DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-024-05520-w
PMID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38286861
تاريخ النشر: 2024-01-30
تحريك الأضراس الخلفية في تقويم الأسنان: تحليل ببليومتري
© المؤلفون 2024
الملخص
الأهداف تسعى الدراسة إلى إجراء تحليل ببليومتري حول إبعاد الأضراس، بهدف تسليط الضوء على مسارها التطوري، والحالة الحالية، وتوقع النقاط الساخنة والاتجاهات البحثية المستقبلية. المواد والأساليب تم إجراء استكشاف شامل للأدبيات المتعلقة بإبعاد الأضراس من خلال البحث في قاعدة بيانات Web of Science (WOS) الأساسية لمكتبة جامعة هونغ كونغ الإلكترونية. تم استخدام مصطلحات موضوعية في البحث تشمل “إبعاد الأضراس”، “إبعاد الأضراس”، “تحريك الضرس بعيدًا”، “حركة الضرس بعيدًا”، و”الضرس للخلف”. تم إخضاع نتائج البحث لتحليل دقيق باستخدام برنامج CiteSpace. شمل هذا التحليل جوانب مختلفة مثل عدد الاقتباسات؛ التوزيع الجغرافي للدول، المؤسسات، والمجلات المسؤولة عن نشر المقالات؛ توزيع المؤلفين؛ استخدام الكلمات الرئيسية داخل المقالات؛ وتحليل المراجع. النتائج تم تضمين ما مجموعه 516 مقالة في التحليل. كانت الدول الخمس الأولى من حيث عدد الأوراق المنشورة هي الولايات المتحدة (USA)، كوريا الجنوبية، تركيا، إيطاليا، وألمانيا، وكانت المؤسسات الخمس الأولى من حيث عدد الأوراق المنشورة هي جامعة كيونغ هي، جامعة A.T. Still للعلوم الصحية، الجامعة الكاثوليكية في كوريا، مستشفى سانت ماري في سيول، وجامعة ساو باولو. كان المؤلفون الخمسة الأوائل من حيث عدد الأوراق المنشورة هم بارك، كوك، بايوم، جانسون، ولي. كان هناك القليل من التعاون بشكل عام. كانت المجلات الثلاثة الأولى من حيث عدد المقالات المنشورة المتعلقة هي جميعها مجلات متعلقة بتقويم الأسنان. بعد إبعاد الأضراس والتثبيت، كانت الكلمات الرئيسية الأكثر استخدامًا هي الإبعاد، الحركة، وجهاز البندول. كينزينجر GSM هو المؤلف الأكثر اقتباسًا في المراجع، وأحد مقالاته أيضًا لديه أعلى درجة مركزية في المراجع. الاستنتاجات مع تغير الزمن وظهور التزام متزايد من العلماء لكشف تعقيدات هذه الوسيلة العلاجية، شهد مجال إبعاد الأضراس تقدمًا ملحوظًا في التكنولوجيا. في البداية، كانت الأجهزة التقليدية تعاني من عيوب جمالية وعدم الراحة. ومع ذلك، تجاوزت النسخ المعاصرة من الجهاز هذه القيود، حيث تتمتع بأناقة وراحة محسنتين بينما تعزز فعاليتها في الوقت نفسه. ومع ذلك، لا تزال قيود الأجهزة الحالية، بما في ذلك متانتها وميولها للعودة بعد العلاج، تستدعي المزيد من التقدم. ومن ثم، تهدف الأبحاث العلمية المستمرة إلى التعمق في تحسين أساليب العلاج وتصنيع أجهزة متطورة في هذا المجال. الأهمية السريرية. تحمل هذه الدراسة القدرة على تعزيز قدرة أطباء تقويم الأسنان بشكل كبير على وضع بروتوكولات العلاج وتقديم توصيات سريرية متطورة، مما يمكّنهم من تقديم تدخلات تقويم أسنان متقدمة ومكررة.
