DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042338
PMID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38397015
تاريخ النشر: 2024-02-16
دور اللبتين في السمنة وأمراض القلب والأوعية الدموية ومرض السكري من النوع الثاني
تمت المراجعة: 7 فبراير 2024
تم القبول: 9 فبراير 2024
نُشر: 16 فبراير 2024
2 قسم الكيمياء الحيوية الطبية وعلم الأحياء الجزيئي، وعلم المناعة، كلية الطب، مستشفى فيرجن ماكارينا الجامعي، جامعة إشبيلية، 41009، إسبانيا؛maria.polonio@hotmail.com (م.ل.ب.-ج.)؛ antonioresi@gmail.com (أ.ب.-ب.)
4 خدمة الغدد الصماء والتغذية، مستشفى رامون و كاخال الجامعي، 28034 مدريد، إسبانيا؛arri68@hotmail.com
5 خدمة الغدد الصماء والتغذية، مستشفى بويرتا ديل مار الجامعي، معهد البحث والابتكار في العلوم الطبية الحيوية في محافظة قادس (INiBICA)، جامعة قادس (UCA)، 11001 قادس، إسبانيا؛manuelaguilardiosdado@gmail.com
6 مركز تشوبيرا الصحي، الرعاية الأولية في ألكوبينداس، ألكوبينداس 28100 مدريد، إسبانيا؛juancarlosobaya@yahoo.es
قسم الغدد الصماء والتغذية، مستشفى كلينيكو الجامعي لوزانو بليسا، 1550009 سرقسطة، إسبانيا؛jagimeno@salud.aragon.es
8 خدمة الغدد الصماء والتغذية، مستشفى بويرتا دي هيررو الجامعي، ماجاداهوندا، 28220 مدريد، إسبانيا؛piglo65@gmail.com
10 إندو ديابيسيداد كلينيكا دوران وشركاه، 41018 إشبيلية، إسبانيا؛sduran@duransanz.com
11 وحدة الدهون ومخاطر القلب والأوعية الدموية، مستشفى ديل مار، الجامعة المستقلة في برشلونة، 08003 برشلونة، إسبانيا؛ jpedrobotet@psmar.cat
12 معهد الطب الحيوي في إشبيلية (IBIS)، مستشفى جامعة فيرجن ديل روكيو/فيرجن ماكارينا، CSIC، جامعة إشبيلية، 41013 إشبيلية، إسبانيا
- المراسلات:margalet@us.es
ساهم هؤلاء المؤلفون بالتساوي في هذا العمل.
الملخص
داء السكري (DM) هو مرض شائع للغاية في جميع أنحاء العالم، يُقدّر أنه يؤثر على 1 من كل 11 بالغًا؛ من بينهم،
1. المقدمة
2. السمنة وأمراض القلب والأوعية الدموية
3. السمنة والسكري
تستجيب عن طريق إفراز الأنسولين بشكل غير كافٍ في محاولة للتغلب على هذه المقاومة، وهي ظاهرة لوحظت في المراحل المبكرة من المرض [28،29].
لقد أظهرت الدراسات أنه في النظام الغذائي عالي الدهون، لا يؤثر استنفاد خلايا NK على النتائج الأيضية. ويدعم هذا الافتراض أن النهج المعاكس، وهو توسيع خلايا NK باستخدام IL-15، يؤدي إلى تفاقم مقاومة الأنسولين لدى الأشخاص الذين يتبعون أنظمة غذائية عالية الدهون. كما لوحظ أنه مع زيادة السمنة، يتم تنشيط البلعميات الدهنية، ولها عملان رئيسيان. أولاً، تنتج كيموكينات تجذب خلايا NK المتداولة، مما يزيد من عددها في الدهون الإبيديديمية؛ وثانياً، تقوم بتخليق IL-15، مما ينشط ويوسع خلايا NK في الدهون الإبيديديمية، مما يعزز المزيد من الزيادة في البلعميات الدهنية (التنشيط المتبادل). هذه الدورة التي تتشكل تحفز الالتهاب في السمنة، وبالتالي، مقاومة الأنسولين من خلال أفعال وسطاء مختلفين في الكبد والعضلات التي تطلق الدهون الإبيديديمية. في هذا السياق، تدعم البيانات الحديثة أيضًا مساهمة خلايا NK في الأنسجة الدهنية الحشوية في الالتهاب منخفض الدرجة المرتبط بمقاومة الأنسولين.
4. السكري وأمراض القلب والأوعية الدموية
5. اللبتين
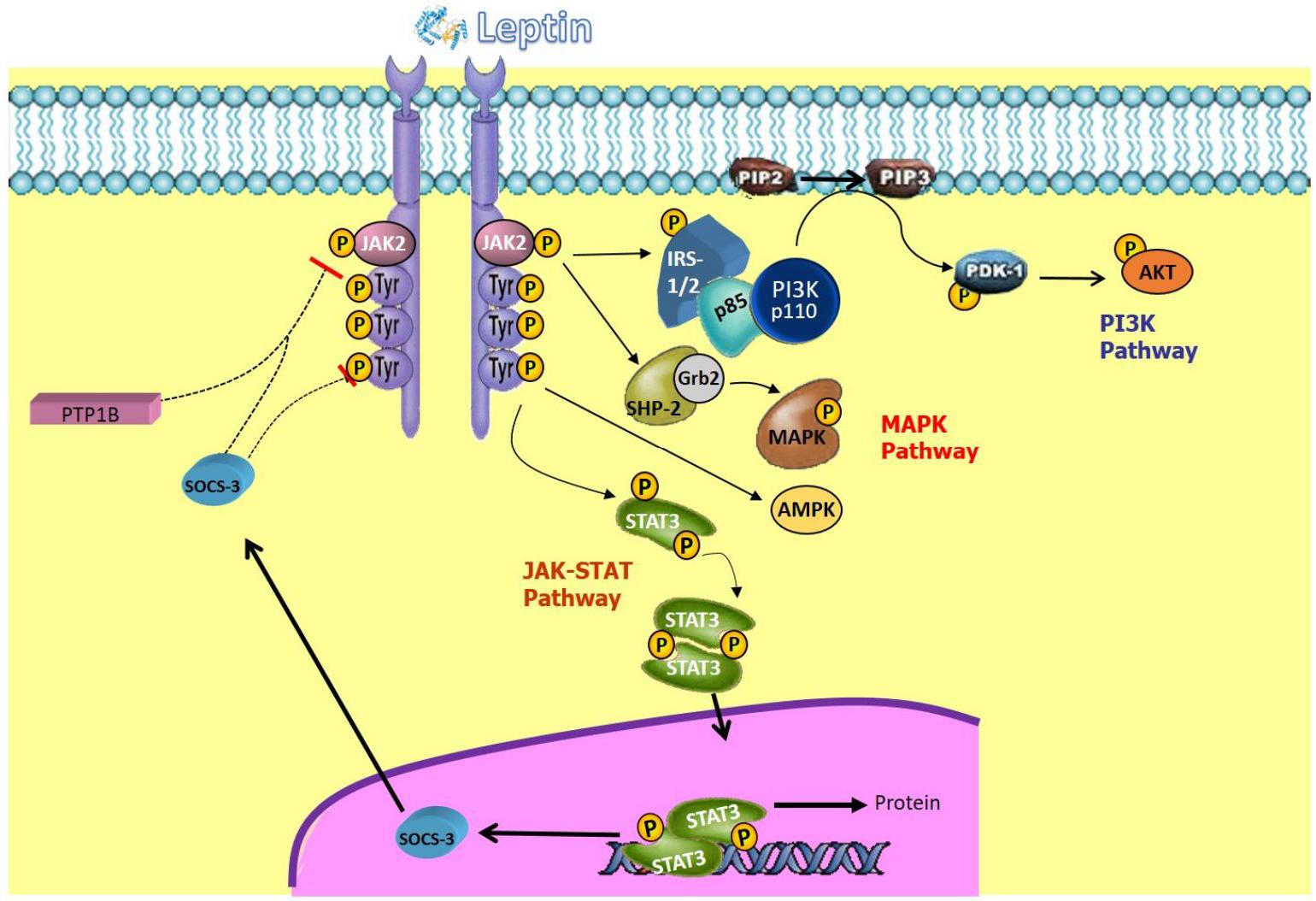
هرمون محفز (
6. اللبتين والسمنة
بتغييرات في التمايز الجنسي في الببتيد العصبي Y (NPY) والبروأوبيوميلانوكورتين (POMC) المشاركين في النواة البارافنتريكولارية في الوطاء. ومع ذلك، لا تزال الآليات الدقيقة لعمل اللبتين في النساء والرجال البدينين غير واضحة تمامًا [106].
7. اللبتين والسكري من النوع 2
8. اللبتين وأمراض القلب والأوعية الدموية
(ص38)، وزيادة في أنواع الأكسجين التفاعلية داخل الخلايا. ومع ذلك، فإن توفير مستويات كافية من اللبتين يعيد سمك القلب إلى طبيعته [18،119].
