DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-024-01276-1
تاريخ النشر: 2024-06-28
عندما تلتقي نماذج اللغة الكبيرة بالتخصيص: آفاق التحديات والفرص
تم النشر على الإنترنت: 28 يونيو 2024
© المؤلفون 2024
الملخص
يمثل ظهور نماذج اللغة الكبيرة اختراقًا ثوريًا في الذكاء الاصطناعي. مع الحجم غير المسبوق للتدريب ومعلمات النموذج، تحسنت قدرة نماذج اللغة الكبيرة بشكل كبير، مما أدى إلى أداء يشبه البشر في الفهم، وتوليد اللغة، والتفكير السليم، وما إلى ذلك. ستغير هذه القفزة الكبيرة في قدرة الذكاء الاصطناعي العام بشكل جذري نمط كيفية إجراء التخصيص. من ناحية، ستعيد تشكيل طريقة التفاعل بين البشر وأنظمة التخصيص. بدلاً من أن تكون وسيلة سلبية لتصفية المعلومات، مثل أنظمة التوصية التقليدية ومحركات البحث، تقدم نماذج اللغة الكبيرة الأساس لمشاركة نشطة من المستخدمين. على هذا الأساس الجديد، يمكن استكشاف طلبات المستخدمين بشكل استباقي، ويمكن تقديم المعلومات المطلوبة من قبل المستخدمين بطريقة طبيعية وقابلة للتفاعل وقابلة للتفسير. من ناحية أخرى، ستوسع أيضًا نطاق التخصيص بشكل كبير، مما يجعلها تنمو من الوظيفة الوحيدة لجمع المعلومات الشخصية إلى الوظيفة المركبة لتقديم الخدمات الشخصية. من خلال الاستفادة من نماذج اللغة الكبيرة كواجهة متعددة الأغراض، يمكن أن تقوم أنظمة التخصيص بتجميع طلبات المستخدمين في خطط، واستدعاء وظائف الأدوات الخارجية (مثل محركات البحث، الآلات الحاسبة، واجهات برمجة التطبيقات للخدمات، إلخ) لتنفيذ الخطط، ودمج مخرجات الأدوات لإكمال مهام التخصيص من البداية إلى النهاية. اليوم، لا تزال نماذج اللغة الكبيرة تتطور بسرعة، بينما لا يزال التطبيق في التخصيص غير مستكشف إلى حد كبير. لذلك، نعتبر أن الوقت مناسب لمراجعة التحديات في التخصيص والفرص لمعالجتها باستخدام نماذج اللغة الكبيرة. على وجه الخصوص، نكرس هذه الورقة للنقاش حول الجوانب التالية: التطور والتحديات للنظام الحالي للتخصيص، القدرات الجديدة التي ظهرت لنماذج اللغة الكبيرة، والطرق المحتملة للاستفادة من نماذج اللغة الكبيرة للتخصيص.
1 المقدمة
أدوات متنوعة معزز بشكل كبير بقدرات نماذج اللغة الكبيرة، مما يوسع بشكل كبير من الإمكانيات والسيناريوهات لأنظمة التخصيص. من خلال تحويل متطلبات المستخدمين إلى خطط، بما في ذلك فهمها وتوليدها وتنفيذها، يمكن للمستخدمين الوصول إلى مجموعة متنوعة من المعلومات والخدمات. من المهم أن يظل المستخدمون غير مدركين للتحولات المعقدة التي تحدث خلف الكواليس، حيث يختبرون نموذجًا سلسًا من البداية إلى النهاية. لا تزال إمكانيات نماذج اللغة الكبيرة في التخصيص غير مستكشفة إلى حد كبير.
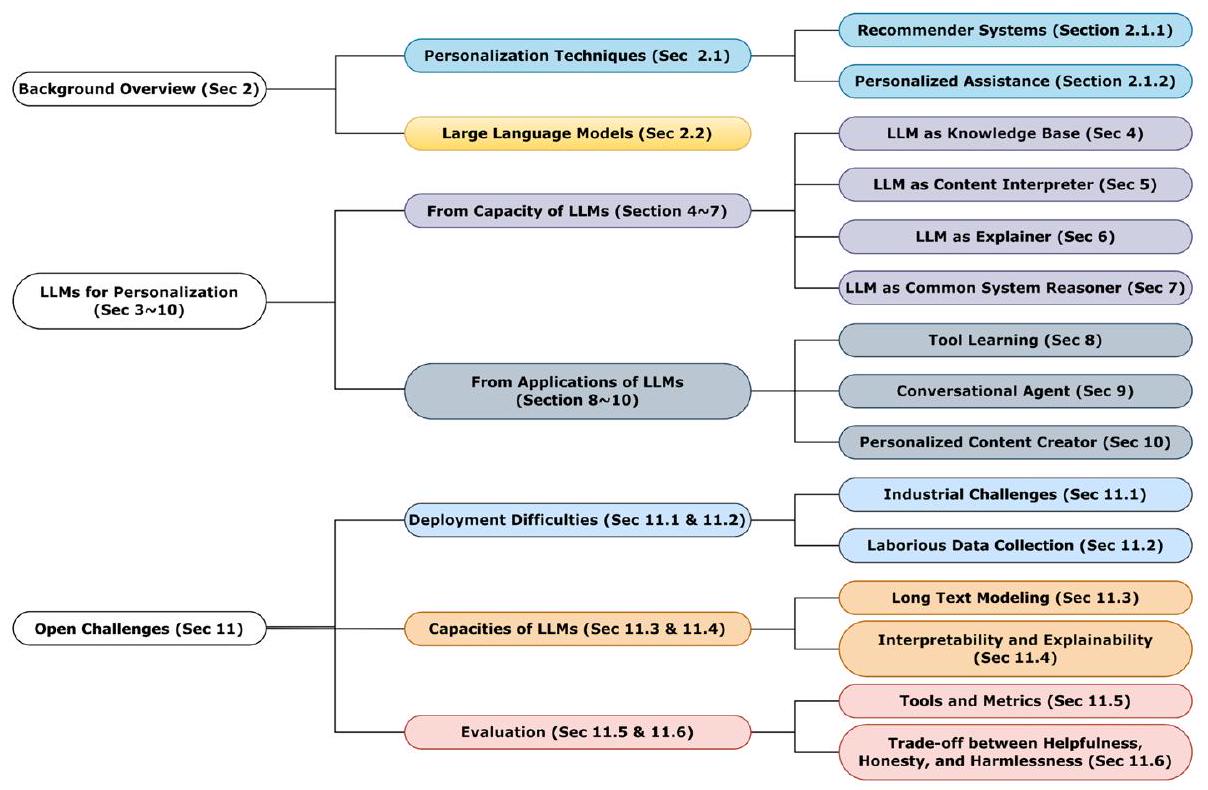
2 نظرة عامة على الخلفية
2.1 تقنيات التخصيص
2.1.1 أنظمة التوصية
نمذجة البيانات التسلسلية في أنظمة التوصية. تتفوق هذه النماذج في التقاط الاعتمادات الزمنية والسياق، مما يجعلها مناسبة تمامًا لمهام مثل توصية العنصر التالي وتوصية قائمة الجلسة. يمكن للنماذج المعتمدة على التسلسل أن تأخذ في الاعتبار الترتيب الذي يتم فيه التفاعل مع العناصر وتتعلم أنماط سلوك المستخدم التي تتطور. علاوة على ذلك، فإن ظهور نماذج اللغة مثل BERT قد تقدم بشكل أكبر أنظمة التوصية من خلال تمكين فهم أفضل لكل من ميزات اللغة الطبيعية وسلوكيات المستخدم التسلسلية. يمكن لهذه النماذج اللغوية أن تلتقط تمثيلات دلالية عميقة ومعرفة بالعالم، مما يثري عملية التوصية ويسهل تقديم توصيات أكثر تخصيصًا ووعيًا بالسياق. بشكل عام، فإن تطبيق تقنيات التعلم العميق في أنظمة التوصية قد فتح آفاقًا جديدة للبحث والابتكار، واعدًا بثورة في مجال التوصيات الشخصية وتعزيز تجارب المستخدمين.
2.1.2 المساعدة الشخصية
2.2 نماذج اللغة الكبيرة
ملاحظات حول المعلومات المهمة للمستخدمين داخل ذاكرتهم، وضع خطط مخصصة بناءً على المعلومات المحفوظة عند ظهور مطالب جديدة، وتنفيذ الخطط من خلال الاستفادة من أدوات مثل محركات البحث وأنظمة التوصية.
3 نماذج لغوية كبيرة للتخصيص
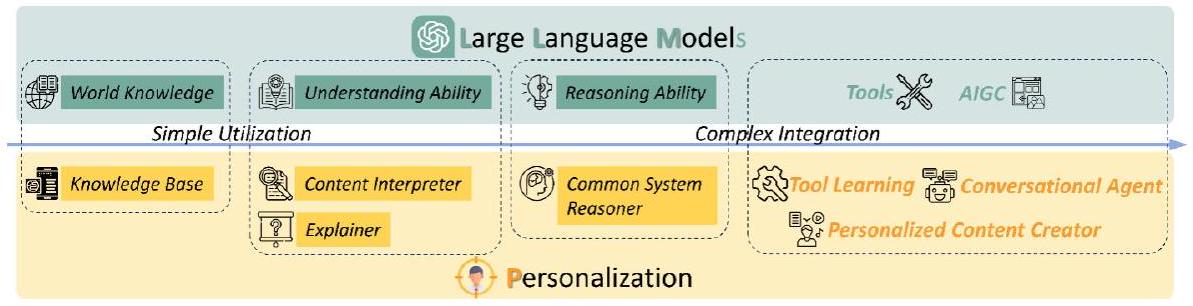
4 نماذج اللغة الكبيرة كقاعدة معرفة
مطالبات مخصصة للتنبؤ بالكيان النهائي. أما بالنسبة للمهمة المهمة الأخرى، أي بناء الرسم البياني للمعرفة، والتي تشير إلى إنشاء تمثيل منظم للمعرفة، يمكن تطبيق نماذج اللغة الكبيرة في عملية بناء الرسوم البيانية للمعرفة، بما في ذلك اكتشاف الكيانات [71، 72]، وحل الإشارة المرجعية [73، 74] واستخراج العلاقات [75، 76]. يمكن أن تحقق نماذج اللغة الكبيرة أيضًا البناء من البداية إلى النهاية [
5 نماذج اللغة الكبيرة كمفسر للمحتوى
| النهج | المعرفة | المهمة | العمود الفقري لنموذج اللغة الكبيرة | مجموعات البيانات |
| KAR [80] | معرفة واقعية | توقع CTR وإعادة الترتيب | gpt-3.5-turbo | Ml-1M، كتاب أمازون |
| LLMRec [81] | تفاعلات المستخدم-العنصر، معلومات جانبية | توصية TopK | gpt-3.5-turbo | ML، نتفليكس |
| KRec [82] | علاقة تكميلية | توقع CTR | ChatGPT 3.5، ChatGLM 2 | بيانات Alipay |
5.1 مفسر المحتوى التقليدي
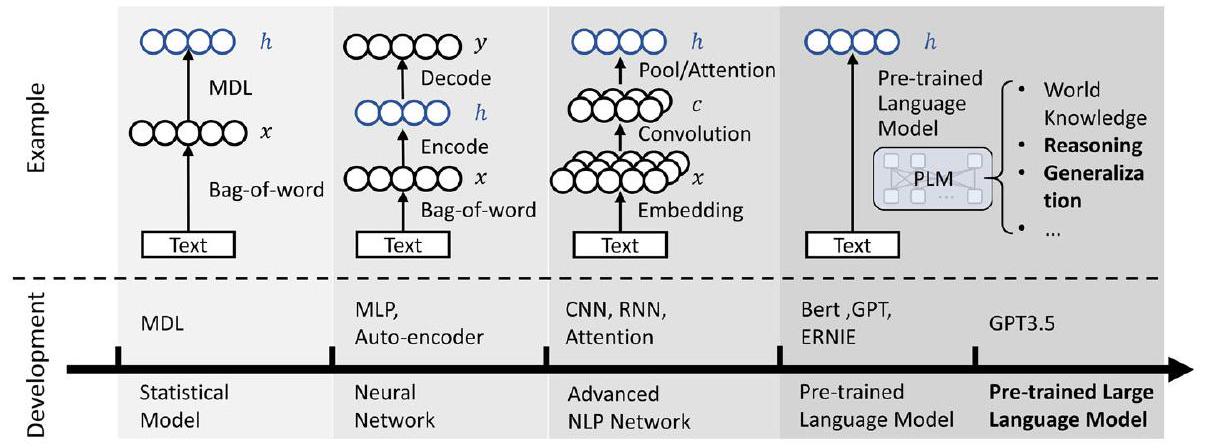
5.2 مفسر المحتوى المعتمد على نموذج اللغة
6 نماذج اللغة الكبيرة كمفسر
| النهج | المهمة | هيكل نموذج اللغة | استراتيجية الضبط | المجموعات البيانية |
| TALLRe [119] | التوصية التسلسلية | LLaMA-7B | ضبط التعليمات & الضبط الدقيق | MovieLens100k، BookCrossing |
| LLMs-Rec [120] | توقع التقييم | Flan-T5-Base، Flan-T5-XXL | الضبط الدقيق | MovieLens-1M، كتاب أمازون |
| PALR [121] | توصية العناصر | LLaMa-7B | ضبط التعليمات | MovieLens-1M، جمال أمازون |
| InstructRec [122] | التوصية التسلسلية البحث المخصص | Flan-T5-XL | ضبط التعليمات | Amazon-Games، CDs |
7 نماذج اللغة الكبيرة كمنطق نظام شائع
الذكاء لاتخاذ القرارات وحل المشكلات. من خلال تزويد النماذج بـ ‘سلسلة الأفكار’ [38]، مثل التحفيز بعبارة ‘دعنا نفكر في الأمر خطوة بخطوة’، تظهر نماذج اللغة الكبيرة قدرات ناشئة للتفكير المنطقي ويمكن أن تصل إلى استنتاجات أو أحكام وفقًا للأدلة أو المنطق. وبناءً عليه، فإن أنظمة التوصية، قادرة على التفكير لمساعدة استخراج اهتمامات المستخدم، مما يحسن الأداء.
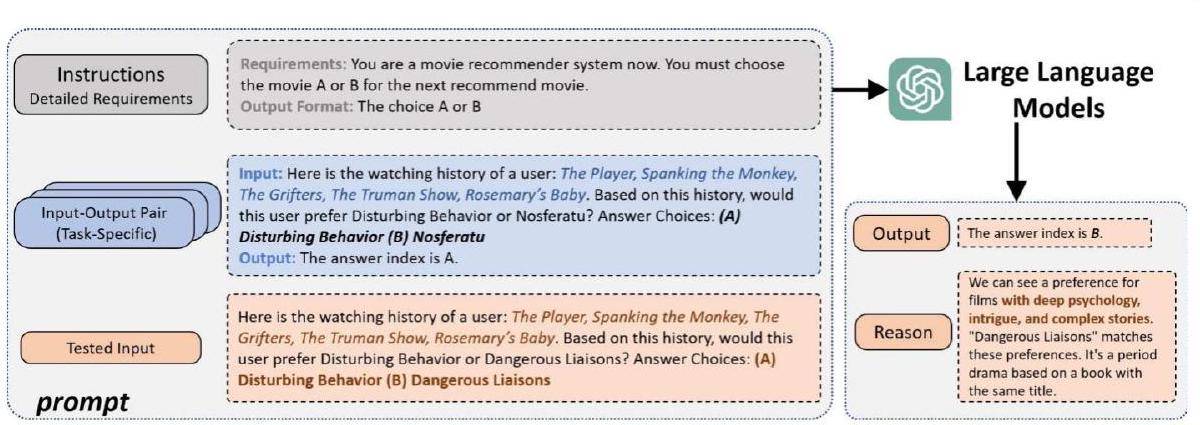
7.1 تقديم توصيات مباشرة
- ركزت الدراسات المذكورة أعلاه بشكل أساسي على تقييم المستشارين بدون لقطة/بضع لقطات باستخدام مجموعات بيانات مفتوحة النطاق، بشكل رئيسي في مجالات مثل الأفلام والكتب. تم تدريب نماذج اللغة الكبيرة على مجموعات بيانات مفتوحة النطاق واسعة، مما يمكنها من امتلاك كمية كبيرة من المعرفة العامة، بما في ذلك المعلومات حول الأفلام المعروفة. ومع ذلك، عندما يتعلق الأمر ببيانات المجال الخاص، مثل منتجات التجارة الإلكترونية أو المواقع المحددة، فإن قدرة المستشارين بدون لقطة تفتقر إلى التحقق، وهو ما يُتوقع أن يكون تحديًا.
- تتطلب طرق الاختبار الحالية دمج وحدات إضافية للتحقق من أداء المستشارين بدون لقطة لمهام محددة. على وجه الخصوص، بالنسبة لمهام الترتيب التي تتضمن تقديم قائمة من العناصر حسب التفضيل، يتم استخدام وحدة توليد المرشحين لتقليص مجموعة العناصر [164] و [165]. تولد النماذج المعتمدة على التوليد مثل gpt-3.5-turbo النتائج بطريقة توليدية بدلاً من الاعتماد على الاسترجاع من الذكريات الموجودة، مما يتطلب وحدات إضافية لتنفيذ توصيات العناصر المعتمدة على الهوية.
- من منظور أداء التوصية، تظهر المستشارين بدون لقطة بعض القدرات ويؤدي المتعلمون بضع لقطات بشكل أفضل. ومع ذلك، لا يزال هناك فجوة كبيرة عند مقارنتها بنماذج التوصية التقليدية، وخاصة نماذج اللغة الكبيرة المضبوطة بشكل خاص للمستشارين، مثل P5 [174] و M6-Rec [175]. وهذا يبرز أن نماذج اللغة الكبيرة لا تمتلك ميزة كبيرة في النمذجة الشخصية.
| النهج | العمود الفقري لنموذج اللغة الكبيرة | المهمة | المقياس | مجموعات البيانات | ICL | COT | |||||||
| [162] | gpt-3.5-turbo | توقع التقييم، التوصية التسلسلية، التوصية المباشرة، توليد الشرح، تلخيص المراجعات |
|
أمازون الجمال |
|
||||||||
| [163] |
|
نقطة-واحدة، زوجية، قائمة-واحدة | NDCG، MRR |
|
|
||||||||
| [120] | Flan-U-PALM gpt-3.5-turbo text-davinci-003 | توقع التقييم، توقع الترتيب |
|
|
|
||||||||
| [164] | Text-davinci-003 | إعادة الترتيب | NDCG، HR | MovieLens 100 K |
|
|
|||||||
| [165] | gpt-3.5-turbo | إعادة الترتيب | NDCG |
|
|
||||||||
| [166] | gpt-3.5-turbo | إعادة الترتيب | الدقة | MIND |
|
7.2 التفكير للاختيار الآلي
الكفاءة وقابلية التفسير، إحدى الطرق هي دمج نماذج اللغة الكبيرة في استراتيجيات بحث معينة، حيث توجه خوارزمية الجينات عملية البحث وتولد نماذج اللغة الكبيرة التبادلات المرشحة. تستخدم LLMatic [196] و EvoPrompting [197] نماذج اللغة الكبيرة كعوامل طفرات وتبادلات لخوارزمية NAS الجينية. خلال عملية التطور، كل جيل لديه احتمال معين لتحديد ما إذا كان سيتم إجراء تبادل أو طفرة لإنتاج نسل جديد. يتم توليد التبادلات والطفرات من خلال تحفيز نماذج اللغة الكبيرة. مثل هذا الحل يدمج نماذج اللغة الكبيرة في خوارزمية البحث الجيني، مما يحقق أداءً أفضل من التفكير المباشر على المساحة الكاملة.