مقدمة
طرق
قاعدة البيانات
استراتيجية البحث
فرز البيانات وجمعها
التحليل الإحصائي
النتائج
معلومات عامة
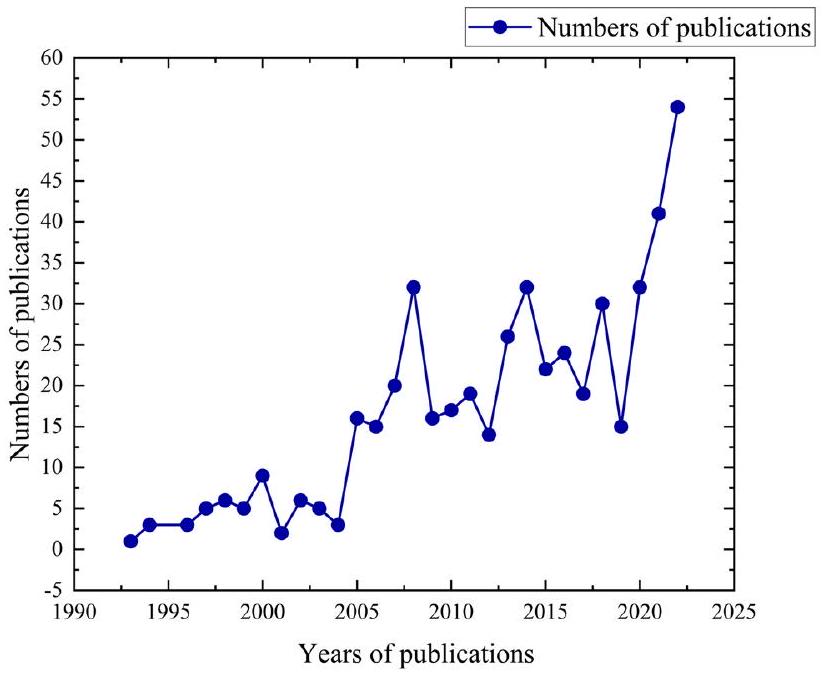
12.14 استشهادًا لكل مقال. من بين هذه المقالات، كان هناك 481 مقالًا أصليًا، و34 مراجعة، و1 ورقة مؤتمرات (انظر الجدول 1). لم يتغير عدد الأوراق المنشورة سنويًا كثيرًا قبل عام 2005 ولكنه أظهر اتجاه نمو عام بعد عام 2005، وبلغ عدد الأوراق المنشورة ذروته في عام 2022 (انظر الشكل 2).
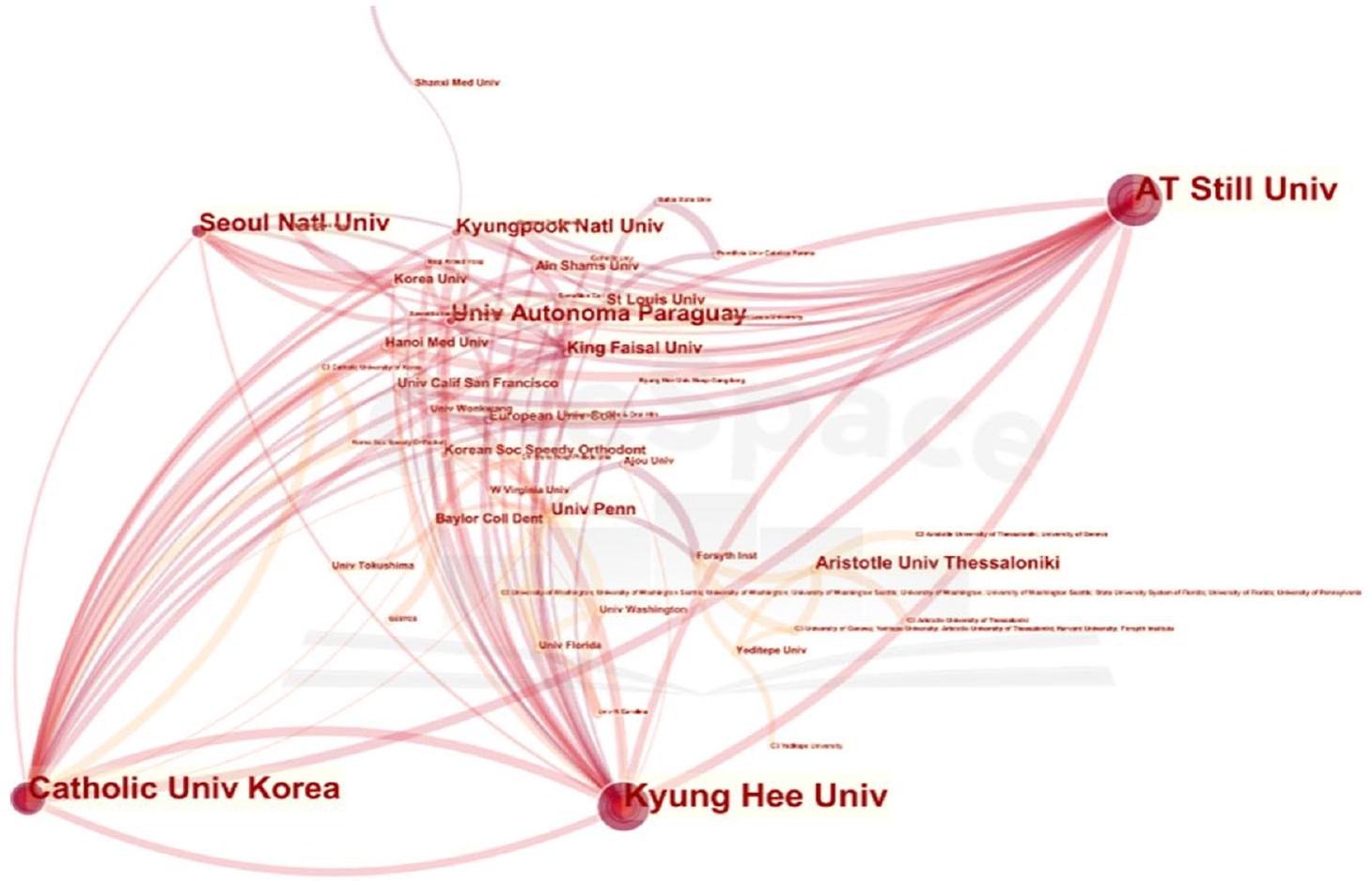
الدول والمؤسسات
| نوع المقال | سجلات | % من 516 |
| مقالة | ٤٨١ | 93.22 |
| مراجعة | ٣٤ | ٦.٥٩ |
| ورقة أعمال المؤتمر | 1 | 0.19 |
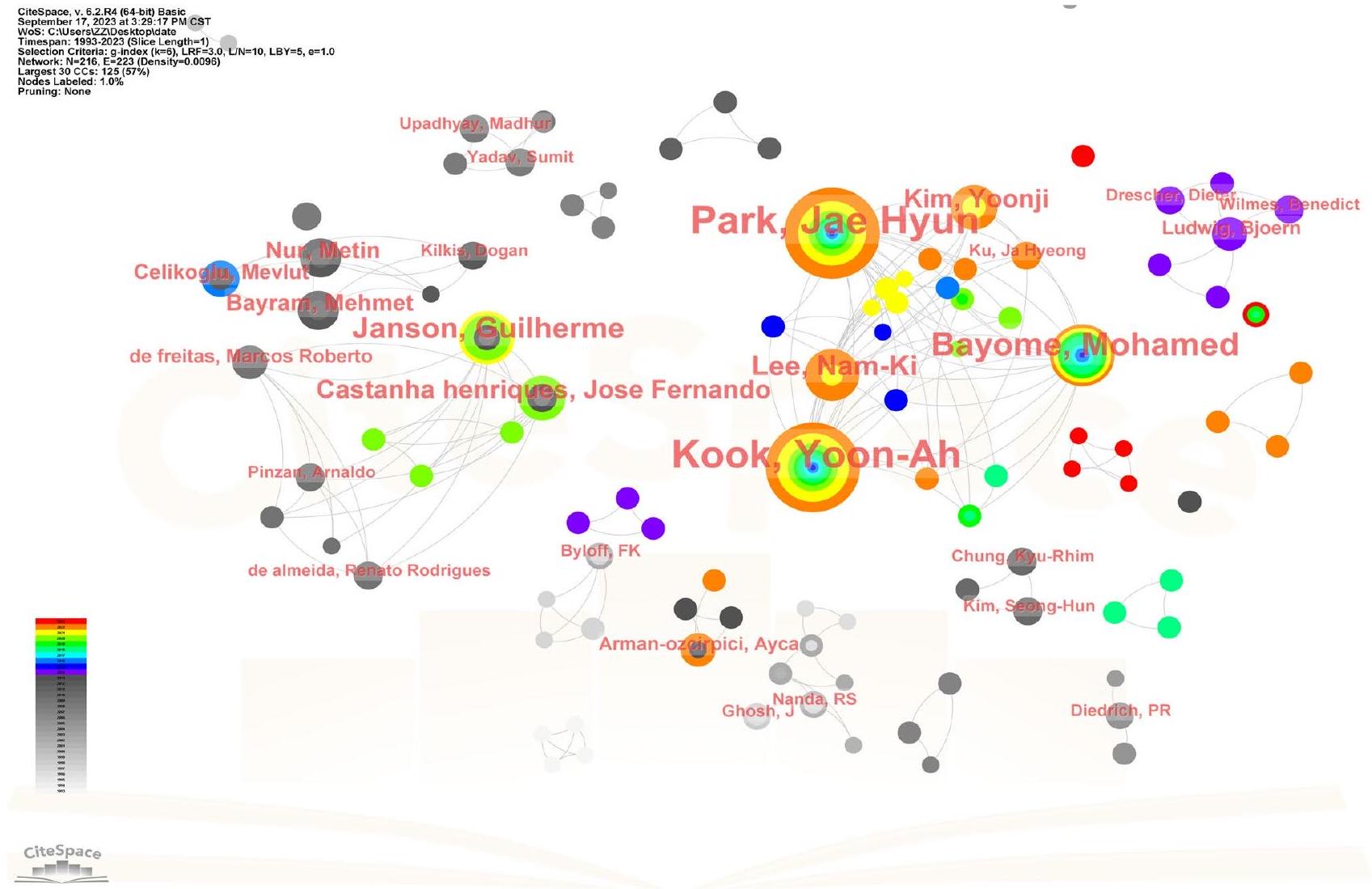
المؤلفون

| رتبة | دول | تردد |
| 1 | الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية | 114 |
| 2 | كوريا الجنوبية | 78 |
| ٣ | تركيا | 73 |
| ٤ | إيطاليا | ٤٥ |
| ٥ | ألمانيا | 42 |
| ٦ | الصين | 40 |
| ٧ | البرازيل | ٣٦ |
| ٨ | الهند | ٣٤ |
| ٩ | اليابان | ٣٤ |
| 10 | سويسرا | 14 |
| رتبة | دول | المركزية |
| 1 | الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية | 0.72 |
| ٢ | إيطاليا | 0.35 |
| ٣ | سلوفاكيا | 0.16 |
| ٤ | المملكة العربية السعودية | 0.11 |
| ٥ | جمهورية التشيك | 0.11 |
| ٦ | الصين | 0.10 |
| ٧ | كوريا الجنوبية | 0.08 |
| ٨ | ألمانيا | 0.07 |
| 9 | البرازيل | 0.06 |
| 10 | الهند | 0.06 |
المجلات
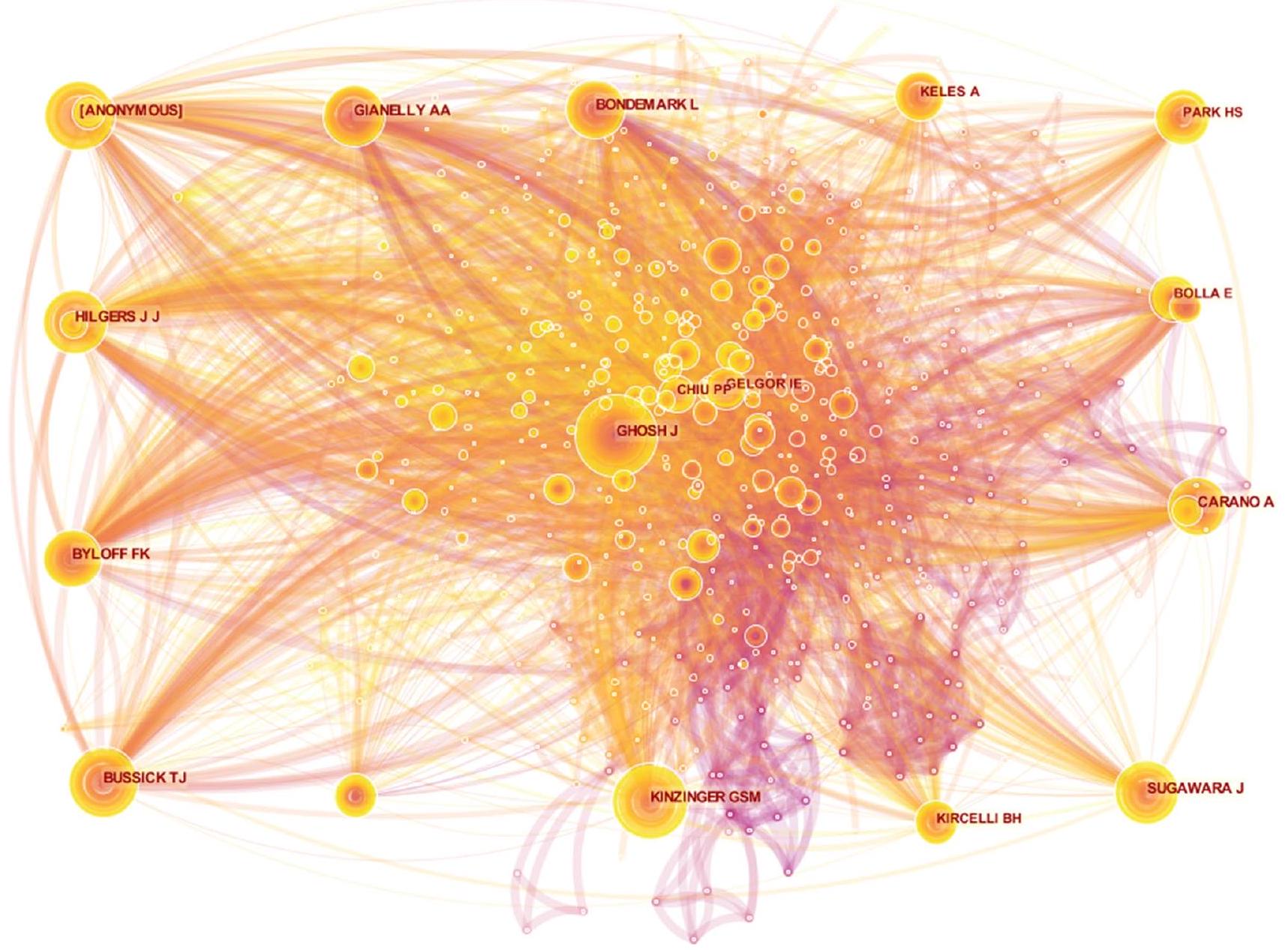
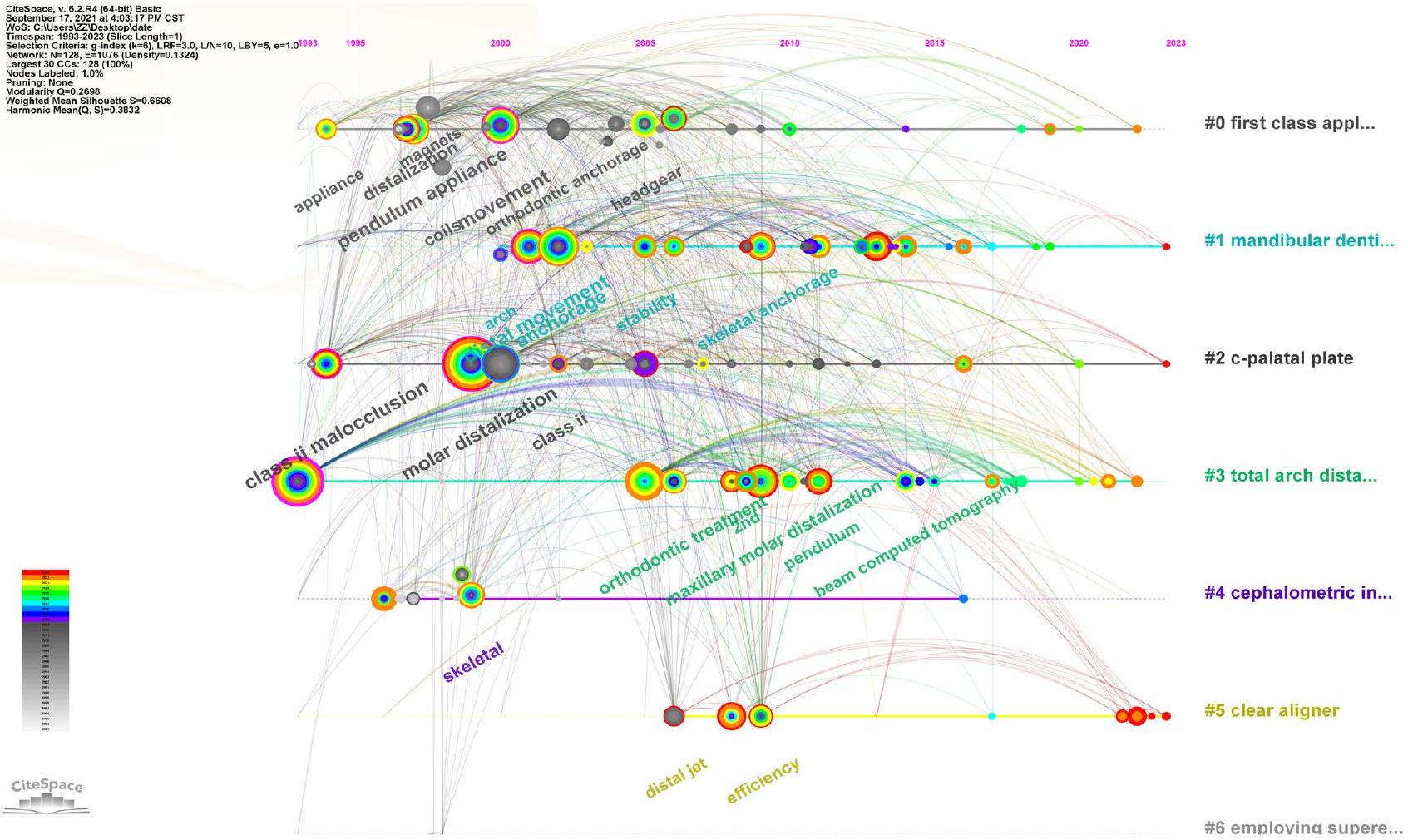
تراوحت درجات المركزية لأقل من 0.01، باستثناء بارك جاي هيون، الذي حصل على درجة مركزية قدرها 0.01. ومن الجدير بالذكر أن أفضل خمسة مؤلفين تم الاستشهاد بهم معًا هم هيلجرز جي جي، كينزينجر جي إس إم، غوش جي، جيانيللي إيه إيه، و[مجهول] (انظر الجدول 7). ومن الأهمية بمكان أن بوسيك تي جي ظهر كالمؤلف الذي يمتلك أعلى درجة مركزية للاستشهاد المشترك (انظر الجدول 8). يتضح من خريطة التصور للاستشهاد المشترك أن الترابطات بين الدراسات المستشهد بها كانت واسعة النطاق، مما يشير إلى ارتباط وثيق بين هذه الجهود الأكاديمية (انظر الشكل 6).
