DOI: https://doi.org/10.2463/mrms.rev.2023-0175
PMID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38569866
تاريخ النشر: 2024-01-01
تحليل صور موتر الانتشار على طول الفضاء المحيط بالأوعية (DTI-ALPS): إعادة النظر في معنى وأهمية الطريقة
الملخص
لقد مرت أكثر من 5 سنوات منذ اقتراح طريقة تحليل صور الموجات الانتشارية على طول الفضاء المحيط بالأوعية الدموية (DTI-ALPS) بهدف تقييم النظام الغليمفاتي. هذه الطريقة مفيدة بسبب عدم تدخّلها، وتوفيرها لمؤشر بسيط في صيغة مباشرة، وإمكانية التحليل الرجعي. لذلك، تم اعتماد طريقة ALPS لتقييم النظام الغليمفاتي للعديد من الاضطرابات في العديد من الدراسات. الغرض من هذه المراجعة هو النظر إلى الوراء ومناقشة طريقة ALPS في هذه اللحظة.
تم العثور على مؤشر ALPS كدليل على عدد من الحالات المتعلقة بالنظام الغليمفاتي. وبالتالي، على الرغم من أن هذا كان متوقعًا في التقرير الأصلي، إلا أن نتائج طريقة ALPS غالبًا ما تُفسر على أنها تتعلق بشكل فريد بوظيفة النظام الغليمفاتي. ومع ذلك، أشارت عدد من الدراسات اللاحقة إلى المشاكل في تفسير البيانات. كما أنهم يشيرون بشكل صحيح، فإن ارتفاع مؤشر ALPS يدل على الحركة البراونية السائدة لجزيئات الماء في الاتجاه الشعاعي عند مستوى جسم البطين الجانبي، لا أكثر ولا أقل. لحسن الحظ، أصبح مصطلح “مؤشر ALPS” شائعًا ويعرف الآن كمصطلح شائع من قبل العديد من الباحثين. لذلك، يجب التعبير عن مؤشر ALPS ببساطة على أنه مرتفع أو منخفض، وما إذا كان يعكس نظامًا غليمفاتيًا من الأفضل مناقشته بعناية. بعبارة أخرى، عندما يتم ملاحظة انخفاض في مؤشر ALPS، يجب التعبير عنه على أنه “مؤشر ALPS منخفض” وليس مباشرة كـ “خلل في النظام الغليمفاتي”. مؤخرًا، تم اقتراح طرق مختلفة لتقييم النظام الغليمفاتي. وقد أصبح من الواضح أن هذه الطرق أيضًا لا تبدو أنها تعكس كمال النظام الغليمفاتي المعقد للغاية. وهذا يعني أنه سيكون من المرغوب استخدام طرق متنوعة بشكل مشترك لتقييم النظام الغليمفاتي بطريقة شاملة.
مقدمة
تم تقديم طريقة DTI-ALPS بالإضافة إلى عدة طرق أخرى لتقييم ديناميات السائل بين الخلايا بشكل غير جراحي، وقد تم الإبلاغ عن تطبيقها في أمراض وحالات مختلفة. تستعرض هذه المقالة الاتجاهات في دراسة النظام الغليمفاتي، مع التركيز على طريقة ALPS. تناقش المعنى والأهمية لهذه الطريقة وتستكشف كيفية استخدامها في هذا المجال.
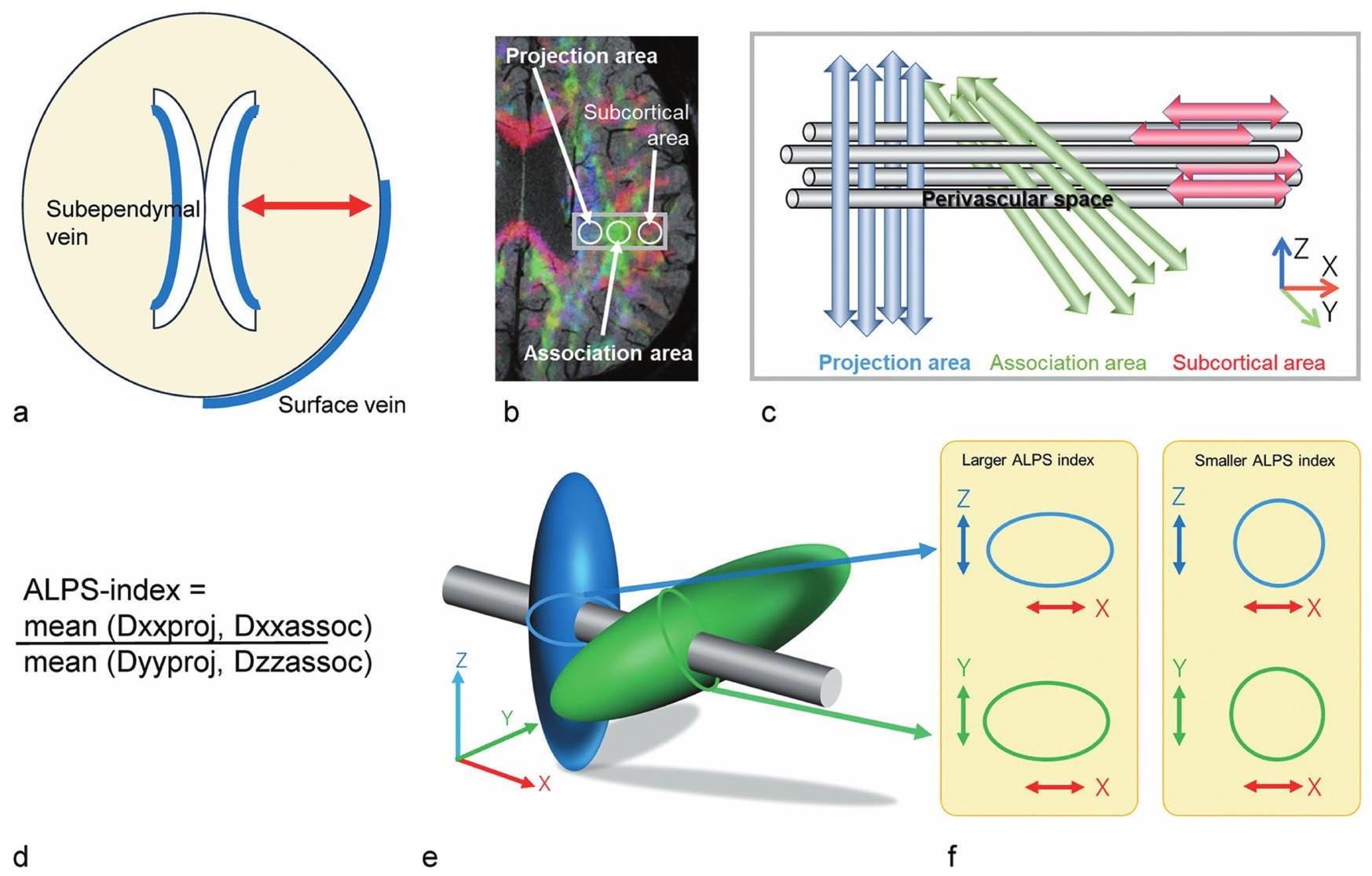
مفهوم DTI-ALPS
الاتجاه الشعاعي، تحديدًا اليسار-اليمين أو
دقة صورة الانتشار، بوحدات المليمترات. فقط اتجاه الانتشار هو القابل للتمييز. ومع ذلك، ما تحاول طريقة ALPS تقييمه هو الحركة الكلية أو الماكروسكوبية للماء في اتجاه اتجاه PVS، وليس حركة الماء في PVS نفسه. وبالتالي، فإن هذه القيود ليست عائقًا أمام هذا المفهوم. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، نظرًا لأن الطريقة تستخدم صور الانتشار، فإنها تقيم “حركة” الماء، وليس “تدفق” الماء. وبالتالي، فإن حركة الماء نحو سطح الدماغ ونحو البطينات تخضع للتقييم بشكل متساوٍ. سيتم النظر في قضايا أخرى في قسم “الجدل في طريقة DTI-ALPS”.
تطبيق DTI-ALPS
طلب لمرض الزهايمر
طلب لمرض باركنسون وأمراض التنكس الأخرى
فقدان الخلايا العصبية الدوبامينية في المادة السوداء.
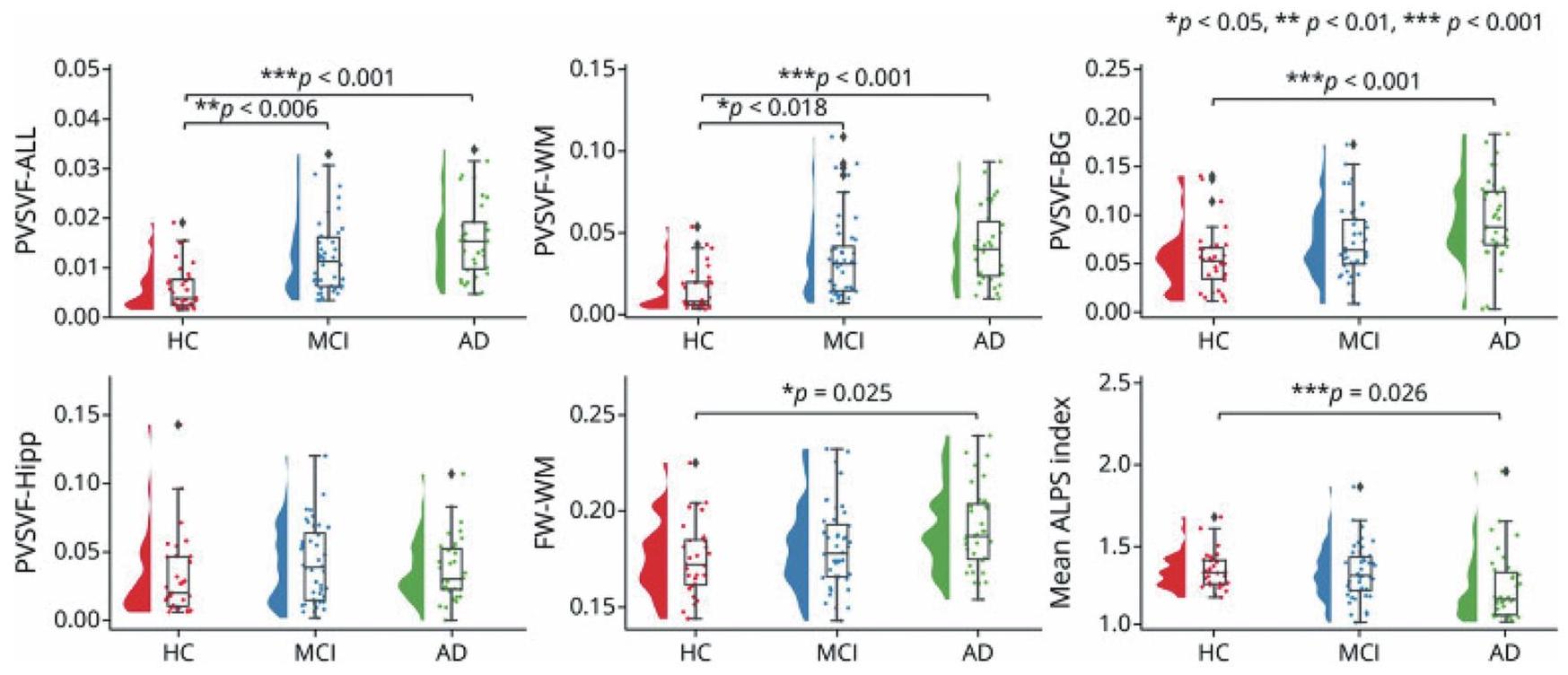
طلب لأمراض الأوعية الدموية الصغيرة
خلل وظيفي، وخلل حركي، وقد جذبت أيضًا الانتباه كحالة مرضية خلفية للأمراض التنكسية العصبية مثل مرض الزهايمر.
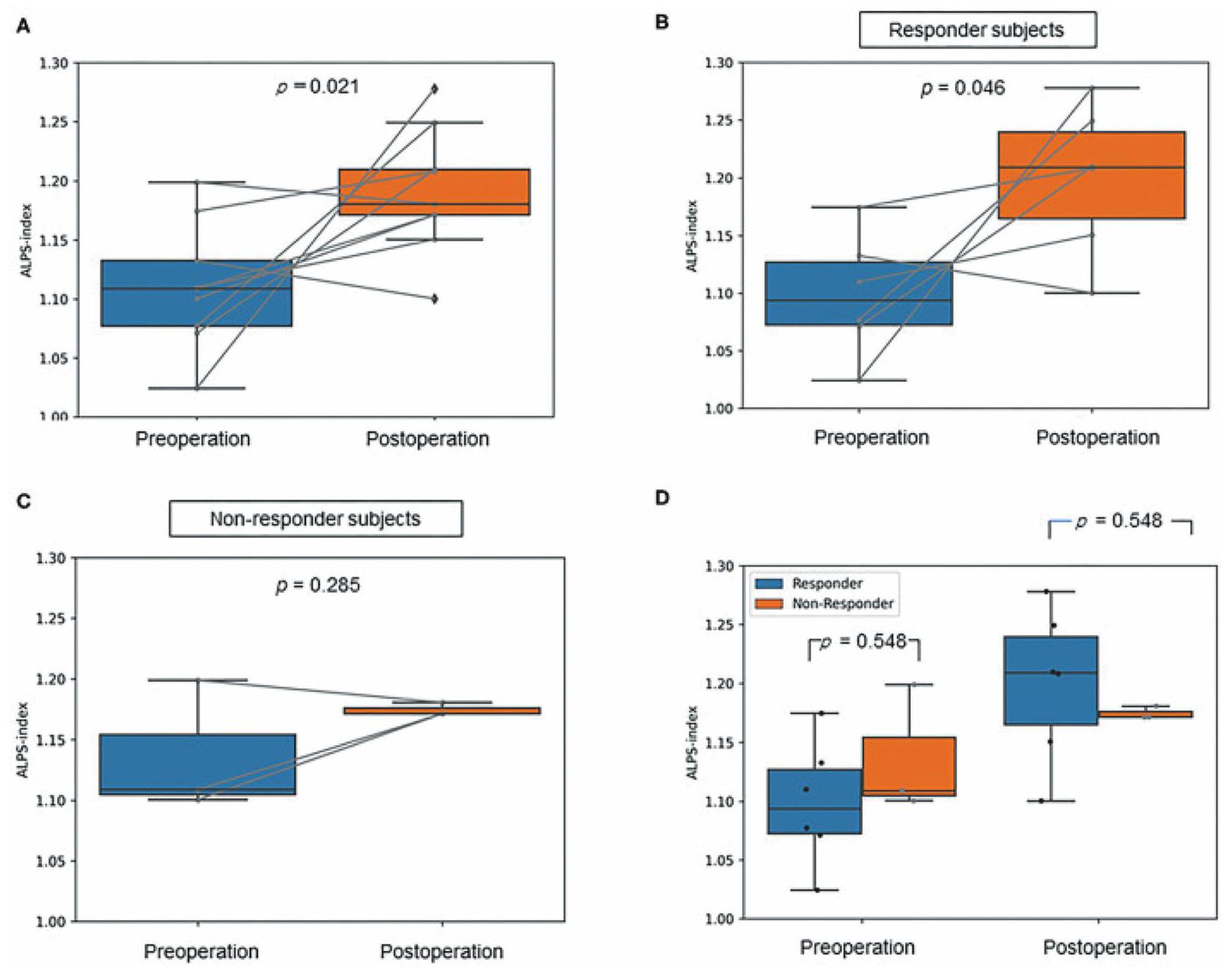
طلب لفرط الضغط الدماغي الطبيعي مجهول السبب
تحسنًا في الأعراض بعد جراحة التحويل، بينما لم يكن هناك زيادة ملحوظة في مؤشر ALPS بعد الجراحة في المجموعة التي لم تشهد تحسنًا في الأعراض (الشكل 4).