8 نماذج اللغة الكبيرة كوكيل محادثة
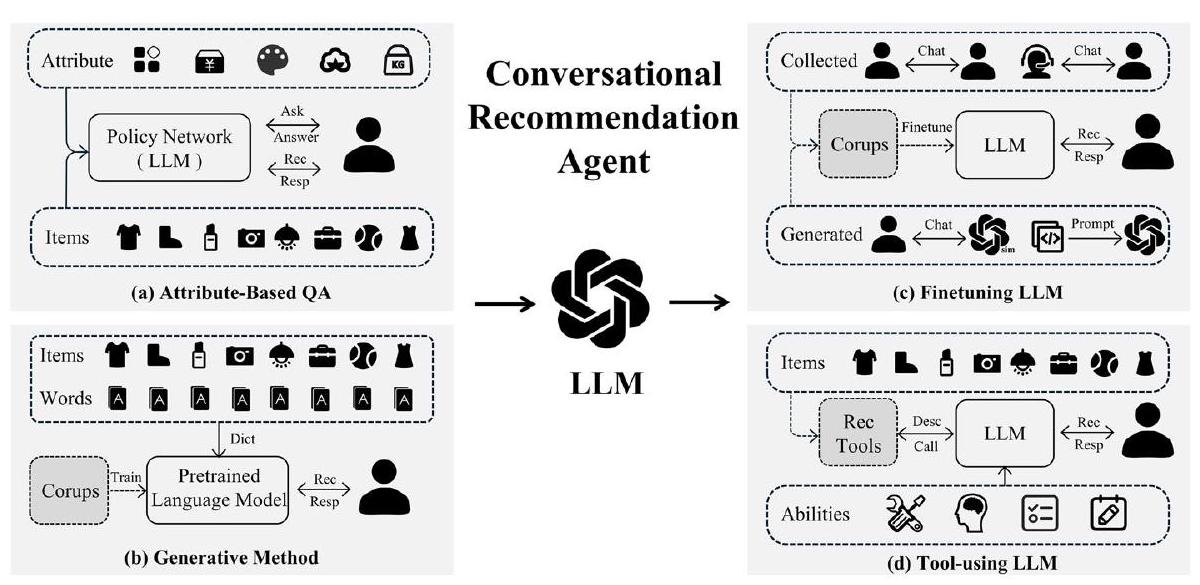
يفيد قدرة استخدام الأداة. وقد اقترحت الدراسات اللاحقة مثل ToT [228] وPlan-and-Solve [229] وReAct [230] تقنيات أكثر تقدمًا لتصميم المطالبات للمساعدة في توجيه النموذج اللغوي الكبير للانخراط في تفكير أعمق وتخطيط الأدوات.
9 تعلم الأدوات وتطبيقاته في التوصية
9.1 تعلم الأدوات القائم على النماذج اللغوية الكبيرة
- يعتبر التعلم المعزز بالأدوات أدوات متخصصة كمساعدين من أجل تحسين جودة ودقة المهام، أو أداة للذكاء الاصطناعي؛
- يركز التعلم الموجه بالأدوات أكثر على تدريب النماذج لاستخدام الأدوات بشكل فعال، والتحكم في عمليات تطبيق الأدوات وتحسينها، أو الذكاء الاصطناعي من أجل الأداة.
لقد وجد تعلم الأدوات تطبيقات في مجالات متنوعة، ويركز هذا القسم بشكل أساسي على نماذج تعلم الأدوات القائمة على النماذج اللغوية الكبيرة (LLMs). بينما تتضمن الأعمال الأخيرة غالبًا مزيجًا من هذين المنظورين، فإننا لا نصنف كل عمل بشكل محدد في نوع واحد. النماذج اللغوية الكبيرة، مثل GPT، مناسبة تمامًا لتطبيقات تعلم الأدوات [233]. بفضل قدراتها القوية في معالجة اللغة الطبيعية، يمكن للنماذج اللغوية الكبيرة تقسيم المهام المعقدة إلى مهام فرعية أصغر وتحويلها إلى تعليمات قابلة للتنفيذ. تتيح الأدوات المتخصصة للنماذج اللغوية الكبيرة الوصول إلى المعرفة التي تتجاوز فهمها الخاص. من خلال دمج الأدوات المتخصصة، يمكن للنماذج اللغوية الكبيرة فهم المشكلات المعقدة بشكل أفضل ثم معالجتها، مما يوفر حلولًا أكثر دقة وكفاءة للأنظمة المخصصة.
9.2 التطبيقات في سيناريوهات التخصيص
| النهج | استخدام الأداة | العمود الفقري لنموذج اللغة الكبيرة | المهمة |
| Re3 [234] | نموذج اللغة الكبيرة | gpt3-instruct-175B gpt3-instruct13B | توليد قصص طويلة |
| PEER [235] | نموذج اللغة الكبيرة | T5 المعدل | الإصدارات، الاقتباسات، الاقتباسات |
| METALM [236] | مشفرات مدربة مسبقًا مع أوضاع متنوعة | محول (مدرب من الصفر) | مهام اللغة فقط مهام اللغة البصرية |
| Atlas [237] | مسترجع كثيف | T5 | مهام اللغة المعتمدة على المعرفة فهم اللغة متعددة المهام الإجابة على الأسئلة التحقق من الحقائق |
| LaMDA [238] | مسترجع مترجم آلة حاسبة | محول فقط للترميز | الحوار |
| WebGPT [239] | متصفح الويب | gpt-3 | الإجابة على الأسئلة |
| عين العقل [240] | محرك فيزياء نص إلى كود LM | gpt-3 PaLM | التفكير |
| PAL [241] | مترجم بايثون | CODEX(code-davinci-002) | التفكير الرمزي الرياضي الخوارزمي |
| SayCan [242] | روبوتات | PaLM | المهام الروبوتية في العالم الحقيقي |
| HuggingGPT [243] | نماذج الذكاء الاصطناعي في مجتمع Hugging Face | gpt-3.5-turbo text-davinci-003 gpt4 | تصنيف الصور، وصف الصور، كشف الكائنات، إلخ. |
| Auto-GPT | متصفح الويب | gpt-3.5-turbo text-davinci-003 gpt4 | المهام المحددة من قبل المستخدم |
| Visual ChatGPT [244] Taskmatrix.AI [245] | نماذج الأساس البصرية نماذج مخصصة مع شكل واجهة برمجة التطبيقات الموحدة | text-davinci-003 | المهام المخصصة البصرية |
| ReAct [230] | واجهة برمجة تطبيقات ويكيبيديا | PaLM-540B | الإجابة على الأسئلة التحقق من الوجه |
| Toolformer [246] | آلة حاسبة نظام الأسئلة والأجوبة محرك البحث نظام الترجمة التقويم | GPT-J | المهام اللاحقة |
يمكن أن تعزز العلاقات الاجتماعية المعرفة المتاحة لنماذج اللغة الكبيرة، مما يمكّن من تقديم توصيات أكثر دقة وتخصيصًا.
10 نماذج اللغة الكبيرة كمنشئ محتوى مخصص
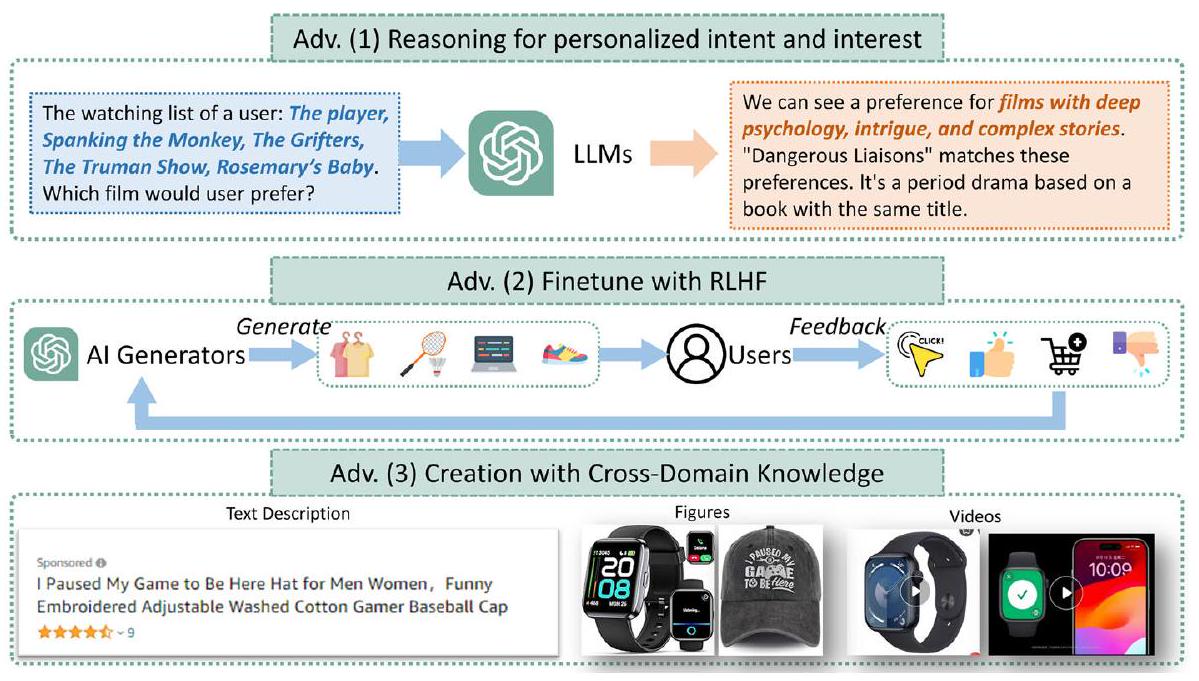
نماذج تتذكر بيانات المستخدم الحساسة. أظهرت الأعمال السابقة [284] أن نماذج اللغة الكبيرة، وخاصة GPT-2 [285]، تتذكر وتكشف عن أمثلة تدريب فردية. وهذا يبرز الحاجة إلى موافقة صارمة من المستخدم والتعامل الحذر مع بيانات المعلقين لتقليل مخاطر الخصوصية. من الضروري تطوير تقنيات جديدة تعطي الأولوية للحفاظ على الخصوصية خلال عملية التدريب.
11 التحديات المفتوحة
11.1 صعوبات النشر
11.1.1 التحديات الصناعية
11.1.2 جمع البيانات الشاق
يمكن للباحثين والممارسين توجيه النموذج لإنتاج مخرجات تلبي بشكل أفضل التطبيقات المخصصة، مما يزيد من الأداء والفعالية.
11.2 قدرات نماذج اللغة الكبيرة
11.2.1 نمذجة النصوص الطويلة
11.2.2 القابلية للتفسير والشرح
التي تكشف عن كيفية عمل نماذج اللغة، وتسهيل توليد تفسيرات ذات مغزى ودقيقة، وتمكين طرق تقييم قوية هو التركيز الرئيسي. من خلال تقديم توصيات شفافة وقابلة للتفسير، يمكن للمستخدمين بناء الثقة، وفهم الأسباب وراء التوصيات، واتخاذ قرارات مستنيرة.
11.3 التقييم
11.3.1 الأدوات والمعايير
11.3.2 التوازن بين الفائدة، الصدق، وعدم الإيذاء
محمي، مع أذونات مستخدم صارمة لمشاركة معلوماتهم الشخصية. بالنسبة للتمييز، قد تعكس نماذج اللغة الكبيرة بشكل لا مفر منه التحيزات الموجودة في بيانات التدريب، مما يؤدي إلى توصيات تمييزية. بالنظر إلى توزيع المستخدمين والعناصر المتحيز، والذي يكون أكثر أهمية في أنظمة التوصية ذات تأثير الذيل الطويل، حيث يمكن أن يؤدي توزيع المستخدمين والعناصر المتحيز إلى قرارات تفضل الخيارات الأكثر شيوعًا، مما يؤدي إلى التمييز ضد بعض المستخدمين. تتعلق القلق النهائي بالاعتبارات الأخلاقية. يمكن أن توجه الرسائل الضارة، إذا تم النقر عليها من قبل المستخدمين بشكل غير واعٍ، نماذج اللغة الكبيرة نحو إنتاج محتوى ضار مشابه. ومع ذلك، عند المساعدة في اتخاذ القرارات الشخصية، من الضروري أن تمتلك نماذج اللغة الكبيرة القدرة على تقليل التعرض للرسائل الضارة وتوجيه المستخدمين بطريقة مسؤولة. قد تقدم أساليب مثل بناء ذكاء اصطناعي دستوري، حيث يتم اعتماد النقد والمراجعات والتعلم تحت الإشراف لتحسين نماذج التدريب، رؤى قيمة.
12 الخاتمة
الإعلانات
الموافقة الأخلاقية لا تتضمن هذه البحث مشاركين بشريين أو تشكل خطرًا محتملاً على الأفراد. وبالتالي، لم تكن الموافقة الأخلاقية الرسمية مطلوبة. ومع ذلك، نود أن نؤكد التزامنا بممارسات البحث الأخلاقية ونؤكد أن الدراسة تتماشى مع الإرشادات والمبادئ الأخلاقية المنصوص عليها في مدونة الأخلاقيات التابعة لجمعية الحاسبات الآلية.
References
- Zhao, W.X., Zhou, K., Li, J., Tang, T., Wang, X., Hou, Y., Min, Y., Zhang, B., Zhang, J., Dong, Z., et al.: A survey of large language models. arXiv:2303.18223 (2023)
- Huang, J., Chang, K.C.-C.: Towards reasoning in large language models: a survey. arXiv:2212.10403 (2022)
- Brown, T., Mann, B., Ryder, N., Subbiah, M., Kaplan, J.D., Dhariwal, P., Neelakantan, A., Shyam, P., Sastry, G., Askell, A., et al.: Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 1877-1901 (2020)
- Salemi, A., Mysore, S., Bendersky, M., Zamani, H.: Lamp: When large language models meet personalization. arXiv:2304.11406 (2023)
- Wu, L., Zheng, Z., Qiu, Z., Wang, H., Gu, H., Shen, T., Qin, C., Zhu, C., Zhu, H., Liu, Q., et al.: A survey on large language models for recommendation. arXiv:2305.19860 (2023)
- Lin, J., Dai, X., Xi, Y., Liu, W., Chen, B., Li, X., Zhu, C., Guo, H., Yu, Y., Tang, R., et al.: How can recommender systems benefit from large language models: a survey. arXiv:2306.05817 (2023)
- Fan, W., Zhao, Z., Li, J., Liu, Y., Mei, X., Wang, Y., Tang, J., Li, Q.: Recommender systems in the era of large language models (llms). arXiv:2307.02046 (2023)
- Resnick, P., Iacovou, N., Suchak, M., Bergstrom, P., Riedl, J.: Grouplens: an open architecture for collaborative filtering of netnews. In: Proceedings of the 1994 ACM Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work, pp. 175-186 (1994)
- Pan, R., Zhou, Y., Cao, B., Liu, N.N., Lukose, R., Scholz, M., Yang, Q.: One-class collaborative filtering. In: 2008 Eighth IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, pp. 502-511 (2008). IEEE
- Koren, Y., Bell, R., Volinsky, C.: Matrix factorization techniques for recommender systems. Computer 42(8), 30-37 (2009)
- Wang, J., De Vries, A.P., Reinders, M.J.: Unifying user-based and item-based collaborative filtering approaches by similarity fusion. In: Proceedings of the 29th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 501-508 (2006)
- Pazzani, M.J., Billsus, D.: Content-based recommendation systems. In: The adaptive Web: Methods and Strategies of Web Personalization, pp. 325-341. Springer (2007)
- Wang, C., Blei, D.M.: Collaborative topic modeling for recommending scientific articles. In: Proceedings of the 17th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 448-456 (2011)
- Zhang, F., Yuan, N.J., Lian, D., Xie, X., Ma, W.-Y.: Collaborative knowledge base embedding for recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 353-362 (2016)
- Liu, H., Wu, F., Wang, W., Wang, X., Jiao, P., Wu, C., Xie, X.: Nrpa: neural recommendation with personalized attention. In: Proceedings of the 42nd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 1233-1236 (2019)
- Wang, H., Wang, N., Yeung, D.-Y.: Collaborative deep learning for recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 21th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 1235-1244 (2015)
- Zhou, G., Zhu, X., Song, C., Fan, Y., Zhu, H., Ma, X., Yan, Y., Jin, J., Li, H., Gai, K.: Deep interest network for click-through rate prediction. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 1059-1068 (2018)
- Zhou, G., Mou, N., Fan, Y., Pi, Q., Bian, W., Zhou, C., Zhu, X., Gai, K.: Deep interest evolution network for click-through rate prediction. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 33, pp. 5941-5948 (2019)
- Wang, X., He, X., Wang, M., Feng, F., Chua, T.-S.: Neural graph collaborative filtering. In: Proceedings of the 42 nd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 165-174 (2019)
- Kang, W.-C., McAuley, J.: Self-attentive sequential recommendation. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), pp. 197-206 (2018). IEEE
- Hidasi, B., Karatzoglou, A., Baltrunas, L., Tikk, D.: Session-based recommendations with recurrent neural networks. arXiv:1511.06939 (2015)
- Sun, F., Liu, J., Wu, J., Pei, C., Lin, X., Ou, W., Jiang, P.: Bert4rec: Sequential recommendation with bidirectional encoder representations from transformer. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, pp. 1441-1450 (2019)
- Paschou, M., Sakkopoulos, E.: Personalized assistant apps in healthcare: a systematic review. In: 2019 10th International Conference on Information, Intelligence, Systems and Applications (IISA), pp. 1-8 (2019). IEEE
- Sun, Y., Zhang, Y.: Conversational recommender system. In: The 41st International Acm Sigir Conference on Research & Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 235-244 (2018)
- Jannach, D., Manzoor, A., Cai, W., Chen, L.: A survey on conversational recommender systems. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) 54(5), 1-36 (2021)
- Bengio, Y., Ducharme, R., Vincent, P.: A neural probabilistic language model. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 13 (2000)
- Mikolov, T., Karafiát, M., Burget, L., Cernockỳ, J., Khudanpur, S.: Recurrent neural network based language model. In: Interspeech, vol. 2, pp. 1045-1048 (2010). Makuhari
- Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A.N., Kaiser, Ł., Polosukhin, I.: Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 30 (2017)
- Kenton, J.D.M.-W.C., Toutanova, L.K.: Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In: Proceedings of NAACL-HLT, pp. 4171-4186 (2019)
- Shanahan, M.: Talking about large language models. Commun. ACM 67(2), 68-79 (2024)
- Chowdhery, A., Narang, S., Devlin, J., Bosma, M., Mishra, G., Roberts, A., Barham, P., Chung, H.W., Sutton, C., Gehrmann, S., et al.: Palm: scaling language modeling with pathways. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 24(240), 1-113 (2023)
- Touvron, H., Lavril, T., Izacard, G., Martinet, X., Lachaux, M.-A., Lacroix, T., Rozière, B., Goyal, N., Hambro, E., Azhar, F., et al.: Llama: open and efficient foundation language models. arXiv:2302.13971 (2023)
- Le Scao, T., Wang, T., Hesslow, D., Bekman, S., Bari, M.S., Biderman, S., Elsahar, H., Muennighoff, N., Phang, J., Press, O., et al.: What language model to train if you have one million gpu hours?. In: Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2022, pp. 765-782 (2022)
- Kaplan, J., McCandlish, S., Henighan, T., Brown, T.B., Chess, B., Child, R., Gray, S., Radford, A., Wu, J., Amodei, D.: Scaling laws for neural language models. arXiv:2001.08361 (2020)
- Hoffmann, J., Borgeaud, S., Mensch, A., Buchatskaya, E., Cai, T., Rutherford, E., Casas, D.d.L., Hendricks, L.A., Welbl, J., Clark, A., et al.: Training compute-optimal large language models. arXiv:2203.15556 (2022)
- Sanh, V., Webson, A., Raffel, C., Bach, S., Sutawika, L., Alyafeai, Z., Chaffin, A., Stiegler, A., Raja, A., Dey, M., et al.: Multitask prompted training enables zero-shot task generalization. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2021)
- Ouyang, L., Wu, J., Jiang, X., Almeida, D., Wainwright, C., Mishkin, P., Zhang, C., Agarwal, S., Slama, K., Ray, A., et al.: Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 27730-27744 (2022)
- Wei, J., Wang, X., Schuurmans, D., Bosma, M., Chi, E., Le, Q., Zhou, D.: Chain of thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models. arXiv:2201.11903 (2022)
- Fu, Y., Peng, H., Khot, T.: How does gpt obtain its ability? tracing emergent abilities of language models to their sources. Yao Fu’s Notion (2022)
- Zhang, Y., Chen, X., Ai, Q., Yang, L., Croft, W.B.: Towards conversational search and recommendation: system ask, user respond. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, pp. 177-186 (2018)
- Wang, H., Zhang, F., Xie, X., Guo, M.: Dkn: deep knowledge-aware network for news recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 2018 World Wide Web Conference, pp. 1835-1844 (2018)
- Huang, J., Zhao, W.X., Dou, H., Wen, J.-R., Chang, E.Y.: Improving sequential recommendation with knowledge-enhanced memory networks. In: The 41st international ACM SIGIR Conference on Research & Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 505-514 (2018)
- Wang, H., Zhang, F., Hou, M., Xie, X., Guo, M., Liu, Q.: Shine: signed heterogeneous information network embedding for sentiment link prediction. In: Proceedings of the Eleventh ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, pp. 592-600 (2018)
- Yu, X., Ren, X., Gu, Q., Sun, Y., Han, J.: Collaborative filtering with entity similarity regularization in heterogeneous information networks. IJCAI HINA 27 (2013)
- Shi, C., Zhang, Z., Luo, P., Yu, P.S., Yue, Y., Wu, B.: Semantic path based personalized recommendation on weighted heterogeneous information networks. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM International on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, pp. 453-462 (2015)
- Ma, W., Zhang, M., Cao, Y., Jin, W., Wang, C., Liu, Y., Ma, S., Ren, X.: Jointly learning explainable rules for recommendation with knowledge graph. In: The World Wide Web Conference, pp. 1210-1221 (2019)
- Huang, X., Fang, Q., Qian, S., Sang, J., Li, Y., Xu, C.: Explainable interaction-driven user modeling over knowledge graph for sequential recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 548-556 (2019)
- Wang, H., Zhang, F., Wang, J., Zhao, M., Li, W., Xie, X., Guo, M.: Ripplenet: propagating user preferences on the knowledge graph for recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, pp. 417-426 (2018)
- Wang, H., Zhao, M., Xie, X., Li, W., Guo, M.: Knowledge graph convolutional networks for recommender systems. In: The World Wide Web Conference, pp. 3307-3313 (2019)
- Wang, X., He, X., Cao, Y., Liu, M., Chua, T.-S.: Kgat: knowledge graph attention network for recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 950-958 (2019)
- Tang, X., Wang, T., Yang, H., Song, H.: Akupm: attention-enhanced knowledge-aware user preference model for recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 1891-1899 (2019)
- Zhao, J., Zhou, Z., Guan, Z., Zhao, W., Ning, W., Qiu, G., He, X.: Intentgc: a scalable graph convolution framework fusing heterogeneous information for recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 2347-2357 (2019)
- Petroni, F., Rocktäschel, T., Lewis, P., Bakhtin, A., Wu, Y., Miller, A.H., Riedel, S.: Language models as knowledge bases?. arXiv:1909.01066 (2019)
- Roberts, A., Raffel, C., Shazeer, N.: How much knowledge can you pack into the parameters of a language model?. arXiv:2002.08910 (2020)
- Petroni, F., Lewis, P., Piktus, A., Rocktäschel, T., Wu, Y., Miller, A.H., Riedel, S.: How context affects language models’ factual predictions. In: Automated Knowledge Base Construction
- Jiang, Z., Xu, F.F., Araki, J., Neubig, G.: How can we know what language models know? Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist 8, 423-438 (2020)
- Wang, C., Liu, X., Song, D.: Language models are open knowledge graphs. arXiv:2010.11967 (2020)
- Poerner, N., Waltinger, U., Schütze, H.: E-bert: efficient-yet-effective entity embeddings for bert. In: Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2020, pp. 803-818 (2020)
- Heinzerling, B., Inui, K.: Language models as knowledge bases: On entity representations, storage capacity, and paraphrased queries. In: Proceedings of the 16th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Main Volume, pp. 1772-1791 (2021)
- Wang, C., Liu, P., Zhang, Y.: Can generative pre-trained language models serve as knowledge bases for closed-book qa?. In: Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (vol. 1: long papers), pp. 3241-3251 (2021)
- Guu, K., Lee, K., Tung, Z., Pasupat, P., Chang, M.: Retrieval augmented language model pre-training. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 3929-3938 (2020). PMLR
- Bordes, A., Usunier, N., Garcia-Duran, A., Weston, J., Yakhnenko, O.: Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 26 (2013)
- Zhu, Y., Wang, X., Chen, J., Qiao, S., Ou, Y., Yao, Y., Deng, S., Chen, H., Zhang, N.: Llms for knowledge graph construction and reasoning: recent capabilities and future opportunities. arXiv:2305.13168 (2023)
- Zhang, Z., Liu, X., Zhang, Y., Su, Q., Sun, X., He, B.: Pretrain-kge: learning knowledge representation from pretrained language models. In: Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2020, pp. 259-266 (2020)
- Kumar, A., Pandey, A., Gadia, R., Mishra, M.: Building knowledge graph using pre-trained language model for learning entity-aware relationships. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Computing, Power and Communication Technologies (GUCON), pp. 310-315 (2020). IEEE
- Kim, B., Hong, T., Ko, Y., Seo, J.: Multi-task learning for knowledge graph completion with pre-trained language models. In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, pp. 1737-1743 (2020)
- Choi, B., Jang, D., Ko, Y.: Mem-kgc: masked entity model for knowledge graph completion with pretrained language model. IEEE Access 9, 132025-132032 (2021)