| رتبة | المؤسسات | تردد |
| 1 | جامعة كيونغ هي | 40 |
| 2 | جامعة A.T. ستيل للعلوم الصحية | ٣٥ |
| ٣ | الجامعة الكاثوليكية في كوريا | ٣٤ |
| ٤ | مستشفى سيول سانت ماري | ٣٣ |
| ٥ | جامعة ساو باولو | 19 |
| ٦ | الجامعة المستقلة في باراغواي | 12 |
| ٧ | جامعة سيول الوطنية | 12 |
| ٨ | جامعة باشكنت | 11 |
| 9 | البنك المصري للمعرفة | 9 |
| 10 | كلية سافيثا لطب الأسنان | ٨ |
| رتبة | المؤسسات | المركزية |
| 1 | جامعة كيونغ هي | 0.03 |
| 2 | البنك المصري للمعرفة (EKB) | 0.01 |
| ٣ | جامعة A.T. ستيل للعلوم الصحية | 0 |
| ٤ | الجامعة الكاثوليكية في كوريا | 0 |
| ٥ | مستشفى سيول سانت ماري | 0 |
| رتبة | المؤلفون | تردد |
| 1 | بارك، جاي هيون | 32 |
| 2 | كوك، يون آه | 31 |
| ٣ | بيومه، محمد | 17 |
| ٤ | جانسون، غيليرمي | 12 |
| ٥ | لي، نام-كي | 10 |
| ٦ | كاستانيا هنريكيز، خوسيه فرناندو | ٨ |
| ٧ | كيم، يونجي | ٨ |
| ٨ | بايرام، محمد | ٦ |
| 9 | نور، متين | ٦ |
| 10 | جيلك أوغلو، مفلوت | ٥ |
الرياضة، الصحة، التغذية والطب، وما إلى ذلك. بشكل عام، يتميز توسيع الأضراس الخلفية بكونه يجمع بين مجال طب الأسنان ومجال التغذية الصحية للإنسان.
الكلمات الرئيسية
تحليل المرجع
نقاش
| رتبة | المؤلفون | تردد |
| 1 | هيلجرز جي جي | ١٤٢ |
| 2 | كينزينجر جي إس إم | ١٣٧ |
| ٣ | غوش ج | ١٣٠ |
| ٤ | جيانيللي AA | 121 |
| ٥ | [مجهول] | ١١٨ |
| ٦ | بيولوف إف كيه | ١١٥ |
| ٧ | بوسيك تي جي | 111 |
| ٨ | كارانو أ | ١١٠ |
| 9 | بونديمارك L | ٨٨ |
| 10 | بارك الثانوية | 82 |
| رتبة | المؤلفون | المركزية |
| 1 | بوسيك تي جي | 0.19 |
| ٢ | جيانيللي AA | 0.17 |
| ٣ | كينزينجر جي إس إم | 0.15 |
| ٤ | بارك الثانوية | 0.14 |
| ٥ | [مجهول] | 0.13 |
| ٦ | بونديمارك ل | 0.13 |
| ٧ | كارانو أ | 0.12 |
| ٨ | كيليس أ | 0.1 |
| 9 | جيلغور آي إي | 0.09 |
| 10 | غوش ج | 0.08 |
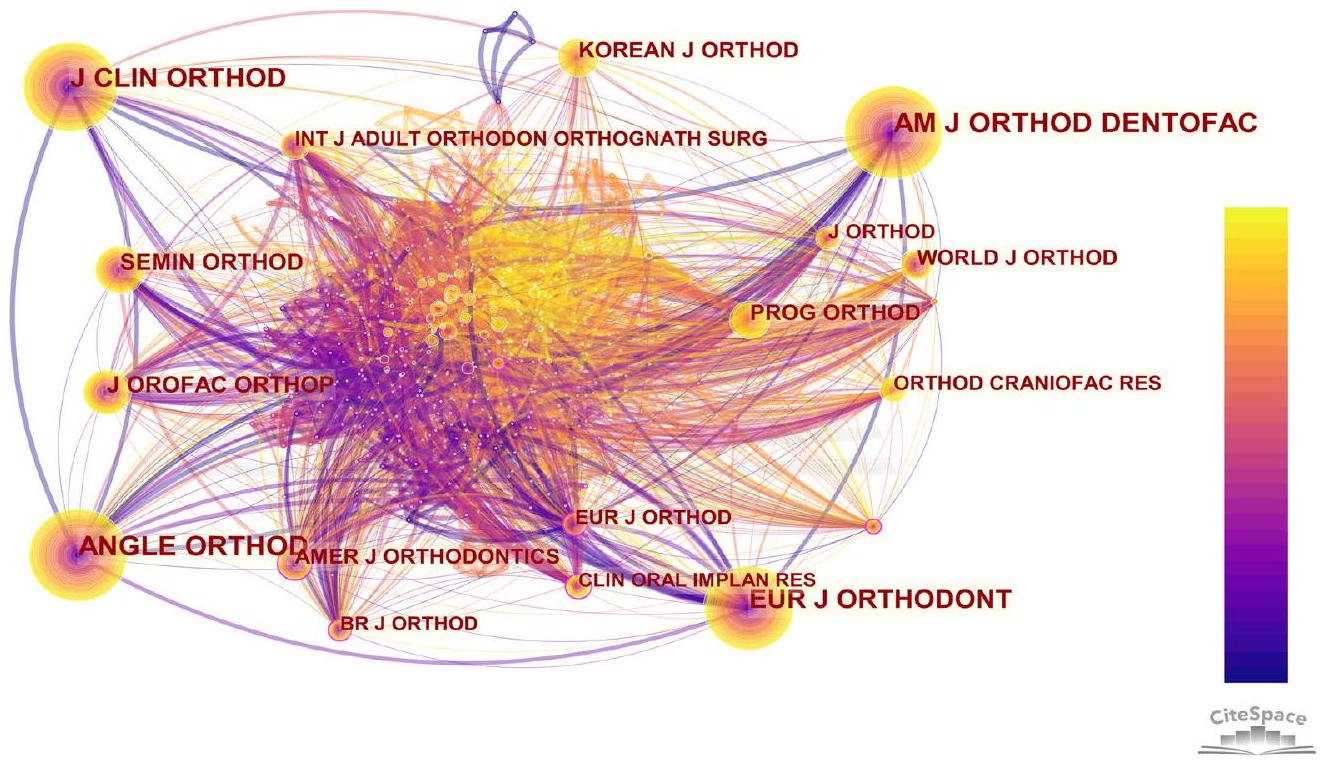
| رتبة | المجلات المستشهد بها | تردد |
| 1 | AM J ORTHOD DENTOFAC | 498 |
| 2 | زاوية أورثود | ٤٧٧ |
| ٣ | مجلة تقويم الأسنان السريرية | ٣٨٠ |
| ٤ | يور ج أورثودونت | ٣٤٠ |
| ٥ | ج أوروفاك أورثوب | 163 |
| رتبة | المجلات المستشهد بها | المركزية |
| 1 | أمير ج. تقويم الأسنان | 0.15 |
| 2 | بي آر ج أورثود | 0.13 |
| ٣ | تقويم الأسنان المستمر | 0.11 |
| ٤ | EUR J ORTHOD | 0.11 |
| ٥ | مجلة زراعة الأسنان السريرية | 0.10 |

تقديم الحل لكل من التقدم الفك العلوي والسفلي. في الوقت الحالي، يركز البحث بشكل رئيسي على إبعاد الأضراس العلوية. تمتد مؤشرات الإبعاد