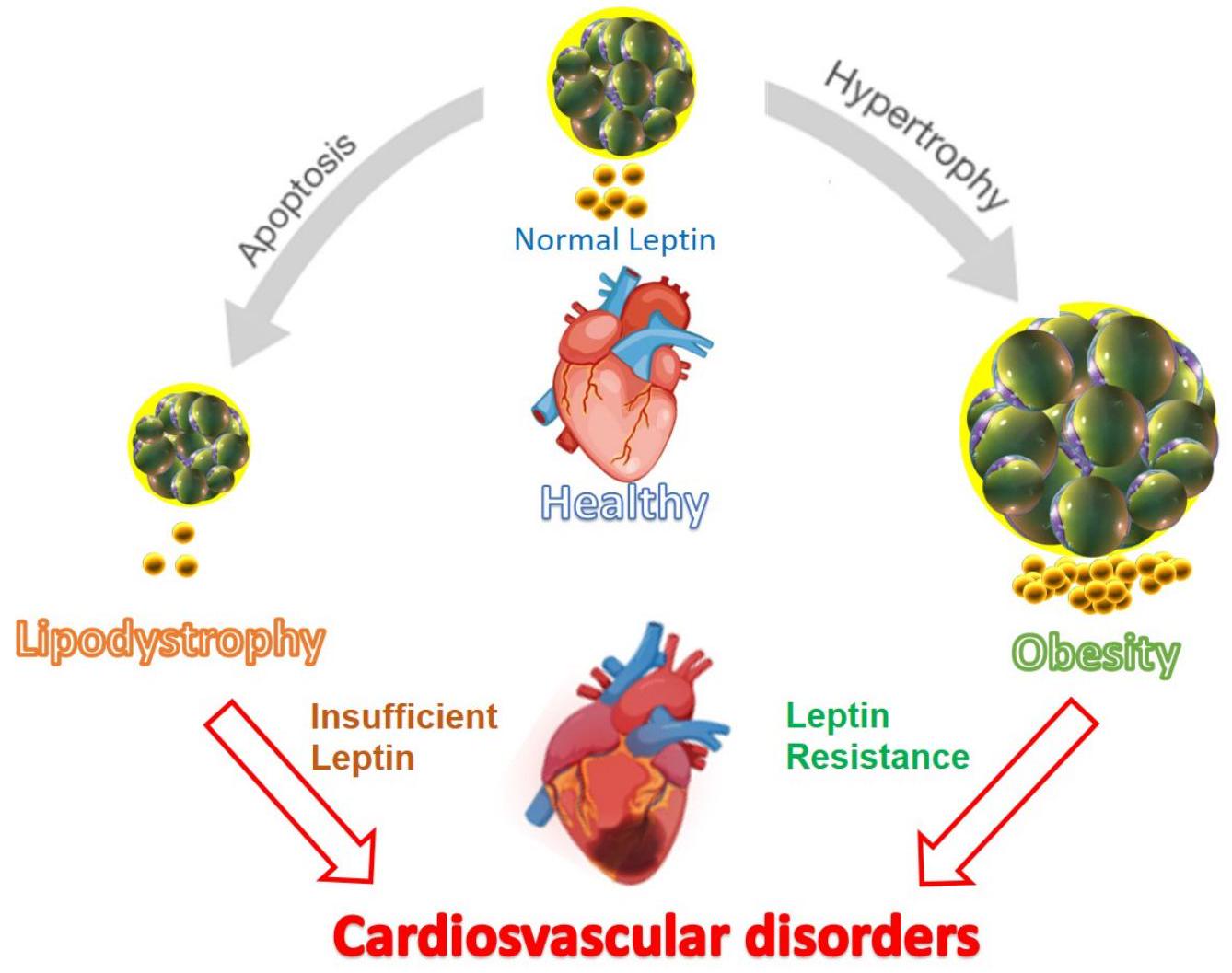
ضروري لنقل الكالسيوم بين الخلايا العضلية والسيتوبلازم. يمكن أن تؤدي الاضطرابات في دوران الكالسيوم داخل الشبكة الساركوبلازمية إلى أمراض القلب مثل فشل القلب وتصلب الشرايين، مما يساهم في تقدم المرض. فهم هذه الآليات أمر حاسم لفهم الفيزيولوجيا المرضية للاضطرابات القلبية [122،123]. أظهرت الدراسات التي أجريت على الفئران التي تعاني من نقص الليبتين انخفاضًا في تنشيط SERCA2 و
تأثيرات اللبتين من خلال تقليل الكوليسترول الكبدي (تقليل تنظيم السيتوكينات المؤيدة للالتهابات مثل TNF-
9. اللبتين كهدف علاجي
في المرضى الذين يعانون من مستويات مرتفعة من اللبتين. لا يزال هذا الآلية قيد الدراسة، ولكن يُفترض أنها مرتبطة بتعبير مستقبل IL-1 1 في الوطاء [147-149].
10. الاستنتاجات
مساهمات المؤلفين: ساهم كل من ت.ف.-ج، م.ل.ب.-ج، أ.ب.-ب، ج.ر، ف.أ، م.أ، ج.س.أ، ج.أ.ج.-أ، ب.أ، ج.ن، س.د، ج.ب.-ب، ف.س.-م. ومجموعة عمل أمراض القلب والأوعية الدموية التابعة للجمعية الإسبانية للسكري (SED) في وضع المفهوم، والبحث في الأدبيات ومراجعة المسودة. كتب ت.ف.-ج، م.ل.ب.-ج وف.س.-م المسودة. قرأ جميع المؤلفين ووافقوا على النسخة المنشورة من المخطوطة.
تعارض المصالح: يعلن المؤلفون عدم وجود أي تعارض في المصالح.
References
- Glovaci, D.; Fan, W.; Wong, N.D. Epidemiology of Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2019, 21, 21. [CrossRef]
- Kerner, W.; Brückel, J. Definition, classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2014, 122, 384-386. [CrossRef]
- Coraci, D.; Giovannini, S.; Loreti, C.; Pecchioli, C.; Piccinini, G.; Padua, L. The past encounters the future: “old” diagnostic methods to check innovative treatments for carpal tunnel syndrome. Comment on: “Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome: From ultrasonography to ultrasound surgery” by Petrover and Richette. Joint Bone Spine 2017 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2017.11.003. Jt. Bone Spine 2018, 85, 783-784. [CrossRef]
- Endalifer, M.L.; Diress, G. Epidemiology, Predisposing Factors, Biomarkers, and Prevention Mechanism of Obesity: A Systematic Review. J. Obes. 2020, 2020, 6134362. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chobot, A.; Górowska-Kowolik, K.; Sokołowska, M.; Jarosz-Chobot, P. Obesity and diabetes-Not only a simple link between two epidemics. Diabetes. Metab. Res. Rev. 2018, 34, e3042. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Hu, F.B. Epidemiology of Obesity and Diabetes and Their Cardiovascular Complications. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1723-1735. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Sala, L.; Pontiroli, A.E. Prevention of Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease in Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8178. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Proenca, R.; Maffei, M.; Barone, M.; Leopold, L.; Friedman, J.M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994, 372, 425-432. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.M. Leptin, leptin receptors, and the control of body weight. Nutr. Rev. 1998, 56, S38-S46. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Considine, R.V.; Caro, J.F. Leptin and the regulation of body weight. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997, 29, 1255-1272. [CrossRef]
- White, D.W.; Tartaglia, L.A. Leptin and OB-R: Body weight regulation by a cytokine receptor. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1996, 7, 303-309. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obradovic, M.; Sudar-Milovanovic, E.; Soskic, S.; Essack, M.; Arya, S.; Stewart, A.J.; Gojobori, T.; Isenovic, E.R. Leptin and Obesity: Role and Clinical Implication. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 585887. [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pérez, A.; Sánchez-Jiménez, F.; Vilariño-García, T.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Role of Leptin in Inflammation and Vice Versa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5887. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chang, L.; Wang, J.; Xia, L.; Cao, L.; Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Gao, H. Leptin and risk factors for atherosclerosis: A review. Medicine 2023, 102, E36076. [CrossRef]
- Raman, P.; Khanal, S. Leptin in Atherosclerosis: Focus on Macrophages, Endothelial and Smooth Muscle Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5446. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neeland, I.J.; Ross, R.; Després, J.P.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Yamashita, S.; Shai, I.; Seidell, J.; Magni, P.; Santos, R.D.; Arsenault, B.; et al. Visceral and ectopic fat, atherosclerosis, and cardiometabolic disease: A position statement. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 715-725. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Corral, A.; Montori, V.M.; Somers, V.K.; Korinek, J.; Thomas, R.J.; Allison, T.G.; Mookadam, F.; Lopez-Jimenez, F. Association of bodyweight with total mortality and with cardiovascular events in coronary artery disease: A systematic review of cohort studies. Lancet 2006, 368, 666-678. [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.W.; Ok, M.; Lee, S.K. Leptin as a Key between Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 29, 248-259. [CrossRef]
- Bombelli, M.; Facchetti, R.; Sega, R.; Carugo, S.; Fodri, D.; Brambilla, G.; Giannattasio, C.; Grassi, G.; Mancia, G. Impact of body mass index and waist circumference on the long-term risk of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and cardiac organ damage. Hypertension 2011, 58, 1029-1035. [CrossRef]
- Wensveen, F.M.; Valentić, S.; Šestan, M.; Turk Wensveen, T.; Polić, B. The “Big Bang” in obese fat: Events initiating obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 2446-2456. [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.S.; Qasim, A.; Reilly, M.P. Leptin resistance: A possible interface of inflammation and metabolism in obesity-related cardiovascular disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 1201-1210. [CrossRef]
- Recinella, L.; Orlando, G.; Ferrante, C.; Chiavaroli, A.; Brunetti, L.; Leone, S. Adipokines: New Potential Therapeutic Target for Obesity and Metabolic, Rheumatic, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 578966. [CrossRef]
- Carbone, S.; Canada, J.M.; Billingsley, H.E.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Elagizi, A.; Lavie, C.J. Obesity paradox in cardiovascular disease: Where do we stand? Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2019, 15, 89-100. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blüher, M. Metabolically Healthy Obesity. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, 405-420. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Huang, R.; Jiang, M.; Wang, W.; Chai, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Han, Y.; Yan, F.; Lu, Q.; et al. Myocardial Tissue-Level Characteristics of Adults with Metabolically Healthy Obesity. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2023, 16, 889-901. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksson, P.; Henriksson, H.; Tynelius, P.; Berglind, D.; Löf, M.; Lee, I.M.; Shiroma, E.J.; Ortega, F.B. Fitness and Body Mass Index During Adolescence and Disability Later in Life: A Cohort Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 170, 230-239. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksson, H.; Henriksson, P.; Tynelius, P.; Ekstedt, M.; Berglind, D.; Labayen, I.; Ruiz, J.R.; Lavie, C.J.; Ortega, F.B. Cardiorespiratory fitness, muscular strength, and obesity in adolescence and later chronic disability due to cardiovascular disease: A cohort study of 1 million men. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 1503-1510. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutari, C.; DeMarsilis, A.; Mantzoros, C.S. Obesity and diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 202, 110773. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.; Gastaldelli, A.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Scherer, P.E. Why does obesity cause diabetes? Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 11-20. [CrossRef]
- Hocking, S.; Samocha-Bonet, D.; Milner, K.L.; Greenfield, J.R.; Chisholm, D.J. Adiposity and insulin resistance in humans: The role of the different tissue and cellular lipid depots. Endocr. Rev. 2013, 34, 463-500. [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.; Fisch, G.; Teague, B.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Banyas, B.; Allen, K.; Savoye, M.; Rieger, V.; Taksali, S.; Barbetta, G.; et al. Prevalence of impaired glucose tolerance among children and adolescents with marked obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 802-810. [CrossRef]
- D’Adamo, E.; Cali, A.M.G.; Weiss, R.; Santoro, N.; Pierpont, B.; Northrup, V.; Caprio, S. Central role of fatty liver in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance in obese adolescents. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1817-1822. [CrossRef]
- Kahkoska, A.R.; Pokaprakarn, T.; Rumay Alexander, G.; Crume, T.L.; Dabelea, D.; Divers, J.; Dolan, L.M.; Jensen, E.T.; Lawrence, J.M.; Marcovina, S.; et al. The Impact of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities in Diabetes Management on Clinical Outcomes: A Reinforcement Learning Analysis of Health Inequity Among Youth and Young Adults in the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 108-118. [CrossRef]
- Al Amiri, E.; Abdullatif, M.; Abdulle, A.; Al Bitar, N.; Afandi, E.Z.; Parish, M.; Darwiche, G. The prevalence, risk factors, and screening measure for prediabetes and diabetes among Emirati overweight/obese children and adolescents. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 1298. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeb, A.; Salima, A.; Samia, M.; Ghada, E.; Abubaker, E. Insulin Resistance, Impaired fasting, Glucose Intolerance and Type II Diabetes Mellitus in Overweight and Obese Children in Abu Dhabi. J. Diabetes Obes. 2017, 4, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Dilworth, L.; Facey, A.; Omoruyi, F. Diabetes Mellitus and Its Metabolic Complications: The Role of Adipose Tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7644. [CrossRef]