- Wang, B., Shen, T., Long, G., Zhou, T., Wang, Y., Chang, Y.: Structure-augmented text representation learning for efficient knowledge graph completion. In: Proceedings of the Web Conference 2021, pp. 1737-1748 (2021)
- Xie, X., Zhang, N., Li, Z., Deng, S., Chen, H., Xiong, F., Chen, M., Chen, H.: From discrimination to generation: knowledge graph completion with generative transformer. In: Companion Proceedings of the Web Conference 2022, pp. 162-165 (2022)
- Jiang, P., Agarwal, S., Jin, B., Wang, X., Sun, J., Han, J.: Text-augmented open knowledge graph completion via pre-trained language models. arXiv:2305.15597 (2023)
- Yan, H., Gui, T., Dai, J., Guo, Q., Zhang, Z., Qiu, X.: A unified generative framework for various ner subtasks. In: Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (vol. 1: long papers), pp. 5808-5822 (2021)
- Li, B., Yin, W., Chen, M.: Ultra-fine entity typing with indirect supervision from natural language inference. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 10, 607-622 (2022)
- Kirstain, Y., Ram, O., Levy, O.: Coreference resolution without span representations. In: Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (vol. 2: short papers), pp. 14-19 (2021)
- Cattan, A., Eirew, A., Stanovsky, G., Joshi, M., Dagan, I.: Cross-document coreference resolution over predicted mentions. In: Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL-IJCNLP 2021, pp. 5100-5107 (2021)
- Lyu, S., Chen, H.: Relation classification with entity type restriction. In: Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL-IJCNLP 2021, pp. 390-395 (2021)
- Wang, H., Focke, C., Sylvester, R., Mishra, N., Wang, W.: Fine-tune bert for docred with two-step process. arXiv:1909.11898 (2019)
- Han, J., Collier, N., Buntine, W., Shareghi, E.: Pive: prompting with iterative verification improving graph-based generative capability of llms. arXiv:2305.12392 (2023)
- Trajanoska, M., Stojanov, R., Trajanov, D.: Enhancing knowledge graph construction using large language models. arXiv:2305.04676 (2023)
- West, P., Bhagavatula, C., Hessel, J., Hwang, J., Jiang, L., Le Bras, R., Lu, X., Welleck, S., Choi, Y.: Symbolic knowledge distillation: from general language models to commonsense models. In: Proceedings of the 2022 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, pp. 4602-4625 (2022)
- Xi, Y., Liu, W., Lin, J., Zhu, J., Chen, B., Tang, R., Zhang, W., Zhang, R., Yu, Y.: Towards open-world recommendation with knowledge augmentation from large language models. arXiv:2306.10933 (2023)
- Wei, W., Ren, X., Tang, J., Wang, Q., Su, L., Cheng, S., Wang, J., Yin, D., Huang, C.: Llmrec: large language models with graph augmentation for recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 17th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, pp. 806-815 (2024)
- Zhao, Q., Qian, H., Liu, Z., Zhang, G.-D., Gu, L.: Breaking the barrier: utilizing large language models for industrial recommendation systems through an inferential knowledge graph. arXiv:2402.13750 (2024)
- Razniewski, S., Yates, A., Kassner, N., Weikum, G.: Language models as or for knowledge bases. arXiv:2110.04888 (2021)
- Yu, J., Wang, X., Tu, S., Cao, S., Zhang-Li, D., Lv, X., Peng, H., Yao, Z., Zhang, X., Li, H., et al.: Kola: Carefully benchmarking world knowledge of large language models. arXiv:2306.09296 (2023)
- Ye, D., Lin, Y., Li, P., Sun, M.: Packed levitated marker for entity and relation extraction. In: Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (vol. 1: long papers), pp. 4904-4917 (2022)
- Lang, K.: Newsweeder: Learning to filter netnews. In: Machine Learning Proceedings 1995, pp. 331-339. Elsevier (1995)
- Wang, H., Shi, X., Yeung, D.-Y.: Collaborative recurrent autoencoder: recommend while learning to fill in the blanks. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 29 (2016)
- Dong, X., Yu, L., Wu, Z., Sun, Y., Yuan, L., Zhang, F.: A hybrid collaborative filtering model with deep structure for recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 31 (2017)
- Li, X., She, J.: Collaborative variational autoencoder for recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 305-314 (2017)
- Wu, C., Wu, F., Huang, Y., Xie, X.: Personalized news recommendation: methods and challenges. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 41(1), 24-12450 (2023)
- Le, Q.V., Mikolov, T.: Distributed representations of sentences and documents. In: ICML. JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings, vol. 32, pp. 1188-1196. JMLR.org (2014)
- Song, Y., Elkahky, A.M., He, X.: Multi-rate deep learning for temporal recommendation. In: SIGIR, pp. 909-912. ACM (2016)
- Kumar, V., Khattar, D., Gupta, S., Gupta, M., Varma, V.: Deep neural architecture for news recommendation. In: CLEF (Working Notes). CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol. 1866. CEUR-WS.org (2017)
- Okura, S., Tagami, Y., Ono, S., Tajima, A.: Embedding-based news recommendation for millions of users. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 1933-1942 (2017)
- Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G., Dean, J.: Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. In: ICLR (Workshop Poster) (2013)
- Wu, C., Wu, F., An, M., Huang, J., Huang, Y., Xie, X.: NPA: neural news recommendation with personalized attention. In: KDD, pp. 2576-2584. ACM (2019)
- An, M., Wu, F., Wu, C., Zhang, K., Liu, Z., Xie, X.: Neural news recommendation with long- and short-term user representations. In: ACL (1), pp. 336-345. Association for Computational Linguistics (2019)
- Wu, C., Wu, F., Ge, S., Qi, T., Huang, Y., Xie, X.: Neural news recommendation with multi-head selfattention. In: EMNLP/IJCNLP (1), pp. 6388-6393. Association for Computational Linguistics (2019)
- Wu, C., Wu, F., Qi, T., Huang, Y.: User modeling with click preference and reading satisfaction for news recommendation. In: IJCAI, pp. 3023-3029. ijcai.org (2020)
- Khattar, D., Kumar, V., Varma, V., Gupta, M.: Weave&rec: a word embedding based 3-d convolutional network for news recommendation. In: CIKM, pp. 1855-1858. ACM (2018)
- Zhu, Q., Zhou, X., Song, Z., Tan, J., Guo, L.: DAN: deep attention neural network for news recommendation. In: AAAI, pp. 5973-5980. rAAAI Press (2019)
- Qiu, Z., Wu, X., Gao, J., Fan, W.: U-bert: Pre-training user representations for improved recommendation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, pp. 4320-4327 (2021)
- Zhang, Q., Li, J., Jia, Q., Wang, C., Zhu, J., Wang, Z., He, X.: Unbert: user-news matching bert for news recommendation. In: IJCAI, pp. 3356-3362 (2021)
- Wu, C., Wu, F., Qi, T., Huang, Y.: Empowering news recommendation with pre-trained language models. In: Proceedings of the 44th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 1652-1656 (2021)
- Liu, Q., Zhu, J., Dai, Q., Wu, X.: Boosting deep ctr prediction with a plug-and-play pre-trainer for news recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, pp. 2823-2833 (2022)
- Wu, C., Wu, F., Qi, T., Zhang, C., Huang, Y., Xu, T.: Mm-rec: visiolinguistic model empowered multimodal news recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 45th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 2560-2564 (2022)
- Yu, Y., Wu, F., Wu, C., Yi, J., Liu, Q.: Tiny-newsrec: effective and efficient plm-based news recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 5478-5489 (2022)
- Zou, L., Zhang, S., Cai, H., Ma, D., Cheng, S., Wang, S., Shi, D., Cheng, Z., Yin, D.: Pre-trained language model based ranking in baidu search. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 4014-4022 (2021)
- Liu, Y., Lu, W., Cheng, S., Shi, D., Wang, S., Cheng, Z., Yin, D.: Pre-trained language model for webscale retrieval in baidu search. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 3365-3375 (2021)
- Muhamed, A., Keivanloo, I., Perera, S., Mracek, J., Xu, Y., Cui, Q., Rajagopalan, S., Zeng, B., Chilimbi, T.: Ctr-bert: cost-effective knowledge distillation for billion-parameter teacher models. In: NeurIPS Efficient Natural Language and Speech Processing Workshop (2021)
- He, J., Xu, B., Yang, Z., Han, D., Yang, C., Lo, D.: Ptm4tag: sharpening tag recommendation of stack overflow posts with pre-trained models. In: Proceedings of the 30th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Program Comprehension, pp. 1-11 (2022)
- Zhang, X., Malkov, Y., Florez, O., Park, S., McWilliams, B., Han, J., El-Kishky, A.: Twhin-bert: a socially-enriched pre-trained language model for multilingual tweet representations. arXiv:2209.07562 (2022)
- Rahmani, S., Naghshzan, A., Guerrouj, L.: Improving code example recommendations on informal documentation using bert and query-aware 1sh: a comparative study. arXiv:2305.03017 (2023)
- Ding, H., Ma, Y., Deoras, A., Wang, Y., Wang, H.: Zero-shot recommender systems. arXiv:2105.08318 (2021)
- Hou, Y., Mu, S., Zhao, W.X., Li, Y., Ding, B., Wen, J.-R.: Towards universal sequence representation learning for recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 585-593 (2022)
- Hou, Y., He, Z., McAuley, J., Zhao, W.X.: Learning vector-quantized item representation for transferable sequential recommenders. In: Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2023, pp. 1162-1171 (2023)
- Yuan, Z., Yuan, F., Song, Y., Li, Y., Fu, J., Yang, F., Pan, Y., Ni, Y.: Where to go next for recommender systems? id-vs. modality-based recommender models revisited. arXiv:2303.13835 (2023)
- Fu, J., Yuan, F., Song, Y., Yuan, Z., Cheng, M., Cheng, S., Zhang, J., Wang, J., Pan, Y.: Exploring adapter-based transfer learning for recommender systems: empirical studies and practical insights. arXiv:2305.15036 (2023)
- Bao, K., Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., Wang, W., Feng, F., He, X.: Tallrec: an effective and efficient tuning framework to align large language model with recommendation. arXiv:2305.00447 (2023)
- Kang, W.-C., Ni, J., Mehta, N., Sathiamoorthy, M., Hong, L., Chi, E., Cheng, D.Z.: Do llms understand user preferences?. evaluating llms on user rating prediction. arXiv:2305.06474 (2023)
- Chen, Z.: Palr: Personalization aware llms for recommendation. arXiv:2305.07622 (2023)
- Zhang, J., Xie, R., Hou, Y., Zhao, W.X., Lin, L., Wen, J.-R.: Recommendation as instruction following: a large language model empowered recommendation approach. arXiv:2305.07001 (2023)
- Li, R., Deng, W., Cheng, Y., Yuan, Z., Zhang, J., Yuan, F.: Exploring the upper limits of text-based collaborative filtering using large language models: discoveries and insights. arXiv:2305.11700 (2023)
- Wang, X., Chen, Y., Yang, J., Wu, L., Wu, Z., Xie, X.: A reinforcement learning framework for explainable recommendation. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), pp. 587-596 (2018). IEEE
- Gao, J., Wang, X., Wang, Y., Xie, X.: Explainable recommendation through attentive multi-view learning. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 33, pp. 3622-3629 (2019)
- Lee, S., Wang, X., Han, S., Yi, X., Xie, X., Cha, M.: Self-explaining deep models with logic rule reasoning. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. (2022)
- Nye, M., Andreassen, A.J., Gur-Ari, G., Michalewski, H., Austin, J., Bieber, D., Dohan, D., Lewkowycz, A., Bosma, M., Luan, D., et al.: Show your work: scratchpads for intermediate computation with language models. arXiv:2112.00114 (2021)
- Lampinen, A.K., Dasgupta, I., Chan, S.C., Matthewson, K., Tessler, M.H., Creswell, A., McClelland, J.L., Wang, J.X., Hill, F.: Can language models learn from explanations in context?. arXiv:2204.02329 (2022)
- Zelikman, E., Wu, Y., Mu, J., Goodman, N.: Star: bootstrapping reasoning with reasoning. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 15476-15488 (2022)
- Zhang, Y., Chen, X., et al.: Explainable recommendation: a survey and new perspectives. Found. Trends® in Inf. Retr. 14(1), 1-101 (2020)
- Schafer, J.B., Konstan, J., Riedl, J.: Recommender systems in e-commerce. In: Proceedings of the 1st ACM Conference on Electronic Commerce, pp. 158-166 (1999)
- Linden, G., Smith, B., York, J.: Amazon. com recommendations: item-to-item collaborative filtering. IEEE Internet Comput. 7(1), 76-80 (2003)
- Gomez-Uribe, C.A., Hunt, N.: The netflix recommender system: algorithms, business value, and innovation. ACM Trans. Manage. Inf. Syst. (TMIS) 6(4), 1-19 (2015)
- Sinha, R., Swearingen, K.: The role of transparency in recommender systems. In: CHI’02 Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pp. 830-831 (2002)
- Xian, Y., Zhao, T., Li, J., Chan, J., Kan, A., Ma, J., Dong, X.L., Faloutsos, C., Karypis, G., Muthukrishnan, S., et al.: Ex3: explainable attribute-aware item-set recommendations. In: Proceedings of the 15th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, pp. 484-494 (2021)
- Wang, X., Li, Q., Yu, D., Xu, G.: Reinforced path reasoning for counterfactual explainable recommendation. arXiv:2207.06674 (2022)
- Verma, S., Beniwal, A., Sadagopan, N., Seshadri, A.: Recxplainer: post-hoc attribute-based explanations for recommender systems. arXiv:2211.14935 (2022)
- Zhang, W., Yan, J., Wang, Z., Wang, J.: Neuro-symbolic interpretable collaborative filtering for attributebased recommendation. In: Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022, pp. 3229-3238 (2022)
- Li, P., Wang, Z., Ren, Z., Bing, L., Lam, W.: Neural rating regression with abstractive tips generation for recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 40th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 345-354 (2017)
- Dong, L., Huang, S., Wei, F., Lapata, M., Zhou, M., Xu, K.: Learning to generate product reviews from attributes. In: Proceedings of the 15th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: volume 1, long papers, pp. 623-632 (2017)
- Li, L., Zhang, Y., Chen, L.: Generate neural template explanations for recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, pp. 755-764 (2020)
- Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9(8), 1735-1780 (1997)
- Cho, K., Van Merriënboer, B., Gulcehre, C., Bahdanau, D., Bougares, F., Schwenk, H., Bengio, Y.: Learning phrase representations using rnn encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv:1406.1078 (2014)
- Li, L., Zhang, Y., Chen, L.: Personalized transformer for explainable recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (vol. 1: Long papers) (2021)
- Zhan, H., Li, L., Li, S., Liu, W., Gupta, M., Kot, A.C.: Towards explainable recommendation via bertguided explanation generator. In: ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 1-5 (2023). IEEE
- Ni, J., Li, J., McAuley, J.: Justifying recommendations using distantly-labeled reviews and fine-grained aspects. In: Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), pp. 188-197 (2019)
- Liu, Z., Ma, Y., Schubert, M., Ouyang, Y., Rong, W., Xiong, Z.: Multimodal contrastive transformer for explainable recommendation. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems (2023)
- Qu, Y., Nobuhara, H.: Explanation generated for sequential recommendation based on transformer model. In: 2022 Joint 12th International Conference on Soft Computing and Intelligent Systems and 23rd International Symposium on Advanced Intelligent Systems (SCIS&ISIS), pp. 1-6 (2022). IEEE
- Bai, P., Xia, Y., Xia, Y.: Fusing knowledge and aspect sentiment for explainable recommendation. IEEE Access 8, 137150-137160 (2020)
- Wang, L., Zhang, S., Wang, Y., Lim, E.-P., Wang, Y.: Llm4vis: explainable visualization recommendation using chatgpt. arXiv:2310.07652 (2023)
- Lei, Y., Lian, J., Yao, J., Huang, X., Lian, D., Xie, X.: Recexplainer: aligning large language models for recommendation model interpretability. arXiv:2311.10947 (2023)
- Bommasani, R., Hudson, D.A., Adeli, E., Altman, R., Arora, S., Arx, S., Bernstein, M.S., Bohg, J., Bosselut, A., Brunskill, E., et al.: On the opportunities and risks of foundation models. arXiv:2108.07258 (2021)
- Li, L., Zhang, Y., Chen, L.: Personalized prompt learning for explainable recommendation. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 41(4), 1-26 (2023)
- Bills, S., Cammarata, N., Mossing, D., Tillman, H., Gao, L., Goh, G., Sutskever, I., Leike, J., Wu, J., Saunders, W.: Language models can explain neurons in language models (2023)
- Wu, Z., Geiger, A., Potts, C., Goodman, N.D.: Interpretability at scale: identifying causal mechanisms in alpaca. arXiv:2305.08809 (2023)
- Li, Y., Lin, Z., Zhang, S., Fu, Q., Chen, B., Lou, J.-G., Chen, W.: Making large language models better reasoners with step-aware verifier (2023)
- Turpin, M., Michael, J., Perez, E., Bowman, S.R.: Language models don’t always say what they think: unfaithful explanations in chain-of-thought prompting. arXiv:2305.04388 (2023)
- Li, S., Liu, H., Dong, T., Zhao, B.Z.H., Xue, M., Zhu, H., Lu, J.: Hidden backdoors in human-centric language models. In: Proceedings of the 2021 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, pp. 3123-3140 (2021)
- Wang, J., Hu, X., Hou, W., Chen, H., Zheng, R., Wang, Y., Yang, L., Huang, H., Ye, W., Geng, X., et al.: On the robustness of chatgpt: an adversarial and out-of-distribution perspective. arXiv:2302.12095 (2023)
- Han, R., Peng, T., Yang, C., Wang, B., Liu, L., Wan, X.: Is information extraction solved by chatgpt? an analysis of performance, evaluation criteria, robustness and errors. arXiv:2305.14450 (2023)
- Wei, J., Tay, Y., Bommasani, R., Raffel, C., Zoph, B., Borgeaud, S., Yogatama, D., Bosma, M., Zhou, D., Metzler, D., et al.: Emergent abilities of large language models. arXiv:2206.07682 (2022)
- Liu, J., Liu, C., Lv, R., Zhou, K., Zhang, Y.: Is chatgpt a good recommender? a preliminary study. arXiv:2304.10149 (2023)
- Dai, S., Shao, N., Zhao, H., Yu, W., Si, Z., Xu, C., Sun, Z., Zhang, X., Xu, J.: Uncovering chatgpt’s capabilities in recommender systems. arXiv:2305.02182 (2023)