ما وراء إدارة مرضى الفئة الثانية، لتشمل مرضى الفئة الثالثة الذين يحتاجون إلى جراحة بسبب عدم التعويض في القوس العلوي، خاصة إذا كانت إعادة سحب القواطع العلوية تعتبر ضرورية. وأفضل وقت لـ
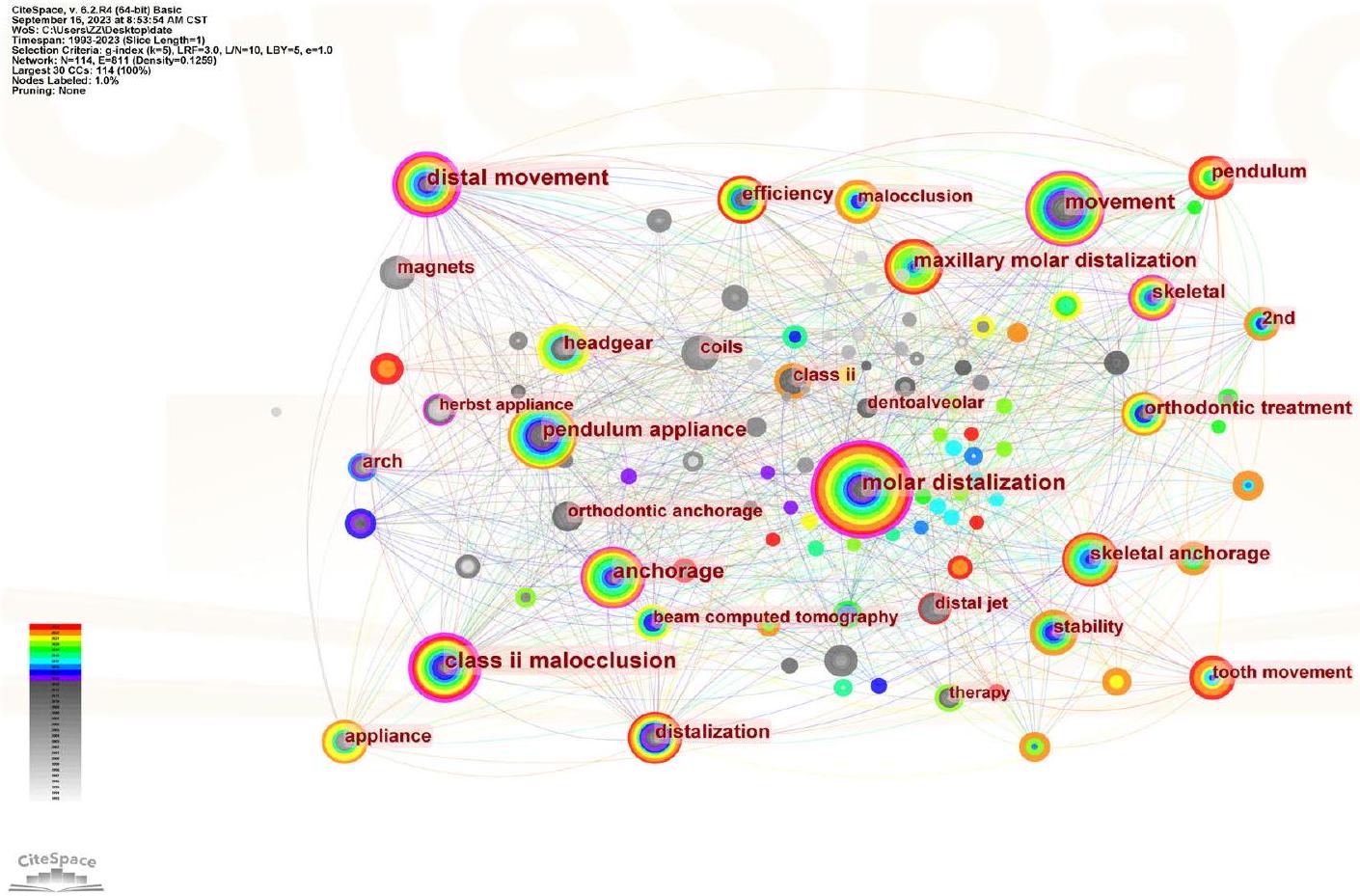
| رتبة | الكلمات الرئيسية | تردد |
| 1 | إبعاد الأضراس | ١٣٠ |
| 2 | حركة | 68 |
| ٣ | سوء الإطباق من الدرجة الثانية | 66 |
| ٤ | الحركة البعيدة | 66 |
| ٥ | جهاز البندول | 65 |
| رتبة | الكلمات الرئيسية | المركزية |
| 1 | سوء الإطباق من الدرجة الثانية | 0.31 |
| 2 | إبعاد الضواحك | 0.23 |
| ٣ | الحركة البعيدة | 0.20 |
| ٤ | أنكوراج | 0.12 |
| ٥ | حركة | 0.11 |
القيود، تم تطوير أجهزة داخل الفم مثل البندول، وأجهزة داخل الفم غير المتوافقة، وأجهزة النفاثة البعيدة، التي لا تتطلب تعاون المريض. خذ جهاز داخل الفم غير المتوافق كمثال، يمكن إجراء إبعاد الأضراس العلوية بشكل فعال باستخدام أجهزة داخل الفم غير المتوافقة. تراوحت إبعاد الأضراس العلوية الأولى من 6.4 إلى 0.5 مم مع ميل بعيد متزامن من
| الكلمات الرئيسية | سنة القوة البداية النهاية | 1993-2023 | |||
| جهاز هيربست | 1994 | 5.031994 | 2001 | ||
| ملفات | 1998 | 91998 | 2008 | ||
| المغناطيس | 1998 | 7.981998 | 2008 | ||
| تثبيت تقويم الأسنان | ٢٠٠٢ | 6.142002 | 2012 | ||
| أجهزة الرأس العنقية | ٢٠٠٣ | ٤.٣٢٠٠٣ | 2008 | ||
| تغيرات هيكلية | 2004 | 5.312004 | 2010 | ||
| نفاثة بعيدة | 2006 | 5.412006 | 2011 | ||
| جهاز كهربائي | 1994 | ٣.٦٣٢٠٠٦ | 2007 | ||
| الفئة الثانية | ٢٠٠٢ | ٣.٩٦٢٠٠٩ | 2013 | ||
| زراعة | 2011 | 5.532011 | 2015 | ||
| نفاثة | 2011 | ٣.٥٥٢٠١١ | 2013 | ||
| فكي | 2013 | 3.522013 | 2019 | ||
| تثبيت هيكلي | 2012 | 5.452014 | 2017 | ||
| تصوير مقطعي محوسب بالليزر | 2014 | ٤.٠٥٢٠١٤ | 2018 | ||
| البندول | 2016 | 5.852018 | ٢٠٢٣ | ||
| استخراج | 2010 | ٤.٣١٢٠١٨ | ٢٠٢١ | ||
| إبعاد الأضراس العلوية | 2009 | ٤.١٩٢٠١٨ | ٢٠٢٠ | ||
| حركة الأسنان | 1994 | ٤.٤١٢٠٢١ | ٢٠٢٣ | ||
| توسيع القوس الكلي | 2021 | 4.082021 | ٢٠٢٣ | ||
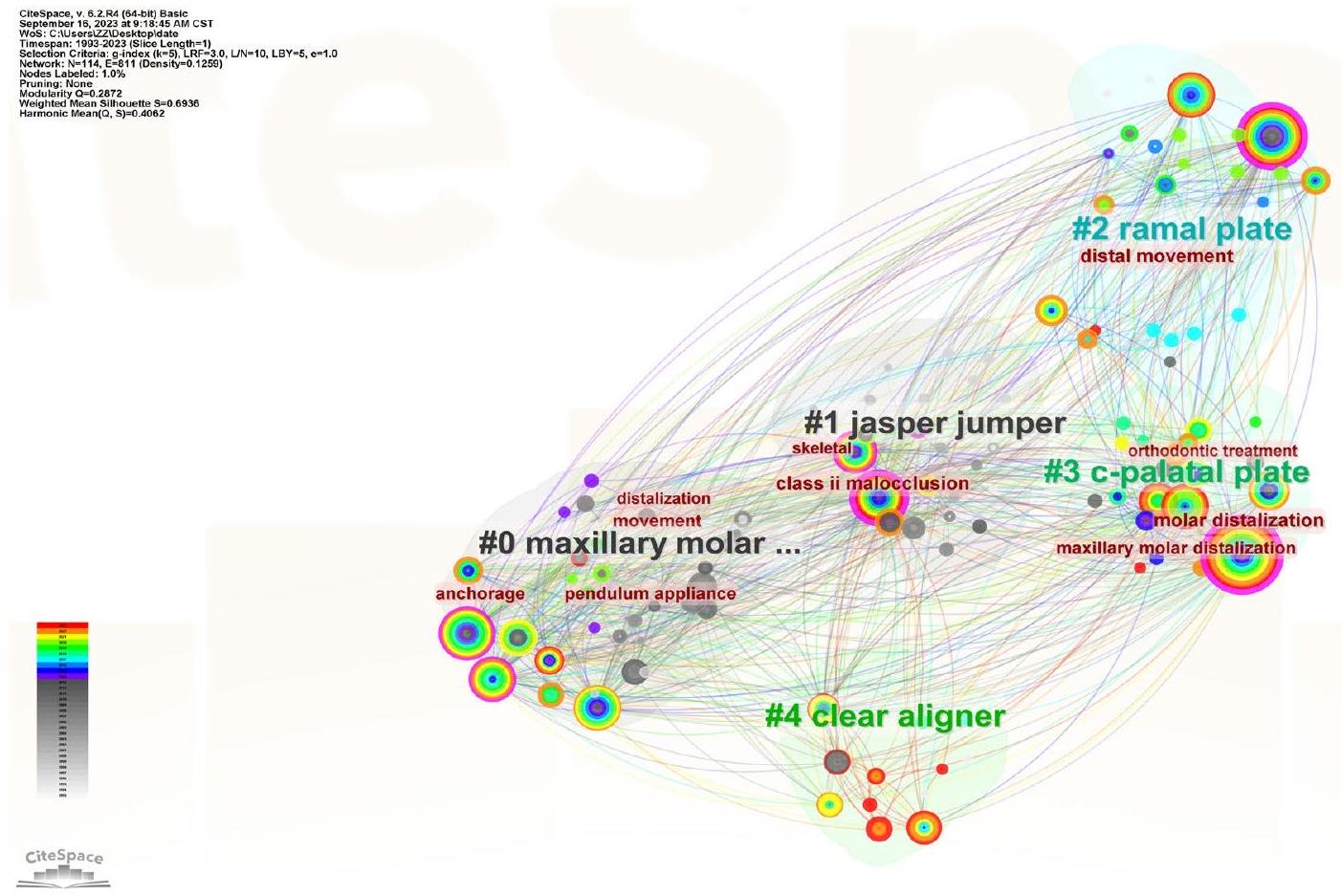
لقد قدمت ميزة واضحة تتمثل في حركة ضرس خلفي كبيرة تتراوح تقريبًا بين 2.1 مم [42]. تسهل أجهزة التقويم الشفافة تحقيق مستوى ملحوظ من الدقة (88%) في إحداث الحركة الجسدية للأضراس العلوية [43-47]، خاصة عندما تكون الحركة المتوسطة المطلوبة نحو الخلف 2.7 مم [48]. هذه الدقة تعزز بشكل كبير من خلال استخدام الملحقات. وبالتالي، يُوصى بشدة باستخدام أجهزة التقويم في الحالات التي تتطلب فيها الأفراد غير الناميين.