- Saltiel, A.R.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammatory mechanisms linking obesity and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1-4. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mclaughlin, T.; Ackerman, S.E.; Shen, L.; Engleman, E. Role of innate and adaptive immunity in obesity-associated metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 5-13. [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pérez, A.; Vilariño-García, T.; Fernández-Riejos, P.; Martín-González, J.; Segura-Egea, J.J.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Role of leptin as a link between metabolism and the immune system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017, 35, 71-84. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Margalet, V.; Martín-Romero, C.; Santos-Alvarez, J.; Goberna, R.; Najib, S.; Gonzalez-Yanes, C. Role of leptin as an immunomodulator of blood mononuclear cells: Mechanisms of action. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 133, 11-19. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Margalet, V.; Fernández-Riejos, P.; Najib, S.; Santos-Alvarez, J.; Martín-Romero, C.; Pérez-Pérez, A.; González-Yanes, C. Role of leptin in the activation of immune cells. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 568343. [CrossRef]
- Bonamichi, B.D.S.F.; Lee, J. Unusual Suspects in the Development of Obesity-Induced Inflammation and Insulin Resistance: NK cells, iNKT cells, and ILCs. Diabetes Metab. J. 2017, 41, 229-250. [CrossRef]
- Wouters, K.; Kusters, Y.H.A.M.; Bijnen, M.; Wetzels, S.; Zhang, X.; Linssen, P.B.C.; Gaens, K.; Houben, A.J.H.M.; Joris, P.J.; Plat, J.; et al. NK cells in human visceral adipose tissue contribute to obesity-associated insulin resistance through low-grade inflammation. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, e192. [CrossRef]
- Caussy, C.; Aubin, A.; Loomba, R. The Relationship Between Type 2 Diabetes, NAFLD, and Cardiovascular Risk. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2021, 21, 15. [CrossRef]
- Naito, R.; Kasai, T. Coronary artery disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Recent treatment strategies and future perspectives. World J. Cardiol. 2015, 7, 119. [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.D.; Langenberg, C.; Rapsomaniki, E.; Denaxas, S.; Pujades-Rodriguez, M.; Gale, C.P.; Deanfield, J.; Smeeth, L.; Timmis, A.; Hemingway, H. Type 2 diabetes and incidence of cardiovascular diseases: A cohort study in 1.9 million people. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 105-113. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punthakee, Z.; Goldenberg, R.; Katz, P. Definition, Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes, Prediabetes and Metabolic Syndrome. Can. J. Diabetes 2018, 42 (Suppl. S1), S10-S15. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prandi, F.R.; Evangelista, I.; Sergi, D.; Palazzuoli, A.; Romeo, F. Mechanisms of cardiac dysfunction in diabetic cardiomyopathy: Molecular abnormalities and phenotypical variants. Heart Fail. Rev. 2023, 28, 597-606. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.L.; Pietz, K.; Battleman, D.S.; Beyth, R.J. Prevalence of Comorbid Hypertension and Dyslipidemia and Associated Cardiovascular Disease. Heart Dis. 2004, 2, 3.
- Piché, M.E.; Tchernof, A.; Després, J.P. Obesity Phenotypes, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1477-1500. [CrossRef]
- Barrett-Connor, E. Hypercholesterolemia predicts early death from coronary heart disease in elderly men but not women. The Rancho Bernardo Study. Ann. Epidemiol. 1992, 2, 77-83. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, C.; Hong, J.; Zeng, J.; Lai, S.; Lv, A.; Su, Q.; Dong, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, W.; et al. Lipid profiling reveals different therapeutic effects of metformin and glipizide in patients with type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2804-2812. [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.J.; Pagidipati, N.J.; Aroda, V.R.; Cavender, M.A.; Green, J.B.; Lopes, R.D.; Al-Khalidi, H.; Gaynor, T.; Kaltenbach, L.A.; Kirk, J.K.; et al. Incorporating SGLT2i and GLP-1RA for Cardiovascular and Kidney Disease Risk Reduction: Call for Action to the Cardiology Community. Circulation 2021, 144, 74-84. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strain, W.D.; Paldánius, P.M. Diabetes, cardiovascular disease and the microcirculation. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 57. [CrossRef]
- Halaas, J.L.; Gajiwala, K.S.; Maffei, M.; Cohen, S.L.; Chait, B.T.; Rabinowitz, D.; Lallone, R.L.; Burley, S.K.; Friedman, J.M. Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science 1995, 269, 543-546. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Considine, R.V.; Sinha, M.K.; Heiman, M.L.; Kriauciunas, A.; Stephens, T.W.; Nyce, M.R.; Ohannesian, J.P.; Marco, C.C.; McKee, L.J.; Bauer, T.L.; et al. Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 292-295. [CrossRef]
- Fain, J.N.; Madan, A.K.; Hiler, M.L.; Cheema, P.; Bahouth, S.W. Comparison of the release of adipokines by adipose tissue, adipose tissue matrix, and adipocytes from visceral and subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissues of obese humans. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 2273-2282. [CrossRef]
- Wajchenberg, B.L. Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: Their relation to the metabolic syndrome. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 697-738. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Pérez, A.; Maymó, J.; Gambino, Y.; Guadix, P.; Dueñas, J.L.; Varone, C.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Insulin enhances leptin expression in human trophoblastic cells. Biol. Reprod. 2013, 89, 20. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miell, J.P.; Englaro, P.; Blum, W.F. Dexamethasone induces an acute and sustained rise in circulating leptin levels in normal human subjects. Horm. Metab. Res. 1996, 28, 704-707. [CrossRef]
- De Vos, P.; Saladin, R.; Auwerx, J.; Staels, B. Induction of ob gene expression by corticosteroids is accompanied by body weight loss and reduced food intake. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 15958-15961. [CrossRef]
- Ahima, R.S.; Flier, J.S. Leptin. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2000, 62, 413-437. [CrossRef]
- Margetic, S.; Gazzola, C.; Pegg, G.G.; Hill, R.A. Leptin: A review of its peripheral actions and interactions. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2002, 26, 1407-1433. [CrossRef]
- Mantzoros, C.S.; Magkos, F.; Brinkoetter, M.; Sienkiewicz, E.; Dardeno, T.A.; Kim, S.Y.; Hamnvik, O.P.R.; Koniaris, A. Leptin in human physiology and pathophysiology. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 301, E567-E584. [CrossRef]
- Hickey, M.S.; Israel, R.G.; Gardiner, S.N.; Considine, R.V.; McCammon, M.R.; Tyndall, G.L.; Houmard, J.A.; Marks, R.H.L.; Caro, J.F. Gender Differences in Serum Leptin Levels in Humans. Biochem. Mol. Med. 1996, 59, 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Arch, J.R.S.; Stock, M.J.; Trayhurn, P. Leptin resistance in obese humans: Does it exist and what does it mean? Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1998, 22, 1159-1163. [CrossRef]
- Knight, Z.A.; Hannan, K.S.; Greenberg, M.L.; Friedman, J.M. Hyperleptinemia is required for the development of leptin resistance. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11376. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poetsch, M.S.; Strano, A.; Guan, K. Role of Leptin in Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 354. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J. Leptin and hyperleptinemia-From friend to foe for cardiovascular function. J. Endocrinol. 2004, 181, 1-10. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Kusminski, C.M.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin, Leptin and Cardiovascular Disorders. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 136-149. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, M.J.; Clifton, D.K.; Steiner, R.A. Leptin’s actions on the reproductive axis: Perspectives and mechanisms. Biol. Reprod. 1999, 60, 216-222. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, G.A. Obesity and reproduction. Hum. Reprod. 1997, 12 (Suppl. S1), 26-32. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, D.L.; Nagatani, S. Physiological perspectives on leptin as a regulator of reproduction: Role in timing puberty. Biol. Reprod. 1999, 60, 205-215. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Pérez, A.; Sánchez-Jiménez, F.; Maymó, J.; Dueñas, J.L.; Varone, C.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Role of leptin in female reproduction. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2015, 53, 15-28. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Pérez, A.; Toro, A.; Vilariño-García, T.; Maymó, J.; Guadix, P.; Dueñas, J.L.; Fernández-Sánchez, M.; Varone, C.; SánchezMargalet, V. Leptin action in normal and pathological pregnancies. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 716-727. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, R.B.S. Leptin-Much more than a satiety signal. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2000, 20, 45-75. [CrossRef]
- Meister, B. Control of food intake via leptin receptors in the hypothalamus. Vitam. Horm. 2000, 59, 265-304. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Margalet, V.; Martin-Romero, C. Human leptin signaling in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: Activation of the JAK-STAT pathway. Cell. Immunol. 2001, 211, 30-36. [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, E.C.; Myers, M.G. Leptin receptor signaling and the regulation of mammalian physiology. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32 (Suppl. S7), S8-S12. [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.H.; Myers, M.G. The role of leptin receptor signaling in feeding and neuroendocrine function. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 14, 447-452. [CrossRef]