- Wang, L., Lim, E.-P.: Zero-shot next-item recommendation using large pretrained language models. arXiv:2304.03153 (2023)
- Hou, Y., Zhang, J., Lin, Z., Lu, H., Xie, R., McAuley, J., Zhao, W.X.: Large language models are zero-shot rankers for recommender systems. arXiv:2305.08845 (2023)
- Li, X., Zhang, Y., Malthouse, E.C.: A preliminary study of chatgpt on news recommendation: personalization, provider fairness, fake news. arXiv:2306.10702 (2023)
- Dong, Q., Li, L., Dai, D., Zheng, C., Wu, Z., Chang, B., Sun, X., Xu, J., Sui, Z.: A survey for in-context learning. arXiv:2301.00234 (2022)
- Dai, D., Sun, Y., Dong, L., Hao, Y., Sui, Z., Wei, F.: Why can gpt learn in-context? language models secretly perform gradient descent as meta optimizers. arXiv:2212.10559 (2022)
- Min, S., Lyu, X., Holtzman, A., Artetxe, M., Lewis, M., Hajishirzi, H., Zettlemoyer, L.: Rethinking the role of demonstrations: What makes in-context learning work?. arXiv:2202.12837 (2022)
- Levy, I., Bogin, B., Berant, J.: Diverse demonstrations improve in-context compositional generalization. arXiv:2212.06800 (2022)
- Xie, S.M., Raghunathan, A., Liang, P., Ma, T.: An explanation of in-context learning as implicit bayesian inference. In: International Conference on Learning Representations
- Olsson, C., Elhage, N., Nanda, N., Joseph, N., DasSarma, N., Henighan, T., Mann, B., Askell, A., Bai, Y., Chen, A., et al.: In-context learning and induction heads. arXiv:2209.11895 (2022)
- Akyürek, E., Schuurmans, D., Andreas, J., Ma, T., Zhou, D.: What learning algorithm is in-context learning? investigations with linear models. arXiv:2211.15661 (2022)
- Geng, S., Liu, S., Fu, Z., Ge, Y., Zhang, Y.: Recommendation as language processing (rlp): a unified pretrain, personalized prompt & predict paradigm (p5). In: Proceedings of the 16th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, pp. 299-315 (2022)
- Cui, Z., Ma, J., Zhou, C., Zhou, J., Yang, H.: M6-rec: generative pretrained language models are openended recommender systems. arXiv:2205.08084 (2022)
- Liu, S., Gao, C., Chen, Y., Jin, D., Li, Y.: Learnable embedding sizes for recommender systems. arXiv:2101.07577 (2021)
- Liu, H., Zhao, X., Wang, C., Liu, X., Tang, J.: Automated embedding size search in deep recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 43rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 2307-2316 (2020)
- Deng, W., Pan, J., Zhou, T., Kong, D., Flores, A., Lin, G.: Deeplight: deep lightweight feature interactions for accelerating ctr predictions in ad serving. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, pp. 922-930 (2021)
- Ginart, A.A., Naumov, M., Mudigere, D., Yang, J., Zou, J.: Mixed dimension embeddings with application to memory-efficient recommendation systems. In: 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), pp. 2786-2791 (2021). IEEE
- Wang, Y., Zhao, X., Xu, T., Wu, X.: Autofield: automating feature selection in deep recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022, pp. 1977-1986 (2022)
- Lin, W., Zhao, X., Wang, Y., Xu, T., Wu, X.: Adafs: adaptive feature selection in deep recommender system. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 3309-3317 (2022)
- Tsang, M., Cheng, D., Liu, H., Feng, X., Zhou, E., Liu, Y.: Feature interaction interpretability: a case for explaining ad-recommendation systems via neural interaction detection. arXiv:2006.10966 (2020)
- Yuanfei, L., Mengshuo, W., Hao, Z., Quanming, Y., WeiWei, T., Yuqiang, C., Qiang, Y., Wenyuan, D.: Autocross: automatic feature crossing for tabular data in real-world applications. arXiv:1904.12857 (2019)
- Liu, B., Zhu, C., Li, G., Zhang, W., Lai, J., Tang, R., He, X., Li, Z., Yu, Y.: Autofis: automatic feature interaction selection in factorization models for click-through rate prediction. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 26362645 (2020)
- Liu, B., Xue, N., Guo, H., Tang, R., Zafeiriou, S., He, X., Li, Z.: Autogroup: automatic feature grouping for modelling explicit high-order feature interactions in ctr prediction. In: Proceedings of the 43rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 199208 (2020)
- Chen, Y., Ren, P., Wang, Y., Rijke, M.: Bayesian personalized feature interaction selection for factorization machines. In: Proceedings of the 42nd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 665-674 (2019)
- Xie, Y., Wang, Z., Li, Y., Ding, B., Gürel, N.M., Zhang, C., Huang, M., Lin, W., Zhou, J.: Fives: feature interaction via edge search for large-scale tabular data. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 3795-3805 (2021)
- Su, Y., Zhang, R., Erfani, S., Xu, Z.: Detecting beneficial feature interactions for recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, pp. 4357-4365 (2021)
- Song, Q., Cheng, D., Zhou, H., Yang, J., Tian, Y., Hu, X.: Towards automated neural interaction discovery for click-through rate prediction. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 945-955 (2020)
- Zhao, P., Xiao, K., Zhang, Y., Bian, K., Yan, W.: Ameir: automatic behavior modeling, interaction exploration and mlp investigation in the recommender system. In: IJCAI, pp. 2104-2110 (2021)
- Wei, Z., Wang, X., Zhu, W.: Autoias: automatic integrated architecture searcher for click-trough rate prediction. In: Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, pp. 2101-2110 (2021)
- Cheng, M., Liu, Z., Liu, Q., Ge, S., Chen, E.: Towards automatic discovering of deep hybrid network architecture for sequential recommendation. In: Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022, pp. 1923-1932 (2022)
- Yu, C., Liu, X., Tang, C., Feng, W., Lv, J.: Gpt-nas: Neural architecture search with the generative pre-trained model. arXiv:2305.05351 (2023)
- Ying, C., Klein, A., Christiansen, E., Real, E., Murphy, K., Hutter, F.: Nas-bench-101: Towards reproducible neural architecture search. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 7105-7114 (2019). PMLR
- Zheng, M., Su, X., You, S., Wang, F., Qian, C., Xu, C., Albanie, S.: Can gpt-4 perform neural architecture search? arXiv:2304.10970 (2023)
- Nasir, M.U., Earle, S., Togelius, J., James, S., Cleghorn, C.: Llmatic: Neural architecture search via large language models and quality-diversity optimization. arXiv:2306.01102 (2023)
- Chen, A., Dohan, D.M., So, D.R.: Evoprompting: language models for code-level neural architecture search. arXiv:2302.14838 (2023)
- Shang, L., Lu, Z., Li, H.: Neural responding machine for short-text conversation. arXiv:1503.02364 (2015)
- Vinyals, O., Le, Q.: A neural conversational model. arXiv:1506.05869 (2015)
- Sordoni, A., Galley, M., Auli, M., Brockett, C., Ji, Y., Mitchell, M., Nie, J.-Y., Gao, J., Dolan, B.: A neural network approach to context-sensitive generation of conversational responses. arXiv:1506.06714 (2015)
- Wu, W., Yan, R.: Deep chit-chat: deep learning for chatbots. In: Proceedings of the 42 nd international ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 1413-1414 (2019)
- Qiu, X., Huang, X.: Convolutional neural tensor network architecture for community-based question answering. In: Twenty-Fourth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2015)
- Wan, S., Lan, Y., Guo, J., Xu, J., Pang, L., Cheng, X.: A deep architecture for semantic matching with multiple positional sentence representations. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 30 (2016)
- Greco, C., Suglia, A., Basile, P., Semeraro, G.: Converse-et-impera: exploiting deep learning and hierarchical reinforcement learning for conversational recommender systems. In: AI* IA 2017 Advances in Artificial Intelligence: XVIth International Conference of the Italian Association for Artificial Intelligence, Bari, Italy, November 14-17, 2017, Proceedings 16, pp. 372-386 (2017). Springer
- Yao, K., Zweig, G., Hwang, M.-Y., Shi, Y., Yu, D.: Recurrent neural networks for language understanding. In: Interspeech, pp. 2524-2528 (2013)
- Mesnil, G., He, X., Deng, L., Bengio, Y.: Investigation of recurrent-neural-network architectures and learning methods for spoken language understanding. In: Interspeech, pp. 3771-3775 (2013)
- Goddeau, D., Meng, H., Polifroni, J., Seneff, S., Busayapongchai, S.: A form-based dialogue manager for spoken language applications. In: Proceeding of Fourth International Conference on Spoken Language Processing. ICSLP’96, vol. 2, pp. 701-704 (1996). IEEE
- Henderson, M., Thomson, B., Young, S.: Deep neural network approach for the dialog state tracking challenge. In: Proceedings of the SIGDIAL 2013 Conference, pp. 467-471 (2013)
- Mrkšić, N., Séaghdha, D.O., Wen, T.-H., Thomson, B., Young, S.: Neural belief tracker: data-driven dialogue state tracking. arXiv:1606.03777 (2016)
- Cuayáhuitl, H., Keizer, S., Lemon, O.: Strategic dialogue management via deep reinforcement learning. arXiv:1511.08099 (2015)
- Zhou, H., Huang, M., Zhu, X.: Context-aware natural language generation for spoken dialogue systems. In: Proceedings of COLING 2016, the 26th International Conference on Computational Linguistics: Technical Papers, pp. 2032-2041 (2016)
- Dušek, O., Jurčíćek, F.: Sequence-to-sequence generation for spoken dialogue via deep syntax trees and strings. arXiv:1606.05491 (2016)
- Wen, T.-H., Vandyke, D., Mrksic, N., Gasic, M., Rojas-Barahona, L.M., Su, P.-H., Ultes, S., Young, S.: A network-based end-to-end trainable task-oriented dialogue system. arXiv:1604.04562 (2016)
- Bordes, A., Boureau, Y.-L., Weston, J.: Learning end-to-end goal-oriented dialog. arXiv:1605.07683 (2016)
- Zhang, Y., Sun, S., Galley, M., Chen, Y.-C., Brockett, C., Gao, X., Gao, J., Liu, J., Dolan, B.: Dialogpt: large-scale generative pre-training for conversational response generation. arXiv:1911.00536 (2019)
- Lei, W., He, X., Miao, Y., Wu, Q., Hong, R., Kan, M.-Y., Chua, T.-S.: Estimation-action-reflection: towards deep interaction between conversational and recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, pp. 304-312 (2020)
- Lei, W., Zhang, G., He, X., Miao, Y., Wang, X., Chen, L., Chua, T.-S.: Interactive path reasoning on graph for conversational recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 2073-2083 (2020)
- Deng, Y., Li, Y., Sun, F., Ding, B., Lam, W.: Unified conversational recommendation policy learning via graph-based reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 44th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 1431-1441 (2021)
- Li, R., Ebrahimi Kahou, S., Schulz, H., Michalski, V., Charlin, L., Pal, C.: Towards deep conversational recommendations. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 31 (2018)
- Wang, T.-C., Su, S.-Y., Chen, Y.-N.: Barcor: Towards a unified framework for conversational recommendation systems. arXiv:2203.14257 (2022)
- Wang, X., Zhou, K., Wen, J.-R., Zhao, W.X.: Towards unified conversational recommender systems via knowledge-enhanced prompt learning. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 1929-1937 (2022)
- Wang, L., Hu, H., Sha, L., Xu, C., Jiang, D., Wong, K.-F.: Recindial: a unified framework for conversational recommendation with pretrained language models. In: Proceedings of the 2nd Conference of the Asia-Pacific Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 12th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, pp. 489-500 (2022)
- Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: Bert: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv:1810.04805 (2018)
- Radford, A., Narasimhan, K., Salimans, T., Sutskever, I., et al.: Improving language understanding by generative pre-training (2018)
- Gao, Y., Sheng, T., Xiang, Y., Xiong, Y., Wang, H., Zhang, J.: Chat-rec: towards interactive and explainable llms-augmented recommender system. arXiv:2303.14524 (2023)
- Friedman, L., Ahuja, S., Allen, D., Tan, T., Sidahmed, H., Long, C., Xie, J., Schubiner, G., Patel, A., Lara, H., et al.: Leveraging large language models in conversational recommender systems. arXiv:2305.07961 (2023)
- Wang, X., Tang, X., Zhao, W.X., Wang, J., Wen, J.-R.: Rethinking the evaluation for conversational recommendation in the era of large language models. arXiv:2305.13112 (2023)
- Yao, S., Yu, D., Zhao, J., Shafran, I., Griffiths, T.L., Cao, Y., Narasimhan, K.: Tree of thoughts: deliberate problem solving with large language models. arXiv:2305.10601 (2023)
- Wang, L., Xu, W., Lan, Y., Hu, Z., Lan, Y., Lee, R.K.-W., Lim, E.-P.: Plan-and-solve prompting: improving zero-shot chain-of-thought reasoning by large language models. arXiv:2305.04091 (2023)
- Yao, S., Zhao, J., Yu, D., Du, N., Shafran, I., Narasimhan, K., Cao, Y.: React: synergizing reasoning and acting in language models. arXiv:2210.03629 (2022)
- Madaan, A., Tandon, N., Clark, P., Yang, Y.: Memory-assisted prompt editing to improve gpt-3 after deployment. arXiv:2201.06009 (2022)
- Qin, Y., Hu, S., Lin, Y., Chen, W., Ding, N., Cui, G., Zeng, Z., Huang, Y., Xiao, C., Han, C., et al.: Tool learning with foundation models. arXiv:2304.08354 (2023)
- Mialon, G., Dessì, R., Lomeli, M., Nalmpantis, C., Pasunuru, R., Raileanu, R., Rozière, B., Schick, T., Dwivedi-Yu, J., Celikyilmaz, A., et al.: Augmented language models: a survey. arXiv:2302.07842 (2023)
- Yang, K., Peng, N., Tian, Y., Klein, D.: Re3: Generating longer stories with recursive reprompting and revision. arXiv:2210.06774 (2022)
- Schick, T., Dwivedi-Yu, J., Jiang, Z., Petroni, F., Lewis, P., Izacard, G., You, Q., Nalmpantis, C., Grave, E., Riedel, S.: Peer: a collaborative language model. arXiv:2208.11663 (2022)
- Hao, Y., Song, H., Dong, L., Huang, S., Chi, Z., Wang, W., Ma, S., Wei, F.: Language models are general-purpose interfaces. arXiv:2206.06336 (2022)
- Izacard, G., Lewis, P., Lomeli, M., Hosseini, L., Petroni, F., Schick, T., Dwivedi-Yu, J., Joulin, A., Riedel, S., Grave, E.: Few-shot learning with retrieval augmented language models. arXiv:2208.03299 (2022)
- Thoppilan, R., De Freitas, D., Hall, J., Shazeer, N., Kulshreshtha, A., Cheng, H.-T., Jin, A., Bos, T., Baker, L., Du, Y., et al.: Lamda: language models for dialog applications. arXiv:2201.08239 (2022)
- Nakano, R., Hilton, J., Balaji, S., Wu, J., Ouyang, L., Kim, C., Hesse, C., Jain, S., Kosaraju, V., Saunders, W., et al.: Webgpt: browser-assisted question-answering with human feedback. arXiv:2112.09332 (2021)
- Liu, R., Wei, J., Gu, S.S., Wu, T.-Y., Vosoughi, S., Cui, C., Zhou, D., Dai, A.M.: Mind’s eye: grounded language model reasoning through simulation. arXiv:2210.05359 (2022)
- Gao, L., Madaan, A., Zhou, S., Alon, U., Liu, P., Yang, Y., Callan, J., Neubig, G.: Pal: Program-aided language models. arXiv:2211.10435 (2022)
- Ahn, M., Brohan, A., Brown, N., Chebotar, Y., Cortes, O., David, B., Finn, C., Fu, C., Gopalakrishnan, K., Hausman, K., et al.: Do as i can, not as i say: grounding language in robotic affordances. arXiv:2204.01691 (2022)
- Shen, Y., Song, K., Tan, X., Li, D., Lu, W., Zhuang, Y.: Hugginggpt: solving ai tasks with chatgpt and its friends in huggingface. arXiv:2303.17580 (2023)
- Wu, C., Yin, S., Qi, W., Wang, X., Tang, Z., Duan, N.: Visual chatgpt: talking, drawing and editing with visual foundation models. arXiv:2303.04671 (2023)
- Liang, Y., Wu, C., Song, T., Wu, W., Xia, Y., Liu, Y., Ou, Y., Lu, S., Ji, L., Mao, S., et al.: Taskmatrix. ai: completing tasks by connecting foundation models with millions of apis. arXiv:2303.16434 (2023)
- Schick, T., Dwivedi-Yu, J., Dessì, R., Raileanu, R., Lomeli, M., Zettlemoyer, L., Cancedda, N., Scialom, T.: Toolformer: language models can teach themselves to use tools. arXiv:2302.04761 (2023)
- Li, J., Li, D., Xiong, C., Hoi, S.: Blip: Bootstrapping language-image pre-training for unified visionlanguage understanding and generation. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1288812900 (2022). PMLR
- Rombach, R., Blattmann, A., Lorenz, D., Esser, P., Ommer, B.: High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10684-10695 (2022)
- Cai, T., Wang, X., Ma, T., Chen, X., Zhou, D.: Large language models as tool makers. arXiv:2305.17126 (2023)
- Shuster, K., Xu, J., Komeili, M., Ju, D., Smith, E.M., Roller, S., Ung, M., Chen, M., Arora, K., Lane, J., et al.: Blenderbot 3: a deployed conversational agent that continually learns to responsibly engage. arXiv:2208.03188 (2022)
- Liu, J., Jin, J., Wang, Z., Cheng, J., Dou, Z., Wen, J.-R.: Reta-llm: a retrieval-augmented large language model toolkit. arXiv:2306.05212 (2023)
- Pan, S., Luo, L., Wang, Y., Chen, C., Wang, J., Wu, X.: Unifying large language models and knowledge graphs: a roadmap. arXiv:2306.08302 (2023)
- Vempati, S., Malayil, K.T., Sruthi, V., Sandeep, R.: Enabling hyper-personalisation: automated ad creative generation and ranking for fashion e-commerce. In: Fashion Recommender Systems, pp. 25-48 (2020). Springer
- Thomaidou, S., Lourentzou, I., Katsivelis-Perakis, P., Vazirgiannis, M.: Automated snippet generation for online advertising. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, pp. 1841-1844 (2013)
- Zhang, X., Zou, Y., Zhang, H., Zhou, J., Diao, S., Chen, J., Ding, Z., He, Z., He, X., Xiao, Y., et al.: Automatic product copywriting for e-commerce. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 36, pp. 12423-12431 (2022)
- Lei, Z., Zhang, C., Xu, X., Wu, W., Niu, Z.-Y., Wu, H., Wang, H., Yang, Y., Li, S.: Plato-ad: a unified advertisement text generation framework with multi-task prompt learning. In: Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: Industry Track, pp. 512-520 (2022)
- Bartz, K., Barr, C., Aijaz, A.: Natural language generation for sponsored-search advertisements. In: Proceedings of the 9th ACM Conference on Electronic Commerce, pp. 1-9 (2008)
- Fujita, A., Ikushima, K., Sato, S., Kamite, R., Ishiyama, K., Tamachi, O.: Automatic generation of listing ads by reusing promotional texts. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Electronic Commerce: Roadmap for the Future of Electronic Business, pp. 179-188 (2010)
- Hughes, J.W., Chang, K.-h., Zhang, R.: Generating better search engine text advertisements with deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 2269-2277 (2019)