| رتبة | تكرار الاقتباس | سنة النشر | مؤلف | عنوان |
| 1 | ٢٦ | 2004 | كينزينجر جي إس إم | كفاءة جهاز البندول لتوسيع الأضراس المتعلقة بمرحلة بزوغ الأضراس الثانية والثالثة [20] |
| 2 | 19 | ٢٠٠٤ | جيلغور آي إي | تحريك الأضراس العلوية الخلفية المدعومة بمسامير داخل العظم [21] |
| ٣ | ١٨ | ٢٠٢٠ | بيشتولد تي | الاستقرار طويل الأمد لتقنية إبعاد الأضراس العلوية المدعومة بالبراغي الصغيرة في علاج الفئة الثانية [11] |
| ٤ | 17 | 2013 | سار سي | مقارنة بين نظامين لدعم الزرعات لتحريك الأضراس الخلفية [22] |
| ٥ | 17 | 2007 | إسكوبار SA | إبعاد الأضراس العلوية باستخدام البندول المدعوم بالعظام: دراسة سريرية [23] |
| رتبة | درجة المركزية | سنة النشر | مؤلف | عنوان |
| 1 | 0.34 | 2009 | كينزينجر جي إس إم | كفاءة جهاز نفاث بعيد الهيكل مدعوم بتثبيت الميني سكرو لتقليل الأضراس العلوية غير المتوافقة [24] |
| 2 | 0.22 | 2006 | كيرسيلي بي إتش | إبعاد الأضراس العلوية باستخدام جهاز بندول مثبت بالعظام [25] |
| ٣ | 0.21 | 2004 | كينزينجر جي إس إم | كفاءة جهاز البندول لتوسيع الأضراس المتعلقة بمرحلة بزوغ الأضراس الثانية والثالثة [20] |
| ٤ | 0.21 | 2013 | سار سي | مقارنة بين نظامين لدعم الزرعات لتحريك الأضراس الخلفية [22] |
| ٥ | 0.18 | 2007 | إسكوبار SA | إبعاد الأضراس العلوية باستخدام البندول المدعوم بالعظام: دراسة سريرية [23] |
الاستنتاجات
المزايا والقيود
قد يؤدي ذلك إلى تجاهل نتائج البحث الحاسمة. علاوة على ذلك، هناك احتمال لوجود تحيز في بيانات الاقتباس، حيث إن الأوراق التي تحصل على عدد كبير من الاقتباسات ليست بالضرورة مرادفة لتكون الأبحاث العلمية الأهم أو الأكثر دقة.
الإعلانات
المصالح المتنافسة يعلن المؤلفون عدم وجود مصالح متنافسة.
References
- Bolla E, Muratore F, Carano A, Bowman SJ (2002) Evaluation of maxillary molar distalization with the distal jet: a comparison with other contemporary methods. Angle Orthod 72:481-494. https:// doi.org/10.1043/0003-3219(2002)072<0481:Eommdw>2.0. Co;2
- Fontana M, Cozzani M, Caprioglio A (2012) Non-compliance maxillary molar distalizing appliances: an overview of the last decade. Prog Orthod 13:173-184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pio. 2011.10.002
- Gracco A, Luca L, Siciliani G (2007) Molar distalisation with skeletal anchorage. Aust Orthod J 23:147-152
- Chiu PP, McNamara JA Jr, Franchi L (2005) A comparison of two intraoral molar distalization appliances: distal jet versus pendulum. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 128:353-365. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2004.04.031
- Brickman CD, Sinha PK, Nanda RS (2000) Evaluation of the Jones jig appliance for distal molar movement. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 118:526-534. https://doi.org/10.1067/mod. 2000.110332
- Cozzani M, Pasini M, Zallio F, Ritucci R, Mutinelli S, Mazzotta L, Giuca MR, Piras V (2014) Comparison of maxillary molar distalization with an implant-supported distal jet and a traditional
tooth-supported distal jet appliance. Int J Dent 2014:937059. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/937059 - Sfondrini MF, Cacciafesta V, Sfondrini G (2002) Upper molar distalization: a critical analysis. Orthod Craniofac Res 5:114-126. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0544.2002.01155.x
- Verma SK, Rastogi K, Bhushan R, Sagar M (2013) Molar distalisation by pendulum appliance. BMJ Case Rep 2013. https://doi. org/10.1136/bcr-2012-008461
- Caprioglio A, Cafagna A, Fontana M, Cozzani M (2015) Comparative evaluation of molar distalization therapy using pendulum and distal screw appliances. Korean J Orthod 45:171-179. https:// doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2015.45.4.171
- Bayome M, Park JH, Bay C, Kook YA (2021) Distalization of maxillary molars using temporary skeletal anchorage devices: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Orthod Craniofac Res 24(Suppl 1):103-112. https://doi.org/10.1111/ocr. 12470
- Bechtold TE, Park YC, Kim KH, Jung H, Kang JY, Choi YJ (2020) Long-term stability of miniscrew anchored maxillary molar distalization in Class II treatment. Angle Orthod 90:362368. https://doi.org/10.2319/051619-335.1
- Cassetta M, Brandetti G, Altieri F (2019) Miniscrew-supported distal jet versus conventional distal jet appliance: a pilot study. J Clin Exp Dent 11:e650-e658. https://doi.org/10.4317/jced. 55780
- Cozzani M, Zallio F, Lombardo L, Gracco A (2010) Efficiency of the distal screw in the distal movement of maxillary molars. World J Orthod 11:341-345
- Shi X, Mao J, Liu Y (2022) Clinical efficacy and influencing factors of molar distalization with clear aligner. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi 57:762-768. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j. cn112144-20210907-00399
- Wu D, Zhao Y, Ma M, Zhang Q, Lei H, Wang Y, Li Y, Chen X (2021) Efficacy of mandibular molar distalization by clear aligner treatment. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 46:11141121. https://doi.org/10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2021.200391
- Železnik D, BlažunVošner H, Kokol P (2017) A bibliometric analysis of the Journal of Advanced Nursing, 1976-2015. J Adv Nurs 73:2407-2419. https://doi.org/10.1111/jan. 13296
- Guerrero-Gironés J, Forner L, Sanz JL, Rodríguez-Lozano FJ, Ghilotti J, Llena C, Lozano A, Melo M (2022) Scientific production on silicate-based endodontic materials: evolution and current state: a bibliometric analysis. Clin Oral Investig 26:5611-5624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-022-04605-8
- Xu D, Wang YL, Wang KT, Wang Y, Dong XR, Tang J, Cui YL (2021) A scientometrics analysis and visualization of depressive disorder. Curr Neuropharmacol 19:766-786. https://doi.org/10.
- Sun S, Mao Z, Wang H (2022) Relationship between periodontitis and diabetes: a bibliometrics analysis. Ann Transl Med 10:401. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-22-1067
- Kinzinger GS, Fritz UB, Sander FG, Diedrich PR (2004) Efficiency of a pendulum appliance for molar distalization related to second and third molar eruption stage. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 125:8-23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2003.02.002
- Gelgör IE, Büyükyilmaz T, Karaman AI, Dolanmaz D, Kalayci A (2004) Intraosseous screw-supported upper molar distalization. Angle Orthod 74:838-850. https://doi.org/10.1043/00033219(2004)074<0838:Isumd>2.0.Co;2
- Sar C, Kaya B, Ozsoy O, Özcirpici AA (2013) Comparison of two implant-supported molar distalization systems. Angle Orthod 83:460-467. https://doi.org/10.2319/080512-630.1
- Escobar SA, Tellez PA, Moncada CA, Villegas CA, Latorre CM, Oberti G (2007) Distalization of maxillary molars with the bonesupported pendulum: a clinical study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 131:545-549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2006.08.012
- Kinzinger GS, Gülden N, Yildizhan F, Diedrich PR (2009) Efficiency of a skeletonized distal jet appliance supported by miniscrew anchorage for noncompliance maxillary molar distalization. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 136:578-586. https://doi.org/10. 1016/j.ajodo.2007.10.049
- Kircelli BH, Pektaş ZO, Kircelli C (2006) Maxillary molar distalization with a bone-anchored pendulum appliance. Angle Orthod 76:650-659. https://doi.org/10.1043/0003-3219(2006)076[0650: Mmdwab]2.0.Co;2
- Al-Thomali Y, Basha S, Mohamed RN (2017) Pendulum and modified pendulum appliances for maxillary molar distalization in class II malocclusion – a systematic review. Acta Odontol Scand 75:394-401. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016357.2017.1324636
- Hashem AS (2021) Effect of second molar eruption on efficiency of maxillary first molar distalization using Carriere distalizer appliance. Dental Press J Orthod 26:e2119146. https://doi.org/ 10.1590/2177-6709.26.4.e2119146.oar
- Wilmes B, Katyal V, Drescher D (2014) Mini-implant-borne Pendulum B appliance for maxillary molar distalisation: design and clinical procedure. Aust Orthod J 30:230-239
- Karlsson I, Bondemark L (2006) Intraoral maxillary molar distalization. Angle Orthod 76:923-929. https://doi.org/10.2319/ 110805-390
- Catalfamo L, Gasperoni E, Celli D (2022) Smart distalization of the upper arch with an easy, efficient and no-compliance procedure. J Orthod 49:304-315. https://doi.org/10.1177/1465312521 1057566
- Jambi S, Thiruvenkatachari B, O’Brien KD, Walsh T (2013) Orthodontic treatment for distalising upper first molars in children and adolescents. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013:Cd008375. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD008375.pub2
- Muse DS, Fillman MJ, Emmerson WJ, Mitchell RD (1993) Molar and incisor changes with Wilson rapid molar distalization. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 104:556-565. https://doi.org/10.1016/ s0889-5406(05)80439-1
- Keles A, Sayinsu K (2000) A new approach in maxillary molar distalization: intraoral bodily molar distalizer. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 117:39-48. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0889-5406(00)70246-0
- Jacques L (2016) Upper arch molar distalization appliances in treatment of class II malocclusion: a critical analysis. Int J Orthod Milwaukee 27:67-74