- Bjørbaek, C.; Kahn, B.B. Leptin signaling in the central nervous system and the periphery. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 2004, 59, 305-331. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jéquier, E. Leptin signaling, adiposity, and energy balance. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 967, 379-388. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Murakami, T.; Otani, S.; Kuwajima, M.; Shima, K. Leptin receptor signal transduction: OBRa and OBRb of fa type. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 246, 752-759. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Okimura, Y.; Mizuno, I.; Iida, K.; Takahashi, T.; Kaji, H.; Abe, H.; Chihara, K. Leptin induces mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent proliferation of C3H10T1/2 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 12897-12900. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørbæk, C.; Uotani, S.; Da Silva, B.; Flier, J.S. Divergent signaling capacities of the long and short isoforms of the leptin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 32686-32695. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, H.; Morella, K.K.; White, D.W.; Dembski, M.; Bailon, P.S.; Kim, H.; Lai, C.F.; Tartaglia, L.A. The full-length leptin receptor has signaling capabilities of interleukin 6-type cytokine receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 8374-8378. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørbæk, C.; El-Haschimi, K.; Frantz, J.D.; Flier, J.S. The role of SOCS-3 in leptin signaling and leptin resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 30059-30065. [CrossRef]
- Zabolotny, J.M.; Bence-Hanulec, K.K.; Stricker-Krongrad, A.; Haj, F.; Wang, Y.; Minokoshi, Y.; Kim, Y.B.; Elmquist, J.K.; Tartaglia, L.A.; Kahn, B.B.; et al. PTP1B regulates leptin signal transduction in vivo. Dev. Cell 2002, 2, 489-495. [CrossRef]
- Martín-Romero, C.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Human leptin activates PI3K and MAPK pathways in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: Possible role of Sam68. Cell. Immunol. 2001, 212, 83-91. [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Li, M.; Duan, C.; Rui, L. Identification of SH2-B as a key regulator of leptin sensitivity, energy balance, and body weight in mice. Cell Metab. 2005, 2, 95-104. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lai, F.; Hou, Y.; Zheng, R. Leptin signaling and leptin resistance. Med. Rev. 2022, 2, 363-384. [CrossRef]
- Minokoshi, Y.; Alquier, T.; Furukawa, H.; Kim, Y.B.; Lee, A.; Xue, B.; Mu, J.; Foufelle, F.; Ferré, P.; Birnbaum, M.J.; et al. AMP-kinase regulates food intake by responding to hormonal and nutrient signals in the hypothalamus. Nature 2004, 428, 569-574. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minokoshi, Y.; Kim, Y.B.; Peroni, O.D.; Fryer, L.G.D.; Müller, C.; Carling, D.; Kahn, B.B. Leptin stimulates fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nature 2002, 415, 339-343. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardie, D.G. AMP-activated protein kinase: A key regulator of energy balance with many roles in human disease. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 276, 543-559. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaszuk, A.; Simpson, C.; Williams, G. Neuropeptide Y, the hypothalamus and the regulation of energy homeostasis. Horm. Res. 1996, 46, 53-58. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeley, R.J.; Yagaloff, K.A.; Fisher, S.L.; Burn, P.; Thiele, T.E.; Van Dijk, G.; Baskin, D.G.; Schwartz, M.W. Melanocortin receptors in leptin effects. Nature 1997, 390, 349. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matson, C.A.; Wiater, M.F.; Kuijper, J.L.; Weigle, D.S. Synergy between leptin and cholecystokinin (CCK) to control daily caloric intake. Peptides 1997, 18, 1275-1278. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellacott, K.L.J.; Halatchev, I.G.; Cone, R.D. Interactions between gut peptides and the central melanocortin system in the regulation of energy homeostasis. Peptides 2006, 27, 340-349. [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Coppack, S.W.; Mohamed-Ali, V.; Landt, M. Adipose tissue leptin production and plasma leptin kinetics in humans. Diabetes 1996, 45, 984-987. [CrossRef]
- Niskanen, L.; Haffner, S.; Karhunen, L.J.; Turpeinen, A.K.; Miettinen, H.; Uusitupa, M.I.J. Serum leptin in relation to resting energy expenditure and fuel metabolism in obese subjects. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1997, 21, 309-313. [CrossRef]
- Frederich, R.C.; Hamann, A.; Anderson, S.; Löllmann, B.; Lowell, B.B.; Flier, J.S. Leptin levels reflect body lipid content in mice: Evidence for diet-induced resistance to leptin action. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 1311-1314. [CrossRef]
- Myers, M.G.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Haft, C.; Kahn, B.B.; Laughlin, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Tschöp, M.H.; Yanovski, J.A. Challenges and opportunities of defining clinical leptin resistance. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 150-156. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wabitsch, M.; Funcke, J.-B.; Lennerz, B.; Kuhnle-Krahl, U.; Lahr, G.; Debatin, K.-M.; Vatter, P.; Gierschik, P.; Moepps, B.; Fischer-Posovszky, P. Biologically inactive leptin and early-onset extreme obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 48-54. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantzoros, C.S. The role of leptin in human obesity and disease: A review of current evidence. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999, 130, 671-680. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, A.L. Selective leptin resistance revisited. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 305, R566-R581. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J. 20 years of leptin: Leptin at 20: An overview. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 223, T1-T8. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Wong, J.; Brooks, V.L. Obesity: Sex and sympathetics. Biol. Sex Differ. 2020, 11, 10. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade-Oliveira, V.; Câmara, N.O.S.; Moraes-Vieira, P.M. Adipokines as drug targets in diabetes and underlying disturbances. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 681612. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, M.W.; Seeley, R.J.; Campfield, L.A.; Burn, P.; Baskin, D.G. Identification of targets of leptin action in rat hypothalamus. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 1101-1106. [CrossRef]
- German, J.P.; Thaler, J.P.; Wisse, B.E.; Oh-I, S.; Sarruf, D.A.; Matsen, M.E.; Fischer, J.D.; Taborsky, G.J.; Schwartz, M.W.; Morton, G.J. Leptin activates a novel CNS mechanism for insulin-independent normalization of severe diabetic hyperglycemia. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 394-404. [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.P. The Effect of Sitagliptin on Obese Patients with Insulin Treatment-Induced Diabetes Mellitus. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 3490-3495. [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Li, J.; Xiang, W.; Cui, Y.; Xie, B.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Gan, L. Metformin increases hepatic leptin receptor and decreases steatosis in mice. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 230, 227-237. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, R.; Amin, S.; Hayat Bhat, M.; Malik, R.; Wani, H.A.; Majid, S. Type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome-Adipokine levels and effect of drugs. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2017, 33, 75-78. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greer, J.J.M.; Ware, D.P.; Lefer, D.J. Myocardial infarction and heart failure in the
diabetic mouse. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 290, H146-H153. [CrossRef] [PubMed] - Belke, D.D.; Larsen, T.S.; Gibbs, E.M.; Severson, D.L. Altered metabolism causes cardiac dysfunction in perfused hearts from diabetic (db/db) mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 279, E1104-E1113. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, D.; Rodrigues, B. Role of changes in cardiac metabolism in development of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 291, H1489-H1506. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmazyn, M.; Purdham, D.M.; Rajapurohitam, V.; Zeidan, A. Leptin as a cardiac hypertrophic factor: A potential target for therapeutics. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2007, 17, 206-211. [CrossRef]
- Katsiki, N.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Banach, M. Leptin, cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1176-1188. [CrossRef]
- Lieb, W.; Sullivan, L.M.; Harris, T.B.; Roubenoff, R.; Benjamin, E.; Levy, D.; Fox, C.S.; Wang, T.J.; Wilson, P.W.; Kannel, W.B.; et al. Plasma leptin levels and incidence of heart failure, cardiovascular disease, and total mortality in elderly individuals. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 612-616. [CrossRef]
- Rajapurohitam, V.; Izaddoustdar, F.; Martinez-Abundis, E.; Karmazyn, M. Leptin-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy reveals both calcium-dependent and calcium-independent/RhoA-dependent calcineurin activation and NFAT nuclear translocation. Cell. Signal. 2012, 24, 2283-2290. [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.E.; Harmancey, R.; Stec, D.E. Lean heart: Role of leptin in cardiac hypertrophy and metabolism. World J. Cardiol. 2015, 7,511. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leifheit-Nestler, M.; Wagner, N.M.; Gogiraju, R.; Didié, M.; Konstantinides, S.; Hasenfuss, G.; Schäfer, K. Importance of leptin signaling and signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 activation in mediating the cardiac hypertrophy associated with obesity. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 170. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, G.; Hill, M.A.; Sowers, J.R. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: An Update of Mechanisms Contributing to This Clinical Entity. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 624-638. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L.; Matthes, J.; Schuster, I.; Valdivia, H.H.; Herzig, S.; Richard, S.; Gómez, A.M. Mechanisms of
transient decrease in cardiomyopathy of type 2 diabetic mice. Diabetes 2006, 55, 608-615. [CrossRef] [PubMed] - Kho, C.; Lee, A.; Hajjar, R.J. Altered sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium cycling-targets for heart failure therapy. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2012, 9, 717-733. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Gustafsson, Å.B. Role of apoptosis in cardiovascular disease. Apoptosis 2009, 14, 536-548. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, S.; Jin, C.; Wang, M.; Fu, G. Leptin confers protection against TNF-