تطبيق لإصابة الدماغ الرضحية
تطبيق لمرض إزالة الميالين
ولا كانت مرتبطة بدرجات مقياس حالة الإعاقة الموسعة.
تطبيق للنوم
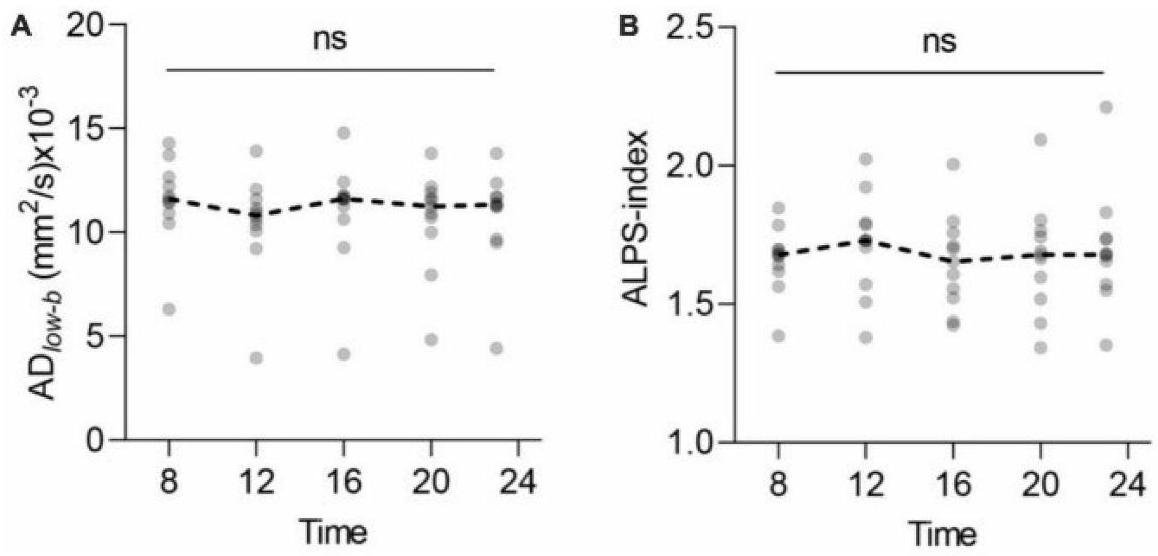
المعلمات مرتبطة إيجابيًا مع الاستيقاظ بعد بدء النوم وطول نوم حركة العين السريعة لدى المرضى الذين يعانون من النعاس من النوع 2.
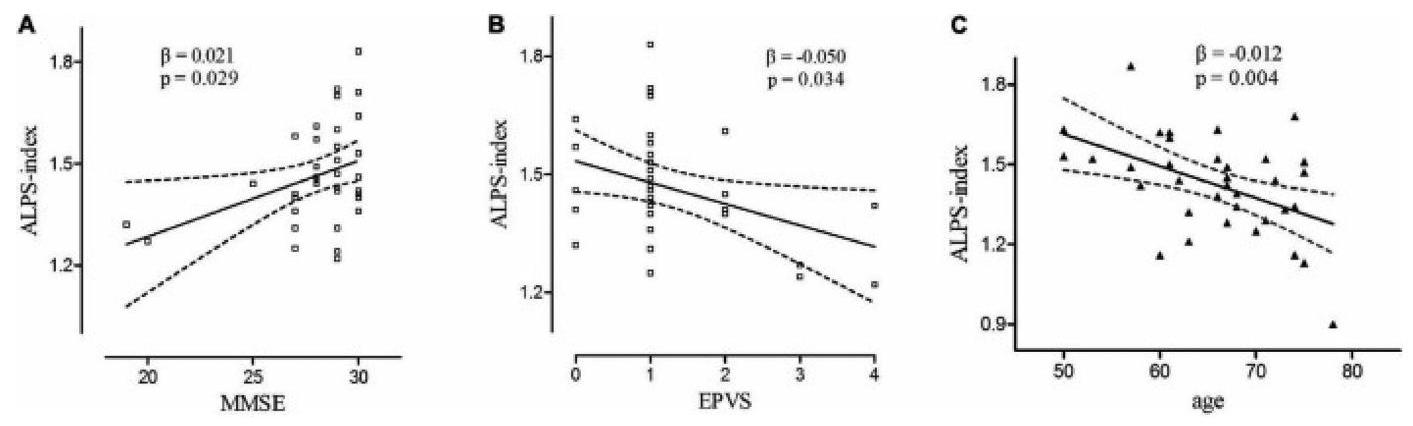
النتائج حول الشيخوخة
ارتباط سلبي بين العمر ومؤشر ALPS في كبار السن الذين يعيشون في المجتمع والذين تتراوح أعمارهم من 60 عامًا وما فوق، مع معامل انحدار جزئي قياسي من
طرق أخرى لتقييم النظام اللمفاوي الدماغي
GBCA داخل السائل النخاعي
يعتبر استخدام دراسات المتعقب باستخدام التصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي مع مادة التباين المعطلة داخل السائل الشوكي (GBCA) هو المعيار الذهبي. ومع ذلك، يجب ملاحظة أن الوزن الجزيئي لمادة التباين المعطلة هو 0.6 كيلودالتون (Gadobtrol)، في حين أن وزن
GBCA عن طريق الوريد
| طريقة | تسلسل الرنين المغناطيسي | ظاهرة الهدف | موقع الهدف | الأدوار المفترضة في النظام الغليمفاتي |
| GBCA داخل السحايا | T1WI | اختراق عبر سطح الدماغ (المتتبع: GBCA) | سطح الدماغ | تدفق السائل الدماغي الشوكي إلى نسيج الدماغ |
| نفاذية الحاجز الدموي الدماغي (المتتبع: GBCA) | نسيج الدماغ | إنتاج ISF | ||
| GBCA عن طريق الوريد | T1WI | نفاذية جدار الوريد (المؤشر: GBCA) | وريد سطحي | حركة نفايات |
| تتبع GBCA | وعاء لمفاوي سحائي / الفضاء المحيط بالأوعية الدموية | حركة نفايات | ||
| وريدي
|
تسلسل الحالة المستقرة | نفاذية الحاجز الدموي الدماغي (المتتبع: الماء المعلم) | نسيج الدماغ | إنتاج ISF |
| دي تي آي – ألبس | DTI | الحركة البراونية لجزيء الماء في نسيج الدماغ | المادة البيضاء العميقة المجاورة للبُطين الجانبي | حركة السائل بين الأنسجة |
| تحليل مياه مجاني | DTI وغيرها. | زيادة نسبة الماء الحر | نسيج الدماغ | توسيع الفضاء بين الخلايا |
| حجم الفضاء المحيط بالأوعية | 3D-T2WI وغيرها. | توسع الفضاء المحيط بالأوعية | الفراغ المحيط بالأوعية | تراكم النفايات الأيضية |
| حجم المشيمية الوعائية | 3D-T1WI إلخ. | تضخم المشيمية | الضفيرة المشيمية | إزالة النفايات / رد الفعل المناعي إلخ. |
| ASL مع TI طويلة | ASL | نفاذية BBB (المؤشر: الماء المعلم) | نسيج الدماغ | إنتاج ISF |
| اقتران BOLD-CSF | جريء | تزامن النشاط العصبي وحركة الدماغ/السائل الدماغي الشوكي | نسيج الدماغ | البيئة الدقيقة للأنسجة |
| المرونة التصويرية | المرونة التصويرية | الخصائص اللزجة المرنة للدماغ | نسيج الدماغ | البيئة الدقيقة للأنسجة |
بعد إعطاء جرعة عادية من GBCA، لوحظ تسرب من الأوردة القشرية إلى السائل الدماغي الشوكي. تم ملاحظة تعزيز داخل المساحات المحيطة بالأوعية الدموية في العقد القاعدية وحول الأوردة القشرية بعد 4 ساعات من إعطاء GBCA عن طريق الوريد.
بعد إجراء IV-GBCA. كما درست الدراسة في الوقت نفسه تعزيز الفضاء المحيط بالأوعية الدموية في العقد القاعدية (PVS-BG)، وقد تم رؤية PVS-BG في 21 من 42 حالة.
تقييم تسرب الحاجز الدموي الدماغي. ومع ذلك، فإن تسرب الحاجز الدموي الدماغي من عوامل التباين المعتمدة على الجادولينيوم في الأنسجة الدماغية السليمة صغير جداً لدرجة أن القياس يتم تقييمه دائماً بالقرب من مستوى الضوضاء. في هذا الصدد، من المتوقع أن تتأثر القياسات بشكل كبير بتلوث الضوضاء، وظروف التصوير، وطرق التحليل. يجب أيضاً ملاحظة أن تقييم تسرب الحاجز الدموي الدماغي لا يقيم النظام الغليمفاتي بالكامل، بل جزءاً فقط من النظام بأكمله.
حجم الفضاء المحيط بالأوعية الدموية
اعتلال العين العصبي. أظهر رواد الفضاء الذين قضوا 6 أشهر في محطة الفضاء الدولية تضخمًا في الفضاءات المحيطة بالأوعية الدموية في العقد القاعدية والمادة البيضاء بعد رحلتهم في الفضاء. علاوة على ذلك، كان لدى رواد الفضاء الذين تطور لديهم اعتلال العين العصبي المرتبط برحلة الفضاء تضخم أكبر في الفضاءات المحيطة بالأوعية الدموية في المادة البيضاء مقارنةً بأولئك الذين لم يتطور لديهم المتلازمة، مما يشير إلى أن التغيرات طويلة الأمد في الجاذبية قد تؤثر على وظيفة النظام الغليمفاتي.
حجم المشيمية الوعائية
تم تحديد الدماغ وتنظيم تركيبة السائل الدماغي الشوكي لوظيفة الدماغ المتوازنة.
طرق الانتشار بخلاف طريقة ALPS
توسيم الدوران الشرياني
تصوير حركيات أنسجة الدماغ
كان الارتباط مرتبطًا بالتدهور المعرفي الذي لوحظ في المرضى الذين يعانون من مرض باركنسون. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، كان الارتباط المنخفض بين BOLD-CSF في مرضى باركنسون مرتبطًا بقشرة الحُقُب اليمنى الأرق.