- Wang, X., Gu, X., Cao, J., Zhao, Z., Yan, Y., Middha, B., Xie, X.: Reinforcing pretrained models for generating attractive text advertisements. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 3697-3707 (2021)
- Chen, C., Wang, X., Yi, X., Wu, F., Xie, X., Yan, R.: Personalized chit-chat generation for recommendation using external chat corpora. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 2721-2731 (2022)
- Zhang, C., Zhou, J., Zang, X., Xu, Q., Yin, L., He, X., Liu, L., Xiong, H., Dou, D.: Chase: commonsenseenriched advertising on search engine with explicit knowledge. In: Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, pp. 4352-4361 (2021)
- Kanungo, Y.S., Negi, S., Rajan, A.: Ad headline generation using self-critical masked language model. In: Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies: Industry Papers, pp. 263-271 (2021)
- Wei, P., Yang, X., Liu, S., Wang, L., Zheng, B.: Creater: ctr-driven advertising text generation with controlled pre-training and contrastive fine-tuning. arXiv:2205.08943 (2022)
- Kanungo, Y.S., Das, G., Negi, S.: Cobart: controlled, optimized, bidirectional and auto-regressive transformer for ad headline generation. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 3127-3136 (2022)
- Chen, Q., Lin, J., Zhang, Y., Yang, H., Zhou, J., Tang, J.: Towards knowledge-based personalized product description generation in e-commerce. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 3040-3050 (2019)
- Cao, Y., Li, S., Liu, Y., Yan, Z., Dai, Y., Yu, P.S., Sun, L.: A comprehensive survey of ai-generated content (aigc): a history of generative ai from gan to chatgpt. arXiv:2303.04226 (2023)
- Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., Bengio, Y.: Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 27 (2014)
- Kingma, D.P., Welling, M.: Auto-encoding variational bayes. arXiv:1312.6114 (2013)
- Dinh, L., Krueger, D., Bengio, Y.: Nice: non-linear independent components estimation. arXiv:1410.8516 (2014)
- Ho, J., Jain, A., Abbeel, P.: Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 6840-6851 (2020)
- Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., Weissenborn, D., Zhai, X., Unterthiner, T., Dehghani, M., Minderer, M., Heigold, G., Gelly, S., et al.: An image is worth
words: transformers for image recognition at scale. In: International Conference on Learning Representations - Liu, Z., Lin, Y., Cao, Y., Hu, H., Wei, Y., Zhang, Z., Lin, S., Guo, B.: Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 10012-10022 (2021)
- Radford, A., Kim, J.W., Hallacy, C., Ramesh, A., Goh, G., Agarwal, S., Sastry, G., Askell, A., Mishkin, P., Clark, J., et al.: Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 8748-8763 (2021). PMLR
- Chen, M., Tan, X., Li, B., Liu, Y., Qin, T., Liu, T.-Y., et al.: Adaspeech: adaptive text to speech for custom voice. In: International Conference on Learning Representations
- Li, X., Taheri, A., Tu, L., Gimpel, K.: Commonsense knowledge base completion. In: Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (vol. 1: long papers), pp. 1445-1455 (2016)
- Feng, Z., Guo, D., Tang, D., Duan, N., Feng, X., Gong, M., Shou, L., Qin, B., Liu, T., Jiang, D., et al.: Codebert: a pre-trained model for programming and natural languages. In: Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2020, pp. 1536-1547 (2020)
- OpenAI: ChatGPT: A Large-Scale Generative Model for Conversation. OpenAI Blog (2020)
- Ramesh, A., Pavlov, M., Goh, G., Gray, S., Voss, C., Radford, A., Chen, M., Sutskever, I.: Zero-shot text-to-image generation. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 8821-8831 (2021). PMLR
- Chen, M., Tworek, J., Jun, H., Yuan, Q., Pinto, H.P.d.O., Kaplan, J., Edwards, H., Burda, Y., Joseph, N., Brockman, G., et al.: Evaluating large language models trained on code. arXiv:2107.03374 (2021)
- Midjourney: Midjourney. Retrieved from. https://midjourney.com (2022)
- Wang, W., Lin, X., Feng, F., He, X., Chua, T.-S.: Generative recommendation: towards next-generation recommender paradigm. arXiv:2304.03516 (2023)
- Borji, A.: A categorical archive of chatgpt failures. arXiv:2302.03494 (2023)
- Carlini, N., Tramer, F., Wallace, E., et al.: Extracting training data from large language models. (2021)
- Radford, A., Wu, J., Child, R., Luan, D., Amodei, D., Sutskever, I., et al.: Language models are unsupervised multitask learners
- Hu, E.J., Wallis, P., Allen-Zhu, Z., Li, Y., Wang, S., Wang, L., Chen, W., et al.: Lora: low-rank adaptation of large language models. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2021)
- Dettmers, T., Pagnoni, A., Holtzman, A., Zettlemoyer, L.: Qlora: Efficient finetuning of quantized llms. arXiv:2305.14314 (2023)
- Bai, Y., Kadavath, S., Kundu, S., Askell, A., Kernion, J., Jones, A., Chen, A., Goldie, A., Mirhoseini, A., McKinnon, C., et al.: Constitutional ai: Harmlessness from ai feedback. arXiv:2212.08073 (2022)
المؤلفون والانتماءات
جين تشين@ust.hk
تشنغ ليو
zhengliu1026@gmail.com
شو هوانغ
xuhuangcs@mail.ustc.edu.cn
تشينوانغ وو
wcw1996@mail.ustc.edu.cn
تشي ليو
qiliu67@mail.ustc.edu.cn
جانغوي جيانغ
gwjiang@mail.ustc.edu.cn
يوانهاو بو
puyuanhao@mail.ustc.edu.cn
يوشوان لي
lyx180812@mail.ustc.edu.cn
شياولونغ تشين
chenxiaolong@mail.ustc.edu.cn
شينغمي وانغ
xingmeiwang@mail.ustc.edu.cn
كاي زينغ
zhengkai@uestc.edu.cn
ديفو ليان
liandefu@ustc.edu.cn
إنهونغ تشين
cheneh@ustc.edu.cn
1 جامعة هونغ كونغ للعلوم والتكنولوجيا، هونغ كونغ، الصين
أكاديمية بكين للذكاء الاصطناعي، بكين، الصين
3 جامعة العلوم والتكنولوجيا في الصين، هيفي، الصين
4 جامعة علوم وتكنولوجيا الإلكترونيات في الصين، تشنغدو، الصين
- جين تشين وزينغ ليو ساهموا بالتساوي في هذا العمل.
- معلومات المؤلف الموسعة متاحة في الصفحة الأخيرة من المقال
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-024-01276-1
Publication Date: 2024-06-28
When large language models meet personalization: perspectives of challenges and opportunities
Published online: 28 June 2024
© The Author(s) 2024
Abstract
The advent of large language models marks a revolutionary breakthrough in artificial intelligence. With the unprecedented scale of training and model parameters, the capability of large language models has been dramatically improved, leading to human-like performances in understanding, language synthesizing, common-sense reasoning, etc. Such a major leap forward in general AI capacity will fundamentally change the pattern of how personalization is conducted. For one thing, it will reform the way of interaction between humans and personalization systems. Instead of being a passive medium of information filtering, like conventional recommender systems and search engines, large language models present the foundation for active user engagement. On top of such a new foundation, users’ requests can be proactively explored, and users’ required information can be delivered in a natural, interactable, and explainable way. For another thing, it will also considerably expand the scope of personalization, making it grow from the sole function of collecting personalized information to the compound function of providing personalized services. By leveraging large language models as a general-purpose interface, the personalization systems may compile user’s requests into plans, calls the functions of external tools (e.g., search engines, calculators, service APIs, etc.) to execute the plans, and integrate the tools’ outputs to complete the end-to-end personalization tasks. Today, large language models are still being rapidly developed, whereas the application in personalization is largely unexplored. Therefore, we consider it to be right the time to review the challenges in personalization and the opportunities to address them with large language models. In particular, we dedicate this perspective paper to the discussion of the following aspects: the development and challenges for the existing personalization system, the newly emerged capabilities of large language models, and the potential ways of making use of large language models for personalization.
1 Introduction
various tools is greatly enhanced by the capabilities of large language models, significantly broadening the possibilities and scenarios for personalized systems. By transforming user requirements into plans, including understanding, generating, and executing them, users can access a diverse range of information and services. Importantly, users remain unaware of the intricate and complex transformations happening behind the scenes, as they experience a seamless end-to-end model. The potential of large language models in personal is largely unexplored.

2 Background overview
2.1 Personalization techniques
2.1.1 Recommender systems
modeling sequential data in recommender systems. These models excel in capturing temporal dependencies and context, making them well-suited for tasks like next-item recommendation and session-based recommendation. Sequential-based models can take into account the order in which items are interacted with and learn patterns of user behavior that evolve. Furthermore, the rise of language models like BERT has further advanced recommender systems by enabling a better understanding of both natural language features and user sequential behaviors [22]. These language models can capture deep semantic representations and world knowledge, enriching the recommendation process and facilitating more personalized and context-aware recommendations. Overall, the application of deep learning techniques in recommender systems has opened new avenues for research and innovation, promising to revolutionize the field of personalized recommendations and enhance user experiences.
2.1.2 Personalized assistance
2.2 Large language models
notes of users’ important information within their memory, make personalized plans based on memorized information when new demands are raised, and execute plans by leveraging tools like search engines and recommendation systems.
3 LLMs for personalization

4 LLMs as knowledge base
prompts to predict the tail entity. As for the another important task, i.e., knowledge graph construction, which refers to creating a structured representation of knowledge, LLMs can be applied in the process of constructing knowledge graphs, including entity discovery [71, 72], coreference resolution [73, 74] and relation extraction [75, 76]. LLMs can also achieve the end-to-end construction [
5 LLMs as content interpreter
| Approach | Knowledge | Task | LLM backbone | Datasets |
| KAR [80] | Factual knowledge | CTR prediction & Rerank | gpt-3.5-turbo | Ml-1M, Amazon Book |
| LLMRec [81] | User-item interactions, side information | TopK Recommendation | gpt-3.5-turbo | ML, Netflix |
| KRec [82] | Complementary relationship | CTR Prediction | ChatGPT 3.5, ChatGLM 2 | Alipay Data |
5.1 Conventional content interpreter

5.2 Language model based content interpreter
6 LLMs as explainer
| Approach | Task | LLM backbone | Tuning strategy | Datasets |
| TALLRe [119] | Sequential recommendation | LLaMA-7B | Instruct tuning & Fine tuning | MovieLens100k, BookCrossing |
| LLMs-Rec [120] | Rating prediction | Flan-T5-Base, Flan-T5-XXL | Fine tuning | MovieLens-1M, Amazon book |
| PALR [121] | Item recommendation | LLaMa-7B | Instruction tuning | MovieLens-1M, Amazon beauty |
| InstructRec [122] | Sequential recommendation personalized search | Flan-T5-XL | Instruction tuning | Amazon-Games, CDs |
7 LLMs as common system reasoner
intelligence for decision-making and problem-solving. By providing the models with the ‘chain of thoughts’ [38], such as prompting with ‘let us think about it step by step’, the large language models exhibit emergent abilities for reasoning and can arrive at conclusions or judgments according to the evidence or logics. Accordingly, for recommender systems, large language models are capable of reasoning to help user interest mining, thus improving performance.
7.1 Making direct recommendations
- The aforementioned studies primarily focused on evaluating zero-shot/few-shot recommenders using open-domain datasets, predominantly in domains such as movies and books. Large language models are trained on extensive open-domain datasets, enabling them to possess a significant amount of common-sense knowledge, including information about well-known movies. However, when it comes to private domain data, such as e-commerce products or specific locations, the ability of zero-shot recommenders lacks of validation, which is expected to be challenging.
- Current testing methods necessitate the integration of additional modules to validate the performance of zero-shot recommenders for specific tasks. In particular, for ranking tasks that involve providing a list of items in order of preference, a candidate generation module is employed to narrow down the pool of items [164] and [165]. Generative-based models like gpt-3.5-turbo generate results in a generative manner rather than relying on recall from existing memories, thus requiring additional modules to implement ID-based item recommendations.
- From the perspective of recommendation performance, zero-shot recommenders exhibit some capabilities and few-shot learners perform better. However, there still exists a substantial gap when compared to traditional recommendation models, particularly finetuned large language models designed specifically for recommenders, such as P5 [174] and M6-Rec [175]. This highlights that large language models do not possess a significant advantage in personalized modeling.
| Approach | LLM backbone | Task | Metric | Datasets | ICL | COT | |||||||
| [162] | gpt-3.5-turbo | Rating prediction sequential recommendation direct recommendation explanation generation review summarization |
|
Amazon beauty |
|
||||||||
| [163] |
|
Point-wise pairwise list-wise | NDCG,MRR |
|
|
||||||||
| [120] | Flan-U-PALM gpt-3.5-turbo text-davinci-003 | Rating prediction ranking prediction |
|
|
|
||||||||
| [164] | Text-davinci-003 | Reranking | NDCG,HR | MovieLens 100 K |
|
|
|||||||
| [165] | gpt-3.5-turbo | Reranking | NDCG |
|
|
||||||||
| [166] | gpt-3.5-turbo | Reranking | Precision | MIND |
|

7.2 Reasoning for automated selection
efficiency and interpretability, one approach is to integrate the LLMs into certain search strategies, where the genetic algorithm guides the search process and LLMs generate the candidate crossovers. LLMatic [196] and EvoPrompting [197] use code-LLMs as mutation and crossover operators for a genetic NAS algorithm. During the evolution process, each generation has a certain probability of deciding whether to perform crossover or mutation to produce new offspring. Crossover and mutation are generated by prompting LLMs. Such a solution integrates LLM into the genetic search algorithm, which would achieve better performances than direct reasoning over the whole space.
8 LLMs as conversational agent

benefits the tool-using capability. Subsequent studies like ToT [228], Plan-and-Solve [229] and ReAct [230] have proposed more advanced techniques for prompt design to assist in guiding LLM to engage in deeper thinking and tool planning.
9 Tool-learning and its applications in recommendation
9.1 LLM-based tool learning
- Tool-augmented learning treats specialized tools as assistants in order for improving the quality and accuracy of tasks, or Tool for AI;
- Tool-oriented learning focuses more on training models to effectively use tools, controlling and optimizing tool-applying processes, or AI for Tool.
Tool learning has found applications in various fields, and this section primarily focuses on tool learning paradigms based on large language models (LLMs). While recent works often involve a combination of these two perspectives, we do not specifically categorize each work into one type. LLMs, such as GPT, are well-suited for tool learning applications [233]. With their powerful natural language processing capabilities, LLMs can break down complex tasks into smaller sub-tasks and convert them into executable instructions. Specialized tools allow LLMs to access knowledge that is beyond their own understanding. By integrating specialized tools, LLMs can better understand and then address complex problems, offering more accurate and efficient solutions for personalized systems.
9.2 Applications in personalization scenarios
| Approach | Tool usage | LLM backbone | Task |
| Re3 [234] | LLM | gpt3-instruct-175B gpt3-instruct13B | Long stories generation |
| PEER [235] | LLM | LM-Adapted T5 | Editions, citations, quotes |
| METALM [236] | Pretrained encoders with diverse modalities | Transformer (pretrained from scratch) | language-only tasks visionlanguage tasks |
| Atlas [237] | Dense retriever | T5 | Knowledge-intensive language tasks massively-multitask language understanding question answering fact checking |
| LaMDA [238] | Retriever translator calculator | Decoder-only transformer | Dialog |
| WebGPT [239] | Web browser | gpt-3 | Question answering |
| Mind’s Eye [240] | Physics engine text-to-code LM | gpt-3 PaLM | Reasoning |
| PAL [241] | Python interpreter | CODEX(code-davinci-002) | Mathematical symbolic algorithmic reasoning |
| SayCan [242] | Robots | PaLM | Real-world robotic tasks |
| HuggingGPT [243] | AI models in hugging face community | gpt-3.5-turbo text-davinci-003 gpt4 | Image classification image captioning object detection etc. |
| Auto-GPT | Web browser | gpt-3.5-turbo text-davinci-003 gpt4 | User-specified tasks |
| Visual ChatGPT [244] Taskmatrix.AI [245] | Visual foundation models customized models with unified API form | text-davinci-003 | Visual customized tasks |
| ReAct [230] | Wikipedia API | PaLM-540B | Question answering face verificaiton |
| Toolformer [246] | Calculator Q&A system search engine translation system calendar | GPT-J | Downstream tasks |
relationships can enhance the knowledge available to LLMs, enabling more accurate and tailored recommendations.