-induced apoptosis in rat cardiomyocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 455, 126-132. [CrossRef] [PubMed] - Martinez-Abundis, E.; Rajapurohitam, V.; Haist, J.V.; Gan, X.T.; Karmazyn, M. The obesity-related peptide leptin sensitizes cardiac mitochondria to calcium-induced permeability transition pore opening and apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41612. [CrossRef]
- Dixon, R.A.; Davidson, S.M.; Wynne, A.M.; Yellon, D.M.; Smith, C.C.T. The cardioprotective actions of leptin are lost in the Zucker obese (fa/fa) rat. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2009, 53, 311-317. [CrossRef]
- McGaffin, K.R.; Witham, W.G.; Yester, K.A.; Romano, L.C.; Odoherty, R.M.; McTiernan, C.F.; Odonnell, C.P. Cardiac-specific leptin receptor deletion exacerbates ischaemic heart failure in mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 89, 60-71. [CrossRef]
- Procopio, C.; Andreozzi, F.; Laratta, E.; Cassese, A.; Beguinot, F.; Arturi, F.; Hribal, M.L.; Perticone, F.; Sesti, G. Leptinstimulated endothelial nitric-oxide synthase via an adenosine
-monophosphate-activated protein kinase/ Akt signaling pathway is attenuated by interaction with C-reactive protein. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 3584-3593. [CrossRef] - Bełtowski, J.; Wójcicka, G.; Jamroz-Wiśniewska, A.; Borkowska, E. Role of PI3K and PKB/Akt in acute natriuretic and NO-mimetic effects of leptin. Regul. Pept. 2007, 140, 168-177. [CrossRef]
- Jamroz-Wiśniewska, A.; Gertler, A.; Solomon, G.; Wood, M.E.; Whiteman, M.; Beltowski, J. Leptin-induced endotheliumdependent vasorelaxation of peripheral arteries in lean and obese rats: Role of nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86744. [CrossRef]
- Rahmouni, K.; Morgan, D.A.; Morgan, G.M.; Mark, A.L.; Haynes, W.G. Role of selective leptin resistance in diet-induced obesity hypertension. Diabetes 2005, 54, 2012-2018. [CrossRef]
- Bell, B.B.; Rahmouni, K. Leptin as a Mediator of Obesity-Induced Hypertension. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2016, 5, 397-404. [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, J.L.; Bruder-Nascimento, T.; Belin De Chantemèle, E.J. The regulation of aldosterone secretion by leptin: Implications in obesity-related cardiovascular disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2018, 27, 63-69. [CrossRef]
- Beldhuis, I.E.; Myhre, P.L.; Bristow, M.; Claggett, B.; Damman, K.; Fang, J.C.; Fleg, J.L.; McKinlay, S.; Lewis, E.F.; O’Meara, E.; et al. Spironolactone in Patients With Heart Failure, Preserved Ejection Fraction, and Worsening Renal Function. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 1211-1221. [CrossRef]
- Beltowski, J. Leptin and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2006, 189, 47-60. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanPatten, S.; Karkanias, G.B.; Rossetti, L.; Cohen, D.E. Intracerebroventricular leptin regulates hepatic cholesterol metabolism. Biochem. J. 2004, 379, 229-233. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, L.K.; Steinberg, G.R. AMPK and the Endocrine Control of Metabolism. Endocr. Rev. 2023, 44, 910-933. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tommerdahl, K.L.; Baumgartner, K.; Schäfer, M.; Bjornstad, P.; Melena, I.; Hegemann, S.; Baumgartner, A.D.; Pyle, L.; Cree-Green, M.; Truong, U.; et al. Impact of Obesity on Measures of Cardiovascular and Kidney Health in Youth with Type 1 Diabetes as Compared with Youth with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 795-803. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruder-Nascimento, T.; Kress, T.C.; Belin De Chantemele, E.J. Recent advances in understanding lipodystrophy: A focus on lipodystrophy-associated cardiovascular disease and potential effects of leptin therapy on cardiovascular function. F1000Research 2019, 8, F1000. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo, A.G.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Casanueva, F.F.; Carreira, M.C. Leptin, Obesity, and Leptin Resistance: Where Are We 25 Years Later? Nutrients 2019, 11, 2704. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, A.; Mattace Raso, G.; Meli, R. Drug targeting of leptin resistance. Life Sci. 2015, 140, 64-74. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, J.D.; Roland, B.L.; Cole, R.L.; Trevaskis, J.L.; Weyer, C.; Koda, J.E.; Anderson, C.M.; Parkes, D.G.; Baron, A.D. Leptin responsiveness restored by amylin agonism in diet-induced obesity: Evidence from nonclinical and clinical studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7257-7262. [CrossRef]
- Trevaskis, J.L.; Coffey, T.; Cole, R.; Lei, C.; Wittmer, C.; Walsh, B.; Weyer, C.; Koda, J.; Baron, A.D.; Parkes, D.G.; et al. Amylin-mediated restoration of leptin responsiveness in diet-induced obesity: Magnitude and mechanisms. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 5679-5687. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lee, J.; Hernandez, M.A.S.; Mazitschek, R.; Ozcan, U. Treatment of obesity with celastrol. Cell 2015, 161, 999-1011. [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Guan, D.; Auen, T.; Choi, J.W.; Salazar Hernández, M.A.; Lee, J.; Chun, H.; Faruk, F.; Kaplun, E.; Herbert, Z.; et al. IL1R1 is required for celastrol’s leptin-sensitization and antiobesity effects. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 575-582. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Duan, X.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, M. Celastrol: A Promising Agent Fighting against Cardiovascular Diseases. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1597. [CrossRef]
- Berglund, E.D.; Grobe, J.L.; Rahmouni, K.; Cui, H.; Saito, K.; Davis, K.C.; Morgan, D.A.; Toth, B.A.; Jiang, J.; Singh, U. Celastrol Reduces Obesity in MC4R Deficiency and Stimulates Sympathetic Nerve Activity Affecting Metabolic and Cardiovascular Functions. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1210-1220. [CrossRef]
- Chakhtoura, M.; Haber, R.; Ghezzawi, M.; Rhayem, C.; Tcheroyan, R.; Mantzoros, C.S. Pharmacotherapy of obesity: An update on the available medications and drugs under investigation. eClinicalMedicine 2023, 58, 101882. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042338
PMID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38397015
Publication Date: 2024-02-16
Role of Leptin in Obesity, Cardiovascular Disease, and Type 2 Diabetes
Revised: 7 February 2024
Accepted: 9 February 2024
Published: 16 February 2024
2 Department of Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, and Immunology, School of Medicine, Virgen Macarena University Hospital, University of Seville, 41009, Spain; maria.polonio@hotmail.com (M.L.P.-G.); antonioresi@gmail.com (A.P.-P.)
4 Endocrinology and Nutrition Service, Ramón y Cajal University Hospital, 28034 Madrid, Spain; arri68@hotmail.com
5 Endocrinology and Nutrition Service, Puerta del Mar University Hospital, Instituto de Investigación e Innovación en Ciencias Biomédicas de la Provincia de Cádiz (INiBICA), Cádiz University (UCA), 11001 Cádiz, Spain; manuelaguilardiosdado@gmail.com
6 Chopera Helath Center, Alcobendas Primary Care,Alcobendas 28100 Madrid, Spain; juancarlosobaya@yahoo.es
7 Endocrinology and Nutrition Department, Hospital Clinico Universitario Lozano Blesa, 1550009 Zaragoza, Spain; jagimeno@salud.aragon.es
8 Endocrinology and Nutrition Service, Puerta de Hierro University Hospital, Majadahonda, 28220 Madrid, Spain; piglo65@gmail.com
10 Endodiabesidad Clínica Durán & Asociados,41018 Seville, Spain; sduran@duransanz.com
11 Lipids and Cardiovascular Risk Unit, Hospital del Mar, Autonomous University of Barcelona, 08003 Barcelona, Spain; jpedrobotet@psmar.cat
12 Institute of Biomedicine of Seville (IBIS), Hospital Universitario Virgen del Rocío/Virgen Macarena, CSIC, Universidad de Sevilla, 41013 Seville, Spain
- Correspondence: margalet@us.es
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a highly prevalent disease worldwide, estimated to affect 1 in every 11 adults; among them,
1. Introduction
2. Obesity and CVD
3. Obesity and Diabetes
respond by inadequately secreting insulin in an attempt to overcome this resistance, a phenomenon observed in the early stages of the disease [28,29].
high-fat diet, NK cell depletion has been shown to have no impact on metabolic outcomes. Consistent with this hypothesis, the opposite approach, expanding NK cells with IL-15, worsens insulin resistance in those subjects with high-fat diets. It has also been observed that, as obesity increases, adipose tissue macrophages are activated, and they have two primary actions [42]. First, they produce chemokines that attract circulating NK cells, thereby increasing their number in epididymal fat; and second, they synthesize IL-15, activating and expanding NK cells in epididymal fat, further promoting the increase in adipose tissue macrophages (cross-activation). This cycle that is established induces inflammation in obesity and, consequently, insulin resistance through the actions of various mediators in the liver and muscle that release epididymal fat [42]. In this context, recent data also support the contribution of NK cells of visceral adipose tissue in the low-grade inflammation associated with insulin resistance [43].
4. Diabetes and CVD
5. Leptin

stimulating hormone (
6. Leptin and Obesity
with alterations in sexual dimorphism in neuropeptide Y (NPY) and proopiomelanocortin (POMC) participants in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. However, the precise mechanisms of leptin action in obese women and men are not entirely clear [106].
7. Leptin and T2DM
8. Leptin and CVD
(p38), and increases in intracellular reactive oxygen species. However, providing adequate levels of leptin restores cardiac thickness to normal [18,119].

vital for calcium transport between myocytes and the cytoplasm. Disruptions in calcium circulation within the sarcoplasmic reticulum can lead to heart diseases such as heart failure and arteriosclerosis, contributing to disease progression. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for comprehending the pathophysiology of cardiac disorders [122,123]. Studies conducted in mice with leptin deficiency revealed reduced activation of SERCA2 and
fects of leptin by reducing hepatic cholesterol (downregulating proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-
9. Leptin as a Therapeutic Target
weight in patients with elevated leptin levels. This mechanism is still under study, but it is assumed to be related to the expression of IL-1 receptor 1 in the hypothalamus [147-149].