طرق أخرى لدراسة المتتبعين
كان تراكم المادة المشعة خارج الجمجمة في القرينات الأنفية. في المرضى الذين يعانون من
اعتبار منهجية DTI-ALPS
وضع العائد على الاستثمار
إمكانية إعادة إنتاج طريقة ALPS
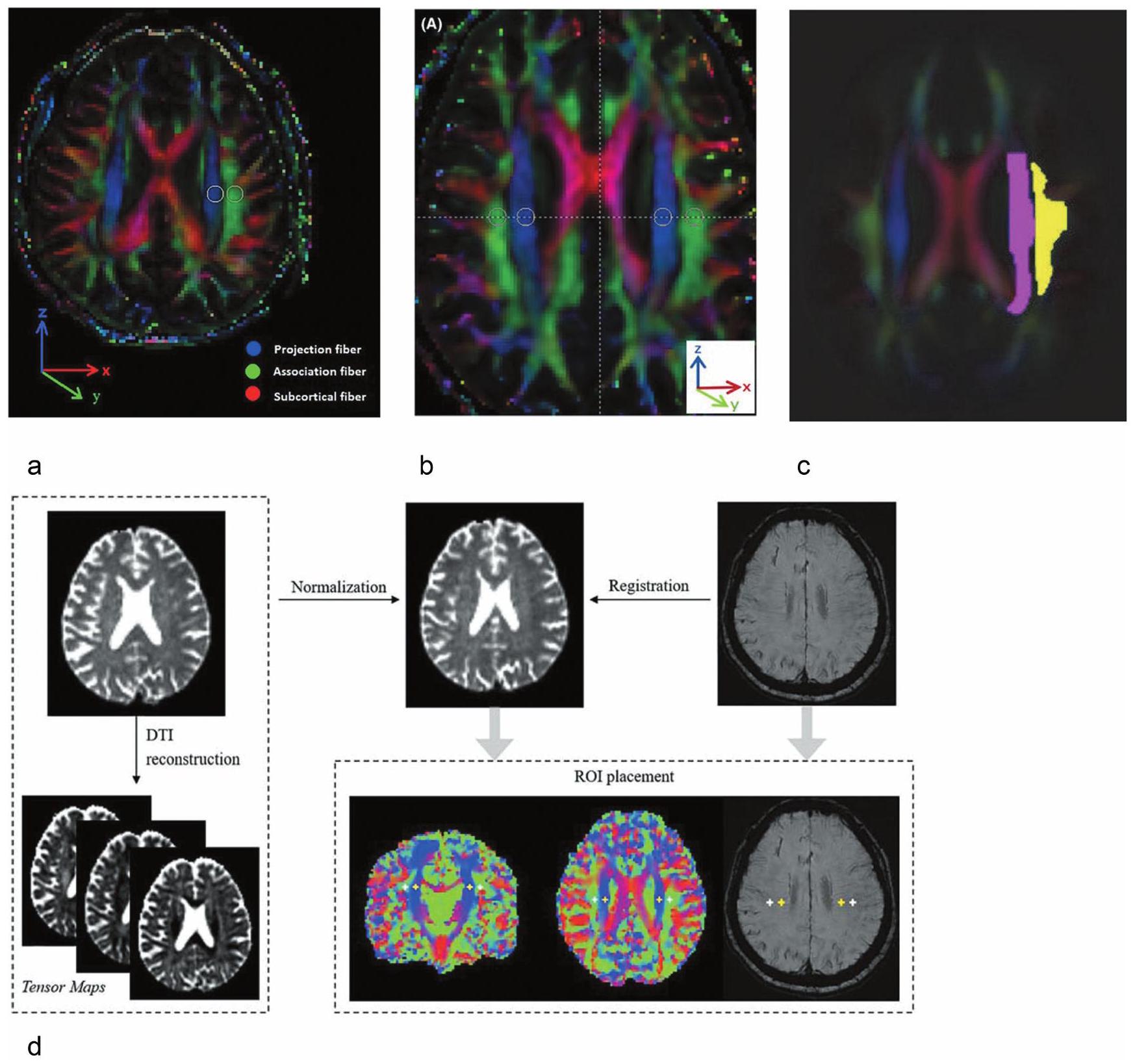
تعديل طريقة ALPS
وأظهرت تقنية التصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي ثلاثي المحاور ارتباطًا جيدًا. وهذا يشير إلى إمكانية استخدام طريقة DWI-ALPS مع MPG ثلاثي المحاور.
الامتحانات.
الجدل في طريقة DTI-ALPS
الخاتمة
كمصطلح شائع في هذا المجال البحثي. سيكون من الصحيح وصف مؤشر ALPS فقط بأنه مرتفع أو منخفض، زاد أو انخفض، وما إذا كان يعكس النظام الغليمفاتي أم لا يجب أن يعتبر موضوعًا للنقاش. بعبارة أخرى، إذا لوحظ انخفاض في مؤشر ALPS، يجب أن يقول عنوان الورقة “انخفاض في مؤشر ALPS” وليس “خلل في الغليمفاتي” مباشرة على الأقل في عنوان الورقة. فيما يتعلق بطريقة ALPS، ذكر البروفيسور إيلف أن “التغيرات في القياس تُرى في ظل ظروف حيث تتعطل وظيفة الغليمفاتي – لذا بينما ليس لدينا فهم قوي لطبيعة الإشارة بالضبط، يبدو أنها تعمل على مستوى ما” (تواصل شخصي)، ويتفق المؤلف مع رأيه.
تعارض المصالح
References
- Iliff JJ, Wang M, Liao Y, et al. A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid
. Sci Transl Med 2012; 4:147ra111. - Gaberel T, Gakuba C, Goulay R, et al. Impaired glymphatic perfusion after strokes revealed by contrast-enhanced MRI: A new target for fibrinolysis? Stroke 2014; 45:3092-3096.
- Ringstad G, Vatnehol SAS, Eide PK. Glymphatic MRI in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Brain 2017; 140:2691-2705.
- Taoka T, Masutani Y, Kawai H, et al. Evaluation of glymphatic system activity with the diffusion MR technique: diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTIALPS) in Alzheimer’s disease cases. Ipn I Radiol 2017; 35:172-178.
- Okudera T, Huang YP, Fukusumi A, Nakamura Y, Hatazawa J, Uemura K. Micro-angiographical studies of the medullary venous system of the cerebral hemisphere. Neuropathology 1999; 19:93-111.
- Taoka T, Fukusumi A, Miyasaka T, et al. Structure of the medullary veins of the cerebral hemisphere and related disorders. Radiographics 2017; 37:281-297.
- Simon MJ, Iliff JJ. Regulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow in neurodegenerative, neurovascular and neuroinflammatory disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2016; 1862:442-451.
- Matsuda H, Shigemoto Y, Sato N. Neuroimaging of Alzheimer’s disease: Focus on amyloid and tau PET. Jpn J Radiol 2019; 37:735-749.
- Nakata T, Shimada K, Iba A, et al. Differential diagnosis of MCI with Lewy bodies and MCI due to Alzheimer’s disease by visual assessment of occipital hypoperfusion on SPECT images. Jpn J Radiol 2024; 42:308-318.
- Thientunyakit T, Thongpraparn T, Sethanandha C, et al. Relationship between F-18 florbetapir uptake in occipital lobe and neurocognitive performance in Alzheimer’s disease. Jpn J Radiol 2021; 39:984-993.
- Taoka T, Naganawa S. Imaging for central nervous system (CNS) interstitial fluidopathy: Disorders with impaired interstitial fluid dynamics. Jpn J Radiol 2021; 39:1-14.
- Taoka T, Ito R, Nakamichi R, Nakane T, Kawai H, Naganawa S. Interstitial fluidopathy of the central nervous system: An umbrella term for disorders with impaired neurofluid dynamics. Magn Reson Med Sci 2024; 23:1-13.
- Sparacia G, Sakai K, Yamada K, et al. Assessment of brain core temperature using MR DWI-thermometry in Alzheimer disease patients compared to healthy subjects. Jpn J Radiol 2017; 35:168-171.
- Chang H-I, Huang C-W, Hsu S-W, et al. Gray matter reserve determines glymphatic system function in young-onset Alzheimer’s disease: Evidenced by DTI-ALPS and compared with age-matched controls. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2023; 77:401-409.
- Kamagata K, Andica C, Hatano T, et al. Advanced diffusion magnetic resonance imaging in patients with Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Neural Regen Res 2020; 15:1590-1600.
- Zhong J, Zhang X, Xu H, et al. Unlocking the enigma: Unraveling multiple cognitive dysfunction linked to glymphatic impairment in early Alzheimer’s disease. Front Neurosci 2023; 17:1222857.
- Matsushita S, Tatekawa H, Ueda D, et al. The association of metabolic brain MRI, amyloid PET, and clinical factors: A study of Alzheimer’s disease and normal controls from the open access series of imaging studies dataset. J Magn Reson Imaging 2024; 59:1341-1348.
- Steward CE, Venkatraman VK, Lui E, et al. Assessment of the DTI-ALPS parameter along the perivascular space in older adults at risk of dementia. J Neuroimaging 2021; 31:569-578.
- Ota M, Sato N, Nakaya M, et al. Relationships between the deposition of amyloid-
and tau protein and glymphatic system activity in Alzheimer’s disease: Diffusion tensor image study. J Alzheimers Dis 2022; 90:295-303. - Kamagata K, Andica C, Takabayashi K, et al. Association of MRI indices of glymphatic system with amyloid deposition and cognition in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2022; 99:e2648-e2660.
- Zhang X, Wang Y, Jiao B, et al. Glymphatic system impairment in Alzheimer’s disease: Associations with perivascular space volume and cognitive function. Eur Radiol 2024; 34:1314-1323.
- Park CJ, Kim S-Y, Kim JH, et al. Evaluation of glymphatic system activity using diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space and amyloid PET in older adults with objectively normal cognition: a preliminary study. Front Aging Neurosci 2023; 15:1221667.
- Dickson DW, Braak H, Duda JE, et al. Neuropathological assessment of Parkinson’s disease: refining the diagnostic criteria. Lancet Neurol 2009; 8:1150-1157.
- Oshima S, Fushimi Y, Miyake KK, et al. Denoising approach with deep learning-based reconstruction for neuromelaninsensitive MRI: Image quality and diagnostic performance. Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:1216-1225.
- Maekawa T, Sato N, Ota M, et al. Correlations between dopamine transporter density measured by 123I-FP-CIT SPECT and regional gray matter volume in Parkinson’s disease. Jpn J Radiol 2017; 35:755-759.
- Shen T, Yue Y, Ba F, et al. Diffusion along perivascular spaces as marker for impairment of glymphatic system in Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 2022; 8:174.
- McKnight CD, Trujillo P, Lopez AM, et al. Diffusion along perivascular spaces reveals evidence supportive of glymphatic function impairment in Parkinson disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2021; 89:98-104..
- Ma X, Li S, Li C, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging along the perivascular space index in different stages of Parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 2021; 13:773951.
- Chen H-L, Chen P-C, Lu C-H, et al. Associations among cognitive functions, plasma DNA, and diffusion tensor image along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021; 2021:4034509.
- Cai X , Chen
, et al. Diffusion along perivascular spaces provides evidence interlinking compromised glymphatic function with aging in Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurosci Ther 2023; 29:111-121. - Ruan X, Huang X, Li Y, Li E, Li M, Wei X. Diffusion tensor imaging analysis along the perivascular space index in primary Parkinson’s disease patients with and without freezing of gait. Neuroscience 2022; 506:51-57.
- Gu L, Dai S, Guo T, et al. Noninvasive neuroimaging provides evidence for deterioration of the glymphatic system in Parkinson’s disease relative to essential tremor. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2023; 107:105254.
- Bae YJ, Kim J-M, Choi BS, et al. Glymphatic function assessment in Parkinson’s disease using diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2023; 114:105767.
- Qin Y, He R, Chen J, et al. Neuroimaging uncovers distinct relationships of glymphatic dysfunction and motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 2023; 270:2649-2658.
- He P, Shi L, Li Y, et al. The association of the glymphatic function with Parkinson’s disease symptoms: Neuroimaging evidence from longitudinal and cross-sectional studies. Ann Neurol 2023; 94:672-683.
- Meng J-C, Shen M-Q, Lu Y-L, et al. Correlation of glymphatic system abnormalities with Parkinson’s disease progression: A clinical study based on non-invasive fMRI. J Neurol 2024; 271:457-471.
- Postuma RB, Iranzo A, Hu M, et al. Risk and predictors of dementia and parkinsonism in idiopathic REM sleep behaviour disorder: A multicentre study. Brain 2019; 142:744759.
- Si X, Guo T, Wang Z, et al. Neuroimaging evidence of glymphatic system dysfunction in possible REM sleep behavior disorder and Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 2022; 8:54.
- Bae YJ, Kim J-M, Choi BS, et al. Altered brain glymphatic flow at diffusion-tensor MRI in rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. Radiology 2023; 307:e221848.
- Ota M, Sato N, Takahashi Y, et al. Correlation between the regional brain volume and glymphatic system activity in progressive supranuclear palsy. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2023; 52:177-183.
- Saito Y, Kamagata K, Andica C, et al. Glymphatic system impairment in corticobasal syndrome: Diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS). Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:1226-1235.
- Wang
, Wang , Gao , et al. Characterizing the penumbras of white matter hyperintensities in patients with cerebral small vessel disease. Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:928-937. - Kikuta J, Kamagata K, Takabayashi K, et al. An investigation of water diffusivity changes along the perivascular space in elderly subjects with hypertension. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2022; 43:48-55.
- Wardlaw JM, Smith C, Dichgans M. Small vessel disease: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol 2019; 18:684-696.
- Benveniste H, Nedergaard M. Cerebral small vessel disease: A glymphopathy? Curr Opin Neurobiol 2022; 72:15-21.
- Tang J, Zhang M, Liu N, et al. The association between glymphatic system dysfunction and cognitive impairment in cerebral small vessel disease. Front Aging Neurosci 2022; 14:916633.
- Tian
, Cai , Zhou , et al. Impaired glymphatic system as evidenced by low diffusivity along perivascular spaces is associated with cerebral small vessel disease: A populationbased study. Stroke Vasc Neurol 2023; 8:e002191. - Xu J, Su Y, Fu J, et al. Glymphatic dysfunction correlates with severity of small vessel disease and cognitive impairment in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Eur J Neurol 2022; 29:2895-2904.
- Ishii K, Kanda T, Harada A, et al. Clinical impact of the callosal angle in the diagnosis of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Eur Radiol 2008; 18:2678-2683.
- Irie R, Tsuruta K, Hori M, et al. Neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging for evaluation of corticospinal tract in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus.
Radiol 2017; 35:25-30. - Ishii K. Diagnostic imaging of dementia with Lewy bodies, frontotemporal lobar degeneration, and normal pressure hydrocephalus. Jpn J Radiol 2020; 38:64-76.
- Nakajima M, Kuriyama N, Miyajima M, et al. Background risk factors associated with shunt intervention for possible idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: A nationwide hospital-based survey in Japan. J Alzheimers Dis 2019; 68:735-744.
- Iseki C, Takahashi Y, Adachi M, et al. Prevalence and development of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: A 16year longitudinal study in Japan. Acta Neurol Scand 2022; 146:680-689.
- Eide PK, Lashkarivand A, Hagen-Kersten ÅA, et al. Intrathecal contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of cerebrospinal fluid dynamics and glymphatic enhancement in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Front Neurol 2022; 13:857328.
- Eide PK, Pripp AH, Ringstad G. Magnetic resonance imaging biomarkers of cerebrospinal fluid tracer dynamics in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Brain Commun 2020; 2:fcaa187.
- Yokota H, Vijayasarathi A, Cekic M, et al. Diagnostic performance of glymphatic system evaluation using diffusion tensor imaging in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus and mimickers. Curr Gerontol Geriatr Res 2019; 2019:5675014.