- Fudalej P, Antoszewska J (2011) Are orthodontic distalizers reinforced with the temporary skeletal anchorage devices effective? Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 139:722-729. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.ajodo.2011.01.019
- Quinzi V, Marchetti E, Guerriero L, Bosco F, Marzo G, Mummolo S (2020) Dentoskeletal class II malocclusion: maxillary molar distalization with no-compliance fixed orthodontic equipment. Dent J (Basel) 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj8010026
- Antonarakis GS, Kiliaridis S (2008) Maxillary molar distalization with noncompliance intramaxillary appliances in class II malocclusion. A systematic review. Angle Orthod 78:1133-1140. https://doi.org/10.2319/101507-406.1
- Mohamed RN, Basha S, Al-Thomali Y (2018) Maxillary molar distalization with miniscrew-supported appliances in class II malocclusion: a systematic review. Angle Orthod 88:494-502. https:// doi.org/10.2319/091717-624.1
- Vilanova L, Castillo AA, Bellini-Pereira SA, Henriques JFC, Janson G, Garib D, Patel MP, da Costa Grec RH, Yatabe M, Cevidanes L, Ruellas AC (2023) Three-dimensional changes after maxillary molar distalization with a miniscrew-anchored cantilever. Angle Orthod 93:513-523. https://doi.org/10.2319/ 091222-640.1
- Lione R, Balboni A, Di Fazio V, Pavoni C, Cozza P (2022) Effects of pendulum appliance versus clear aligners in the vertical
dimension during class II malocclusion treatment: a randomized prospective clinical trial. BMC Oral Health 22:441. https://doi. org/10.1186/s12903-022-02483-w - Altieri F, Mezio M, Guarnieri R, Cassetta M (2022) Comparing distal-jet with dental anchorage to distal-jet with skeletal anchorage: a prospective parallel cohort study. Dent J (Basel) 10. https:// doi.org/10.3390/dj10100179
- Durcekar SG, Kolur V (2016) Anchorage reinforcement post molar distalization. Int J Orthod Milwaukee 27:37-38
- Liu X, Wang W, Gao J, Qin W, Wen Y, Luo H, Ma Y, Jin Z (2023) Actual contribution ratio of maxillary and mandibular molars for total molar relationship correction during maxillary molar sequential distalization using clear aligners with class II elastics: a finite element analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 164:e106e120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2023.07.007
- Mao B, Tian Y, Xiao Y, Li J, Zhou Y (2023) The effect of maxillary molar distalization with clear aligner: a 4D finite-element study with staging simulation. Prog Orthod 24:16. https://doi.org/ 10.1186/s40510-023-00468-1
- Ravera S, Castroflorio T, Garino F, Daher S, Cugliari G, Deregibus A (2016) Maxillary molar distalization with aligners in adult patients: a multicenter retrospective study. Prog Orthod 17:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40510-016-0126-0
- Rossini G, Parrini S, Castroflorio T, Deregibus A, Debernardi CL (2015) Efficacy of clear aligners in controlling orthodontic tooth movement: a systematic review. Angle Orthod 85:881-889. https://doi.org/10.2319/061614-436.1
- Simon M, Keilig L, Schwarze J, Jung BA, Bourauel C (2014) Treatment outcome and efficacy of an aligner technique-regarding incisor torque, premolar derotation and molar distalization. BMC Oral Health 14:68. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6831-14-68
- Liu X, Cheng Y, Qin W, Fang S, Wang W, Ma Y, Jin Z (2022) Effects of upper-molar distalization using clear aligners in combination with class II elastics: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. BMC Oral Health 22:546. https://doi.org/10.1186/ s12903-022-02526-2
- Saif BS, Pan F, Mou Q, Han M, Bu W, Zhao J, Guan L, Wang F, Zou R, Zhou H, Guo YC (2022) Efficiency evaluation of maxillary molar distalization using Invisalign based on palatal rugae
المؤلفون والانتماءات
50. هوي في إل زد، شيا ي، تشانغ ك، تشين هـ، هان و، تيان ي، يين ي، هان
51. كابيلا إس دي، نيرفينا جي إم (2015) التصوير المقطعي المحوسب في تقويم الأسنان: تقييم نتائج العلاج ومؤشرات استخدامه. مجلة الأشعة السنية والفكية 44:20140282.https://doi.org/10.1259/dmfr.20140282
52. مانغانو ف، غاندولفي أ، لونغو ج، لوجوتزو س (2017) الماسحات الضوئية داخل الفم في طب الأسنان: مراجعة للأدبيات الحالية. BMC صحة الفم 17:149.https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-017-0442-x
53. باي إم جي، كيم جي واي، بارك جي تي، تشا جي واي، كيم إتش جي، يو إتش إس، هوانغ سي جي (2013) دقة أدلة الجراحة المصغرة التي تم تقييمها من التصوير المقطعي المحوسب باستخدام الأشعة المخروطية والنماذج الرقمية. المجلة الأمريكية لتقويم الأسنان وطب الأسنان الوجه 143:893-901.https://doi.org/10. 1016/j.ajodo.2013.02.018
54. فاسوغلو ج، ستيفانيداكيس إ، أبستولوبولوس ك، فوتاكيدو إ، فاسوغلو م (2022) دقة وضع الزرعات الصغيرة باستخدام دليل جراحي مصمم بواسطة الكمبيوتر، مع معلومات من المسح داخل الفم واستخدام التصوير المقطعي المحوسب ذو الشعاع المخروطي. مجلة الأسنان (بازل) 10.https://doi.org/10.3390/dj10060104
55. بارتكوفيك ت، والكوفيك-سليزيوك أ (2018) تكنولوجيا الطباعة ثلاثية الأبعاد في تقويم الأسنان – مراجعة للتطبيقات الحالية. مجلة طب الفم 71:356-364.https://doi.org/10.5114/jos.2018.83410
56. تارتاليا جي إم، مابيلي أ، ماسبيرو ج، سانتانييلو ت، سيرافين م، فاروناتو م، كابريوليو أ (2021) الطباعة ثلاثية الأبعاد المباشرة للموائمات التقويمية الشفافة: الحالة الحالية والاحتمالات المستقبلية. المواد (بازل) 14.https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14071799
57. شهناز م (2016) MAaHA (2016) تطبيقات الطباعة ثلاثية الأبعاد في تقويم الأسنان: مراجعة. المجلة الدولية للدراسات العلمية 3:267-270.https://doi. org/10.17354/ijss/2016/99
لين تشينغ
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-024-05520-w
PMID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38286861
Publication Date: 2024-01-30
Molar distalization in orthodontics: a bibliometric analysis
© The Author(s) 2024
Abstract
Objectives The study endeavors to undertake a bibliometric analysis on molar distalization, with the objective of illuminating its evolutionary trajectory, current status, and prognosticating future research hotspots and trends. Material and methods A comprehensive exploration of the literature on molar distalization was carried out by conducting a search in the Web of Science (WOS) core database of the University of Hong Kong Electronic Library. The search for topic terms employed included “molar distalization,” “molar distalisation,” “move molar distally,” “molar distal movement,” and “molar backwards.” The search results were subsequently subjected to meticulous analysis using CiteSpace software. This analysis encompassed various facets such as the citation count; the geographical distribution of the countries, institutions, and journals responsible for publishing the articles; the distribution of the authors; the utilization of keywords within the articles; and the analysis of references. Results A total of 516 articles were included in the analysis. The top 5 countries in terms of the number of published papers were the United States (USA), South Korea, Turkey, Italy, and Germany, and the top 5 institutions in terms of the number of published papers were Kyung Hee University, A.T. Still University of Health Sciences, Catholic University of Korea, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, and Universidade de Sao Paulo. The top 5 authors in terms of the number of published papers were Park, Kook, Bayome, Janson, and Lee. There was little cooperation overall. The top 3 journals in terms of the most published related articles were all orthodontic-related journals. After molar distalization and anchorage, the most frequently used keywords were distalization, movement, and pendulum appliance. Kinzinger GSM is the most frequently cited author in references, and one of his articles also has the highest centrality score in references. Conclusions As the tides of time shift and scholars display an ever-growing dedication to unraveling the intricacies of this therapeutic modality, the realm of molar distalization has undergone notable advancements in technology. Initially, the traditional appliance suffered from aesthetic drawbacks and discomfort. However, contemporary iterations of the appliance have transcended these limitations, boasting enhanced elegance and convenience while concurrently elevating their efficacy. Nevertheless, limitations of current appliances, including their durability and propensity for recurrence post-treatment, continue to necessitate further advancement. Hence, the ongoing scientific inquiry aims to delve deeper into refining treatment modalities and fabricating cutting-edge appliances within this realm. Clinical relevance. This study holds the potential to significantly enhance the ability of orthodontists to devise treatment protocols and offer state-of-the-art clinical recommendations, thereby empowering them to deliver advanced and refined orthodontic interventions.
Introduction
Methods
Database
Search strategy
Data screening and collection

Statistical analysis
Results
General information
12.14 citations per article. Among these articles, there were 481 original articles, 34 reviews, and 1 proceeding papers (see Table 1). The number of published papers per year did not change much before 2005 but showed an overall growth trend after 2005, and the number of published papers reached its peak in 2022 (see Fig. 2).