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions: T.V.-G., M.L.P.-G., A.P.-P., J.R., F.A., M.A., J.C.O., J.A.G.-O., P.I., J.N., S.D., J.P.-B., V.S.-M. and Cardiovascular Disease Working Group of the Spanish Society of Diabetes (SED) contributed to conceptualization, literature search and reviewing the draft. T.V.-G., M.L.P.-G. and V.S.-M. wrote the draft. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Glovaci, D.; Fan, W.; Wong, N.D. Epidemiology of Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2019, 21, 21. [CrossRef]
- Kerner, W.; Brückel, J. Definition, classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2014, 122, 384-386. [CrossRef]
- Coraci, D.; Giovannini, S.; Loreti, C.; Pecchioli, C.; Piccinini, G.; Padua, L. The past encounters the future: “old” diagnostic methods to check innovative treatments for carpal tunnel syndrome. Comment on: “Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome: From ultrasonography to ultrasound surgery” by Petrover and Richette. Joint Bone Spine 2017 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2017.11.003. Jt. Bone Spine 2018, 85, 783-784. [CrossRef]
- Endalifer, M.L.; Diress, G. Epidemiology, Predisposing Factors, Biomarkers, and Prevention Mechanism of Obesity: A Systematic Review. J. Obes. 2020, 2020, 6134362. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chobot, A.; Górowska-Kowolik, K.; Sokołowska, M.; Jarosz-Chobot, P. Obesity and diabetes-Not only a simple link between two epidemics. Diabetes. Metab. Res. Rev. 2018, 34, e3042. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Hu, F.B. Epidemiology of Obesity and Diabetes and Their Cardiovascular Complications. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1723-1735. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Sala, L.; Pontiroli, A.E. Prevention of Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease in Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8178. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Proenca, R.; Maffei, M.; Barone, M.; Leopold, L.; Friedman, J.M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994, 372, 425-432. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.M. Leptin, leptin receptors, and the control of body weight. Nutr. Rev. 1998, 56, S38-S46. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Considine, R.V.; Caro, J.F. Leptin and the regulation of body weight. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997, 29, 1255-1272. [CrossRef]
- White, D.W.; Tartaglia, L.A. Leptin and OB-R: Body weight regulation by a cytokine receptor. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1996, 7, 303-309. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obradovic, M.; Sudar-Milovanovic, E.; Soskic, S.; Essack, M.; Arya, S.; Stewart, A.J.; Gojobori, T.; Isenovic, E.R. Leptin and Obesity: Role and Clinical Implication. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 585887. [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pérez, A.; Sánchez-Jiménez, F.; Vilariño-García, T.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Role of Leptin in Inflammation and Vice Versa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5887. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chang, L.; Wang, J.; Xia, L.; Cao, L.; Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Gao, H. Leptin and risk factors for atherosclerosis: A review. Medicine 2023, 102, E36076. [CrossRef]
- Raman, P.; Khanal, S. Leptin in Atherosclerosis: Focus on Macrophages, Endothelial and Smooth Muscle Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5446. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neeland, I.J.; Ross, R.; Després, J.P.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Yamashita, S.; Shai, I.; Seidell, J.; Magni, P.; Santos, R.D.; Arsenault, B.; et al. Visceral and ectopic fat, atherosclerosis, and cardiometabolic disease: A position statement. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 715-725. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Corral, A.; Montori, V.M.; Somers, V.K.; Korinek, J.; Thomas, R.J.; Allison, T.G.; Mookadam, F.; Lopez-Jimenez, F. Association of bodyweight with total mortality and with cardiovascular events in coronary artery disease: A systematic review of cohort studies. Lancet 2006, 368, 666-678. [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.W.; Ok, M.; Lee, S.K. Leptin as a Key between Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 29, 248-259. [CrossRef]
- Bombelli, M.; Facchetti, R.; Sega, R.; Carugo, S.; Fodri, D.; Brambilla, G.; Giannattasio, C.; Grassi, G.; Mancia, G. Impact of body mass index and waist circumference on the long-term risk of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and cardiac organ damage. Hypertension 2011, 58, 1029-1035. [CrossRef]
- Wensveen, F.M.; Valentić, S.; Šestan, M.; Turk Wensveen, T.; Polić, B. The “Big Bang” in obese fat: Events initiating obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 2446-2456. [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.S.; Qasim, A.; Reilly, M.P. Leptin resistance: A possible interface of inflammation and metabolism in obesity-related cardiovascular disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 1201-1210. [CrossRef]
- Recinella, L.; Orlando, G.; Ferrante, C.; Chiavaroli, A.; Brunetti, L.; Leone, S. Adipokines: New Potential Therapeutic Target for Obesity and Metabolic, Rheumatic, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 578966. [CrossRef]
- Carbone, S.; Canada, J.M.; Billingsley, H.E.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Elagizi, A.; Lavie, C.J. Obesity paradox in cardiovascular disease: Where do we stand? Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2019, 15, 89-100. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blüher, M. Metabolically Healthy Obesity. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, 405-420. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Huang, R.; Jiang, M.; Wang, W.; Chai, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Han, Y.; Yan, F.; Lu, Q.; et al. Myocardial Tissue-Level Characteristics of Adults with Metabolically Healthy Obesity. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2023, 16, 889-901. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksson, P.; Henriksson, H.; Tynelius, P.; Berglind, D.; Löf, M.; Lee, I.M.; Shiroma, E.J.; Ortega, F.B. Fitness and Body Mass Index During Adolescence and Disability Later in Life: A Cohort Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 170, 230-239. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksson, H.; Henriksson, P.; Tynelius, P.; Ekstedt, M.; Berglind, D.; Labayen, I.; Ruiz, J.R.; Lavie, C.J.; Ortega, F.B. Cardiorespiratory fitness, muscular strength, and obesity in adolescence and later chronic disability due to cardiovascular disease: A cohort study of 1 million men. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 1503-1510. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutari, C.; DeMarsilis, A.; Mantzoros, C.S. Obesity and diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 202, 110773. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.; Gastaldelli, A.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Scherer, P.E. Why does obesity cause diabetes? Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 11-20. [CrossRef]
- Hocking, S.; Samocha-Bonet, D.; Milner, K.L.; Greenfield, J.R.; Chisholm, D.J. Adiposity and insulin resistance in humans: The role of the different tissue and cellular lipid depots. Endocr. Rev. 2013, 34, 463-500. [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.; Fisch, G.; Teague, B.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Banyas, B.; Allen, K.; Savoye, M.; Rieger, V.; Taksali, S.; Barbetta, G.; et al. Prevalence of impaired glucose tolerance among children and adolescents with marked obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 802-810. [CrossRef]
- D’Adamo, E.; Cali, A.M.G.; Weiss, R.; Santoro, N.; Pierpont, B.; Northrup, V.; Caprio, S. Central role of fatty liver in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance in obese adolescents. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1817-1822. [CrossRef]
- Kahkoska, A.R.; Pokaprakarn, T.; Rumay Alexander, G.; Crume, T.L.; Dabelea, D.; Divers, J.; Dolan, L.M.; Jensen, E.T.; Lawrence, J.M.; Marcovina, S.; et al. The Impact of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities in Diabetes Management on Clinical Outcomes: A Reinforcement Learning Analysis of Health Inequity Among Youth and Young Adults in the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 108-118. [CrossRef]
- Al Amiri, E.; Abdullatif, M.; Abdulle, A.; Al Bitar, N.; Afandi, E.Z.; Parish, M.; Darwiche, G. The prevalence, risk factors, and screening measure for prediabetes and diabetes among Emirati overweight/obese children and adolescents. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 1298. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeb, A.; Salima, A.; Samia, M.; Ghada, E.; Abubaker, E. Insulin Resistance, Impaired fasting, Glucose Intolerance and Type II Diabetes Mellitus in Overweight and Obese Children in Abu Dhabi. J. Diabetes Obes. 2017, 4, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Dilworth, L.; Facey, A.; Omoruyi, F. Diabetes Mellitus and Its Metabolic Complications: The Role of Adipose Tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7644. [CrossRef]
- Saltiel, A.R.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammatory mechanisms linking obesity and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1-4. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mclaughlin, T.; Ackerman, S.E.; Shen, L.; Engleman, E. Role of innate and adaptive immunity in obesity-associated metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 5-13. [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pérez, A.; Vilariño-García, T.; Fernández-Riejos, P.; Martín-González, J.; Segura-Egea, J.J.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Role of leptin as a link between metabolism and the immune system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017, 35, 71-84. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Margalet, V.; Martín-Romero, C.; Santos-Alvarez, J.; Goberna, R.; Najib, S.; Gonzalez-Yanes, C. Role of leptin as an immunomodulator of blood mononuclear cells: Mechanisms of action. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 133, 11-19. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Margalet, V.; Fernández-Riejos, P.; Najib, S.; Santos-Alvarez, J.; Martín-Romero, C.; Pérez-Pérez, A.; González-Yanes, C. Role of leptin in the activation of immune cells. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 568343. [CrossRef]
- Bonamichi, B.D.S.F.; Lee, J. Unusual Suspects in the Development of Obesity-Induced Inflammation and Insulin Resistance: NK cells, iNKT cells, and ILCs. Diabetes Metab. J. 2017, 41, 229-250. [CrossRef]
- Wouters, K.; Kusters, Y.H.A.M.; Bijnen, M.; Wetzels, S.; Zhang, X.; Linssen, P.B.C.; Gaens, K.; Houben, A.J.H.M.; Joris, P.J.; Plat, J.; et al. NK cells in human visceral adipose tissue contribute to obesity-associated insulin resistance through low-grade inflammation. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, e192. [CrossRef]
- Caussy, C.; Aubin, A.; Loomba, R. The Relationship Between Type 2 Diabetes, NAFLD, and Cardiovascular Risk. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2021, 21, 15. [CrossRef]
- Naito, R.; Kasai, T. Coronary artery disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Recent treatment strategies and future perspectives. World J. Cardiol. 2015, 7, 119. [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.D.; Langenberg, C.; Rapsomaniki, E.; Denaxas, S.; Pujades-Rodriguez, M.; Gale, C.P.; Deanfield, J.; Smeeth, L.; Timmis, A.; Hemingway, H. Type 2 diabetes and incidence of cardiovascular diseases: A cohort study in 1.9 million people. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 105-113. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punthakee, Z.; Goldenberg, R.; Katz, P. Definition, Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes, Prediabetes and Metabolic Syndrome. Can. J. Diabetes 2018, 42 (Suppl. S1), S10-S15. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prandi, F.R.; Evangelista, I.; Sergi, D.; Palazzuoli, A.; Romeo, F. Mechanisms of cardiac dysfunction in diabetic cardiomyopathy: Molecular abnormalities and phenotypical variants. Heart Fail. Rev. 2023, 28, 597-606. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.L.; Pietz, K.; Battleman, D.S.; Beyth, R.J. Prevalence of Comorbid Hypertension and Dyslipidemia and Associated Cardiovascular Disease. Heart Dis. 2004, 2, 3.