- Georgiopoulos C, Tisell A, Holmgren RT, et al. Noninvasive assessment of glymphatic dysfunction in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus with diffusion tensor imaging.
Neurosurg 2023 [Online ahead of print]. - Ishikawa M, Hashimoto M, Mori E, Kuwana N, Kazui H. The value of the cerebrospinal fluid tap test for predicting shunt effectiveness in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Fluids Barriers CNS 2012; 9:1.
- Miyati T, Mase M, Kasai H, et al. Noninvasive MRI assessment of intracranial compliance in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J Magn Reson Imaging 2007; 26:274-278.
- Mase M, Miyati T, Kasai H, et al. Noninvasive estimation of intracranial compliance in idiopathic NPH using MRI. Acta Neurochir Suppl 2008; 102:115-118.
- Bae YJ, Choi BS, Kim J-M, Choi J-H, Cho SJ, Kim JH. Altered glymphatic system in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2021; 82:56-60.
- Kikuta J, Kamagata K, Taoka T, et al. Water diffusivity changes along the perivascular space after lumboperitoneal shunt surgery in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Front Neurol 2022; 28:843883.
- Graham NS, Sharp DJ. Understanding neurodegeneration after traumatic brain injury: From mechanisms to clinical trials in dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2019; 90:1221-1233.
- Iliff JJ, Chen MJ, Plog BA, et al. Impairment of glymphatic pathway function promotes tau pathology after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci 2014; 34:16180-16193.
- Goulay R, Aron Badin R, Flament J, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid leakage after posterior fossa surgery may impair brain metabolite clearance. Neurochirurgie 2018; 64:422-424.
- Park JH, Bae YJ, Kim JS, et al. Glymphatic system evaluation using diffusion tensor imaging in patients with traumatic brain injury. Neuroradiology 2023; 65:551-557.
- Dai Z, Yang Z, Li Z, et al. Increased glymphatic system activity in patients with mild traumatic brain injury. Front Neurol 2023; 14:1148878.
- Yang D-X, Sun Z, Yu M-M, et al. Associations of MRIderived glymphatic system impairment with global white matter damage and cognitive impairment in mild traumatic brain injury: A DTI-ALPS study. J Magn Reson Imaging 2024; 59:639-647.
- Morita Y, Kamagata K, Andica C, et al. Glymphatic system impairment in nonathlete older male adults who played contact sports in their youth associated with cognitive decline: A diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space study. Front Neurol 2023; 14:1100736.
- Carotenuto A, Cacciaguerra L, Pagani E, Preziosa P, Filippi M, Rocca MA. Glymphatic system impairment in multiple sclerosis: Relation with brain damage and disability. Brain 2022; 145:2785-2795.
- Rocca MA, Margoni M, Battaglini M, et al. Emerging perspectives on MRI application in multiple sclerosis: Moving from pathophysiology to clinical practice. Radiology 2023; 307:e221512.
- Hagiwara A, Tomizawa Y, Hoshino Y, et al. Glymphatic system dysfunction in myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein immunoglobulin G antibody-associated disorders: Association with clinical disability. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2024; 45:66-71.
- Xie L, Kang H, Xu Q, et al. Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain. Science 2013; 342:373-377.
- Siow TY, Toh CH, Hsu J-L, et al. Association of sleep, neuropsychological performance, and gray matter volume with glymphatic function in community-dwelling older adults. Neurology 2022; 98:e829-e838.
- Roy B, Nunez A, Aysola RS, Kang DW, Vacas S, Kumar R. Impaired glymphatic system actions in obstructive sleep apnea adults. Front Neurosci 2022; 16:884234.
- Saito Y, Hayakawa Y, Kamagata K, et al. Glymphatic system impairment in sleep disruption: diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS). Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:1335-1343.
- Gumeler E, Aygun E, Tezer FI, Saritas EU, Oguz KK. Assessment of glymphatic function in narcolepsy using DTI-ALPS index. Sleep Med 2023; 101:522-527.
- Han G, Zhou Y, Zhang K, et al. Age- and time-of-day dependence of glymphatic function in the human brain measured via two diffusion MRI methods. Front Aging Neurosci 2023; 15:1173221.
- Thomas C, Sadeghi N, Nayak A, et al. Impact of time-of-day on diffusivity measures of brain tissue derived from diffusion tensor imaging. Neuroimage 2018; 173:25-34.
- Zhou W, Shen B, Shen W-Q, Chen H, Zheng Y-F, Fei J-J. Dysfunction of the glymphatic system might be related to iron deposition in the normal aging brain. Front Aging Neurosci 2020; 12:559603.
- Yang G, Deng N, Liu Y, Gu Y, Yao X. Evaluation of Glymphatic System Using Diffusion MR Technique in T2DM Cases. Front Hum Neurosci 2020; 14:300.
- Toh CH, Siow TY, Castillo M. Peritumoral brain edema in meningiomas may be related to glymphatic dysfunction. Front Neurosci 2021; 15:674898.
- Toh CH, Siow TY. Glymphatic dysfunction in patients with ischemic stroke. Front Aging Neurosci 2021; 13:756249.
- Toh CH, Siow TY, Castillo M. Peritumoral brain edema in metastases may be related to glymphatic dysfunction. Front Oncol 2021; 11:725354.
- Zhang W, Zhou Y, Wang J, et al. Glymphatic clearance function in patients with cerebral small vessel disease. Neuroimage 2021; 238:118257.
- Taoka T, Ito R, Nakamichi R, et al. Reproducibility of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) for evaluating interstitial fluid diffusivity and glymphatic function: CHanges in Alps index on Multiple conditiON acquIsition eXperiment (CHAMONIX) study. Jpn J Radiol 2022; 40:147-158.
- Lee H-J, Lee DA, Shin KJ, Park KM. Glymphatic system dysfunction in patients with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy.
Neurol 2022; 269:2133-2139. - Lee DA, Lee H-J, Park KM. Glymphatic dysfunction in isolated REM sleep behavior disorder. Acta Neurol Scand 2022; 145:464-470.
- Wang J, Zhou Y, Zhang K, et al. Glymphatic function plays a protective role in ageing-related cognitive decline. Age Ageing 2023; 52:afad107.
- Wei Y-C, Hsu C-CH, Huang W-Y, et al. Vascular risk factors and astrocytic marker for the glymphatic system activity. Radiol Med 2023; 128:1148-1161.
- Taoka T, Ito R, Nakamichi R, et al. Evaluation of alterations in interstitial fluid dynamics in cases of whole-brain radiation using the diffusion-weighted image analysis along the perivascular space method. NMR Biomed 2023:e5030.
- Kim S-T, Kim SE, Lee DA, Lee H-J, Park KM. Anti-seizure medication response and the glymphatic system in patients with focal epilepsy. Eur J Neurol 2024; 31:e16097.
- Toh CH, Siow TY. Factors associated with dysfunction of glymphatic system in patients with glioma. Front Oncol 2021; 11:744318.
- Dai
, Yang , Chen , et al. The aging of glymphatic system in human brain and its correlation with brain charts and neuropsychological functioning. Cereb Cortex 2023; 33:7896-7903. - Taoka T, Ito R, Nakamichi R, et al. Diffusion-weighted image analysis along the perivascular space (DWI-ALPS) for evaluating interstitial fluid status: Age dependence in normal subjects. Jpn J Radiol 2022; 40:894-902.
- Li X, Ruan C, Zibrila AI, et al. Children with autism spectrum disorder present glymphatic system dysfunction evidenced by diffusion tensor imaging along the perivascular space. Medicine (Baltimore) 2022; 101:e32061.
- Lin L-P, Su S, Hou W, et al. Glymphatic system dysfunction in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia without clinically diagnosed central nervous system infiltration: A novel DTIALPS method. Eur Radiol 2023; 33:3726-3734.
- Chen Y, Wang M, Su S, et al. Assessment of the glymphatic function in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Eur Radiol 2024; 34:1444-1452.
- Haller S, Moy L, Anzai Y. Evaluation of diffusion tensor imaging analysis along the perivascular space as a marker of the glymphatic system. Radiology 2024; 310:e232899.
- Wright AM, Wu Y-C, Chen N-K, Wen Q. Exploring radial asymmetry in mr diffusion tensor imaging and its impact on the interpretation of glymphatic mechanisms. J Magn Reson Imaging 2023; jmri. 29203.
- Piantino JA, Iliff JJ, Lim MM, Levendovszky SR. Reader response: Association of sleep, neuropsychological performance, and gray matter volume with glymphatic function in community-dwelling older adults. Neurology 2023; 100:355356.
- Ringstad G. Glymphatic imaging: A critical look at the DTIALPS index. Neuroradiology 2024; 66:157-160.
- Chen G-F, Xu T-H, Yan Y, et al. Amyloid beta: structure, biology and structure-based therapeutic development. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2017; 38:1205-1235.
- Eide PK, Ringstad G. MRI with intrathecal MRI gadolinium contrast medium administration: A possible method to assess glymphatic function in human brain. Acta Radiol Open 2015; 4:2058460115609635.
- Vinje V, Zapf B, Ringstad G, Eide PK, Rognes ME, Mardal K-A. Human brain solute transport quantified by glymphatic MRI-informed biophysics during sleep and sleep deprivation. Fluids Barriers CNS 2023; 20:62.
- Dyke JP, Xu HS, Verma A, Voss HU, Chazen JL. MRI characterization of early CNS transport kinetics post intrathecal gadolinium injection: Trends of subarachnoid and parenchymal distribution in healthy volunteers. Clin Imaging 2020; 68:1-6.
- Taoka T, Jost G, Frenzel T, Naganawa S, Pietsch H. Impact of the glymphatic system on the kinetic and distribution of gadodiamide in the rat brain: Observations by dynamic MRI and effect of circadian rhythm on tissue gadolinium concentrations. Invest Radiol 2018; 53:529-534.
- Naganawa S, Nakane T, Kawai H, Taoka T. Gd-based contrast enhancement of the perivascular spaces in the basal ganglia. Magn Reson Med Sci 2017; 16:61-65.
- Naganawa S, Nakane T, Kawai H, Taoka T. Age dependence of gadolinium leakage from the cortical veins into the cerebrospinal fluid assessed with whole brain 3D-real inversion recovery MR imaging. Magn Reson Med Sci 2019; 18:163169.
- Naganawa S, Ito R, Kawai H, Taoka T, Yoshida T, Sone M. Confirmation of age-dependence in the leakage of contrast medium around the cortical veins into cerebrospinal fluid after intravenous administration of gadolinium-based contrast agent. Magn Reson Med Sci 2020; 19:375-381.
- Nakamichi R, Taoka T, Kawai H, Yoshida T, Sone M, Naganawa S. Magnetic resonance cisternography imaging findings related to the leakage of Gadolinium into the subarachnoid space. Jpn J Radiol 2021; 39:927-937.
- Naganawa S, Ito R, Nakamichi R, et al. Relationship between time-dependent signal changes in parasagittal perivenous cysts and leakage of gadolinium-based contrast agents into the subarachnoid space. Magn Reson Med Sci 2021; 20:378-384.
- Naganawa S, Ito R, Nakamichi R, et al. Relationship between parasagittal perivenous cysts and leakage of gadoliniumbased contrast agents into the subarachnoid space around the cortical veins after intravenous administration. Magn Reson Med Sci 2021; 20:245-252.
- Naganawa S, Ito R, Kawamura M, Taoka T, Yoshida T, Sone M. Association between the putative meningeal lymphatics at the posterior wall of the sigmoid sinus and delayed con-trast-agent elimination from the cerebrospinal fluid. Magn Reson Med Sci 2024; 23:80-91.
- Naganawa S, Taoka T, Ito R, Kawamura M. The glymphatic system in humans: Investigations with magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol 2024; 59:1-12.
- van de Haar HJ, Burgmans S, Jansen JFA, et al. Blood-brain barrier leakage in patients with early Alzheimer disease. Radiology 2016; 281:527-535.
- Lee S, Yoo R-E, Choi SH, et al. Contrast-enhanced MRI T1 mapping for quantitative evaluation of putative dynamic glymphatic activity in the human brain in sleep-wake states. Radiology 2021; 300:661-668.
- Wu C-H, Chang F-C, Wang Y-F, et al. Impaired glymphatic and meningeal lymphatic functions in patients with chronic migraine. Ann Neurol 2023 [Online ahead of print].
- Wardlaw JM, Smith EE, Biessels GJ, et al. Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol 2013; 12:822-838.
- Potter GM, Chappell FM, Morris Z, Wardlaw JM. Cerebral perivascular spaces visible on magnetic resonance imaging: Development of a qualitative rating scale and its observer reliability. Cerebrovasc Dis 2015; 39:224-231.
- Weller RO, Hawkes CA, Kalaria RN, Werring DJ, Carare RO. White matter changes in dementia: role of impaired drainage of interstitial fluid. Brain Pathol 2015; 25:63-78.
- Liu H, Yang S, He W, et al. Associations among diffusion tensor image along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS), enlarged perivascular space (ePVS), and cognitive functions in asymptomatic patients with carotid plaque. Front Neurol 2022; 12:789918.
- Donahue EK, Foreman RP, Duran JJ, et al. Increased perivascular space volume in white matter and basal ganglia is associated with cognition in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Imaging Behav 2023; 18:57-65.
- Zeng Q, Li K, Luo X, et al. The association of enlarged perivascular space with microglia-related inflammation and Alzheimer’s pathology in cognitively normal elderly. Neurobiol Dis 2022; 170:105755.
- Yu N, Sinclair B, Posada LMG, et al. Asymmetric distribution of enlarged perivascular spaces in centrum semiovale may be associated with epilepsy after acute ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther 2022; 28:343-353.
- Perosa V, Oltmer J, Munting LP, et al. Perivascular space dilation is associated with vascular amyloid-
accumulation in the overlying cortex. Acta Neuropathol 2022; 143:331348. - Tsai H-H, Pasi M, Tsai L-K, et al. Centrum semiovale perivascular space and amyloid deposition in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2021; 52:2356-2362.
- Dubost F, Adams H, Bortsova G, et al. 3D regression neural network for the quantification of enlarged perivascular spaces in brain MRI. Med Image Anal 2019; 51:89-100.
