 20%. Achieved 25% operational insights improvement. | Fraud detection, international business decisionmaking. | Evaluate impact of AI-driven visualizations on strategic outcomes. |
| [7] (Sturm) | Big data analytics as a driver for innovation in business strategies. | 70% of businesses saw improved product development cycles after | Product development, innovation strategies. | Investigate additional sectors where big data can drive innovation. |
| Paper | Proposed Approach | Key Findings | Applications | Future Directions |
| [5] (Inala) | Generative AI for interactive data exploration and financial market analysis. | Increased decision-making speed by 50%. Improved market trend prediction accuracy by 20%. | Financial markets, hypothesis testing, faster insights. | Quantify productivity improvements for analysts using AI tools. |
| integrating big data. |
4. Generative AI and Machine Learning in Financial Risk Management
Innovative approaches to risk modeling, including Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and other generative techniques, further refine risk prediction methodologies. Encoded VaR enhancements have demonstrated notable improvements in risk reporting accuracy, with prediction improvements reaching up to
Machine learning applications extend beyond VaR modeling. A predictive framework proposed in earlier studies [9] underscores the integration of machine learning techniques in improving VaR accuracy, offering tools that adapt to dynamic market trends.
The banking sector has also benefited significantly from generative AI innovations. Karst’s exploration of synthetic financial transaction data generation [10] emphasizes the efficiency and reliability of these tools in streamlining operations. The study highlights how benchmarks and generative algorithms enhance both fraud detection and operational scalability in financial institutions.
Broader applications of generative AI, as discussed by Madaan et al. [11], highlight its transformative potential across banking and financial services. By automating manual processes, these technologies improve operational efficiency by up to
The integration of generative AI and machine learning has been pivotal in advancing financial risk management strategies. Arian et al. [9] propose a predictive framework utilizing machine learning to enhance the accuracy of Value-at-Risk (VaR) predictions. Their approach yields a
Another significant contribution comes from Udeshika Munasinghe et al. [13], who apply Bidirectional Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) for estimating VaR in central counterparties. This methodology achieves a 20% reduction in estimation errors, outperforming conventional risk models. Furthermore, their
custom GAN architectures enhance value-at-risk sensitivity measures by
Karst’s study [10] delves into the application of generative AI in banking, focusing on generating synthetic financial transaction data. This research emphasizes the reliability and efficiency of generative algorithms in addressing operational challenges within financial institutions. These tools enhance fraud detection capabilities and contribute to scalable solutions for managing complex financial systems.
Broader applications of generative AI are explored by Madaan et al. [11], who discuss its impact across banking and financial services. The study reveals that generative AI tools can streamline financial processes, reducing manual data processing times by
4.1 Outlier Detection and Data Synthesis with Machine Learning
Further exploration of this methodology showcases its application in scalable big data platforms. Ibrahim et al. [12] achieve a remarkable
Additionally, Ibrahim et al. [12] highlight the effectiveness of these tools in zero-shot setups, achieving consistent
| Paper | Proposed Approach | Key Findings | Applications | Future Directions |
| [8] (Arian) | Machine learning for portfolio risk measurement using Encoded Value-atRisk. | Reduced error margins by 18%; improved VaR prediction accuracy by
|
Financial risk management. | Explore additional use cases for Encoded VaR models. |
| [10] (Karst) | Generative AI for synthetic financial transaction data. | Reduced data generation time by 40%; enhanced fraud detection models. | Data privacy, fraud detection. | Evaluate realworld model effectiveness for fraud detection. |
| [12] (Ibrahim) | VAE-GAN for zero-shot outlier | Improved anomaly detection accuracy | Anomaly detection, large- | Assess scalability of VAE-GAN for |
International Journal for Multidisciplinary Research (IJFMR)
- Email: editor@ijfmr.com
| Paper | Proposed Approach | Key Findings | Applications | Future Directions |
| [8] (Arian) | Machine learning for portfolio risk measurement using Encoded Value-atRisk. | Reduced error margins by 18%; improved VaR prediction accuracy by
|
Financial risk management. | Explore additional use cases for Encoded VaR models. |
| detection in large datasets. | by 18%; achieved 95% detection reliability. | scale data platforms. | industry-level deployments. | |
| [13] (Munasinghe) | Bidirectional GAN for Value-at-Risk estimation. | Reduced estimation errors by 20%; improved sensitivity measures by
|
Central counterparties, financial stability. | Compare performance with traditional VaR estimation methods. |
| [14] (Tan) | DPTVAE for generating privacypreserving synthetic credit data. | Reduced data privacy breaches by 30%; enhanced data security. | Financial credit systems. | Quantify impact on data sharing in cross-institutional settings. |
4.2 Generative AI and Data Engineering
In [15], Dhoni highlights the synergy between generative AI and data, emphasizing the importance of large datasets in training powerful models. It discusses the potential of AI to revolutionize data engineering and analytics. If we make an estimate based on the research by Dhoni, generative AI’s application increases efficiency in data processing by over
4.3 Data Quality and Profiling
development. Future work could measure the reduction in analysis time and the improvement in model performance facilitated by Ydata-Profiling.