10 LLMs as personalized content creator

models memorizing sensitive user data. Previous work [284] has demonstrated that large language models, especially GPT-2 [285], memorize and leak individual training examples. This emphasizes the need for strict user approval and careful handling of annotator data to mitigate privacy risks. It is crucial to develop new techniques that prioritize privacy preservation during the training process.
11 Open challenges
11.1 Deployment difficulties
11.1.1 Industrial challenges
11.1.2 Laborious data collection
researchers and practitioners can guide the model to produce outputs that better cater to personalized applications, thereby maximizing performance and effectiveness.
11.2 Capacities of LLMs
11.2.1 Long text modeling
11.2.2 Interpretability and explainability
that unveil the inner workings of language models, facilitate the generation of meaningful and accurate interpretations, and enable robust evaluation methods is the main focus. By providing transparent and interpretable recommendations, users can establish trust, understand the reasoning behind the recommendations, and make informed decisions.
11.3 Evaluation
11.3.1 Tools and metrics
11.3.2 Trade-off between helpfulness, honesty, harmlessness
protected, with strict user permissions for sharing their personal information. For discrimination, large language models may inevitably reflect biases inherent in the training data, leading to discriminatory recommendations. Considering the biased user and item distribution, which is much more significant in recommender systems with the long-tail effect, where biased user and item distribution can lead to decisions that favor majority choices, resulting in discrimination against certain users. The final concern revolves around ethical considerations. Harmful messages, if clicked by users unconsciously, can guide large language models toward generating similar harmful content. However, when assisting in personalized decision-making, it is essential for large language models to have the capability to minimize exposure to harmful messages and guide users in a responsible manner. Approaches like constructing a Constitutional AI [288], where critiques, revisions, and supervised Learning are adopted for better training models, may offer valuable insights.
12 Conclusion
Declarations
Ethical Approval This research does not involve human participants or pose potential harm to individuals. As such, formal ethical approval was not required. However, we would like to emphasize our commitment to ethical research practices and confirm that the study adheres to the ethical guidelines and principles set forth in ACM Code of Ethics.
References
- Zhao, W.X., Zhou, K., Li, J., Tang, T., Wang, X., Hou, Y., Min, Y., Zhang, B., Zhang, J., Dong, Z., et al.: A survey of large language models. arXiv:2303.18223 (2023)
- Huang, J., Chang, K.C.-C.: Towards reasoning in large language models: a survey. arXiv:2212.10403 (2022)
- Brown, T., Mann, B., Ryder, N., Subbiah, M., Kaplan, J.D., Dhariwal, P., Neelakantan, A., Shyam, P., Sastry, G., Askell, A., et al.: Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 1877-1901 (2020)
- Salemi, A., Mysore, S., Bendersky, M., Zamani, H.: Lamp: When large language models meet personalization. arXiv:2304.11406 (2023)
- Wu, L., Zheng, Z., Qiu, Z., Wang, H., Gu, H., Shen, T., Qin, C., Zhu, C., Zhu, H., Liu, Q., et al.: A survey on large language models for recommendation. arXiv:2305.19860 (2023)
- Lin, J., Dai, X., Xi, Y., Liu, W., Chen, B., Li, X., Zhu, C., Guo, H., Yu, Y., Tang, R., et al.: How can recommender systems benefit from large language models: a survey. arXiv:2306.05817 (2023)
- Fan, W., Zhao, Z., Li, J., Liu, Y., Mei, X., Wang, Y., Tang, J., Li, Q.: Recommender systems in the era of large language models (llms). arXiv:2307.02046 (2023)
- Resnick, P., Iacovou, N., Suchak, M., Bergstrom, P., Riedl, J.: Grouplens: an open architecture for collaborative filtering of netnews. In: Proceedings of the 1994 ACM Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work, pp. 175-186 (1994)
- Pan, R., Zhou, Y., Cao, B., Liu, N.N., Lukose, R., Scholz, M., Yang, Q.: One-class collaborative filtering. In: 2008 Eighth IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, pp. 502-511 (2008). IEEE
- Koren, Y., Bell, R., Volinsky, C.: Matrix factorization techniques for recommender systems. Computer 42(8), 30-37 (2009)
- Wang, J., De Vries, A.P., Reinders, M.J.: Unifying user-based and item-based collaborative filtering approaches by similarity fusion. In: Proceedings of the 29th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 501-508 (2006)
- Pazzani, M.J., Billsus, D.: Content-based recommendation systems. In: The adaptive Web: Methods and Strategies of Web Personalization, pp. 325-341. Springer (2007)
- Wang, C., Blei, D.M.: Collaborative topic modeling for recommending scientific articles. In: Proceedings of the 17th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 448-456 (2011)
- Zhang, F., Yuan, N.J., Lian, D., Xie, X., Ma, W.-Y.: Collaborative knowledge base embedding for recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 353-362 (2016)
- Liu, H., Wu, F., Wang, W., Wang, X., Jiao, P., Wu, C., Xie, X.: Nrpa: neural recommendation with personalized attention. In: Proceedings of the 42nd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 1233-1236 (2019)
- Wang, H., Wang, N., Yeung, D.-Y.: Collaborative deep learning for recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 21th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 1235-1244 (2015)
- Zhou, G., Zhu, X., Song, C., Fan, Y., Zhu, H., Ma, X., Yan, Y., Jin, J., Li, H., Gai, K.: Deep interest network for click-through rate prediction. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 1059-1068 (2018)
- Zhou, G., Mou, N., Fan, Y., Pi, Q., Bian, W., Zhou, C., Zhu, X., Gai, K.: Deep interest evolution network for click-through rate prediction. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 33, pp. 5941-5948 (2019)
- Wang, X., He, X., Wang, M., Feng, F., Chua, T.-S.: Neural graph collaborative filtering. In: Proceedings of the 42 nd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 165-174 (2019)
- Kang, W.-C., McAuley, J.: Self-attentive sequential recommendation. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), pp. 197-206 (2018). IEEE
- Hidasi, B., Karatzoglou, A., Baltrunas, L., Tikk, D.: Session-based recommendations with recurrent neural networks. arXiv:1511.06939 (2015)
- Sun, F., Liu, J., Wu, J., Pei, C., Lin, X., Ou, W., Jiang, P.: Bert4rec: Sequential recommendation with bidirectional encoder representations from transformer. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, pp. 1441-1450 (2019)
- Paschou, M., Sakkopoulos, E.: Personalized assistant apps in healthcare: a systematic review. In: 2019 10th International Conference on Information, Intelligence, Systems and Applications (IISA), pp. 1-8 (2019). IEEE
- Sun, Y., Zhang, Y.: Conversational recommender system. In: The 41st International Acm Sigir Conference on Research & Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 235-244 (2018)
- Jannach, D., Manzoor, A., Cai, W., Chen, L.: A survey on conversational recommender systems. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) 54(5), 1-36 (2021)
- Bengio, Y., Ducharme, R., Vincent, P.: A neural probabilistic language model. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 13 (2000)
- Mikolov, T., Karafiát, M., Burget, L., Cernockỳ, J., Khudanpur, S.: Recurrent neural network based language model. In: Interspeech, vol. 2, pp. 1045-1048 (2010). Makuhari
- Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A.N., Kaiser, Ł., Polosukhin, I.: Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 30 (2017)
- Kenton, J.D.M.-W.C., Toutanova, L.K.: Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In: Proceedings of NAACL-HLT, pp. 4171-4186 (2019)
- Shanahan, M.: Talking about large language models. Commun. ACM 67(2), 68-79 (2024)
- Chowdhery, A., Narang, S., Devlin, J., Bosma, M., Mishra, G., Roberts, A., Barham, P., Chung, H.W., Sutton, C., Gehrmann, S., et al.: Palm: scaling language modeling with pathways. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 24(240), 1-113 (2023)
- Touvron, H., Lavril, T., Izacard, G., Martinet, X., Lachaux, M.-A., Lacroix, T., Rozière, B., Goyal, N., Hambro, E., Azhar, F., et al.: Llama: open and efficient foundation language models. arXiv:2302.13971 (2023)
- Le Scao, T., Wang, T., Hesslow, D., Bekman, S., Bari, M.S., Biderman, S., Elsahar, H., Muennighoff, N., Phang, J., Press, O., et al.: What language model to train if you have one million gpu hours?. In: Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2022, pp. 765-782 (2022)
- Kaplan, J., McCandlish, S., Henighan, T., Brown, T.B., Chess, B., Child, R., Gray, S., Radford, A., Wu, J., Amodei, D.: Scaling laws for neural language models. arXiv:2001.08361 (2020)
- Hoffmann, J., Borgeaud, S., Mensch, A., Buchatskaya, E., Cai, T., Rutherford, E., Casas, D.d.L., Hendricks, L.A., Welbl, J., Clark, A., et al.: Training compute-optimal large language models. arXiv:2203.15556 (2022)
- Sanh, V., Webson, A., Raffel, C., Bach, S., Sutawika, L., Alyafeai, Z., Chaffin, A., Stiegler, A., Raja, A., Dey, M., et al.: Multitask prompted training enables zero-shot task generalization. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2021)
- Ouyang, L., Wu, J., Jiang, X., Almeida, D., Wainwright, C., Mishkin, P., Zhang, C., Agarwal, S., Slama, K., Ray, A., et al.: Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 27730-27744 (2022)
- Wei, J., Wang, X., Schuurmans, D., Bosma, M., Chi, E., Le, Q., Zhou, D.: Chain of thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models. arXiv:2201.11903 (2022)
- Fu, Y., Peng, H., Khot, T.: How does gpt obtain its ability? tracing emergent abilities of language models to their sources. Yao Fu’s Notion (2022)
- Zhang, Y., Chen, X., Ai, Q., Yang, L., Croft, W.B.: Towards conversational search and recommendation: system ask, user respond. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, pp. 177-186 (2018)
- Wang, H., Zhang, F., Xie, X., Guo, M.: Dkn: deep knowledge-aware network for news recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 2018 World Wide Web Conference, pp. 1835-1844 (2018)
- Huang, J., Zhao, W.X., Dou, H., Wen, J.-R., Chang, E.Y.: Improving sequential recommendation with knowledge-enhanced memory networks. In: The 41st international ACM SIGIR Conference on Research & Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 505-514 (2018)
- Wang, H., Zhang, F., Hou, M., Xie, X., Guo, M., Liu, Q.: Shine: signed heterogeneous information network embedding for sentiment link prediction. In: Proceedings of the Eleventh ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, pp. 592-600 (2018)
- Yu, X., Ren, X., Gu, Q., Sun, Y., Han, J.: Collaborative filtering with entity similarity regularization in heterogeneous information networks. IJCAI HINA 27 (2013)
- Shi, C., Zhang, Z., Luo, P., Yu, P.S., Yue, Y., Wu, B.: Semantic path based personalized recommendation on weighted heterogeneous information networks. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM International on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, pp. 453-462 (2015)
- Ma, W., Zhang, M., Cao, Y., Jin, W., Wang, C., Liu, Y., Ma, S., Ren, X.: Jointly learning explainable rules for recommendation with knowledge graph. In: The World Wide Web Conference, pp. 1210-1221 (2019)
- Huang, X., Fang, Q., Qian, S., Sang, J., Li, Y., Xu, C.: Explainable interaction-driven user modeling over knowledge graph for sequential recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 548-556 (2019)
- Wang, H., Zhang, F., Wang, J., Zhao, M., Li, W., Xie, X., Guo, M.: Ripplenet: propagating user preferences on the knowledge graph for recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, pp. 417-426 (2018)
- Wang, H., Zhao, M., Xie, X., Li, W., Guo, M.: Knowledge graph convolutional networks for recommender systems. In: The World Wide Web Conference, pp. 3307-3313 (2019)
- Wang, X., He, X., Cao, Y., Liu, M., Chua, T.-S.: Kgat: knowledge graph attention network for recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 950-958 (2019)
- Tang, X., Wang, T., Yang, H., Song, H.: Akupm: attention-enhanced knowledge-aware user preference model for recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 1891-1899 (2019)
- Zhao, J., Zhou, Z., Guan, Z., Zhao, W., Ning, W., Qiu, G., He, X.: Intentgc: a scalable graph convolution framework fusing heterogeneous information for recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 2347-2357 (2019)
- Petroni, F., Rocktäschel, T., Lewis, P., Bakhtin, A., Wu, Y., Miller, A.H., Riedel, S.: Language models as knowledge bases?. arXiv:1909.01066 (2019)
- Roberts, A., Raffel, C., Shazeer, N.: How much knowledge can you pack into the parameters of a language model?. arXiv:2002.08910 (2020)
- Petroni, F., Lewis, P., Piktus, A., Rocktäschel, T., Wu, Y., Miller, A.H., Riedel, S.: How context affects language models’ factual predictions. In: Automated Knowledge Base Construction
- Jiang, Z., Xu, F.F., Araki, J., Neubig, G.: How can we know what language models know? Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist 8, 423-438 (2020)
- Wang, C., Liu, X., Song, D.: Language models are open knowledge graphs. arXiv:2010.11967 (2020)
- Poerner, N., Waltinger, U., Schütze, H.: E-bert: efficient-yet-effective entity embeddings for bert. In: Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2020, pp. 803-818 (2020)
- Heinzerling, B., Inui, K.: Language models as knowledge bases: On entity representations, storage capacity, and paraphrased queries. In: Proceedings of the 16th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Main Volume, pp. 1772-1791 (2021)
- Wang, C., Liu, P., Zhang, Y.: Can generative pre-trained language models serve as knowledge bases for closed-book qa?. In: Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (vol. 1: long papers), pp. 3241-3251 (2021)
- Guu, K., Lee, K., Tung, Z., Pasupat, P., Chang, M.: Retrieval augmented language model pre-training. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 3929-3938 (2020). PMLR
- Bordes, A., Usunier, N., Garcia-Duran, A., Weston, J., Yakhnenko, O.: Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 26 (2013)
- Zhu, Y., Wang, X., Chen, J., Qiao, S., Ou, Y., Yao, Y., Deng, S., Chen, H., Zhang, N.: Llms for knowledge graph construction and reasoning: recent capabilities and future opportunities. arXiv:2305.13168 (2023)
- Zhang, Z., Liu, X., Zhang, Y., Su, Q., Sun, X., He, B.: Pretrain-kge: learning knowledge representation from pretrained language models. In: Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2020, pp. 259-266 (2020)
- Kumar, A., Pandey, A., Gadia, R., Mishra, M.: Building knowledge graph using pre-trained language model for learning entity-aware relationships. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Computing, Power and Communication Technologies (GUCON), pp. 310-315 (2020). IEEE
- Kim, B., Hong, T., Ko, Y., Seo, J.: Multi-task learning for knowledge graph completion with pre-trained language models. In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, pp. 1737-1743 (2020)
- Choi, B., Jang, D., Ko, Y.: Mem-kgc: masked entity model for knowledge graph completion with pretrained language model. IEEE Access 9, 132025-132032 (2021)
- Wang, B., Shen, T., Long, G., Zhou, T., Wang, Y., Chang, Y.: Structure-augmented text representation learning for efficient knowledge graph completion. In: Proceedings of the Web Conference 2021, pp. 1737-1748 (2021)
- Xie, X., Zhang, N., Li, Z., Deng, S., Chen, H., Xiong, F., Chen, M., Chen, H.: From discrimination to generation: knowledge graph completion with generative transformer. In: Companion Proceedings of the Web Conference 2022, pp. 162-165 (2022)
- Jiang, P., Agarwal, S., Jin, B., Wang, X., Sun, J., Han, J.: Text-augmented open knowledge graph completion via pre-trained language models. arXiv:2305.15597 (2023)
- Yan, H., Gui, T., Dai, J., Guo, Q., Zhang, Z., Qiu, X.: A unified generative framework for various ner subtasks. In: Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (vol. 1: long papers), pp. 5808-5822 (2021)
- Li, B., Yin, W., Chen, M.: Ultra-fine entity typing with indirect supervision from natural language inference. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 10, 607-622 (2022)
- Kirstain, Y., Ram, O., Levy, O.: Coreference resolution without span representations. In: Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (vol. 2: short papers), pp. 14-19 (2021)
- Cattan, A., Eirew, A., Stanovsky, G., Joshi, M., Dagan, I.: Cross-document coreference resolution over predicted mentions. In: Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL-IJCNLP 2021, pp. 5100-5107 (2021)
- Lyu, S., Chen, H.: Relation classification with entity type restriction. In: Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL-IJCNLP 2021, pp. 390-395 (2021)
- Wang, H., Focke, C., Sylvester, R., Mishra, N., Wang, W.: Fine-tune bert for docred with two-step process. arXiv:1909.11898 (2019)
- Han, J., Collier, N., Buntine, W., Shareghi, E.: Pive: prompting with iterative verification improving graph-based generative capability of llms. arXiv:2305.12392 (2023)
- Trajanoska, M., Stojanov, R., Trajanov, D.: Enhancing knowledge graph construction using large language models. arXiv:2305.04676 (2023)
- West, P., Bhagavatula, C., Hessel, J., Hwang, J., Jiang, L., Le Bras, R., Lu, X., Welleck, S., Choi, Y.: Symbolic knowledge distillation: from general language models to commonsense models. In: Proceedings of the 2022 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, pp. 4602-4625 (2022)
- Xi, Y., Liu, W., Lin, J., Zhu, J., Chen, B., Tang, R., Zhang, W., Zhang, R., Yu, Y.: Towards open-world recommendation with knowledge augmentation from large language models. arXiv:2306.10933 (2023)
- Wei, W., Ren, X., Tang, J., Wang, Q., Su, L., Cheng, S., Wang, J., Yin, D., Huang, C.: Llmrec: large language models with graph augmentation for recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 17th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, pp. 806-815 (2024)
- Zhao, Q., Qian, H., Liu, Z., Zhang, G.-D., Gu, L.: Breaking the barrier: utilizing large language models for industrial recommendation systems through an inferential knowledge graph. arXiv:2402.13750 (2024)
- Razniewski, S., Yates, A., Kassner, N., Weikum, G.: Language models as or for knowledge bases. arXiv:2110.04888 (2021)
- Yu, J., Wang, X., Tu, S., Cao, S., Zhang-Li, D., Lv, X., Peng, H., Yao, Z., Zhang, X., Li, H., et al.: Kola: Carefully benchmarking world knowledge of large language models. arXiv:2306.09296 (2023)
- Ye, D., Lin, Y., Li, P., Sun, M.: Packed levitated marker for entity and relation extraction. In: Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (vol. 1: long papers), pp. 4904-4917 (2022)