- Barisano G, Sepehrband F, Collins HR, et al. The effect of prolonged spaceflight on cerebrospinal fluid and perivascular spaces of astronauts and cosmonauts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2022; 119:e2120439119.
- Butler T, Zhou L, Ozsahin I, et al. Glymphatic clearance estimated using diffusion tensor imaging along perivascular spaces is reduced after traumatic brain injury and correlates with plasma neurofilament light, a biomarker of injury severity. Brain Commun 2023; 5:fcad134.
- Christensen J, Li C, Mychasiuk R. Choroid plexus function in neurological homeostasis and disorders: The awakening of the circadian clocks and orexins. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2022; 42:1163-1175.
- Jeong SH, Park CJ, Jeong H-J, et al. Association of choroid plexus volume with motor symptoms and dopaminergic degeneration in Parkinson’s disease. I Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2023; 94:1047-1055.
- Li Y, Zhou Y, Zhong W, et al. Choroid plexus enlargement exacerbates white matter hyperintensity growth through glymphatic impairment. Ann Neurol 2023; 94:182-195.
- Tu Y, Li Z, Xiong F, Gao F. Decreased DTI-ALPS and choroid plexus enlargement in fibromyalgia: A preliminary multimodal MRI study. Neuroradiology 2023; 65:1749-1755.
- Eisma JJ, McKnight CD, Hett K, et al. Deep learning segmentation of the choroid plexus from structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): Validation and normative ranges across the adult lifespan. Res Sq 2023 [Preprint].
- Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Grenier P, Cabanis E, Laval-Jeantet M. MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: Application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology 1986; 161:401-407.
- Le Bihan D. Intravoxel incoherent motion imaging using steady-state free precession. Magn Reson Med 1988; 7:346351.
- Taoka T, Naganawa S, Kawai H, Nakane T, Murata K. Can low b value diffusion weighted imaging evaluate the character of cerebrospinal fluid dynamics? Ipn I Radiol 2019; 37:135-144.
- Taoka T, Kawai H, Nakane T, et al. Diffusion analysis of fluid dynamics with incremental strength of motion proving gradient (DANDYISM) to evaluate cerebrospinal fluid dynamics. Jpn J Radiol 2021; 39:315-323.
- Taoka T, Kawai H, Nakane T, et al. Evaluating the effect of arterial pulsation on cerebrospinal fluid motion in the sylvian fissure of patients with middle cerebral artery occlusion using low b-value diffusion-weighted imaging. Magn Reson Med Sci 2021; 20:371-377.
- Bito Y, Harada K, Ochi H, Kudo K. Low b-value diffusion tensor imaging for measuring pseudorandom flow of cerebrospinal fluid. Magn Reson Med 2021; 86:1369-1382.
- Ohene Y, Harrison IF, Nahavandi P, et al. Non-invasive MRI of brain clearance pathways using multiple echo time arterial spin labelling: an aquaporin-4 study. Neuroimage 2019; 188:515-523.
- Joseph CR, Benhatzel CM, Stern LJ, Hopper OM, Lockwood MD. Pilot study utilizing MRI 3D TGSE PASL (arterial spin labeling) differentiating clearance rates of labeled protons in the CNS of patients with early Alzheimer disease from normal subjects. MAGMA 2020; 33:559-568.
- Kiviniemi V, Wang X, Korhonen V, et al. Ultra-fast magnetic resonance encephalography of physiological brain activity – Glymphatic pulsation mechanisms? J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2016; 36:1033-1045.
- Fultz NE, Bonmassar G, Setsompop K, et al. Coupled electrophysiological, hemodynamic, and cerebrospinal fluid oscillations in human sleep. Science 2019; 366:628-631.
- Han F, Brown GL, Zhu Y, et al. Decoupling of global brain activity and cerebrospinal fluid flow in Parkinson’s disease cognitive decline. Mov Disord 2021; 36:2066-2076.
- Jiang D, Liu L, Kong Y, et al. Regional glymphatic abnormality in behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia. Ann Neurol 2023; 94:442-456.
- Manduca A, Bayly PJ, Ehman RL, et al. MR elastography: Principles, guidelines, and terminology. Magn Reson Med 2021; 85:2377-2390.
- Ge GR, Song W, Nedergaard M, Rolland JP, Parker KJ. Theory of sleep/wake cycles affecting brain elastography. Phys Med Biol 2022; 67: 225013.
- Joo B, Won SY, Sinkus R, Lee S-K. Viscoelastic property of the brain assessed with magnetic resonance elastography and its association with glymphatic system in neurologically normal individuals. Korean J Radiol 2023; 24:564-573.
- Alshuhri MS, Gallagher L, Work LM, Holmes WM. Direct imaging of glymphatic transport using
MRI. JCI Insight 2021; 6: e141159. - Huber VJ, Igarashi H, Ueki S, Kwee IL, Nakada T. Aquaporin-4 facilitator TGN-073 promotes interstitial fluid circulation within the blood-brain barrier:
JJVCPE MRI study. Neuroreport 2018; 29:697-703. - Harada T, Kudo K, Kameda H, et al. Phase I randomized trial of
-labeled water: Safety and feasibility study of indirect proton MRI for the evaluation of cerebral water dynamics. J Magn Reson Imaging 2022; 56:1874-1882. - de Leon MJ, Li Y, Okamura N, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid clearance in Alzheimer disease measured with dynamic PET. J Nucl Med 2017; 58:1471-1476.
- Zhou L, Butler TA, Wang XH, et al. Multimodal assessment of brain fluid clearance is associated with amyloid-beta deposition in humans. J Neuroradiol 2023 [Online ahead of print].
- Wang A, Chen L, Tian C, et al. Evaluation of the Glymphatic System With Diffusion Tensor Imaging-Along the Perivascular Space in Cancer Pain. Front Neurosci 2022; 16:823701.
- Ke Z, Mo Y, Li J, et al. Glymphatic dysfunction mediates the influence of white matter hyperintensities on episodic memory in cerebral small vessel disease. Brain Sci 2022; 12:1611.
- Liang T, Chang F, Huang Z, Peng D, Zhou X, Liu W. Evaluation of glymphatic system activity by diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) in dementia patients. Br J Radiol 2023; 96:20220315.
- Zhang Y, Zhang R, Ye Y, et al. The influence of demographics and vascular risk factors on glymphatic function measured by diffusion along perivascular space. Front Aging Neurosci 2021; 13:693787.
- Zhang C, Sha J, Cai L, et al. Evaluation of the glymphatic system using the DTI-ALPS index in patients with spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022; 2022:2694316.
- Song H, Ruan Z, Gao L, et al. Structural network efficiency mediates the association between glymphatic function and cognition in mild VCI: A DTI-ALPS study. Front Aging Neurosci 2022; 14:974114.
- Zhang C, Xu K, Zhang H, et al. Recovery of glymphatic system function in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy after surgery. Eur Radiol 2023; 33:6116-6123.
- Zhang X , Wang W, Zhang X, et al. Normal glymphatic system function in patients with new daily persistent headache using diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space. Headache 2023; 63:663-671.
- Wang L, Qin Y, Li X, et al. Glymphatic-system function is associated with addiction and relapse in heroin dependents undergoing methadone maintenance treatment. Brain Sci 2023; 13:1292.
- Qin Y, Li X, Qiao Y, et al. DTI-ALPS: An MR biomarker for motor dysfunction in patients with subacute ischemic stroke. Front Neurosci 2023; 17:1132393.
- Zhao X, Zhou Y, Li Y, et al. The asymmetry of glymphatic system dysfunction in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy: A DTI-ALPS study. J Neuroradiol 2023; 50:562-567.
- Nguchu BA, Zhao J, Wang Y, et al. Altered glymphatic system in middle-aged cART-treated patients with HIV: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Front Neurol 2022; 13:819594.
- Taoka T. In reply: The improvement technique for reproducibility of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) for evaluating interstitial fluid diffusivity and glymphatic function. Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:1031-1032.
- Saito Y, Kamagata K, Uchida W, Takabayashi K, Aoki S. The improvement technique for reproducibility of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) for evaluating interstitial fluid diffusivity and glymphatic function. Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:1029-1030.
- Saito Y, Kamagata K, Uchida W, Takabayashi K, Aoki S. Improved reproducibility of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) index calculated by manual and automated methods. Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:10331034.
- Hsu J-L, Wei Y-C, Toh CH, et al. Magnetic resonance images implicate that glymphatic alterations mediate cognitive dysfunction in Alzheimer disease. Ann Neurol 2023; 93:164-174.
- Liu S, Sun X, Ren Q, et al. Glymphatic dysfunction in patients with early-stage amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 2024; 147:100-108.
- Zhang
, Wang W, Bai X, et al. Increased glymphatic system activity in migraine chronification by diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space. J Headache Pain 2023; 24:147. - Liu X, Barisano G, Shao X, et al. Cross-vendor test-retest validation of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) for evaluating glymphatic system function. Aging Dis 2023 [Online ahead of print].
- Otake S, Taoka T, Maeda M, Yuh WT. A guide to identification and selection of axial planes in magnetic resonance imaging of the brain. Neuroradiol J 2018; 31:336-344.
- Tatekawa H, Matsushita S, Ueda D, et al. Improved reproducibility of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular
space (DTI-ALPS) index: An analysis of reorientation technique of the OASIS-3 dataset. Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:393-400. - Tatekawa H, Matsushita S, Miki Y. Reply to the letter to the editor: Improved reproducibility of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) index calculated by manual and automated methods. Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:1035-1036.
- Saito Y, Kamagata K, Andica C, et al. Multisite harmonization of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space using the COMBined Association Test. Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:1072-1083.
- Saito Y, Kamagata K, Andica C, et al. Reproducibility of automated calculation technique for diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space. Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:947-954.
- Agarwal N, Lewis LD, Hirschler L, et al. Current understanding of the anatomy, physiology, and magnetic resonance imaging of neurofluids: Update from the 2022 “ISMRM Imaging Neurofluids Study group” workshop in Rome. J Magn Reson Imaging 2024; 59:431-449.
- Andica C, Kamagata K, Takabayashi K, et al. Neuroimaging findings related to glymphatic system alterations in older adults with metabolic syndrome. Neurobiol Dis 2023; 177:105990.
- Heo CM, Lee DA, Park KM, et al. Glymphatic system dysfunction in patients with early chronic kidney disease. Front Neurol 2022; 13:976089.
- Ornello R, Bruno F, Frattale I, et al. White matter hyperintensities in migraine are not mediated by a dysfunction of the glymphatic system-A diffusion tensor imaging magnetic resonance imaging study. Headache 2023; 63:11281134.
- Hsiao W-C, Chang H-I, Hsu S-W, et al. Association of cognition and brain reserve in aging and glymphatic function using diffusion tensor image-along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS). Neuroscience 2023; 524:11-20.
- Park KM, Kim KT, Lee DA, Motamedi GK, Cho YW. Glymphatic system dysfunction in restless legs syndrome: Evidenced by diffusion tensor imaging along the perivascular space. Sleep 2023; 46:zsad239.
- Taoka T, Naganawa S. Neurofluid dynamics and the glymphatic system: A Neuroimaging Perspective. Korean J Radiol 2020; 21:1199-1209.
- Taoka T, Naganawa S. Glymphatic imaging using MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 2020; 51:11-24.
Department of Innovative Biomedical Visualization (iBMV), Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, Nagoya, Aichi, Japan
Department of Radiology, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Aichi, Japan
Department of Radiology, Aichi Medical University, Nagakute, Aichi, Japan
*Corresponding author: Department of Innovative Biomedical Visualization (iBMV), Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, 65 Tsurumai-cho, Showa-ku, Nagoya, Aichi 466-8550, Japan. Phone: +81-52-744-2328, Fax: +81-52-744-2335, E-mail: ttaoka@med.nagoya-u.ac.jpThis work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives International License.
©2024 Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
Received: December 25, 2023 | Accepted: February 22, 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2463/mrms.rev.2023-0175
PMID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38569866
Publication Date: 2024-01-01
Diffusion Tensor Image Analysis ALong the Perivascular Space (DTI-ALPS): Revisiting the Meaning and Significance of the Method
Abstract
More than 5 years have passed since the Diffusion Tensor Image Analysis ALong the Perivascular Space (DTI-ALPS) method was proposed with the intention of evaluating the glymphatic system. This method is handy due to its noninvasiveness, provision of a simple index in a straightforward formula, and the possibility of retrospective analysis. Therefore, the ALPS method was adopted to evaluate the glymphatic system for many disorders in many studies. The purpose of this review is to look back and discuss the ALPS method at this moment.
The ALPS-index was found to be an indicator of a number of conditions related to the glymphatic system. Thus, although this was expected in the original report, the results of the ALPS method are often interpreted as uniquely corresponding to the function of the glymphatic system. However, a number of subsequent studies have pointed out the problems on the data interpretation. As they rightly point out, a higher ALPS-index indicates predominant Brownian motion of water molecules in the radial direction at the lateral ventricular body level, no more and no less. Fortunately, the term “ALPS-index” has become common and is now known as a common term by many researchers. Therefore, the ALPS-index should simply be expressed as high or low, and whether it reflects a glymphatic system is better to be discussed carefully. In other words, when a decreased ALPS-index is observed, it should be expressed as “decreased ALPS-index” and not directly as “glymphatic dysfunction”. Recently, various methods have been proposed to evaluate the glymphatic system. It has become clear that these methods also do not seem to reflect the entirety of the extremely complex glymphatic system. This means that it would be desirable to use various methods in combination to evaluate the glymphatic system in a comprehensive manner.
Introduction

the DTI-ALPS method but also several other approaches to noninvasively evaluate ISF dynamics have been introduced, and their application in various diseases and conditions has been reported. This article reviews trends in the study of the glymphatic system, with a focus on the ALPS method. It discusses the meaning and significance of this method and explores how it should be utilized in the field.