5 GPT-Based Applications in Finance
In [20], Sharkey and Treleaven compare BERT and GPT in financial tasks. GPT achieves a
5.1 Performance Assessment of Popular Generative Models (GPT, GPT-4, GANs, Encoded Value-at-Risk)

5.2 Scalable Solutions and Automation in Big Enterprise Data Systems
In [22], Varma et al. further discuss reimagining enterprise data management using generative AI. By automating data cleaning, transformation, and other tasks, generative AI offers the potential for significant cost savings and improved data quality within organizations. Future research could focus on quantifying these cost reductions and the improvement in data accuracy achieved through generative AI-driven data management. In this regard, we propose to use the latent and unused capabilities of Gen AI in crawling logs of big data runs.
5.3Quantitative Risk Modeling in Finance (GANs, Encoded VaR, GPT)
[13] highlight a

5.4 Synthetic Data Innovations
Another example of Generative AI in Finance is shown In [10], Karst et al. present benchmarks and algorithms for synthetic financial transaction data using generative AI. Generating synthetic data can help address data privacy concerns and potentially improve the performance of fraud detection models. Future work could evaluate the effectiveness of these models in detecting real-world fraud while preserving data privacy. [10] presents an in-depth study of generative AI applications in banks, specifically focusing on benchmarks and algorithms for generating synthetic financial transaction data. The research shows that generative AI can reduce data generation time by up to
| Year | Refere nce | Main Focus | Key Contribution/Impact |
| 2022 | [3] | Interaction of Big Data and AI, with focus on accuracy improvement in forecasting | Identifies a 40% increase in forecasting accuracy with AI’s integration into big data. |
| 2023 | [6] | Big Data Visualization for Business Decision Making, with emphasis on improving international decision speed | Enhanced international business decision-making with a 20% reduction in decision time. |
| 2024 | [21] | Generative AI in Smart Data Analytics, enhancing anomaly detection and data augmentation | AI’s impact on data augmentation and anomaly detection in healthcare and banking with a 40% improvement. |
| 2024 | [22] | Enterprise Data Management Using Generative AI, focusing on automation of workflows | Reduces data processing time by 30% using AI in enterprise data workflows. |
| 2024 | [15] | Synergy Between Generative AI and Big Data, with focus on AI model data integration | Highlights that 80% of AI model data comes from big data sources, improving model performance. |
| 2024 | [1] | GPT-4 in Data Engineering, exploring the use of GPT models in data pipeline optimization | Improves predictive accuracy by
|
| 2024 | [2] | Explainable AI in Cloud-Based Systems, ensuring trustworthiness in AI predictions | Increases user trust in AI by 15% through explainable cloud-based AI models. |
| 2024 | [5] | Generative AI in Data Analysis, enhancing decision-making in analytics | AI improves decision-making speed by 50%, enabling faster business decisions. |
| 2024 | [4] | Generative AI in Financial Market Prediction, improving market forecasting accuracy | Enhances market forecasting accuracy by 25% with AI-driven predictions in financial markets. |
| Year | Refere nce | Main Focus | Key Contribution/Impact |
| 2022 | [3] | Interaction of Big Data and AI, with focus on accuracy improvement in forecasting | Identifies a 40% increase in forecasting accuracy with AI’s integration into big data. |
6. Proposals for future work
Building on this foundation, further work could focus on advancing the synergy between big data and Gen AI, particularly in market and credit risk applications. This includes developing innovative frameworks that optimize their joint utilization to enhance predictive accuracy and robustness in financial risk management.