- Piché, M.E.; Tchernof, A.; Després, J.P. Obesity Phenotypes, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1477-1500. [CrossRef]
- Barrett-Connor, E. Hypercholesterolemia predicts early death from coronary heart disease in elderly men but not women. The Rancho Bernardo Study. Ann. Epidemiol. 1992, 2, 77-83. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, C.; Hong, J.; Zeng, J.; Lai, S.; Lv, A.; Su, Q.; Dong, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, W.; et al. Lipid profiling reveals different therapeutic effects of metformin and glipizide in patients with type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2804-2812. [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.J.; Pagidipati, N.J.; Aroda, V.R.; Cavender, M.A.; Green, J.B.; Lopes, R.D.; Al-Khalidi, H.; Gaynor, T.; Kaltenbach, L.A.; Kirk, J.K.; et al. Incorporating SGLT2i and GLP-1RA for Cardiovascular and Kidney Disease Risk Reduction: Call for Action to the Cardiology Community. Circulation 2021, 144, 74-84. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strain, W.D.; Paldánius, P.M. Diabetes, cardiovascular disease and the microcirculation. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 57. [CrossRef]
- Halaas, J.L.; Gajiwala, K.S.; Maffei, M.; Cohen, S.L.; Chait, B.T.; Rabinowitz, D.; Lallone, R.L.; Burley, S.K.; Friedman, J.M. Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science 1995, 269, 543-546. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Considine, R.V.; Sinha, M.K.; Heiman, M.L.; Kriauciunas, A.; Stephens, T.W.; Nyce, M.R.; Ohannesian, J.P.; Marco, C.C.; McKee, L.J.; Bauer, T.L.; et al. Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 292-295. [CrossRef]
- Fain, J.N.; Madan, A.K.; Hiler, M.L.; Cheema, P.; Bahouth, S.W. Comparison of the release of adipokines by adipose tissue, adipose tissue matrix, and adipocytes from visceral and subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissues of obese humans. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 2273-2282. [CrossRef]
- Wajchenberg, B.L. Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: Their relation to the metabolic syndrome. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 697-738. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Pérez, A.; Maymó, J.; Gambino, Y.; Guadix, P.; Dueñas, J.L.; Varone, C.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Insulin enhances leptin expression in human trophoblastic cells. Biol. Reprod. 2013, 89, 20. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miell, J.P.; Englaro, P.; Blum, W.F. Dexamethasone induces an acute and sustained rise in circulating leptin levels in normal human subjects. Horm. Metab. Res. 1996, 28, 704-707. [CrossRef]
- De Vos, P.; Saladin, R.; Auwerx, J.; Staels, B. Induction of ob gene expression by corticosteroids is accompanied by body weight loss and reduced food intake. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 15958-15961. [CrossRef]
- Ahima, R.S.; Flier, J.S. Leptin. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2000, 62, 413-437. [CrossRef]
- Margetic, S.; Gazzola, C.; Pegg, G.G.; Hill, R.A. Leptin: A review of its peripheral actions and interactions. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2002, 26, 1407-1433. [CrossRef]
- Mantzoros, C.S.; Magkos, F.; Brinkoetter, M.; Sienkiewicz, E.; Dardeno, T.A.; Kim, S.Y.; Hamnvik, O.P.R.; Koniaris, A. Leptin in human physiology and pathophysiology. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 301, E567-E584. [CrossRef]
- Hickey, M.S.; Israel, R.G.; Gardiner, S.N.; Considine, R.V.; McCammon, M.R.; Tyndall, G.L.; Houmard, J.A.; Marks, R.H.L.; Caro, J.F. Gender Differences in Serum Leptin Levels in Humans. Biochem. Mol. Med. 1996, 59, 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Arch, J.R.S.; Stock, M.J.; Trayhurn, P. Leptin resistance in obese humans: Does it exist and what does it mean? Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1998, 22, 1159-1163. [CrossRef]
- Knight, Z.A.; Hannan, K.S.; Greenberg, M.L.; Friedman, J.M. Hyperleptinemia is required for the development of leptin resistance. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11376. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poetsch, M.S.; Strano, A.; Guan, K. Role of Leptin in Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 354. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J. Leptin and hyperleptinemia-From friend to foe for cardiovascular function. J. Endocrinol. 2004, 181, 1-10. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Kusminski, C.M.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin, Leptin and Cardiovascular Disorders. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 136-149. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, M.J.; Clifton, D.K.; Steiner, R.A. Leptin’s actions on the reproductive axis: Perspectives and mechanisms. Biol. Reprod. 1999, 60, 216-222. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, G.A. Obesity and reproduction. Hum. Reprod. 1997, 12 (Suppl. S1), 26-32. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, D.L.; Nagatani, S. Physiological perspectives on leptin as a regulator of reproduction: Role in timing puberty. Biol. Reprod. 1999, 60, 205-215. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Pérez, A.; Sánchez-Jiménez, F.; Maymó, J.; Dueñas, J.L.; Varone, C.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Role of leptin in female reproduction. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2015, 53, 15-28. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Pérez, A.; Toro, A.; Vilariño-García, T.; Maymó, J.; Guadix, P.; Dueñas, J.L.; Fernández-Sánchez, M.; Varone, C.; SánchezMargalet, V. Leptin action in normal and pathological pregnancies. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 716-727. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, R.B.S. Leptin-Much more than a satiety signal. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2000, 20, 45-75. [CrossRef]
- Meister, B. Control of food intake via leptin receptors in the hypothalamus. Vitam. Horm. 2000, 59, 265-304. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Margalet, V.; Martin-Romero, C. Human leptin signaling in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: Activation of the JAK-STAT pathway. Cell. Immunol. 2001, 211, 30-36. [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, E.C.; Myers, M.G. Leptin receptor signaling and the regulation of mammalian physiology. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32 (Suppl. S7), S8-S12. [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.H.; Myers, M.G. The role of leptin receptor signaling in feeding and neuroendocrine function. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 14, 447-452. [CrossRef]
- Bjørbaek, C.; Kahn, B.B. Leptin signaling in the central nervous system and the periphery. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 2004, 59, 305-331. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jéquier, E. Leptin signaling, adiposity, and energy balance. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 967, 379-388. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Murakami, T.; Otani, S.; Kuwajima, M.; Shima, K. Leptin receptor signal transduction: OBRa and OBRb of fa type. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 246, 752-759. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Okimura, Y.; Mizuno, I.; Iida, K.; Takahashi, T.; Kaji, H.; Abe, H.; Chihara, K. Leptin induces mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent proliferation of C3H10T1/2 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 12897-12900. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørbæk, C.; Uotani, S.; Da Silva, B.; Flier, J.S. Divergent signaling capacities of the long and short isoforms of the leptin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 32686-32695. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, H.; Morella, K.K.; White, D.W.; Dembski, M.; Bailon, P.S.; Kim, H.; Lai, C.F.; Tartaglia, L.A. The full-length leptin receptor has signaling capabilities of interleukin 6-type cytokine receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 8374-8378. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørbæk, C.; El-Haschimi, K.; Frantz, J.D.; Flier, J.S. The role of SOCS-3 in leptin signaling and leptin resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 30059-30065. [CrossRef]
- Zabolotny, J.M.; Bence-Hanulec, K.K.; Stricker-Krongrad, A.; Haj, F.; Wang, Y.; Minokoshi, Y.; Kim, Y.B.; Elmquist, J.K.; Tartaglia, L.A.; Kahn, B.B.; et al. PTP1B regulates leptin signal transduction in vivo. Dev. Cell 2002, 2, 489-495. [CrossRef]
- Martín-Romero, C.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Human leptin activates PI3K and MAPK pathways in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: Possible role of Sam68. Cell. Immunol. 2001, 212, 83-91. [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Li, M.; Duan, C.; Rui, L. Identification of SH2-B as a key regulator of leptin sensitivity, energy balance, and body weight in mice. Cell Metab. 2005, 2, 95-104. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lai, F.; Hou, Y.; Zheng, R. Leptin signaling and leptin resistance. Med. Rev. 2022, 2, 363-384. [CrossRef]
- Minokoshi, Y.; Alquier, T.; Furukawa, H.; Kim, Y.B.; Lee, A.; Xue, B.; Mu, J.; Foufelle, F.; Ferré, P.; Birnbaum, M.J.; et al. AMP-kinase regulates food intake by responding to hormonal and nutrient signals in the hypothalamus. Nature 2004, 428, 569-574. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minokoshi, Y.; Kim, Y.B.; Peroni, O.D.; Fryer, L.G.D.; Müller, C.; Carling, D.; Kahn, B.B. Leptin stimulates fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nature 2002, 415, 339-343. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardie, D.G. AMP-activated protein kinase: A key regulator of energy balance with many roles in human disease. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 276, 543-559. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaszuk, A.; Simpson, C.; Williams, G. Neuropeptide Y, the hypothalamus and the regulation of energy homeostasis. Horm. Res. 1996, 46, 53-58. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeley, R.J.; Yagaloff, K.A.; Fisher, S.L.; Burn, P.; Thiele, T.E.; Van Dijk, G.; Baskin, D.G.; Schwartz, M.W. Melanocortin receptors in leptin effects. Nature 1997, 390, 349. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matson, C.A.; Wiater, M.F.; Kuijper, J.L.; Weigle, D.S. Synergy between leptin and cholecystokinin (CCK) to control daily caloric intake. Peptides 1997, 18, 1275-1278. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellacott, K.L.J.; Halatchev, I.G.; Cone, R.D. Interactions between gut peptides and the central melanocortin system in the regulation of energy homeostasis. Peptides 2006, 27, 340-349. [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Coppack, S.W.; Mohamed-Ali, V.; Landt, M. Adipose tissue leptin production and plasma leptin kinetics in humans. Diabetes 1996, 45, 984-987. [CrossRef]
- Niskanen, L.; Haffner, S.; Karhunen, L.J.; Turpeinen, A.K.; Miettinen, H.; Uusitupa, M.I.J. Serum leptin in relation to resting energy expenditure and fuel metabolism in obese subjects. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1997, 21, 309-313. [CrossRef]
- Frederich, R.C.; Hamann, A.; Anderson, S.; Löllmann, B.; Lowell, B.B.; Flier, J.S. Leptin levels reflect body lipid content in mice: Evidence for diet-induced resistance to leptin action. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 1311-1314. [CrossRef]