- Lang, K.: Newsweeder: Learning to filter netnews. In: Machine Learning Proceedings 1995, pp. 331-339. Elsevier (1995)
- Wang, H., Shi, X., Yeung, D.-Y.: Collaborative recurrent autoencoder: recommend while learning to fill in the blanks. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 29 (2016)
- Dong, X., Yu, L., Wu, Z., Sun, Y., Yuan, L., Zhang, F.: A hybrid collaborative filtering model with deep structure for recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 31 (2017)
- Li, X., She, J.: Collaborative variational autoencoder for recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 305-314 (2017)
- Wu, C., Wu, F., Huang, Y., Xie, X.: Personalized news recommendation: methods and challenges. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 41(1), 24-12450 (2023)
- Le, Q.V., Mikolov, T.: Distributed representations of sentences and documents. In: ICML. JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings, vol. 32, pp. 1188-1196. JMLR.org (2014)
- Song, Y., Elkahky, A.M., He, X.: Multi-rate deep learning for temporal recommendation. In: SIGIR, pp. 909-912. ACM (2016)
- Kumar, V., Khattar, D., Gupta, S., Gupta, M., Varma, V.: Deep neural architecture for news recommendation. In: CLEF (Working Notes). CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol. 1866. CEUR-WS.org (2017)
- Okura, S., Tagami, Y., Ono, S., Tajima, A.: Embedding-based news recommendation for millions of users. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 1933-1942 (2017)
- Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G., Dean, J.: Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. In: ICLR (Workshop Poster) (2013)
- Wu, C., Wu, F., An, M., Huang, J., Huang, Y., Xie, X.: NPA: neural news recommendation with personalized attention. In: KDD, pp. 2576-2584. ACM (2019)
- An, M., Wu, F., Wu, C., Zhang, K., Liu, Z., Xie, X.: Neural news recommendation with long- and short-term user representations. In: ACL (1), pp. 336-345. Association for Computational Linguistics (2019)
- Wu, C., Wu, F., Ge, S., Qi, T., Huang, Y., Xie, X.: Neural news recommendation with multi-head selfattention. In: EMNLP/IJCNLP (1), pp. 6388-6393. Association for Computational Linguistics (2019)
- Wu, C., Wu, F., Qi, T., Huang, Y.: User modeling with click preference and reading satisfaction for news recommendation. In: IJCAI, pp. 3023-3029. ijcai.org (2020)
- Khattar, D., Kumar, V., Varma, V., Gupta, M.: Weave&rec: a word embedding based 3-d convolutional network for news recommendation. In: CIKM, pp. 1855-1858. ACM (2018)
- Zhu, Q., Zhou, X., Song, Z., Tan, J., Guo, L.: DAN: deep attention neural network for news recommendation. In: AAAI, pp. 5973-5980. rAAAI Press (2019)
- Qiu, Z., Wu, X., Gao, J., Fan, W.: U-bert: Pre-training user representations for improved recommendation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, pp. 4320-4327 (2021)
- Zhang, Q., Li, J., Jia, Q., Wang, C., Zhu, J., Wang, Z., He, X.: Unbert: user-news matching bert for news recommendation. In: IJCAI, pp. 3356-3362 (2021)
- Wu, C., Wu, F., Qi, T., Huang, Y.: Empowering news recommendation with pre-trained language models. In: Proceedings of the 44th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 1652-1656 (2021)
- Liu, Q., Zhu, J., Dai, Q., Wu, X.: Boosting deep ctr prediction with a plug-and-play pre-trainer for news recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, pp. 2823-2833 (2022)
- Wu, C., Wu, F., Qi, T., Zhang, C., Huang, Y., Xu, T.: Mm-rec: visiolinguistic model empowered multimodal news recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 45th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 2560-2564 (2022)
- Yu, Y., Wu, F., Wu, C., Yi, J., Liu, Q.: Tiny-newsrec: effective and efficient plm-based news recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 5478-5489 (2022)
- Zou, L., Zhang, S., Cai, H., Ma, D., Cheng, S., Wang, S., Shi, D., Cheng, Z., Yin, D.: Pre-trained language model based ranking in baidu search. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 4014-4022 (2021)
- Liu, Y., Lu, W., Cheng, S., Shi, D., Wang, S., Cheng, Z., Yin, D.: Pre-trained language model for webscale retrieval in baidu search. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 3365-3375 (2021)
- Muhamed, A., Keivanloo, I., Perera, S., Mracek, J., Xu, Y., Cui, Q., Rajagopalan, S., Zeng, B., Chilimbi, T.: Ctr-bert: cost-effective knowledge distillation for billion-parameter teacher models. In: NeurIPS Efficient Natural Language and Speech Processing Workshop (2021)
- He, J., Xu, B., Yang, Z., Han, D., Yang, C., Lo, D.: Ptm4tag: sharpening tag recommendation of stack overflow posts with pre-trained models. In: Proceedings of the 30th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Program Comprehension, pp. 1-11 (2022)
- Zhang, X., Malkov, Y., Florez, O., Park, S., McWilliams, B., Han, J., El-Kishky, A.: Twhin-bert: a socially-enriched pre-trained language model for multilingual tweet representations. arXiv:2209.07562 (2022)
- Rahmani, S., Naghshzan, A., Guerrouj, L.: Improving code example recommendations on informal documentation using bert and query-aware 1sh: a comparative study. arXiv:2305.03017 (2023)
- Ding, H., Ma, Y., Deoras, A., Wang, Y., Wang, H.: Zero-shot recommender systems. arXiv:2105.08318 (2021)
- Hou, Y., Mu, S., Zhao, W.X., Li, Y., Ding, B., Wen, J.-R.: Towards universal sequence representation learning for recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 585-593 (2022)
- Hou, Y., He, Z., McAuley, J., Zhao, W.X.: Learning vector-quantized item representation for transferable sequential recommenders. In: Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2023, pp. 1162-1171 (2023)
- Yuan, Z., Yuan, F., Song, Y., Li, Y., Fu, J., Yang, F., Pan, Y., Ni, Y.: Where to go next for recommender systems? id-vs. modality-based recommender models revisited. arXiv:2303.13835 (2023)
- Fu, J., Yuan, F., Song, Y., Yuan, Z., Cheng, M., Cheng, S., Zhang, J., Wang, J., Pan, Y.: Exploring adapter-based transfer learning for recommender systems: empirical studies and practical insights. arXiv:2305.15036 (2023)
- Bao, K., Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., Wang, W., Feng, F., He, X.: Tallrec: an effective and efficient tuning framework to align large language model with recommendation. arXiv:2305.00447 (2023)
- Kang, W.-C., Ni, J., Mehta, N., Sathiamoorthy, M., Hong, L., Chi, E., Cheng, D.Z.: Do llms understand user preferences?. evaluating llms on user rating prediction. arXiv:2305.06474 (2023)
- Chen, Z.: Palr: Personalization aware llms for recommendation. arXiv:2305.07622 (2023)
- Zhang, J., Xie, R., Hou, Y., Zhao, W.X., Lin, L., Wen, J.-R.: Recommendation as instruction following: a large language model empowered recommendation approach. arXiv:2305.07001 (2023)
- Li, R., Deng, W., Cheng, Y., Yuan, Z., Zhang, J., Yuan, F.: Exploring the upper limits of text-based collaborative filtering using large language models: discoveries and insights. arXiv:2305.11700 (2023)
- Wang, X., Chen, Y., Yang, J., Wu, L., Wu, Z., Xie, X.: A reinforcement learning framework for explainable recommendation. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), pp. 587-596 (2018). IEEE
- Gao, J., Wang, X., Wang, Y., Xie, X.: Explainable recommendation through attentive multi-view learning. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 33, pp. 3622-3629 (2019)
- Lee, S., Wang, X., Han, S., Yi, X., Xie, X., Cha, M.: Self-explaining deep models with logic rule reasoning. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. (2022)
- Nye, M., Andreassen, A.J., Gur-Ari, G., Michalewski, H., Austin, J., Bieber, D., Dohan, D., Lewkowycz, A., Bosma, M., Luan, D., et al.: Show your work: scratchpads for intermediate computation with language models. arXiv:2112.00114 (2021)
- Lampinen, A.K., Dasgupta, I., Chan, S.C., Matthewson, K., Tessler, M.H., Creswell, A., McClelland, J.L., Wang, J.X., Hill, F.: Can language models learn from explanations in context?. arXiv:2204.02329 (2022)
- Zelikman, E., Wu, Y., Mu, J., Goodman, N.: Star: bootstrapping reasoning with reasoning. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 15476-15488 (2022)
- Zhang, Y., Chen, X., et al.: Explainable recommendation: a survey and new perspectives. Found. Trends® in Inf. Retr. 14(1), 1-101 (2020)
- Schafer, J.B., Konstan, J., Riedl, J.: Recommender systems in e-commerce. In: Proceedings of the 1st ACM Conference on Electronic Commerce, pp. 158-166 (1999)
- Linden, G., Smith, B., York, J.: Amazon. com recommendations: item-to-item collaborative filtering. IEEE Internet Comput. 7(1), 76-80 (2003)
- Gomez-Uribe, C.A., Hunt, N.: The netflix recommender system: algorithms, business value, and innovation. ACM Trans. Manage. Inf. Syst. (TMIS) 6(4), 1-19 (2015)
- Sinha, R., Swearingen, K.: The role of transparency in recommender systems. In: CHI’02 Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pp. 830-831 (2002)
- Xian, Y., Zhao, T., Li, J., Chan, J., Kan, A., Ma, J., Dong, X.L., Faloutsos, C., Karypis, G., Muthukrishnan, S., et al.: Ex3: explainable attribute-aware item-set recommendations. In: Proceedings of the 15th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, pp. 484-494 (2021)
- Wang, X., Li, Q., Yu, D., Xu, G.: Reinforced path reasoning for counterfactual explainable recommendation. arXiv:2207.06674 (2022)
- Verma, S., Beniwal, A., Sadagopan, N., Seshadri, A.: Recxplainer: post-hoc attribute-based explanations for recommender systems. arXiv:2211.14935 (2022)
- Zhang, W., Yan, J., Wang, Z., Wang, J.: Neuro-symbolic interpretable collaborative filtering for attributebased recommendation. In: Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022, pp. 3229-3238 (2022)
- Li, P., Wang, Z., Ren, Z., Bing, L., Lam, W.: Neural rating regression with abstractive tips generation for recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 40th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 345-354 (2017)
- Dong, L., Huang, S., Wei, F., Lapata, M., Zhou, M., Xu, K.: Learning to generate product reviews from attributes. In: Proceedings of the 15th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: volume 1, long papers, pp. 623-632 (2017)
- Li, L., Zhang, Y., Chen, L.: Generate neural template explanations for recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, pp. 755-764 (2020)
- Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9(8), 1735-1780 (1997)
- Cho, K., Van Merriënboer, B., Gulcehre, C., Bahdanau, D., Bougares, F., Schwenk, H., Bengio, Y.: Learning phrase representations using rnn encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv:1406.1078 (2014)
- Li, L., Zhang, Y., Chen, L.: Personalized transformer for explainable recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (vol. 1: Long papers) (2021)
- Zhan, H., Li, L., Li, S., Liu, W., Gupta, M., Kot, A.C.: Towards explainable recommendation via bertguided explanation generator. In: ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 1-5 (2023). IEEE
- Ni, J., Li, J., McAuley, J.: Justifying recommendations using distantly-labeled reviews and fine-grained aspects. In: Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), pp. 188-197 (2019)
- Liu, Z., Ma, Y., Schubert, M., Ouyang, Y., Rong, W., Xiong, Z.: Multimodal contrastive transformer for explainable recommendation. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems (2023)
- Qu, Y., Nobuhara, H.: Explanation generated for sequential recommendation based on transformer model. In: 2022 Joint 12th International Conference on Soft Computing and Intelligent Systems and 23rd International Symposium on Advanced Intelligent Systems (SCIS&ISIS), pp. 1-6 (2022). IEEE
- Bai, P., Xia, Y., Xia, Y.: Fusing knowledge and aspect sentiment for explainable recommendation. IEEE Access 8, 137150-137160 (2020)
- Wang, L., Zhang, S., Wang, Y., Lim, E.-P., Wang, Y.: Llm4vis: explainable visualization recommendation using chatgpt. arXiv:2310.07652 (2023)
- Lei, Y., Lian, J., Yao, J., Huang, X., Lian, D., Xie, X.: Recexplainer: aligning large language models for recommendation model interpretability. arXiv:2311.10947 (2023)
- Bommasani, R., Hudson, D.A., Adeli, E., Altman, R., Arora, S., Arx, S., Bernstein, M.S., Bohg, J., Bosselut, A., Brunskill, E., et al.: On the opportunities and risks of foundation models. arXiv:2108.07258 (2021)
- Li, L., Zhang, Y., Chen, L.: Personalized prompt learning for explainable recommendation. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 41(4), 1-26 (2023)
- Bills, S., Cammarata, N., Mossing, D., Tillman, H., Gao, L., Goh, G., Sutskever, I., Leike, J., Wu, J., Saunders, W.: Language models can explain neurons in language models (2023)
- Wu, Z., Geiger, A., Potts, C., Goodman, N.D.: Interpretability at scale: identifying causal mechanisms in alpaca. arXiv:2305.08809 (2023)
- Li, Y., Lin, Z., Zhang, S., Fu, Q., Chen, B., Lou, J.-G., Chen, W.: Making large language models better reasoners with step-aware verifier (2023)
- Turpin, M., Michael, J., Perez, E., Bowman, S.R.: Language models don’t always say what they think: unfaithful explanations in chain-of-thought prompting. arXiv:2305.04388 (2023)
- Li, S., Liu, H., Dong, T., Zhao, B.Z.H., Xue, M., Zhu, H., Lu, J.: Hidden backdoors in human-centric language models. In: Proceedings of the 2021 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, pp. 3123-3140 (2021)
- Wang, J., Hu, X., Hou, W., Chen, H., Zheng, R., Wang, Y., Yang, L., Huang, H., Ye, W., Geng, X., et al.: On the robustness of chatgpt: an adversarial and out-of-distribution perspective. arXiv:2302.12095 (2023)
- Han, R., Peng, T., Yang, C., Wang, B., Liu, L., Wan, X.: Is information extraction solved by chatgpt? an analysis of performance, evaluation criteria, robustness and errors. arXiv:2305.14450 (2023)
- Wei, J., Tay, Y., Bommasani, R., Raffel, C., Zoph, B., Borgeaud, S., Yogatama, D., Bosma, M., Zhou, D., Metzler, D., et al.: Emergent abilities of large language models. arXiv:2206.07682 (2022)
- Liu, J., Liu, C., Lv, R., Zhou, K., Zhang, Y.: Is chatgpt a good recommender? a preliminary study. arXiv:2304.10149 (2023)
- Dai, S., Shao, N., Zhao, H., Yu, W., Si, Z., Xu, C., Sun, Z., Zhang, X., Xu, J.: Uncovering chatgpt’s capabilities in recommender systems. arXiv:2305.02182 (2023)
- Wang, L., Lim, E.-P.: Zero-shot next-item recommendation using large pretrained language models. arXiv:2304.03153 (2023)
- Hou, Y., Zhang, J., Lin, Z., Lu, H., Xie, R., McAuley, J., Zhao, W.X.: Large language models are zero-shot rankers for recommender systems. arXiv:2305.08845 (2023)
- Li, X., Zhang, Y., Malthouse, E.C.: A preliminary study of chatgpt on news recommendation: personalization, provider fairness, fake news. arXiv:2306.10702 (2023)
- Dong, Q., Li, L., Dai, D., Zheng, C., Wu, Z., Chang, B., Sun, X., Xu, J., Sui, Z.: A survey for in-context learning. arXiv:2301.00234 (2022)
- Dai, D., Sun, Y., Dong, L., Hao, Y., Sui, Z., Wei, F.: Why can gpt learn in-context? language models secretly perform gradient descent as meta optimizers. arXiv:2212.10559 (2022)
- Min, S., Lyu, X., Holtzman, A., Artetxe, M., Lewis, M., Hajishirzi, H., Zettlemoyer, L.: Rethinking the role of demonstrations: What makes in-context learning work?. arXiv:2202.12837 (2022)
- Levy, I., Bogin, B., Berant, J.: Diverse demonstrations improve in-context compositional generalization. arXiv:2212.06800 (2022)
- Xie, S.M., Raghunathan, A., Liang, P., Ma, T.: An explanation of in-context learning as implicit bayesian inference. In: International Conference on Learning Representations
- Olsson, C., Elhage, N., Nanda, N., Joseph, N., DasSarma, N., Henighan, T., Mann, B., Askell, A., Bai, Y., Chen, A., et al.: In-context learning and induction heads. arXiv:2209.11895 (2022)
- Akyürek, E., Schuurmans, D., Andreas, J., Ma, T., Zhou, D.: What learning algorithm is in-context learning? investigations with linear models. arXiv:2211.15661 (2022)
- Geng, S., Liu, S., Fu, Z., Ge, Y., Zhang, Y.: Recommendation as language processing (rlp): a unified pretrain, personalized prompt & predict paradigm (p5). In: Proceedings of the 16th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, pp. 299-315 (2022)
- Cui, Z., Ma, J., Zhou, C., Zhou, J., Yang, H.: M6-rec: generative pretrained language models are openended recommender systems. arXiv:2205.08084 (2022)
- Liu, S., Gao, C., Chen, Y., Jin, D., Li, Y.: Learnable embedding sizes for recommender systems. arXiv:2101.07577 (2021)
- Liu, H., Zhao, X., Wang, C., Liu, X., Tang, J.: Automated embedding size search in deep recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 43rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 2307-2316 (2020)
- Deng, W., Pan, J., Zhou, T., Kong, D., Flores, A., Lin, G.: Deeplight: deep lightweight feature interactions for accelerating ctr predictions in ad serving. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, pp. 922-930 (2021)
- Ginart, A.A., Naumov, M., Mudigere, D., Yang, J., Zou, J.: Mixed dimension embeddings with application to memory-efficient recommendation systems. In: 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), pp. 2786-2791 (2021). IEEE
- Wang, Y., Zhao, X., Xu, T., Wu, X.: Autofield: automating feature selection in deep recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022, pp. 1977-1986 (2022)
- Lin, W., Zhao, X., Wang, Y., Xu, T., Wu, X.: Adafs: adaptive feature selection in deep recommender system. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 3309-3317 (2022)
- Tsang, M., Cheng, D., Liu, H., Feng, X., Zhou, E., Liu, Y.: Feature interaction interpretability: a case for explaining ad-recommendation systems via neural interaction detection. arXiv:2006.10966 (2020)
- Yuanfei, L., Mengshuo, W., Hao, Z., Quanming, Y., WeiWei, T., Yuqiang, C., Qiang, Y., Wenyuan, D.: Autocross: automatic feature crossing for tabular data in real-world applications. arXiv:1904.12857 (2019)
- Liu, B., Zhu, C., Li, G., Zhang, W., Lai, J., Tang, R., He, X., Li, Z., Yu, Y.: Autofis: automatic feature interaction selection in factorization models for click-through rate prediction. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 26362645 (2020)
- Liu, B., Xue, N., Guo, H., Tang, R., Zafeiriou, S., He, X., Li, Z.: Autogroup: automatic feature grouping for modelling explicit high-order feature interactions in ctr prediction. In: Proceedings of the 43rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 199208 (2020)
- Chen, Y., Ren, P., Wang, Y., Rijke, M.: Bayesian personalized feature interaction selection for factorization machines. In: Proceedings of the 42nd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 665-674 (2019)
- Xie, Y., Wang, Z., Li, Y., Ding, B., Gürel, N.M., Zhang, C., Huang, M., Lin, W., Zhou, J.: Fives: feature interaction via edge search for large-scale tabular data. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 3795-3805 (2021)
- Su, Y., Zhang, R., Erfani, S., Xu, Z.: Detecting beneficial feature interactions for recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, pp. 4357-4365 (2021)