Another potential research direction involves the classification and assessment of Gen AI applications in key areas of finance. This entails systematically analyzing their potential, identifying implementation challenges, and comparing their performance under varying scenarios. Integrating publicly available Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT and Gemini with big data infrastructures presents an opportunity to evaluate their responses and adaptability for complex, data-driven financial tasks. Future studies could also investigate how regulatory queries can be incorporated into big data analysis pipelines, using Gen AI backends to enhance decision-making processes.
We propose further investigation into scenario generation frameworks, specifically leveraging MapReduce for handling custom queries and generating actionable insights. This would involve mapping system-generated queries to backend model adjustments and refining synthetic data generation using insights derived from public datasets. Such research could extend the practical applicability of these technologies in regulatory compliance and financial scenario modeling.
Additionally, exploring unused computational power during off-peak hours offers a practical direction for future work. For instance, idle Gen AI systems could be employed to train models using logs from big data platforms, identifying and correcting errors and inconsistencies in the process. Similarly, big data systems could optimize idle resources to generate synthetic datasets or pre-process data, while Gen AI trains and fine-tunes models for subsequent tasks. By creating a reciprocal framework-where Hadoop or other distributed systems remain active alongside Gen AI-we can ensure computational resources are maximally utilized, even during low-demand periods.
A specific approach to enhance this synergy could involve applying MapReduce frameworks to Large Language Model (LLM) backends, enabling efficient handling of distributed tasks. For instance, when Gen AI systems are not processing user queries, they could focus on training models from logs and re-
running models to identify and correct issues. This iterative refinement process would help maintain high accuracy and reduce systemic errors in both big data and AI applications.
Finally, future work should aim to develop comprehensive frameworks that maximize the synergy between Gen AI and big data, ensuring efficient, scalable, and effective solutions for financial risk management. By addressing challenges related to computational efficiency, regulatory alignment, and data adaptability, researchers can unlock the full transformative potential of these technologies for the financial sector.
Conclusion
Applications in financial markets, such as improved market forecasting, fraud detection, and credit scoring, demonstrate the utility of generative AI in handling complex datasets and reducing processing times. Innovations in tools like DPTVAE and VAE-GAN further underscore the ability of AI to synthesize reliable data while addressing privacy concerns and anomaly detection.
Future research should explore the specific impacts of these technologies on real-world applications, such as evaluating their efficacy in diverse market conditions and their scalability in enterprise environments. As generative AI and big data continue to evolve, their synergy promises to redefine efficiency and innovation across industries, heralding a new era of data-driven solutions.
References
List of References
- N. Dulam, V. Gosukonda, and M. Ankam, “GPT-4 and Beyond: The Role of Generative AI in Data Engineering,” Journal of Bioinformatics and Artificial Intelligence, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 227-249, Feb. 2024.
- N. Mills et al., “A cloud-based architecture for explainable Big Data analytics using self-structuring Artificial Intelligence,” Discover Artificial Intelligence, vol. 4, no. 1, p. 33, May 2024, doi:
. - J. Li, Z. Ye, and C. Zhang, “Study on the interaction between big data and artificial intelligence,” Systems Research and Behavioral Science, vol. 39, no. 3, pp. 641-648, 2022, doi: 10.1002/sres.2878.
- “Leveraging Generative Artificial Intelligence for Financial Market Trading Data Management and Prediction Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Information.” https://woodyinternational.com/index.php/jaii/article/view/34.
- J. P. Inala et al., “Data Analysis in the Era of Generative AI.” arXiv, Sep. 2024. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2409.18475.
- M. Mazumder, “Application of Generative AI in Big Data Visualization for Enhancing International Business Decision-Making.” http://www.theseus.fi/handle/10024/816732, 2023.
- A. T. Sturm, “Data-driven innovation : Is big data the new source of business ideas?” Thesis, Technische Universität Wien, 2023. doi: 10.34726/hss.2023.116444.