- Myers, M.G.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Haft, C.; Kahn, B.B.; Laughlin, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Tschöp, M.H.; Yanovski, J.A. Challenges and opportunities of defining clinical leptin resistance. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 150-156. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wabitsch, M.; Funcke, J.-B.; Lennerz, B.; Kuhnle-Krahl, U.; Lahr, G.; Debatin, K.-M.; Vatter, P.; Gierschik, P.; Moepps, B.; Fischer-Posovszky, P. Biologically inactive leptin and early-onset extreme obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 48-54. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantzoros, C.S. The role of leptin in human obesity and disease: A review of current evidence. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999, 130, 671-680. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, A.L. Selective leptin resistance revisited. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 305, R566-R581. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J. 20 years of leptin: Leptin at 20: An overview. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 223, T1-T8. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Wong, J.; Brooks, V.L. Obesity: Sex and sympathetics. Biol. Sex Differ. 2020, 11, 10. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade-Oliveira, V.; Câmara, N.O.S.; Moraes-Vieira, P.M. Adipokines as drug targets in diabetes and underlying disturbances. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 681612. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, M.W.; Seeley, R.J.; Campfield, L.A.; Burn, P.; Baskin, D.G. Identification of targets of leptin action in rat hypothalamus. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 1101-1106. [CrossRef]
- German, J.P.; Thaler, J.P.; Wisse, B.E.; Oh-I, S.; Sarruf, D.A.; Matsen, M.E.; Fischer, J.D.; Taborsky, G.J.; Schwartz, M.W.; Morton, G.J. Leptin activates a novel CNS mechanism for insulin-independent normalization of severe diabetic hyperglycemia. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 394-404. [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.P. The Effect of Sitagliptin on Obese Patients with Insulin Treatment-Induced Diabetes Mellitus. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 3490-3495. [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Li, J.; Xiang, W.; Cui, Y.; Xie, B.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Gan, L. Metformin increases hepatic leptin receptor and decreases steatosis in mice. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 230, 227-237. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, R.; Amin, S.; Hayat Bhat, M.; Malik, R.; Wani, H.A.; Majid, S. Type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome-Adipokine levels and effect of drugs. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2017, 33, 75-78. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greer, J.J.M.; Ware, D.P.; Lefer, D.J. Myocardial infarction and heart failure in the
diabetic mouse. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 290, H146-H153. [CrossRef] [PubMed] - Belke, D.D.; Larsen, T.S.; Gibbs, E.M.; Severson, D.L. Altered metabolism causes cardiac dysfunction in perfused hearts from diabetic (db/db) mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 279, E1104-E1113. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, D.; Rodrigues, B. Role of changes in cardiac metabolism in development of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 291, H1489-H1506. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmazyn, M.; Purdham, D.M.; Rajapurohitam, V.; Zeidan, A. Leptin as a cardiac hypertrophic factor: A potential target for therapeutics. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2007, 17, 206-211. [CrossRef]
- Katsiki, N.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Banach, M. Leptin, cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1176-1188. [CrossRef]
- Lieb, W.; Sullivan, L.M.; Harris, T.B.; Roubenoff, R.; Benjamin, E.; Levy, D.; Fox, C.S.; Wang, T.J.; Wilson, P.W.; Kannel, W.B.; et al. Plasma leptin levels and incidence of heart failure, cardiovascular disease, and total mortality in elderly individuals. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 612-616. [CrossRef]
- Rajapurohitam, V.; Izaddoustdar, F.; Martinez-Abundis, E.; Karmazyn, M. Leptin-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy reveals both calcium-dependent and calcium-independent/RhoA-dependent calcineurin activation and NFAT nuclear translocation. Cell. Signal. 2012, 24, 2283-2290. [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.E.; Harmancey, R.; Stec, D.E. Lean heart: Role of leptin in cardiac hypertrophy and metabolism. World J. Cardiol. 2015, 7,511. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leifheit-Nestler, M.; Wagner, N.M.; Gogiraju, R.; Didié, M.; Konstantinides, S.; Hasenfuss, G.; Schäfer, K. Importance of leptin signaling and signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 activation in mediating the cardiac hypertrophy associated with obesity. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 170. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, G.; Hill, M.A.; Sowers, J.R. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: An Update of Mechanisms Contributing to This Clinical Entity. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 624-638. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L.; Matthes, J.; Schuster, I.; Valdivia, H.H.; Herzig, S.; Richard, S.; Gómez, A.M. Mechanisms of
transient decrease in cardiomyopathy of type 2 diabetic mice. Diabetes 2006, 55, 608-615. [CrossRef] [PubMed] - Kho, C.; Lee, A.; Hajjar, R.J. Altered sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium cycling-targets for heart failure therapy. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2012, 9, 717-733. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Gustafsson, Å.B. Role of apoptosis in cardiovascular disease. Apoptosis 2009, 14, 536-548. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, S.; Jin, C.; Wang, M.; Fu, G. Leptin confers protection against TNF-
-induced apoptosis in rat cardiomyocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 455, 126-132. [CrossRef] [PubMed] - Martinez-Abundis, E.; Rajapurohitam, V.; Haist, J.V.; Gan, X.T.; Karmazyn, M. The obesity-related peptide leptin sensitizes cardiac mitochondria to calcium-induced permeability transition pore opening and apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41612. [CrossRef]
- Dixon, R.A.; Davidson, S.M.; Wynne, A.M.; Yellon, D.M.; Smith, C.C.T. The cardioprotective actions of leptin are lost in the Zucker obese (fa/fa) rat. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2009, 53, 311-317. [CrossRef]
- McGaffin, K.R.; Witham, W.G.; Yester, K.A.; Romano, L.C.; Odoherty, R.M.; McTiernan, C.F.; Odonnell, C.P. Cardiac-specific leptin receptor deletion exacerbates ischaemic heart failure in mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 89, 60-71. [CrossRef]
- Procopio, C.; Andreozzi, F.; Laratta, E.; Cassese, A.; Beguinot, F.; Arturi, F.; Hribal, M.L.; Perticone, F.; Sesti, G. Leptinstimulated endothelial nitric-oxide synthase via an adenosine
-monophosphate-activated protein kinase/ Akt signaling pathway is attenuated by interaction with C-reactive protein. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 3584-3593. [CrossRef] - Bełtowski, J.; Wójcicka, G.; Jamroz-Wiśniewska, A.; Borkowska, E. Role of PI3K and PKB/Akt in acute natriuretic and NO-mimetic effects of leptin. Regul. Pept. 2007, 140, 168-177. [CrossRef]
- Jamroz-Wiśniewska, A.; Gertler, A.; Solomon, G.; Wood, M.E.; Whiteman, M.; Beltowski, J. Leptin-induced endotheliumdependent vasorelaxation of peripheral arteries in lean and obese rats: Role of nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86744. [CrossRef]
- Rahmouni, K.; Morgan, D.A.; Morgan, G.M.; Mark, A.L.; Haynes, W.G. Role of selective leptin resistance in diet-induced obesity hypertension. Diabetes 2005, 54, 2012-2018. [CrossRef]
- Bell, B.B.; Rahmouni, K. Leptin as a Mediator of Obesity-Induced Hypertension. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2016, 5, 397-404. [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, J.L.; Bruder-Nascimento, T.; Belin De Chantemèle, E.J. The regulation of aldosterone secretion by leptin: Implications in obesity-related cardiovascular disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2018, 27, 63-69. [CrossRef]
- Beldhuis, I.E.; Myhre, P.L.; Bristow, M.; Claggett, B.; Damman, K.; Fang, J.C.; Fleg, J.L.; McKinlay, S.; Lewis, E.F.; O’Meara, E.; et al. Spironolactone in Patients With Heart Failure, Preserved Ejection Fraction, and Worsening Renal Function. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 1211-1221. [CrossRef]
- Beltowski, J. Leptin and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2006, 189, 47-60. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanPatten, S.; Karkanias, G.B.; Rossetti, L.; Cohen, D.E. Intracerebroventricular leptin regulates hepatic cholesterol metabolism. Biochem. J. 2004, 379, 229-233. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, L.K.; Steinberg, G.R. AMPK and the Endocrine Control of Metabolism. Endocr. Rev. 2023, 44, 910-933. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tommerdahl, K.L.; Baumgartner, K.; Schäfer, M.; Bjornstad, P.; Melena, I.; Hegemann, S.; Baumgartner, A.D.; Pyle, L.; Cree-Green, M.; Truong, U.; et al. Impact of Obesity on Measures of Cardiovascular and Kidney Health in Youth with Type 1 Diabetes as Compared with Youth with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 795-803. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruder-Nascimento, T.; Kress, T.C.; Belin De Chantemele, E.J. Recent advances in understanding lipodystrophy: A focus on lipodystrophy-associated cardiovascular disease and potential effects of leptin therapy on cardiovascular function. F1000Research 2019, 8, F1000. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo, A.G.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Casanueva, F.F.; Carreira, M.C. Leptin, Obesity, and Leptin Resistance: Where Are We 25 Years Later? Nutrients 2019, 11, 2704. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, A.; Mattace Raso, G.; Meli, R. Drug targeting of leptin resistance. Life Sci. 2015, 140, 64-74. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, J.D.; Roland, B.L.; Cole, R.L.; Trevaskis, J.L.; Weyer, C.; Koda, J.E.; Anderson, C.M.; Parkes, D.G.; Baron, A.D. Leptin responsiveness restored by amylin agonism in diet-induced obesity: Evidence from nonclinical and clinical studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7257-7262. [CrossRef]
- Trevaskis, J.L.; Coffey, T.; Cole, R.; Lei, C.; Wittmer, C.; Walsh, B.; Weyer, C.; Koda, J.; Baron, A.D.; Parkes, D.G.; et al. Amylin-mediated restoration of leptin responsiveness in diet-induced obesity: Magnitude and mechanisms. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 5679-5687. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lee, J.; Hernandez, M.A.S.; Mazitschek, R.; Ozcan, U. Treatment of obesity with celastrol. Cell 2015, 161, 999-1011. [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Guan, D.; Auen, T.; Choi, J.W.; Salazar Hernández, M.A.; Lee, J.; Chun, H.; Faruk, F.; Kaplun, E.; Herbert, Z.; et al. IL1R1 is required for celastrol’s leptin-sensitization and antiobesity effects. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 575-582. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Duan, X.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, M. Celastrol: A Promising Agent Fighting against Cardiovascular Diseases. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1597. [CrossRef]
- Berglund, E.D.; Grobe, J.L.; Rahmouni, K.; Cui, H.; Saito, K.; Davis, K.C.; Morgan, D.A.; Toth, B.A.; Jiang, J.; Singh, U. Celastrol Reduces Obesity in MC4R Deficiency and Stimulates Sympathetic Nerve Activity Affecting Metabolic and Cardiovascular Functions. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1210-1220. [CrossRef]
- Chakhtoura, M.; Haber, R.; Ghezzawi, M.; Rhayem, C.; Tcheroyan, R.; Mantzoros, C.S. Pharmacotherapy of obesity: An update on the available medications and drugs under investigation. eClinicalMedicine 2023, 58, 101882. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