Countries and institutions
| Article type | Records | % of 516 |
| Article | 481 | 93.22 |
| Review | 34 | 6.59 |
| Proceedings paper | 1 | 0.19 |

Authors


| Rank | Countries | Frequency |
| 1 | USA | 114 |
| 2 | South Korea | 78 |
| 3 | Turkey | 73 |
| 4 | Italy | 45 |
| 5 | Germany | 42 |
| 6 | China | 40 |
| 7 | Brazil | 36 |
| 8 | India | 34 |
| 9 | Japan | 34 |
| 10 | Switzerland | 14 |
| Rank | Countries | Centrality |
| 1 | USA | 0.72 |
| 2 | Italy | 0.35 |
| 3 | Slovakia | 0.16 |
| 4 | Saudi Arabia | 0.11 |
| 5 | Czech Republic | 0.11 |
| 6 | China | 0.10 |
| 7 | South Korea | 0.08 |
| 8 | Germany | 0.07 |
| 9 | Brazil | 0.06 |
| 10 | India | 0.06 |
Journals
centrality scores of less than 0.01 , with the exception of Park Jae Hyun, who had a centrality score of 0.01. Notably, the top five co-cited authors comprised Hilgers JJ, Kinzinger GSM, Ghosh J, Gianelly AA, and [Anonymous] (refer to Table 7). Of particular significance, Bussick TJ emerged as the author boasting the highest co-citation centrality score (refer to Table 8). Evident from the co-citation visualization map, the interconnections among the cited studies were considerably widespread, implying a close linkage between these scholarly endeavors (refer to Fig. 6).
| Rank | Institutions | Frequency |
| 1 | Kyung Hee University | 40 |
| 2 | A.T. Still University of Health Sciences | 35 |
| 3 | Catholic University of Korea | 34 |
| 4 | Seoul St. Mary’s Hosptial | 33 |
| 5 | Universidade De Sao Paulo | 19 |
| 6 | Universidad Autonoma del Paraguay | 12 |
| 7 | Seoul National University | 12 |
| 8 | Baskent University | 11 |
| 9 | Egyptian Knowledge Bank | 9 |
| 10 | Saveetha Dental college | 8 |
| Rank | Institutions | Centrality |
| 1 | Kyung Hee University | 0.03 |
| 2 | Egyptian Knowledge Bank (EKB) | 0.01 |
| 3 | A.T. Still University of Health Sciences | 0 |
| 4 | Catholic University of Korea | 0 |
| 5 | Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital | 0 |
| Rank | Authors | Frequency |
| 1 | Park, Jae Hyun | 32 |
| 2 | Kook, Yoon-Ah | 31 |
| 3 | Bayome, Mohamed | 17 |
| 4 | Janson, Guilherme | 12 |
| 5 | Lee, Nam-Ki | 10 |
| 6 | Castanha henriques, Jose Fernando | 8 |
| 7 | Kim, Yoonji | 8 |
| 8 | Bayram, Mehmet | 6 |
| 9 | Nur, Metin | 6 |
| 10 | Celikoglu, Mevlut | 5 |
sport, health, nutrition and medicine, and so on. Overall, molar distalization has the characteristics of spanning the field of oral medicine and the field of human health nutrition.
Keywords
Reference analysis
Discussion

| Rank | Authors | Frequency |
| 1 | Hilgers JJ | 142 |
| 2 | Kinzinger GSM | 137 |
| 3 | Ghosh J | 130 |
| 4 | Gianelly AA | 121 |
| 5 | [Anonymous] | 118 |
| 6 | Byloff FK | 115 |
| 7 | Bussick TJ | 111 |
| 8 | Carano A | 110 |
| 9 | Bondemark L | 88 |
| 10 | Park HS | 82 |
| Rank | Authors | Centrality |
| 1 | Bussick TJ | 0.19 |
| 2 | Gianelly AA | 0.17 |
| 3 | Kinzinger GSM | 0.15 |
| 4 | Park HS | 0.14 |
| 5 | [Anonymous] | 0.13 |
| 6 | Bondemark L | 0.13 |
| 7 | Carano A | 0.12 |
| 8 | Keles A | 0.1 |
| 9 | Gelgor IE | 0.09 |
| 10 | Ghosh J | 0.08 |

| Rank | Cited journals | Frequency |
| 1 | AM J ORTHOD DENTOFAC | 498 |
| 2 | ANGLE ORTHOD | 477 |
| 3 | J CLIN ORTHOD | 380 |
| 4 | EUR J ORTHODONT | 340 |
| 5 | J OROFAC ORTHOP | 163 |
| Rank | Cited journals | Centrality |
| 1 | AMER J ORTHODONTICS | 0.15 |
| 2 | BR J ORTHOD | 0.13 |
| 3 | CONT ORTHODONTICS | 0.11 |
| 4 | EUR J ORTHOD | 0.11 |
| 5 | CLIN ORAL IMPLAN RES | 0.10 |


distalization of both maxillary and mandibular molars offers a solution for both maxillary and mandibular prognathism. At present, the research focus is mainly on the distalization of maxillary molars. The indication for distalisation extends
beyond the management of Class II patients, to include Class III surgical patients necessitating decompensation in the upper arch, particularly if the retraction of upper incisors is deemed essential [28]. And the most opportune time to

| Rank | Keywords | Frequency |
| 1 | Molar distalization | 130 |
| 2 | Movement | 68 |
| 3 | Class II malocclusion | 66 |
| 4 | Distal movement | 66 |
| 5 | Pendulum appliance | 65 |
| Rank | Keywords | Centrality |
| 1 | Class II malocclusion | 0.31 |
| 2 | Molar distalization | 0.23 |
| 3 | Distal movement | 0.20 |
| 4 | Anchorage | 0.12 |
| 5 | Movement | 0.11 |
limitations, intraoral devices such as pendulum, noncompliance intraoral appliances, and distal jet appliances were developed, which do not necessitate patient cooperation [34]. Take noncompliance intraoral appliance as an example, maxillary molar distalization can be effectively performed with the use of noncompliance intraoral appliances [35, 36]. Maxillary first molar distalization ranged from 6.4 to 0.5 mm with a concomitant distal tipping from
| Keywords | Year Strength Begin End | 1993-2023 | |||
| herbst appliance | 1994 | 5.031994 | 2001 | ||
| coils | 1998 | 91998 | 2008 | ||
| magnets | 1998 | 7.981998 | 2008 | ||
| orthodontic anchorage | 2002 | 6.142002 | 2012 | ||
| cervical headgear | 2003 | 4.32003 | 2008 | ||
| skeletal changes | 2004 | 5.312004 | 2010 | ||
| distal jet | 2006 | 5.412006 | 2011 | ||
| appliance | 1994 | 3.632006 | 2007 | ||
| class ii | 2002 | 3.962009 | 2013 | ||
| implants | 2011 | 5.532011 | 2015 | ||
| jet | 2011 | 3.552011 | 2013 | ||
| maxillary | 2013 | 3.522013 | 2019 | ||
| skeletal anchorage | 2012 | 5.452014 | 2017 | ||
| beam computed tomography | 2014 | 4.052014 | 2018 | ||
| pendulum | 2016 | 5.852018 | 2023 | ||
| extraction | 2010 | 4.312018 | 2021 | ||
| maxillary molar distalization | 2009 | 4.192018 | 2020 | ||
| tooth movement | 1994 | 4.412021 | 2023 | ||
| total arch distalization | 2021 | 4.082021 | 2023 | ||

it offered the distinct advantage of a substantial premolar distal movement ranging from approximately 2.1 mm [42]. Clear aligners facilitate the achievement of a remarkable level of precision (88%) in effecting the bodily movement of upper molars [43-47], particularly when a mean distalization movement of 2.7 mm is desired [48]. This accuracy is significantly enhanced through the utilization of attachments. Thus, the utilization of aligners is strongly recommended in cases where non-growing individuals necessitate

| Rank | Citation frequency | Year of publication | Author | Title |
| 1 | 26 | 2004 | Kinzinger GSM | Efficiency of a pendulum appliance for molar distalization related to second and third molar eruption stage [20] |
| 2 | 19 | 2004 | Gelgor IE | Intraosseous screw-supported upper molar distalization [21] |
| 3 | 18 | 2020 | Bechtold TE | Long-term stability of miniscrew anchored maxillary molar distalization in Class II treatment [11] |
| 4 | 17 | 2013 | Sar C | Comparison of two implant-supported molar distalization systems [22] |
| 5 | 17 | 2007 | Escobar SA | Distalization of maxillary molars with the bone-supported pendulum: a clinical study [23] |
| Rank | Centrality score | Year of publication | Author | Title |
| 1 | 0.34 | 2009 | Kinzinger GSM | Efficiency of a skeletonized distal jet appliance supported by miniscrew anchorage for noncompliance maxillary molar distalization [24] |
| 2 | 0.22 | 2006 | Kircelli BH | Maxillary molar distalization with a bone-anchored pendulum appliance [25] |
| 3 | 0.21 | 2004 | Kinzinger GSM | Efficiency of a pendulum appliance for molar distalization related to second and third molar eruption stage [20] |
| 4 | 0.21 | 2013 | Sar C | Comparison of two implant-supported molar distalization systems [22] |
| 5 | 0.18 | 2007 | Escobar SA | Distalization of maxillary molars with the bone-supported pendulum: a clinical study [23] |
Conclusions
Advantages and limitations
potentially resulting in the oversight of critical research findings. Moreover, there exists the possibility of bias within the citation data, as papers that garner a high number of citations are not unequivocally synonymous with being the foremost or most precise scientific inquiries.
Declarations
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- Bolla E, Muratore F, Carano A, Bowman SJ (2002) Evaluation of maxillary molar distalization with the distal jet: a comparison with other contemporary methods. Angle Orthod 72:481-494. https:// doi.org/10.1043/0003-3219(2002)072<0481:Eommdw>2.0. Co;2
- Fontana M, Cozzani M, Caprioglio A (2012) Non-compliance maxillary molar distalizing appliances: an overview of the last decade. Prog Orthod 13:173-184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pio. 2011.10.002
- Gracco A, Luca L, Siciliani G (2007) Molar distalisation with skeletal anchorage. Aust Orthod J 23:147-152
- Chiu PP, McNamara JA Jr, Franchi L (2005) A comparison of two intraoral molar distalization appliances: distal jet versus pendulum. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 128:353-365. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2004.04.031
- Brickman CD, Sinha PK, Nanda RS (2000) Evaluation of the Jones jig appliance for distal molar movement. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 118:526-534. https://doi.org/10.1067/mod. 2000.110332
- Cozzani M, Pasini M, Zallio F, Ritucci R, Mutinelli S, Mazzotta L, Giuca MR, Piras V (2014) Comparison of maxillary molar distalization with an implant-supported distal jet and a traditional
tooth-supported distal jet appliance. Int J Dent 2014:937059. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/937059 - Sfondrini MF, Cacciafesta V, Sfondrini G (2002) Upper molar distalization: a critical analysis. Orthod Craniofac Res 5:114-126. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0544.2002.01155.x
- Verma SK, Rastogi K, Bhushan R, Sagar M (2013) Molar distalisation by pendulum appliance. BMJ Case Rep 2013. https://doi. org/10.1136/bcr-2012-008461
- Caprioglio A, Cafagna A, Fontana M, Cozzani M (2015) Comparative evaluation of molar distalization therapy using pendulum and distal screw appliances. Korean J Orthod 45:171-179. https:// doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2015.45.4.171
- Bayome M, Park JH, Bay C, Kook YA (2021) Distalization of maxillary molars using temporary skeletal anchorage devices: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Orthod Craniofac Res 24(Suppl 1):103-112. https://doi.org/10.1111/ocr. 12470
- Bechtold TE, Park YC, Kim KH, Jung H, Kang JY, Choi YJ (2020) Long-term stability of miniscrew anchored maxillary molar distalization in Class II treatment. Angle Orthod 90:362368. https://doi.org/10.2319/051619-335.1
- Cassetta M, Brandetti G, Altieri F (2019) Miniscrew-supported distal jet versus conventional distal jet appliance: a pilot study. J Clin Exp Dent 11:e650-e658. https://doi.org/10.4317/jced. 55780
- Cozzani M, Zallio F, Lombardo L, Gracco A (2010) Efficiency of the distal screw in the distal movement of maxillary molars. World J Orthod 11:341-345
- Shi X, Mao J, Liu Y (2022) Clinical efficacy and influencing factors of molar distalization with clear aligner. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi 57:762-768. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j. cn112144-20210907-00399
- Wu D, Zhao Y, Ma M, Zhang Q, Lei H, Wang Y, Li Y, Chen X (2021) Efficacy of mandibular molar distalization by clear aligner treatment. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 46:11141121. https://doi.org/10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2021.200391
- Železnik D, BlažunVošner H, Kokol P (2017) A bibliometric analysis of the Journal of Advanced Nursing, 1976-2015. J Adv Nurs 73:2407-2419. https://doi.org/10.1111/jan. 13296
- Guerrero-Gironés J, Forner L, Sanz JL, Rodríguez-Lozano FJ, Ghilotti J, Llena C, Lozano A, Melo M (2022) Scientific production on silicate-based endodontic materials: evolution and current state: a bibliometric analysis. Clin Oral Investig 26:5611-5624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-022-04605-8
- Xu D, Wang YL, Wang KT, Wang Y, Dong XR, Tang J, Cui YL (2021) A scientometrics analysis and visualization of depressive disorder. Curr Neuropharmacol 19:766-786. https://doi.org/10.