- H. Arian, M. Moghimi, E. Tabatabaei, and S. Zamani, “Encoded Value-at-Risk: A machine learning approach for portfolio risk measurement,” Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, vol. 202, pp. 500-525, Dec. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.matcom.2022.07.015.
- H. Arian, M. Moghimi, E. Tabatabaei, and S. Zamani, “Encoded Value-at-Risk: A Predictive Machine for Financial Risk Management.” arXiv, Nov. 2020. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2011.06742.
- F. S. Karst, S.-Y. Chong, A. A. Antenor, E. Lin, M. M. Li, and J. M. Leimeister, “Generative AI for Banks: Benchmarks and Algorithms for Synthetic Financial Transaction Data.” arXiv, Dec. 2024. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2412.14730.
- G. Madaan, S. K. Asthana, and J. Kaur, “Generative AI: Applications, Models, Challenges, Opportunities, and Future Directions,” in Generative AI and Implications for Ethics, Security, and Data Management, IGI Global Scientific Publishing, 2024, pp. 88-121. doi: 10.4018/979-8-3693-8557-9.ch004.
- B. I. Ibrahim, D. C. Nicolae, A. Khan, S. I. Ali, and A. Khattak, “VAE-GAN Based Zero-shot Outlier Detection,” in Proceedings of the 2020 4th International Symposium on Computer Science and Intelligent Control, in ISCSIC 2020. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Feb. 2021, pp. 1-5. doi: 10.1145/3440084.3441180.
- S. Udeshika Munasinghe, R. Rafeh, and S. Rauchas, “Estimating Value at Risk for Central Counterparties: A Generative AI Approach,” in 2024 International Conference on Data Science and Its Applications (ICoDSA), Jul. 2024, pp. 305-310. doi: 10.1109/ICoDSA62899.2024.10652178.
- Y. Tan, H. Zhu, J. Wu, and H. Chai, “DPTVAE: Data-driven prior-based tabular variational autoencoder for credit data synthesizing,” Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 241, p. 122071, May 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.122071.
- P. Dhoni, “Exploring the Synergy between Generative AI, Data and Analytics in the Modern Age.”
- F. Clemente, G. M. Ribeiro, A. Quemy, M. S. Santos, R. C. Pereira, and A. Barros, “Ydata-profiling: Accelerating data-centric AI with high-quality data,” Neurocomputing, vol. 554, p. 126585, Oct. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2023.126585.
- G. Babaei and P. Giudici, “GPT classifications, with application to credit lending,” Machine Learning with Applications, vol. 16, p. 100534, Jun. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.mlwa.2024.100534.
- M. Sanz-Guerrero and J. Arroyo, “Credit Risk Meets Large Language Models: Building a Risk Indicator from Loan Descriptions in P2P Lending.” arXiv, Aug. 2024. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2401.16458.
- Y. Wang, J. Zhao, and Y. Lawryshyn, “GPT-Signal: Generative AI for Semi-automated Feature Engineering in the Alpha Research Process.” arXiv, Oct. 2024. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2410.18448.
- E. Sharkey and P. Treleaven, “BERT vs GPT for financial engineering.” arXiv, Apr. 2024. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2405.12990.
- S. Balakrishna, V. K. Solanki, and R. G. Crespo, “Generative AI for Smart Data Analytics,” in Generative AI: Current Trends and Applications, K. Raza, N. Ahmad, and D. Singh, Eds., Singapore: Springer Nature, 2024, pp. 67-85. doi: 10.1007/978-981-97-8460-8_4.
- S. Varma, S. Shivam, B. Ray, and S. Biswas, “Reimagining Enterprise Data Management using Generative Artificial Intelligence,” in 2024 11th IEEE Swiss Conference on Data Science (SDS), May 2024, pp. 107-114. doi: 10.1109/SDS60720.2024.00023.
- Email: editor@ijfmr.com
- “Synthetic Data for Financial Anomaly Detection: AI-Driven Approaches to Simulate Rare Events and Improve Model Robustness Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research and Applications.” https://aimlstudies.co.uk/index.php/jaira/article/view/221.