- Song, Q., Cheng, D., Zhou, H., Yang, J., Tian, Y., Hu, X.: Towards automated neural interaction discovery for click-through rate prediction. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 945-955 (2020)
- Zhao, P., Xiao, K., Zhang, Y., Bian, K., Yan, W.: Ameir: automatic behavior modeling, interaction exploration and mlp investigation in the recommender system. In: IJCAI, pp. 2104-2110 (2021)
- Wei, Z., Wang, X., Zhu, W.: Autoias: automatic integrated architecture searcher for click-trough rate prediction. In: Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, pp. 2101-2110 (2021)
- Cheng, M., Liu, Z., Liu, Q., Ge, S., Chen, E.: Towards automatic discovering of deep hybrid network architecture for sequential recommendation. In: Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022, pp. 1923-1932 (2022)
- Yu, C., Liu, X., Tang, C., Feng, W., Lv, J.: Gpt-nas: Neural architecture search with the generative pre-trained model. arXiv:2305.05351 (2023)
- Ying, C., Klein, A., Christiansen, E., Real, E., Murphy, K., Hutter, F.: Nas-bench-101: Towards reproducible neural architecture search. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 7105-7114 (2019). PMLR
- Zheng, M., Su, X., You, S., Wang, F., Qian, C., Xu, C., Albanie, S.: Can gpt-4 perform neural architecture search? arXiv:2304.10970 (2023)
- Nasir, M.U., Earle, S., Togelius, J., James, S., Cleghorn, C.: Llmatic: Neural architecture search via large language models and quality-diversity optimization. arXiv:2306.01102 (2023)
- Chen, A., Dohan, D.M., So, D.R.: Evoprompting: language models for code-level neural architecture search. arXiv:2302.14838 (2023)
- Shang, L., Lu, Z., Li, H.: Neural responding machine for short-text conversation. arXiv:1503.02364 (2015)
- Vinyals, O., Le, Q.: A neural conversational model. arXiv:1506.05869 (2015)
- Sordoni, A., Galley, M., Auli, M., Brockett, C., Ji, Y., Mitchell, M., Nie, J.-Y., Gao, J., Dolan, B.: A neural network approach to context-sensitive generation of conversational responses. arXiv:1506.06714 (2015)
- Wu, W., Yan, R.: Deep chit-chat: deep learning for chatbots. In: Proceedings of the 42 nd international ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 1413-1414 (2019)
- Qiu, X., Huang, X.: Convolutional neural tensor network architecture for community-based question answering. In: Twenty-Fourth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2015)
- Wan, S., Lan, Y., Guo, J., Xu, J., Pang, L., Cheng, X.: A deep architecture for semantic matching with multiple positional sentence representations. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 30 (2016)
- Greco, C., Suglia, A., Basile, P., Semeraro, G.: Converse-et-impera: exploiting deep learning and hierarchical reinforcement learning for conversational recommender systems. In: AI* IA 2017 Advances in Artificial Intelligence: XVIth International Conference of the Italian Association for Artificial Intelligence, Bari, Italy, November 14-17, 2017, Proceedings 16, pp. 372-386 (2017). Springer
- Yao, K., Zweig, G., Hwang, M.-Y., Shi, Y., Yu, D.: Recurrent neural networks for language understanding. In: Interspeech, pp. 2524-2528 (2013)
- Mesnil, G., He, X., Deng, L., Bengio, Y.: Investigation of recurrent-neural-network architectures and learning methods for spoken language understanding. In: Interspeech, pp. 3771-3775 (2013)
- Goddeau, D., Meng, H., Polifroni, J., Seneff, S., Busayapongchai, S.: A form-based dialogue manager for spoken language applications. In: Proceeding of Fourth International Conference on Spoken Language Processing. ICSLP’96, vol. 2, pp. 701-704 (1996). IEEE
- Henderson, M., Thomson, B., Young, S.: Deep neural network approach for the dialog state tracking challenge. In: Proceedings of the SIGDIAL 2013 Conference, pp. 467-471 (2013)
- Mrkšić, N., Séaghdha, D.O., Wen, T.-H., Thomson, B., Young, S.: Neural belief tracker: data-driven dialogue state tracking. arXiv:1606.03777 (2016)
- Cuayáhuitl, H., Keizer, S., Lemon, O.: Strategic dialogue management via deep reinforcement learning. arXiv:1511.08099 (2015)
- Zhou, H., Huang, M., Zhu, X.: Context-aware natural language generation for spoken dialogue systems. In: Proceedings of COLING 2016, the 26th International Conference on Computational Linguistics: Technical Papers, pp. 2032-2041 (2016)
- Dušek, O., Jurčíćek, F.: Sequence-to-sequence generation for spoken dialogue via deep syntax trees and strings. arXiv:1606.05491 (2016)
- Wen, T.-H., Vandyke, D., Mrksic, N., Gasic, M., Rojas-Barahona, L.M., Su, P.-H., Ultes, S., Young, S.: A network-based end-to-end trainable task-oriented dialogue system. arXiv:1604.04562 (2016)
- Bordes, A., Boureau, Y.-L., Weston, J.: Learning end-to-end goal-oriented dialog. arXiv:1605.07683 (2016)
- Zhang, Y., Sun, S., Galley, M., Chen, Y.-C., Brockett, C., Gao, X., Gao, J., Liu, J., Dolan, B.: Dialogpt: large-scale generative pre-training for conversational response generation. arXiv:1911.00536 (2019)
- Lei, W., He, X., Miao, Y., Wu, Q., Hong, R., Kan, M.-Y., Chua, T.-S.: Estimation-action-reflection: towards deep interaction between conversational and recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, pp. 304-312 (2020)
- Lei, W., Zhang, G., He, X., Miao, Y., Wang, X., Chen, L., Chua, T.-S.: Interactive path reasoning on graph for conversational recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 2073-2083 (2020)
- Deng, Y., Li, Y., Sun, F., Ding, B., Lam, W.: Unified conversational recommendation policy learning via graph-based reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 44th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 1431-1441 (2021)
- Li, R., Ebrahimi Kahou, S., Schulz, H., Michalski, V., Charlin, L., Pal, C.: Towards deep conversational recommendations. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 31 (2018)
- Wang, T.-C., Su, S.-Y., Chen, Y.-N.: Barcor: Towards a unified framework for conversational recommendation systems. arXiv:2203.14257 (2022)
- Wang, X., Zhou, K., Wen, J.-R., Zhao, W.X.: Towards unified conversational recommender systems via knowledge-enhanced prompt learning. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 1929-1937 (2022)
- Wang, L., Hu, H., Sha, L., Xu, C., Jiang, D., Wong, K.-F.: Recindial: a unified framework for conversational recommendation with pretrained language models. In: Proceedings of the 2nd Conference of the Asia-Pacific Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 12th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, pp. 489-500 (2022)
- Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: Bert: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv:1810.04805 (2018)
- Radford, A., Narasimhan, K., Salimans, T., Sutskever, I., et al.: Improving language understanding by generative pre-training (2018)
- Gao, Y., Sheng, T., Xiang, Y., Xiong, Y., Wang, H., Zhang, J.: Chat-rec: towards interactive and explainable llms-augmented recommender system. arXiv:2303.14524 (2023)
- Friedman, L., Ahuja, S., Allen, D., Tan, T., Sidahmed, H., Long, C., Xie, J., Schubiner, G., Patel, A., Lara, H., et al.: Leveraging large language models in conversational recommender systems. arXiv:2305.07961 (2023)
- Wang, X., Tang, X., Zhao, W.X., Wang, J., Wen, J.-R.: Rethinking the evaluation for conversational recommendation in the era of large language models. arXiv:2305.13112 (2023)
- Yao, S., Yu, D., Zhao, J., Shafran, I., Griffiths, T.L., Cao, Y., Narasimhan, K.: Tree of thoughts: deliberate problem solving with large language models. arXiv:2305.10601 (2023)
- Wang, L., Xu, W., Lan, Y., Hu, Z., Lan, Y., Lee, R.K.-W., Lim, E.-P.: Plan-and-solve prompting: improving zero-shot chain-of-thought reasoning by large language models. arXiv:2305.04091 (2023)
- Yao, S., Zhao, J., Yu, D., Du, N., Shafran, I., Narasimhan, K., Cao, Y.: React: synergizing reasoning and acting in language models. arXiv:2210.03629 (2022)
- Madaan, A., Tandon, N., Clark, P., Yang, Y.: Memory-assisted prompt editing to improve gpt-3 after deployment. arXiv:2201.06009 (2022)
- Qin, Y., Hu, S., Lin, Y., Chen, W., Ding, N., Cui, G., Zeng, Z., Huang, Y., Xiao, C., Han, C., et al.: Tool learning with foundation models. arXiv:2304.08354 (2023)
- Mialon, G., Dessì, R., Lomeli, M., Nalmpantis, C., Pasunuru, R., Raileanu, R., Rozière, B., Schick, T., Dwivedi-Yu, J., Celikyilmaz, A., et al.: Augmented language models: a survey. arXiv:2302.07842 (2023)
- Yang, K., Peng, N., Tian, Y., Klein, D.: Re3: Generating longer stories with recursive reprompting and revision. arXiv:2210.06774 (2022)
- Schick, T., Dwivedi-Yu, J., Jiang, Z., Petroni, F., Lewis, P., Izacard, G., You, Q., Nalmpantis, C., Grave, E., Riedel, S.: Peer: a collaborative language model. arXiv:2208.11663 (2022)
- Hao, Y., Song, H., Dong, L., Huang, S., Chi, Z., Wang, W., Ma, S., Wei, F.: Language models are general-purpose interfaces. arXiv:2206.06336 (2022)
- Izacard, G., Lewis, P., Lomeli, M., Hosseini, L., Petroni, F., Schick, T., Dwivedi-Yu, J., Joulin, A., Riedel, S., Grave, E.: Few-shot learning with retrieval augmented language models. arXiv:2208.03299 (2022)
- Thoppilan, R., De Freitas, D., Hall, J., Shazeer, N., Kulshreshtha, A., Cheng, H.-T., Jin, A., Bos, T., Baker, L., Du, Y., et al.: Lamda: language models for dialog applications. arXiv:2201.08239 (2022)
- Nakano, R., Hilton, J., Balaji, S., Wu, J., Ouyang, L., Kim, C., Hesse, C., Jain, S., Kosaraju, V., Saunders, W., et al.: Webgpt: browser-assisted question-answering with human feedback. arXiv:2112.09332 (2021)
- Liu, R., Wei, J., Gu, S.S., Wu, T.-Y., Vosoughi, S., Cui, C., Zhou, D., Dai, A.M.: Mind’s eye: grounded language model reasoning through simulation. arXiv:2210.05359 (2022)
- Gao, L., Madaan, A., Zhou, S., Alon, U., Liu, P., Yang, Y., Callan, J., Neubig, G.: Pal: Program-aided language models. arXiv:2211.10435 (2022)
- Ahn, M., Brohan, A., Brown, N., Chebotar, Y., Cortes, O., David, B., Finn, C., Fu, C., Gopalakrishnan, K., Hausman, K., et al.: Do as i can, not as i say: grounding language in robotic affordances. arXiv:2204.01691 (2022)
- Shen, Y., Song, K., Tan, X., Li, D., Lu, W., Zhuang, Y.: Hugginggpt: solving ai tasks with chatgpt and its friends in huggingface. arXiv:2303.17580 (2023)
- Wu, C., Yin, S., Qi, W., Wang, X., Tang, Z., Duan, N.: Visual chatgpt: talking, drawing and editing with visual foundation models. arXiv:2303.04671 (2023)
- Liang, Y., Wu, C., Song, T., Wu, W., Xia, Y., Liu, Y., Ou, Y., Lu, S., Ji, L., Mao, S., et al.: Taskmatrix. ai: completing tasks by connecting foundation models with millions of apis. arXiv:2303.16434 (2023)
- Schick, T., Dwivedi-Yu, J., Dessì, R., Raileanu, R., Lomeli, M., Zettlemoyer, L., Cancedda, N., Scialom, T.: Toolformer: language models can teach themselves to use tools. arXiv:2302.04761 (2023)
- Li, J., Li, D., Xiong, C., Hoi, S.: Blip: Bootstrapping language-image pre-training for unified visionlanguage understanding and generation. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1288812900 (2022). PMLR
- Rombach, R., Blattmann, A., Lorenz, D., Esser, P., Ommer, B.: High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10684-10695 (2022)
- Cai, T., Wang, X., Ma, T., Chen, X., Zhou, D.: Large language models as tool makers. arXiv:2305.17126 (2023)
- Shuster, K., Xu, J., Komeili, M., Ju, D., Smith, E.M., Roller, S., Ung, M., Chen, M., Arora, K., Lane, J., et al.: Blenderbot 3: a deployed conversational agent that continually learns to responsibly engage. arXiv:2208.03188 (2022)
- Liu, J., Jin, J., Wang, Z., Cheng, J., Dou, Z., Wen, J.-R.: Reta-llm: a retrieval-augmented large language model toolkit. arXiv:2306.05212 (2023)
- Pan, S., Luo, L., Wang, Y., Chen, C., Wang, J., Wu, X.: Unifying large language models and knowledge graphs: a roadmap. arXiv:2306.08302 (2023)
- Vempati, S., Malayil, K.T., Sruthi, V., Sandeep, R.: Enabling hyper-personalisation: automated ad creative generation and ranking for fashion e-commerce. In: Fashion Recommender Systems, pp. 25-48 (2020). Springer
- Thomaidou, S., Lourentzou, I., Katsivelis-Perakis, P., Vazirgiannis, M.: Automated snippet generation for online advertising. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, pp. 1841-1844 (2013)
- Zhang, X., Zou, Y., Zhang, H., Zhou, J., Diao, S., Chen, J., Ding, Z., He, Z., He, X., Xiao, Y., et al.: Automatic product copywriting for e-commerce. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 36, pp. 12423-12431 (2022)
- Lei, Z., Zhang, C., Xu, X., Wu, W., Niu, Z.-Y., Wu, H., Wang, H., Yang, Y., Li, S.: Plato-ad: a unified advertisement text generation framework with multi-task prompt learning. In: Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: Industry Track, pp. 512-520 (2022)
- Bartz, K., Barr, C., Aijaz, A.: Natural language generation for sponsored-search advertisements. In: Proceedings of the 9th ACM Conference on Electronic Commerce, pp. 1-9 (2008)
- Fujita, A., Ikushima, K., Sato, S., Kamite, R., Ishiyama, K., Tamachi, O.: Automatic generation of listing ads by reusing promotional texts. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Electronic Commerce: Roadmap for the Future of Electronic Business, pp. 179-188 (2010)
- Hughes, J.W., Chang, K.-h., Zhang, R.: Generating better search engine text advertisements with deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 2269-2277 (2019)
- Wang, X., Gu, X., Cao, J., Zhao, Z., Yan, Y., Middha, B., Xie, X.: Reinforcing pretrained models for generating attractive text advertisements. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 3697-3707 (2021)
- Chen, C., Wang, X., Yi, X., Wu, F., Xie, X., Yan, R.: Personalized chit-chat generation for recommendation using external chat corpora. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 2721-2731 (2022)
- Zhang, C., Zhou, J., Zang, X., Xu, Q., Yin, L., He, X., Liu, L., Xiong, H., Dou, D.: Chase: commonsenseenriched advertising on search engine with explicit knowledge. In: Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, pp. 4352-4361 (2021)
- Kanungo, Y.S., Negi, S., Rajan, A.: Ad headline generation using self-critical masked language model. In: Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies: Industry Papers, pp. 263-271 (2021)
- Wei, P., Yang, X., Liu, S., Wang, L., Zheng, B.: Creater: ctr-driven advertising text generation with controlled pre-training and contrastive fine-tuning. arXiv:2205.08943 (2022)
- Kanungo, Y.S., Das, G., Negi, S.: Cobart: controlled, optimized, bidirectional and auto-regressive transformer for ad headline generation. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 3127-3136 (2022)
- Chen, Q., Lin, J., Zhang, Y., Yang, H., Zhou, J., Tang, J.: Towards knowledge-based personalized product description generation in e-commerce. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 3040-3050 (2019)
- Cao, Y., Li, S., Liu, Y., Yan, Z., Dai, Y., Yu, P.S., Sun, L.: A comprehensive survey of ai-generated content (aigc): a history of generative ai from gan to chatgpt. arXiv:2303.04226 (2023)
- Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., Bengio, Y.: Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 27 (2014)
- Kingma, D.P., Welling, M.: Auto-encoding variational bayes. arXiv:1312.6114 (2013)
- Dinh, L., Krueger, D., Bengio, Y.: Nice: non-linear independent components estimation. arXiv:1410.8516 (2014)
- Ho, J., Jain, A., Abbeel, P.: Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 6840-6851 (2020)
- Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., Weissenborn, D., Zhai, X., Unterthiner, T., Dehghani, M., Minderer, M., Heigold, G., Gelly, S., et al.: An image is worth
words: transformers for image recognition at scale. In: International Conference on Learning Representations - Liu, Z., Lin, Y., Cao, Y., Hu, H., Wei, Y., Zhang, Z., Lin, S., Guo, B.: Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 10012-10022 (2021)
- Radford, A., Kim, J.W., Hallacy, C., Ramesh, A., Goh, G., Agarwal, S., Sastry, G., Askell, A., Mishkin, P., Clark, J., et al.: Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 8748-8763 (2021). PMLR
- Chen, M., Tan, X., Li, B., Liu, Y., Qin, T., Liu, T.-Y., et al.: Adaspeech: adaptive text to speech for custom voice. In: International Conference on Learning Representations
- Li, X., Taheri, A., Tu, L., Gimpel, K.: Commonsense knowledge base completion. In: Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (vol. 1: long papers), pp. 1445-1455 (2016)
- Feng, Z., Guo, D., Tang, D., Duan, N., Feng, X., Gong, M., Shou, L., Qin, B., Liu, T., Jiang, D., et al.: Codebert: a pre-trained model for programming and natural languages. In: Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2020, pp. 1536-1547 (2020)
- OpenAI: ChatGPT: A Large-Scale Generative Model for Conversation. OpenAI Blog (2020)
- Ramesh, A., Pavlov, M., Goh, G., Gray, S., Voss, C., Radford, A., Chen, M., Sutskever, I.: Zero-shot text-to-image generation. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 8821-8831 (2021). PMLR
- Chen, M., Tworek, J., Jun, H., Yuan, Q., Pinto, H.P.d.O., Kaplan, J., Edwards, H., Burda, Y., Joseph, N., Brockman, G., et al.: Evaluating large language models trained on code. arXiv:2107.03374 (2021)
- Midjourney: Midjourney. Retrieved from. https://midjourney.com (2022)
- Wang, W., Lin, X., Feng, F., He, X., Chua, T.-S.: Generative recommendation: towards next-generation recommender paradigm. arXiv:2304.03516 (2023)
- Borji, A.: A categorical archive of chatgpt failures. arXiv:2302.03494 (2023)
- Carlini, N., Tramer, F., Wallace, E., et al.: Extracting training data from large language models. (2021)
- Radford, A., Wu, J., Child, R., Luan, D., Amodei, D., Sutskever, I., et al.: Language models are unsupervised multitask learners
- Hu, E.J., Wallis, P., Allen-Zhu, Z., Li, Y., Wang, S., Wang, L., Chen, W., et al.: Lora: low-rank adaptation of large language models. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2021)
- Dettmers, T., Pagnoni, A., Holtzman, A., Zettlemoyer, L.: Qlora: Efficient finetuning of quantized llms. arXiv:2305.14314 (2023)
- Bai, Y., Kadavath, S., Kundu, S., Askell, A., Kernion, J., Jones, A., Chen, A., Goldie, A., Mirhoseini, A., McKinnon, C., et al.: Constitutional ai: Harmlessness from ai feedback. arXiv:2212.08073 (2022)
Authors and Affiliations
jinchen@ust.hk
Zheng Liu
zhengliu1026@gmail.com
Xu Huang
xuhuangcs@mail.ustc.edu.cn
Chenwang Wu
wcw1996@mail.ustc.edu.cn
Qi Liu
qiliu67@mail.ustc.edu.cn
Gangwei Jiang
gwjiang@mail.ustc.edu.cn
Yuanhao Pu
puyuanhao@mail.ustc.edu.cn
Yuxuan Lei
lyx180812@mail.ustc.edu.cn
Xiaolong Chen
chenxiaolong@mail.ustc.edu.cn
Xingmei Wang
xingmeiwang@mail.ustc.edu.cn
Kai Zheng
zhengkai@uestc.edu.cn
Defu Lian
liandefu@ustc.edu.cn
Enhong Chen
cheneh@ustc.edu.cn
1 Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong, China
2 Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence, Beijing, China
3 University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China
4 University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
- Jin Chen and Zheng Liu contributed equally to this work.
- Extended author information available on the last page of the article