Concept of DTI-ALPS
radial direction, specifically the left-right or
resolution of the diffusion image, in units of millimeters. Only the direction of the diffusion is distinguishable. However, what the ALPS method is trying to evaluate is the total or macroscopic movement of water in the direction of the PVS direction, not the movement of water in the PVS itself. Thus, these limitations are not a hindrance to this concept. In addition, since the method uses diffusion images, it evaluates the “movement” of water, not the “flow” of water. Thus, water movement toward the brain surface and toward the ventricles is equally subject to evaluation. Other issues will be considered in “Controversy in DTI-ALPS method” section.
Application of DTI-ALPS
Application for Alzheimer’s disease

Application for Parkinson’s disease and other degenerative disease
loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra.

Application for small vessel diseases
dysfunction, and motor dysfunction, and has also attracted attention as a background pathology for neurodegenerative diseases such as AD.
Application for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus
symptomatic improvement after shunt surgery, whereas there was no significant increase in postoperative ALPSindex in the group without symptomatic improvement (Fig. 4).
Application for traumatic brain injury
Application for demyelinating disease

nor were they correlated with Expanded Disability Status Scale scores.
Application for sleep

parameters and positively correlated with wake after sleep onset and REM sleep length in patients with type 2 narcolepsy.
Findings on the aging
negative correlation between age and ALPS-index in com-munity-dwelling elderly aged 60 years and older, with a standard partial regression coefficient of
Other Methods for Evaluation of Glymphatic System
Intrathecal GBCA
humans, tracer studies using MR with intrathecal GBCA are considered to be the gold standard. However, it should be noted that the molecular weight of GBCA is 0.6 kDa (Gadobtrol), whereas that of
Intravenous GBCA
| Method | MR sequence | Target phenomenon | Target location | Assumed rolls in glymphatic system |
| Intrathecal GBCA | T1WI | Penetration via the brain surface (Tracer: GBCA) | Brain surface | CSF influx to brain parenchyma |
| BBB permeability (Tracer: GBCA) | Brain parenchyma | ISF production | ||
| Intravenous GBCA | T1WI | Venous wall permeability (Tracer: GBCA) | Surface vein | Movement of waste products |
| Tracking of GBCA | Meningeal lymphatic vessel/ Perivascular space | Movement of waste products | ||
| Intravenous
|
Steady-state sequence | BBB permeability (Tracer: labeled water) | Brain parenchyma | ISF production |
| DTI-ALPS | DTI | Brownian motion of the water molecule in the brain tissue | Deep white matter adjacent the lateral ventricle | Movement of ISF within the tissue |
| Free water analysis | DTI etc. | Increase of free water fraction | Brain parenchyma | Widening of interstitial space |
| Perivascular space volume | 3D-T2WI etc. | Dilatation of perivascular space | Perivascular space | Accumulation of metabolic waste |
| Choroid plexus volume | 3D-T1WI etc. | Enlargement of choroid plexus | Choroid plexus | Removal of waste/ Immune reaction etc. |
| ASL with long TI | ASL | BBB permeability (Tracer: tagged water) | Brain parenchyma | ISF production |
| BOLD-CSF coupling | BOLD | Synchrony of the neural activity and the brain/CSF motion | Brain parenchyma | Tissue microenvironment |
| Elastography | Elastography | Viscoelastic properties of the brain | Brain parenchyma | Tissue microenvironment |
human evaluation after administration of a normal dose of GBCA, leakage from the cortical veins into the CSF was observed. An enhancement within the PVS in the basal ganglia and around the cortical veins was observed after 4 h of IV-GBCA administration.
after IV-GBCA was performed. The study also simultaneously examined the enhancement of the basal ganglia perivascular space (PVS-BG), and PVS-BG was seen in 21 of the 42 cases.
evaluate BBB leakage. However, BBB leakage from GBCA in healthy brain tissue is so small that the measurement is always evaluated near the noise floor. In this respect, the measurements are expected to be greatly affected by noise contamination, imaging conditions, and analysis methods. It should also be noted that the evaluation of BBB leakage does not evaluate the entire glymphatic system, but only a part of the entire system.
Perivascular space volume
ophthalmopathy. Astronauts who spent 6 months on the International Space Station showed enlarged PVSs in the basal ganglia and white matter after their spaceflight. Furthermore, astronauts who developed spaceflightrelated neuro-ophthalmopathy had a more enlarged PVS in the white matter than those who did not develop the syndrome, indicating that long-term changes in gravity may affect the function of the glymphatic system.
Choroid plexus volume
brain, and regulation of CSF composition for homeostatic brain function have been identified.
Diffusion-based methods other than ALPS method
Arterial spin labeling
Imaging for brain tissue kinetics
coupling was associated with the cognitive decline seen in patients with PD. Additionally, lower BOLD-CSF coupling in PD patients was associated with a thinner right entorhinal cortex.
Other tracer study methods
extracranial accumulation of tracer was in the nasal turbinates. In patients with
Consideration for the Methodology of DTI-ALPS
Placement of ROI
Reproducibility of ALPS method

Variation of ALPS method
and 3-axis DWI showed a good correlation. This suggests the possibility of using the DWI-ALPS method with triaxial MPG.
examinations.
Controversy in DTI-ALPS Method
Conclusion
as a common term in this research area. It would be correct to describe the ALPS-index only as high or low, increased or decreased, and whether it reflects the glymphatic system or not should be considered as a subject for discussion. In other words, if a decrease in ALPS-index is observed, the title of the paper should say “decrease in ALPS-index” and not “glymphatic dysfunction” directly at least in the title of the paper. With regard to ALPS method, Professor Iliff mentioned that “Changes in the measure are seen under conditions where glymphatic function are impaired – so while we don’t have a strong handle on the exact nature of the signal it seems to work at some level” (personal communication), and the author agree with his opinion.
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iliff JJ, Wang M, Liao Y, et al. A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid
. Sci Transl Med 2012; 4:147ra111. - Gaberel T, Gakuba C, Goulay R, et al. Impaired glymphatic perfusion after strokes revealed by contrast-enhanced MRI: A new target for fibrinolysis? Stroke 2014; 45:3092-3096.
- Ringstad G, Vatnehol SAS, Eide PK. Glymphatic MRI in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Brain 2017; 140:2691-2705.
- Taoka T, Masutani Y, Kawai H, et al. Evaluation of glymphatic system activity with the diffusion MR technique: diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTIALPS) in Alzheimer’s disease cases. Ipn I Radiol 2017; 35:172-178.
- Okudera T, Huang YP, Fukusumi A, Nakamura Y, Hatazawa J, Uemura K. Micro-angiographical studies of the medullary venous system of the cerebral hemisphere. Neuropathology 1999; 19:93-111.
- Taoka T, Fukusumi A, Miyasaka T, et al. Structure of the medullary veins of the cerebral hemisphere and related disorders. Radiographics 2017; 37:281-297.
- Simon MJ, Iliff JJ. Regulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow in neurodegenerative, neurovascular and neuroinflammatory disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2016; 1862:442-451.
- Matsuda H, Shigemoto Y, Sato N. Neuroimaging of Alzheimer’s disease: Focus on amyloid and tau PET. Jpn J Radiol 2019; 37:735-749.
- Nakata T, Shimada K, Iba A, et al. Differential diagnosis of MCI with Lewy bodies and MCI due to Alzheimer’s disease by visual assessment of occipital hypoperfusion on SPECT images. Jpn J Radiol 2024; 42:308-318.
- Thientunyakit T, Thongpraparn T, Sethanandha C, et al. Relationship between F-18 florbetapir uptake in occipital lobe and neurocognitive performance in Alzheimer’s disease. Jpn J Radiol 2021; 39:984-993.
- Taoka T, Naganawa S. Imaging for central nervous system (CNS) interstitial fluidopathy: Disorders with impaired interstitial fluid dynamics. Jpn J Radiol 2021; 39:1-14.
- Taoka T, Ito R, Nakamichi R, Nakane T, Kawai H, Naganawa S. Interstitial fluidopathy of the central nervous system: An umbrella term for disorders with impaired neurofluid dynamics. Magn Reson Med Sci 2024; 23:1-13.
- Sparacia G, Sakai K, Yamada K, et al. Assessment of brain core temperature using MR DWI-thermometry in Alzheimer disease patients compared to healthy subjects. Jpn J Radiol 2017; 35:168-171.
- Chang H-I, Huang C-W, Hsu S-W, et al. Gray matter reserve determines glymphatic system function in young-onset Alzheimer’s disease: Evidenced by DTI-ALPS and compared with age-matched controls. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2023; 77:401-409.
- Kamagata K, Andica C, Hatano T, et al. Advanced diffusion magnetic resonance imaging in patients with Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Neural Regen Res 2020; 15:1590-1600.
- Zhong J, Zhang X, Xu H, et al. Unlocking the enigma: Unraveling multiple cognitive dysfunction linked to glymphatic impairment in early Alzheimer’s disease. Front Neurosci 2023; 17:1222857.
- Matsushita S, Tatekawa H, Ueda D, et al. The association of metabolic brain MRI, amyloid PET, and clinical factors: A study of Alzheimer’s disease and normal controls from the open access series of imaging studies dataset. J Magn Reson Imaging 2024; 59:1341-1348.
- Steward CE, Venkatraman VK, Lui E, et al. Assessment of the DTI-ALPS parameter along the perivascular space in older adults at risk of dementia. J Neuroimaging 2021; 31:569-578.
- Ota M, Sato N, Nakaya M, et al. Relationships between the deposition of amyloid-
and tau protein and glymphatic system activity in Alzheimer’s disease: Diffusion tensor image study. J Alzheimers Dis 2022; 90:295-303. - Kamagata K, Andica C, Takabayashi K, et al. Association of MRI indices of glymphatic system with amyloid deposition and cognition in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2022; 99:e2648-e2660.
- Zhang X, Wang Y, Jiao B, et al. Glymphatic system impairment in Alzheimer’s disease: Associations with perivascular space volume and cognitive function. Eur Radiol 2024; 34:1314-1323.
- Park CJ, Kim S-Y, Kim JH, et al. Evaluation of glymphatic system activity using diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space and amyloid PET in older adults with objectively normal cognition: a preliminary study. Front Aging Neurosci 2023; 15:1221667.
- Dickson DW, Braak H, Duda JE, et al. Neuropathological assessment of Parkinson’s disease: refining the diagnostic criteria. Lancet Neurol 2009; 8:1150-1157.
- Oshima S, Fushimi Y, Miyake KK, et al. Denoising approach with deep learning-based reconstruction for neuromelaninsensitive MRI: Image quality and diagnostic performance. Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:1216-1225.
- Maekawa T, Sato N, Ota M, et al. Correlations between dopamine transporter density measured by 123I-FP-CIT SPECT and regional gray matter volume in Parkinson’s disease. Jpn J Radiol 2017; 35:755-759.
- Shen T, Yue Y, Ba F, et al. Diffusion along perivascular spaces as marker for impairment of glymphatic system in Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 2022; 8:174.
- McKnight CD, Trujillo P, Lopez AM, et al. Diffusion along perivascular spaces reveals evidence supportive of glymphatic function impairment in Parkinson disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2021; 89:98-104..
- Ma X, Li S, Li C, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging along the perivascular space index in different stages of Parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 2021; 13:773951.
- Chen H-L, Chen P-C, Lu C-H, et al. Associations among cognitive functions, plasma DNA, and diffusion tensor image along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021; 2021:4034509.
- Cai X , Chen
, et al. Diffusion along perivascular spaces provides evidence interlinking compromised glymphatic function with aging in Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurosci Ther 2023; 29:111-121. - Ruan X, Huang X, Li Y, Li E, Li M, Wei X. Diffusion tensor imaging analysis along the perivascular space index in primary Parkinson’s disease patients with and without freezing of gait. Neuroscience 2022; 506:51-57.
- Gu L, Dai S, Guo T, et al. Noninvasive neuroimaging provides evidence for deterioration of the glymphatic system in Parkinson’s disease relative to essential tremor. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2023; 107:105254.
- Bae YJ, Kim J-M, Choi BS, et al. Glymphatic function assessment in Parkinson’s disease using diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2023; 114:105767.
- Qin Y, He R, Chen J, et al. Neuroimaging uncovers distinct relationships of glymphatic dysfunction and motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 2023; 270:2649-2658.
- He P, Shi L, Li Y, et al. The association of the glymphatic function with Parkinson’s disease symptoms: Neuroimaging evidence from longitudinal and cross-sectional studies. Ann Neurol 2023; 94:672-683.
- Meng J-C, Shen M-Q, Lu Y-L, et al. Correlation of glymphatic system abnormalities with Parkinson’s disease progression: A clinical study based on non-invasive fMRI. J Neurol 2024; 271:457-471.
- Postuma RB, Iranzo A, Hu M, et al. Risk and predictors of dementia and parkinsonism in idiopathic REM sleep behaviour disorder: A multicentre study. Brain 2019; 142:744759.
- Si X, Guo T, Wang Z, et al. Neuroimaging evidence of glymphatic system dysfunction in possible REM sleep behavior disorder and Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 2022; 8:54.
- Bae YJ, Kim J-M, Choi BS, et al. Altered brain glymphatic flow at diffusion-tensor MRI in rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. Radiology 2023; 307:e221848.
- Ota M, Sato N, Takahashi Y, et al. Correlation between the regional brain volume and glymphatic system activity in progressive supranuclear palsy. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2023; 52:177-183.
- Saito Y, Kamagata K, Andica C, et al. Glymphatic system impairment in corticobasal syndrome: Diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS). Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:1226-1235.
- Wang
, Wang , Gao , et al. Characterizing the penumbras of white matter hyperintensities in patients with cerebral small vessel disease. Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:928-937. - Kikuta J, Kamagata K, Takabayashi K, et al. An investigation of water diffusivity changes along the perivascular space in elderly subjects with hypertension. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2022; 43:48-55.
- Wardlaw JM, Smith C, Dichgans M. Small vessel disease: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol 2019; 18:684-696.
- Benveniste H, Nedergaard M. Cerebral small vessel disease: A glymphopathy? Curr Opin Neurobiol 2022; 72:15-21.