- Sun S, Mao Z, Wang H (2022) Relationship between periodontitis and diabetes: a bibliometrics analysis. Ann Transl Med 10:401. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-22-1067
- Kinzinger GS, Fritz UB, Sander FG, Diedrich PR (2004) Efficiency of a pendulum appliance for molar distalization related to second and third molar eruption stage. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 125:8-23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2003.02.002
- Gelgör IE, Büyükyilmaz T, Karaman AI, Dolanmaz D, Kalayci A (2004) Intraosseous screw-supported upper molar distalization. Angle Orthod 74:838-850. https://doi.org/10.1043/00033219(2004)074<0838:Isumd>2.0.Co;2
- Sar C, Kaya B, Ozsoy O, Özcirpici AA (2013) Comparison of two implant-supported molar distalization systems. Angle Orthod 83:460-467. https://doi.org/10.2319/080512-630.1
- Escobar SA, Tellez PA, Moncada CA, Villegas CA, Latorre CM, Oberti G (2007) Distalization of maxillary molars with the bonesupported pendulum: a clinical study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 131:545-549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2006.08.012
- Kinzinger GS, Gülden N, Yildizhan F, Diedrich PR (2009) Efficiency of a skeletonized distal jet appliance supported by miniscrew anchorage for noncompliance maxillary molar distalization. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 136:578-586. https://doi.org/10. 1016/j.ajodo.2007.10.049
- Kircelli BH, Pektaş ZO, Kircelli C (2006) Maxillary molar distalization with a bone-anchored pendulum appliance. Angle Orthod 76:650-659. https://doi.org/10.1043/0003-3219(2006)076[0650: Mmdwab]2.0.Co;2
- Al-Thomali Y, Basha S, Mohamed RN (2017) Pendulum and modified pendulum appliances for maxillary molar distalization in class II malocclusion – a systematic review. Acta Odontol Scand 75:394-401. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016357.2017.1324636
- Hashem AS (2021) Effect of second molar eruption on efficiency of maxillary first molar distalization using Carriere distalizer appliance. Dental Press J Orthod 26:e2119146. https://doi.org/ 10.1590/2177-6709.26.4.e2119146.oar
- Wilmes B, Katyal V, Drescher D (2014) Mini-implant-borne Pendulum B appliance for maxillary molar distalisation: design and clinical procedure. Aust Orthod J 30:230-239
- Karlsson I, Bondemark L (2006) Intraoral maxillary molar distalization. Angle Orthod 76:923-929. https://doi.org/10.2319/ 110805-390
- Catalfamo L, Gasperoni E, Celli D (2022) Smart distalization of the upper arch with an easy, efficient and no-compliance procedure. J Orthod 49:304-315. https://doi.org/10.1177/1465312521 1057566
- Jambi S, Thiruvenkatachari B, O’Brien KD, Walsh T (2013) Orthodontic treatment for distalising upper first molars in children and adolescents. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013:Cd008375. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD008375.pub2
- Muse DS, Fillman MJ, Emmerson WJ, Mitchell RD (1993) Molar and incisor changes with Wilson rapid molar distalization. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 104:556-565. https://doi.org/10.1016/ s0889-5406(05)80439-1
- Keles A, Sayinsu K (2000) A new approach in maxillary molar distalization: intraoral bodily molar distalizer. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 117:39-48. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0889-5406(00)70246-0
- Jacques L (2016) Upper arch molar distalization appliances in treatment of class II malocclusion: a critical analysis. Int J Orthod Milwaukee 27:67-74
- Fudalej P, Antoszewska J (2011) Are orthodontic distalizers reinforced with the temporary skeletal anchorage devices effective? Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 139:722-729. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.ajodo.2011.01.019
- Quinzi V, Marchetti E, Guerriero L, Bosco F, Marzo G, Mummolo S (2020) Dentoskeletal class II malocclusion: maxillary molar distalization with no-compliance fixed orthodontic equipment. Dent J (Basel) 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj8010026
- Antonarakis GS, Kiliaridis S (2008) Maxillary molar distalization with noncompliance intramaxillary appliances in class II malocclusion. A systematic review. Angle Orthod 78:1133-1140. https://doi.org/10.2319/101507-406.1
- Mohamed RN, Basha S, Al-Thomali Y (2018) Maxillary molar distalization with miniscrew-supported appliances in class II malocclusion: a systematic review. Angle Orthod 88:494-502. https:// doi.org/10.2319/091717-624.1
- Vilanova L, Castillo AA, Bellini-Pereira SA, Henriques JFC, Janson G, Garib D, Patel MP, da Costa Grec RH, Yatabe M, Cevidanes L, Ruellas AC (2023) Three-dimensional changes after maxillary molar distalization with a miniscrew-anchored cantilever. Angle Orthod 93:513-523. https://doi.org/10.2319/ 091222-640.1
- Lione R, Balboni A, Di Fazio V, Pavoni C, Cozza P (2022) Effects of pendulum appliance versus clear aligners in the vertical
dimension during class II malocclusion treatment: a randomized prospective clinical trial. BMC Oral Health 22:441. https://doi. org/10.1186/s12903-022-02483-w - Altieri F, Mezio M, Guarnieri R, Cassetta M (2022) Comparing distal-jet with dental anchorage to distal-jet with skeletal anchorage: a prospective parallel cohort study. Dent J (Basel) 10. https:// doi.org/10.3390/dj10100179
- Durcekar SG, Kolur V (2016) Anchorage reinforcement post molar distalization. Int J Orthod Milwaukee 27:37-38
- Liu X, Wang W, Gao J, Qin W, Wen Y, Luo H, Ma Y, Jin Z (2023) Actual contribution ratio of maxillary and mandibular molars for total molar relationship correction during maxillary molar sequential distalization using clear aligners with class II elastics: a finite element analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 164:e106e120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2023.07.007
- Mao B, Tian Y, Xiao Y, Li J, Zhou Y (2023) The effect of maxillary molar distalization with clear aligner: a 4D finite-element study with staging simulation. Prog Orthod 24:16. https://doi.org/ 10.1186/s40510-023-00468-1
- Ravera S, Castroflorio T, Garino F, Daher S, Cugliari G, Deregibus A (2016) Maxillary molar distalization with aligners in adult patients: a multicenter retrospective study. Prog Orthod 17:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40510-016-0126-0
- Rossini G, Parrini S, Castroflorio T, Deregibus A, Debernardi CL (2015) Efficacy of clear aligners in controlling orthodontic tooth movement: a systematic review. Angle Orthod 85:881-889. https://doi.org/10.2319/061614-436.1
- Simon M, Keilig L, Schwarze J, Jung BA, Bourauel C (2014) Treatment outcome and efficacy of an aligner technique-regarding incisor torque, premolar derotation and molar distalization. BMC Oral Health 14:68. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6831-14-68
- Liu X, Cheng Y, Qin W, Fang S, Wang W, Ma Y, Jin Z (2022) Effects of upper-molar distalization using clear aligners in combination with class II elastics: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. BMC Oral Health 22:546. https://doi.org/10.1186/ s12903-022-02526-2
- Saif BS, Pan F, Mou Q, Han M, Bu W, Zhao J, Guan L, Wang F, Zou R, Zhou H, Guo YC (2022) Efficiency evaluation of maxillary molar distalization using Invisalign based on palatal rugae
Authors and Affiliations
50. Hui VLZ, Xie Y, Zhang K, Chen H, Han W, Tian Y, Yin Y, Han
51. Kapila SD, Nervina JM (2015) CBCT in orthodontics: assessment of treatment outcomes and indications for its use. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 44:20140282. https://doi.org/10.1259/dmfr.20140282
52. Mangano F, Gandolfi A, Luongo G, Logozzo S (2017) Intraoral scanners in dentistry: a review of the current literature. BMC Oral Health 17:149. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-017-0442-x
53. Bae MJ, Kim JY, Park JT, Cha JY, Kim HJ, Yu HS, Hwang CJ (2013) Accuracy of miniscrew surgical guides assessed from cone-beam computed tomography and digital models. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 143:893-901. https://doi.org/10. 1016/j.ajodo.2013.02.018
54. Vasoglou G, Stefanidaki I, Apostolopoulos K, Fotakidou E, Vasoglou M (2022) Accuracy of mini-implant placement using a computer-aided designed surgical guide, with information of intraoral scan and the use of a cone-beam CT. Dent J (Basel) 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj10060104
55. Bartkowiak T, Walkowiak-Śliziuk A (2018) 3D printing technology in orthodontics – review of current applications. Journal of Stomatology 71:356-364. https://doi.org/10.5114/jos.2018.83410
56. Tartaglia GM, Mapelli A, Maspero C, Santaniello T, Serafin M, Farronato M, Caprioglio A (2021) Direct 3D printing of clear orthodontic aligners: current state and future possibilities. Materials (Basel) 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14071799
57. Shahnaz M (2016) MAaHA (2016) Applications of 3-D printing in orthodontics: a review. Int J Sci Stud 3:267-270. https://doi. org/10.17354/ijss/2016/99