- Tang J, Zhang M, Liu N, et al. The association between glymphatic system dysfunction and cognitive impairment in cerebral small vessel disease. Front Aging Neurosci 2022; 14:916633.
- Tian
, Cai , Zhou , et al. Impaired glymphatic system as evidenced by low diffusivity along perivascular spaces is associated with cerebral small vessel disease: A populationbased study. Stroke Vasc Neurol 2023; 8:e002191. - Xu J, Su Y, Fu J, et al. Glymphatic dysfunction correlates with severity of small vessel disease and cognitive impairment in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Eur J Neurol 2022; 29:2895-2904.
- Ishii K, Kanda T, Harada A, et al. Clinical impact of the callosal angle in the diagnosis of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Eur Radiol 2008; 18:2678-2683.
- Irie R, Tsuruta K, Hori M, et al. Neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging for evaluation of corticospinal tract in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus.
Radiol 2017; 35:25-30. - Ishii K. Diagnostic imaging of dementia with Lewy bodies, frontotemporal lobar degeneration, and normal pressure hydrocephalus. Jpn J Radiol 2020; 38:64-76.
- Nakajima M, Kuriyama N, Miyajima M, et al. Background risk factors associated with shunt intervention for possible idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: A nationwide hospital-based survey in Japan. J Alzheimers Dis 2019; 68:735-744.
- Iseki C, Takahashi Y, Adachi M, et al. Prevalence and development of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: A 16year longitudinal study in Japan. Acta Neurol Scand 2022; 146:680-689.
- Eide PK, Lashkarivand A, Hagen-Kersten ÅA, et al. Intrathecal contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of cerebrospinal fluid dynamics and glymphatic enhancement in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Front Neurol 2022; 13:857328.
- Eide PK, Pripp AH, Ringstad G. Magnetic resonance imaging biomarkers of cerebrospinal fluid tracer dynamics in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Brain Commun 2020; 2:fcaa187.
- Yokota H, Vijayasarathi A, Cekic M, et al. Diagnostic performance of glymphatic system evaluation using diffusion tensor imaging in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus and mimickers. Curr Gerontol Geriatr Res 2019; 2019:5675014.
- Georgiopoulos C, Tisell A, Holmgren RT, et al. Noninvasive assessment of glymphatic dysfunction in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus with diffusion tensor imaging.
Neurosurg 2023 [Online ahead of print]. - Ishikawa M, Hashimoto M, Mori E, Kuwana N, Kazui H. The value of the cerebrospinal fluid tap test for predicting shunt effectiveness in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Fluids Barriers CNS 2012; 9:1.
- Miyati T, Mase M, Kasai H, et al. Noninvasive MRI assessment of intracranial compliance in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J Magn Reson Imaging 2007; 26:274-278.
- Mase M, Miyati T, Kasai H, et al. Noninvasive estimation of intracranial compliance in idiopathic NPH using MRI. Acta Neurochir Suppl 2008; 102:115-118.
- Bae YJ, Choi BS, Kim J-M, Choi J-H, Cho SJ, Kim JH. Altered glymphatic system in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2021; 82:56-60.
- Kikuta J, Kamagata K, Taoka T, et al. Water diffusivity changes along the perivascular space after lumboperitoneal shunt surgery in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Front Neurol 2022; 28:843883.
- Graham NS, Sharp DJ. Understanding neurodegeneration after traumatic brain injury: From mechanisms to clinical trials in dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2019; 90:1221-1233.
- Iliff JJ, Chen MJ, Plog BA, et al. Impairment of glymphatic pathway function promotes tau pathology after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci 2014; 34:16180-16193.
- Goulay R, Aron Badin R, Flament J, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid leakage after posterior fossa surgery may impair brain metabolite clearance. Neurochirurgie 2018; 64:422-424.
- Park JH, Bae YJ, Kim JS, et al. Glymphatic system evaluation using diffusion tensor imaging in patients with traumatic brain injury. Neuroradiology 2023; 65:551-557.
- Dai Z, Yang Z, Li Z, et al. Increased glymphatic system activity in patients with mild traumatic brain injury. Front Neurol 2023; 14:1148878.
- Yang D-X, Sun Z, Yu M-M, et al. Associations of MRIderived glymphatic system impairment with global white matter damage and cognitive impairment in mild traumatic brain injury: A DTI-ALPS study. J Magn Reson Imaging 2024; 59:639-647.
- Morita Y, Kamagata K, Andica C, et al. Glymphatic system impairment in nonathlete older male adults who played contact sports in their youth associated with cognitive decline: A diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space study. Front Neurol 2023; 14:1100736.
- Carotenuto A, Cacciaguerra L, Pagani E, Preziosa P, Filippi M, Rocca MA. Glymphatic system impairment in multiple sclerosis: Relation with brain damage and disability. Brain 2022; 145:2785-2795.
- Rocca MA, Margoni M, Battaglini M, et al. Emerging perspectives on MRI application in multiple sclerosis: Moving from pathophysiology to clinical practice. Radiology 2023; 307:e221512.
- Hagiwara A, Tomizawa Y, Hoshino Y, et al. Glymphatic system dysfunction in myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein immunoglobulin G antibody-associated disorders: Association with clinical disability. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2024; 45:66-71.
- Xie L, Kang H, Xu Q, et al. Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain. Science 2013; 342:373-377.
- Siow TY, Toh CH, Hsu J-L, et al. Association of sleep, neuropsychological performance, and gray matter volume with glymphatic function in community-dwelling older adults. Neurology 2022; 98:e829-e838.
- Roy B, Nunez A, Aysola RS, Kang DW, Vacas S, Kumar R. Impaired glymphatic system actions in obstructive sleep apnea adults. Front Neurosci 2022; 16:884234.
- Saito Y, Hayakawa Y, Kamagata K, et al. Glymphatic system impairment in sleep disruption: diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS). Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:1335-1343.
- Gumeler E, Aygun E, Tezer FI, Saritas EU, Oguz KK. Assessment of glymphatic function in narcolepsy using DTI-ALPS index. Sleep Med 2023; 101:522-527.
- Han G, Zhou Y, Zhang K, et al. Age- and time-of-day dependence of glymphatic function in the human brain measured via two diffusion MRI methods. Front Aging Neurosci 2023; 15:1173221.
- Thomas C, Sadeghi N, Nayak A, et al. Impact of time-of-day on diffusivity measures of brain tissue derived from diffusion tensor imaging. Neuroimage 2018; 173:25-34.
- Zhou W, Shen B, Shen W-Q, Chen H, Zheng Y-F, Fei J-J. Dysfunction of the glymphatic system might be related to iron deposition in the normal aging brain. Front Aging Neurosci 2020; 12:559603.
- Yang G, Deng N, Liu Y, Gu Y, Yao X. Evaluation of Glymphatic System Using Diffusion MR Technique in T2DM Cases. Front Hum Neurosci 2020; 14:300.
- Toh CH, Siow TY, Castillo M. Peritumoral brain edema in meningiomas may be related to glymphatic dysfunction. Front Neurosci 2021; 15:674898.
- Toh CH, Siow TY. Glymphatic dysfunction in patients with ischemic stroke. Front Aging Neurosci 2021; 13:756249.
- Toh CH, Siow TY, Castillo M. Peritumoral brain edema in metastases may be related to glymphatic dysfunction. Front Oncol 2021; 11:725354.
- Zhang W, Zhou Y, Wang J, et al. Glymphatic clearance function in patients with cerebral small vessel disease. Neuroimage 2021; 238:118257.
- Taoka T, Ito R, Nakamichi R, et al. Reproducibility of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) for evaluating interstitial fluid diffusivity and glymphatic function: CHanges in Alps index on Multiple conditiON acquIsition eXperiment (CHAMONIX) study. Jpn J Radiol 2022; 40:147-158.
- Lee H-J, Lee DA, Shin KJ, Park KM. Glymphatic system dysfunction in patients with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy.
Neurol 2022; 269:2133-2139. - Lee DA, Lee H-J, Park KM. Glymphatic dysfunction in isolated REM sleep behavior disorder. Acta Neurol Scand 2022; 145:464-470.
- Wang J, Zhou Y, Zhang K, et al. Glymphatic function plays a protective role in ageing-related cognitive decline. Age Ageing 2023; 52:afad107.
- Wei Y-C, Hsu C-CH, Huang W-Y, et al. Vascular risk factors and astrocytic marker for the glymphatic system activity. Radiol Med 2023; 128:1148-1161.
- Taoka T, Ito R, Nakamichi R, et al. Evaluation of alterations in interstitial fluid dynamics in cases of whole-brain radiation using the diffusion-weighted image analysis along the perivascular space method. NMR Biomed 2023:e5030.
- Kim S-T, Kim SE, Lee DA, Lee H-J, Park KM. Anti-seizure medication response and the glymphatic system in patients with focal epilepsy. Eur J Neurol 2024; 31:e16097.
- Toh CH, Siow TY. Factors associated with dysfunction of glymphatic system in patients with glioma. Front Oncol 2021; 11:744318.
- Dai
, Yang , Chen , et al. The aging of glymphatic system in human brain and its correlation with brain charts and neuropsychological functioning. Cereb Cortex 2023; 33:7896-7903. - Taoka T, Ito R, Nakamichi R, et al. Diffusion-weighted image analysis along the perivascular space (DWI-ALPS) for evaluating interstitial fluid status: Age dependence in normal subjects. Jpn J Radiol 2022; 40:894-902.
- Li X, Ruan C, Zibrila AI, et al. Children with autism spectrum disorder present glymphatic system dysfunction evidenced by diffusion tensor imaging along the perivascular space. Medicine (Baltimore) 2022; 101:e32061.
- Lin L-P, Su S, Hou W, et al. Glymphatic system dysfunction in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia without clinically diagnosed central nervous system infiltration: A novel DTIALPS method. Eur Radiol 2023; 33:3726-3734.
- Chen Y, Wang M, Su S, et al. Assessment of the glymphatic function in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Eur Radiol 2024; 34:1444-1452.
- Haller S, Moy L, Anzai Y. Evaluation of diffusion tensor imaging analysis along the perivascular space as a marker of the glymphatic system. Radiology 2024; 310:e232899.
- Wright AM, Wu Y-C, Chen N-K, Wen Q. Exploring radial asymmetry in mr diffusion tensor imaging and its impact on the interpretation of glymphatic mechanisms. J Magn Reson Imaging 2023; jmri. 29203.
- Piantino JA, Iliff JJ, Lim MM, Levendovszky SR. Reader response: Association of sleep, neuropsychological performance, and gray matter volume with glymphatic function in community-dwelling older adults. Neurology 2023; 100:355356.
- Ringstad G. Glymphatic imaging: A critical look at the DTIALPS index. Neuroradiology 2024; 66:157-160.
- Chen G-F, Xu T-H, Yan Y, et al. Amyloid beta: structure, biology and structure-based therapeutic development. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2017; 38:1205-1235.
- Eide PK, Ringstad G. MRI with intrathecal MRI gadolinium contrast medium administration: A possible method to assess glymphatic function in human brain. Acta Radiol Open 2015; 4:2058460115609635.
- Vinje V, Zapf B, Ringstad G, Eide PK, Rognes ME, Mardal K-A. Human brain solute transport quantified by glymphatic MRI-informed biophysics during sleep and sleep deprivation. Fluids Barriers CNS 2023; 20:62.
- Dyke JP, Xu HS, Verma A, Voss HU, Chazen JL. MRI characterization of early CNS transport kinetics post intrathecal gadolinium injection: Trends of subarachnoid and parenchymal distribution in healthy volunteers. Clin Imaging 2020; 68:1-6.
- Taoka T, Jost G, Frenzel T, Naganawa S, Pietsch H. Impact of the glymphatic system on the kinetic and distribution of gadodiamide in the rat brain: Observations by dynamic MRI and effect of circadian rhythm on tissue gadolinium concentrations. Invest Radiol 2018; 53:529-534.
- Naganawa S, Nakane T, Kawai H, Taoka T. Gd-based contrast enhancement of the perivascular spaces in the basal ganglia. Magn Reson Med Sci 2017; 16:61-65.
- Naganawa S, Nakane T, Kawai H, Taoka T. Age dependence of gadolinium leakage from the cortical veins into the cerebrospinal fluid assessed with whole brain 3D-real inversion recovery MR imaging. Magn Reson Med Sci 2019; 18:163169.
- Naganawa S, Ito R, Kawai H, Taoka T, Yoshida T, Sone M. Confirmation of age-dependence in the leakage of contrast medium around the cortical veins into cerebrospinal fluid after intravenous administration of gadolinium-based contrast agent. Magn Reson Med Sci 2020; 19:375-381.
- Nakamichi R, Taoka T, Kawai H, Yoshida T, Sone M, Naganawa S. Magnetic resonance cisternography imaging findings related to the leakage of Gadolinium into the subarachnoid space. Jpn J Radiol 2021; 39:927-937.
- Naganawa S, Ito R, Nakamichi R, et al. Relationship between time-dependent signal changes in parasagittal perivenous cysts and leakage of gadolinium-based contrast agents into the subarachnoid space. Magn Reson Med Sci 2021; 20:378-384.
- Naganawa S, Ito R, Nakamichi R, et al. Relationship between parasagittal perivenous cysts and leakage of gadoliniumbased contrast agents into the subarachnoid space around the cortical veins after intravenous administration. Magn Reson Med Sci 2021; 20:245-252.
- Naganawa S, Ito R, Kawamura M, Taoka T, Yoshida T, Sone M. Association between the putative meningeal lymphatics at the posterior wall of the sigmoid sinus and delayed con-trast-agent elimination from the cerebrospinal fluid. Magn Reson Med Sci 2024; 23:80-91.
- Naganawa S, Taoka T, Ito R, Kawamura M. The glymphatic system in humans: Investigations with magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol 2024; 59:1-12.
- van de Haar HJ, Burgmans S, Jansen JFA, et al. Blood-brain barrier leakage in patients with early Alzheimer disease. Radiology 2016; 281:527-535.
- Lee S, Yoo R-E, Choi SH, et al. Contrast-enhanced MRI T1 mapping for quantitative evaluation of putative dynamic glymphatic activity in the human brain in sleep-wake states. Radiology 2021; 300:661-668.
- Wu C-H, Chang F-C, Wang Y-F, et al. Impaired glymphatic and meningeal lymphatic functions in patients with chronic migraine. Ann Neurol 2023 [Online ahead of print].
- Wardlaw JM, Smith EE, Biessels GJ, et al. Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol 2013; 12:822-838.
- Potter GM, Chappell FM, Morris Z, Wardlaw JM. Cerebral perivascular spaces visible on magnetic resonance imaging: Development of a qualitative rating scale and its observer reliability. Cerebrovasc Dis 2015; 39:224-231.
- Weller RO, Hawkes CA, Kalaria RN, Werring DJ, Carare RO. White matter changes in dementia: role of impaired drainage of interstitial fluid. Brain Pathol 2015; 25:63-78.
- Liu H, Yang S, He W, et al. Associations among diffusion tensor image along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS), enlarged perivascular space (ePVS), and cognitive functions in asymptomatic patients with carotid plaque. Front Neurol 2022; 12:789918.
- Donahue EK, Foreman RP, Duran JJ, et al. Increased perivascular space volume in white matter and basal ganglia is associated with cognition in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Imaging Behav 2023; 18:57-65.
- Zeng Q, Li K, Luo X, et al. The association of enlarged perivascular space with microglia-related inflammation and Alzheimer’s pathology in cognitively normal elderly. Neurobiol Dis 2022; 170:105755.
- Yu N, Sinclair B, Posada LMG, et al. Asymmetric distribution of enlarged perivascular spaces in centrum semiovale may be associated with epilepsy after acute ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther 2022; 28:343-353.
- Perosa V, Oltmer J, Munting LP, et al. Perivascular space dilation is associated with vascular amyloid-
accumulation in the overlying cortex. Acta Neuropathol 2022; 143:331348. - Tsai H-H, Pasi M, Tsai L-K, et al. Centrum semiovale perivascular space and amyloid deposition in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2021; 52:2356-2362.
- Dubost F, Adams H, Bortsova G, et al. 3D regression neural network for the quantification of enlarged perivascular spaces in brain MRI. Med Image Anal 2019; 51:89-100.
- Barisano G, Sepehrband F, Collins HR, et al. The effect of prolonged spaceflight on cerebrospinal fluid and perivascular spaces of astronauts and cosmonauts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2022; 119:e2120439119.
- Butler T, Zhou L, Ozsahin I, et al. Glymphatic clearance estimated using diffusion tensor imaging along perivascular spaces is reduced after traumatic brain injury and correlates with plasma neurofilament light, a biomarker of injury severity. Brain Commun 2023; 5:fcad134.
- Christensen J, Li C, Mychasiuk R. Choroid plexus function in neurological homeostasis and disorders: The awakening of the circadian clocks and orexins. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2022; 42:1163-1175.
- Jeong SH, Park CJ, Jeong H-J, et al. Association of choroid plexus volume with motor symptoms and dopaminergic degeneration in Parkinson’s disease. I Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2023; 94:1047-1055.
- Li Y, Zhou Y, Zhong W, et al. Choroid plexus enlargement exacerbates white matter hyperintensity growth through glymphatic impairment. Ann Neurol 2023; 94:182-195.
- Tu Y, Li Z, Xiong F, Gao F. Decreased DTI-ALPS and choroid plexus enlargement in fibromyalgia: A preliminary multimodal MRI study. Neuroradiology 2023; 65:1749-1755.
- Eisma JJ, McKnight CD, Hett K, et al. Deep learning segmentation of the choroid plexus from structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): Validation and normative ranges across the adult lifespan. Res Sq 2023 [Preprint].
- Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Grenier P, Cabanis E, Laval-Jeantet M. MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: Application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology 1986; 161:401-407.
- Le Bihan D. Intravoxel incoherent motion imaging using steady-state free precession. Magn Reson Med 1988; 7:346351.
- Taoka T, Naganawa S, Kawai H, Nakane T, Murata K. Can low b value diffusion weighted imaging evaluate the character of cerebrospinal fluid dynamics? Ipn I Radiol 2019; 37:135-144.
- Taoka T, Kawai H, Nakane T, et al. Diffusion analysis of fluid dynamics with incremental strength of motion proving gradient (DANDYISM) to evaluate cerebrospinal fluid dynamics. Jpn J Radiol 2021; 39:315-323.
- Taoka T, Kawai H, Nakane T, et al. Evaluating the effect of arterial pulsation on cerebrospinal fluid motion in the sylvian fissure of patients with middle cerebral artery occlusion using low b-value diffusion-weighted imaging. Magn Reson Med Sci 2021; 20:371-377.
- Bito Y, Harada K, Ochi H, Kudo K. Low b-value diffusion tensor imaging for measuring pseudorandom flow of cerebrospinal fluid. Magn Reson Med 2021; 86:1369-1382.
- Ohene Y, Harrison IF, Nahavandi P, et al. Non-invasive MRI of brain clearance pathways using multiple echo time arterial spin labelling: an aquaporin-4 study. Neuroimage 2019; 188:515-523.
- Joseph CR, Benhatzel CM, Stern LJ, Hopper OM, Lockwood MD. Pilot study utilizing MRI 3D TGSE PASL (arterial spin labeling) differentiating clearance rates of labeled protons in the CNS of patients with early Alzheimer disease from normal subjects. MAGMA 2020; 33:559-568.
- Kiviniemi V, Wang X, Korhonen V, et al. Ultra-fast magnetic resonance encephalography of physiological brain activity – Glymphatic pulsation mechanisms? J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2016; 36:1033-1045.
- Fultz NE, Bonmassar G, Setsompop K, et al. Coupled electrophysiological, hemodynamic, and cerebrospinal fluid oscillations in human sleep. Science 2019; 366:628-631.
- Han F, Brown GL, Zhu Y, et al. Decoupling of global brain activity and cerebrospinal fluid flow in Parkinson’s disease cognitive decline. Mov Disord 2021; 36:2066-2076.
- Jiang D, Liu L, Kong Y, et al. Regional glymphatic abnormality in behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia. Ann Neurol 2023; 94:442-456.
- Manduca A, Bayly PJ, Ehman RL, et al. MR elastography: Principles, guidelines, and terminology. Magn Reson Med 2021; 85:2377-2390.
- Ge GR, Song W, Nedergaard M, Rolland JP, Parker KJ. Theory of sleep/wake cycles affecting brain elastography. Phys Med Biol 2022; 67: 225013.
- Joo B, Won SY, Sinkus R, Lee S-K. Viscoelastic property of the brain assessed with magnetic resonance elastography and its association with glymphatic system in neurologically normal individuals. Korean J Radiol 2023; 24:564-573.
- Alshuhri MS, Gallagher L, Work LM, Holmes WM. Direct imaging of glymphatic transport using
MRI. JCI Insight 2021; 6: e141159. - Huber VJ, Igarashi H, Ueki S, Kwee IL, Nakada T. Aquaporin-4 facilitator TGN-073 promotes interstitial fluid circulation within the blood-brain barrier:
JJVCPE MRI study. Neuroreport 2018; 29:697-703. - Harada T, Kudo K, Kameda H, et al. Phase I randomized trial of
-labeled water: Safety and feasibility study of indirect proton MRI for the evaluation of cerebral water dynamics. J Magn Reson Imaging 2022; 56:1874-1882. - de Leon MJ, Li Y, Okamura N, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid clearance in Alzheimer disease measured with dynamic PET. J Nucl Med 2017; 58:1471-1476.
- Zhou L, Butler TA, Wang XH, et al. Multimodal assessment of brain fluid clearance is associated with amyloid-beta deposition in humans. J Neuroradiol 2023 [Online ahead of print].
- Wang A, Chen L, Tian C, et al. Evaluation of the Glymphatic System With Diffusion Tensor Imaging-Along the Perivascular Space in Cancer Pain. Front Neurosci 2022; 16:823701.
- Ke Z, Mo Y, Li J, et al. Glymphatic dysfunction mediates the influence of white matter hyperintensities on episodic memory in cerebral small vessel disease. Brain Sci 2022; 12:1611.
- Liang T, Chang F, Huang Z, Peng D, Zhou X, Liu W. Evaluation of glymphatic system activity by diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) in dementia patients. Br J Radiol 2023; 96:20220315.
- Zhang Y, Zhang R, Ye Y, et al. The influence of demographics and vascular risk factors on glymphatic function measured by diffusion along perivascular space. Front Aging Neurosci 2021; 13:693787.
- Zhang C, Sha J, Cai L, et al. Evaluation of the glymphatic system using the DTI-ALPS index in patients with spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022; 2022:2694316.
- Song H, Ruan Z, Gao L, et al. Structural network efficiency mediates the association between glymphatic function and cognition in mild VCI: A DTI-ALPS study. Front Aging Neurosci 2022; 14:974114.
- Zhang C, Xu K, Zhang H, et al. Recovery of glymphatic system function in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy after surgery. Eur Radiol 2023; 33:6116-6123.
- Zhang X , Wang W, Zhang X, et al. Normal glymphatic system function in patients with new daily persistent headache using diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space. Headache 2023; 63:663-671.
- Wang L, Qin Y, Li X, et al. Glymphatic-system function is associated with addiction and relapse in heroin dependents undergoing methadone maintenance treatment. Brain Sci 2023; 13:1292.
- Qin Y, Li X, Qiao Y, et al. DTI-ALPS: An MR biomarker for motor dysfunction in patients with subacute ischemic stroke. Front Neurosci 2023; 17:1132393.
- Zhao X, Zhou Y, Li Y, et al. The asymmetry of glymphatic system dysfunction in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy: A DTI-ALPS study. J Neuroradiol 2023; 50:562-567.
- Nguchu BA, Zhao J, Wang Y, et al. Altered glymphatic system in middle-aged cART-treated patients with HIV: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Front Neurol 2022; 13:819594.
- Taoka T. In reply: The improvement technique for reproducibility of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) for evaluating interstitial fluid diffusivity and glymphatic function. Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:1031-1032.
- Saito Y, Kamagata K, Uchida W, Takabayashi K, Aoki S. The improvement technique for reproducibility of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) for evaluating interstitial fluid diffusivity and glymphatic function. Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:1029-1030.
- Saito Y, Kamagata K, Uchida W, Takabayashi K, Aoki S. Improved reproducibility of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) index calculated by manual and automated methods. Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:10331034.
- Hsu J-L, Wei Y-C, Toh CH, et al. Magnetic resonance images implicate that glymphatic alterations mediate cognitive dysfunction in Alzheimer disease. Ann Neurol 2023; 93:164-174.
- Liu S, Sun X, Ren Q, et al. Glymphatic dysfunction in patients with early-stage amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 2024; 147:100-108.
- Zhang
, Wang W, Bai X, et al. Increased glymphatic system activity in migraine chronification by diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space. J Headache Pain 2023; 24:147. - Liu X, Barisano G, Shao X, et al. Cross-vendor test-retest validation of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) for evaluating glymphatic system function. Aging Dis 2023 [Online ahead of print].
- Otake S, Taoka T, Maeda M, Yuh WT. A guide to identification and selection of axial planes in magnetic resonance imaging of the brain. Neuroradiol J 2018; 31:336-344.
- Tatekawa H, Matsushita S, Ueda D, et al. Improved reproducibility of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular
space (DTI-ALPS) index: An analysis of reorientation technique of the OASIS-3 dataset. Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:393-400. - Tatekawa H, Matsushita S, Miki Y. Reply to the letter to the editor: Improved reproducibility of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) index calculated by manual and automated methods. Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:1035-1036.
- Saito Y, Kamagata K, Andica C, et al. Multisite harmonization of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space using the COMBined Association Test. Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:1072-1083.
- Saito Y, Kamagata K, Andica C, et al. Reproducibility of automated calculation technique for diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space. Jpn J Radiol 2023; 41:947-954.
- Agarwal N, Lewis LD, Hirschler L, et al. Current understanding of the anatomy, physiology, and magnetic resonance imaging of neurofluids: Update from the 2022 “ISMRM Imaging Neurofluids Study group” workshop in Rome. J Magn Reson Imaging 2024; 59:431-449.
- Andica C, Kamagata K, Takabayashi K, et al. Neuroimaging findings related to glymphatic system alterations in older adults with metabolic syndrome. Neurobiol Dis 2023; 177:105990.
- Heo CM, Lee DA, Park KM, et al. Glymphatic system dysfunction in patients with early chronic kidney disease. Front Neurol 2022; 13:976089.
- Ornello R, Bruno F, Frattale I, et al. White matter hyperintensities in migraine are not mediated by a dysfunction of the glymphatic system-A diffusion tensor imaging magnetic resonance imaging study. Headache 2023; 63:11281134.
- Hsiao W-C, Chang H-I, Hsu S-W, et al. Association of cognition and brain reserve in aging and glymphatic function using diffusion tensor image-along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS). Neuroscience 2023; 524:11-20.
- Park KM, Kim KT, Lee DA, Motamedi GK, Cho YW. Glymphatic system dysfunction in restless legs syndrome: Evidenced by diffusion tensor imaging along the perivascular space. Sleep 2023; 46:zsad239.
- Taoka T, Naganawa S. Neurofluid dynamics and the glymphatic system: A Neuroimaging Perspective. Korean J Radiol 2020; 21:1199-1209.
- Taoka T, Naganawa S. Glymphatic imaging using MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 2020; 51:11-24.
Department of Innovative Biomedical Visualization (iBMV), Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, Nagoya, Aichi, Japan
Department of Radiology, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Aichi, Japan
Department of Radiology, Aichi Medical University, Nagakute, Aichi, Japan
*Corresponding author: Department of Innovative Biomedical Visualization (iBMV), Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, 65 Tsurumai-cho, Showa-ku, Nagoya, Aichi 466-8550, Japan. Phone: +81-52-744-2328, Fax: +81-52-744-2335, E-mail: ttaoka@med.nagoya-u.ac.jpThis work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives International License.
©2024 Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
Received: December 25, 2023 | Accepted: February 22, 2024
