DOI: https://doi.org/10.31181/sdmap21202524
تاريخ النشر: 2025-01-23
مراجعة شاملة ومنهجية لأساليب اتخاذ القرار متعددة المعايير (MCDM) لحل مشكلات اتخاذ القرار: عقدان من 2004 إلى 2024
معلومات المقال
تاريخ المقال:
تم الاستلام في شكل منقح في 10 ديسمبر 2024
تم القبول في 12 يناير 2025
متاح على الإنترنت في 23 يناير 2025
الكلمات المفتاحية:
الملخص
أصبح اتخاذ القرار في سيناريوهات معقدة ومتعددة الأوجه أمرًا حاسمًا بشكل متزايد عبر قطاعات متنوعة، مما يتطلب أطرًا قوية مثل اتخاذ القرار متعدد المعايير (MCDM). على مدى العقدين الماضيين (2004-2024)، تحولت MCDM من أساليب أساسية مثل AHP وTOPSIS إلى نماذج هجينة ديناميكية تدمج الذكاء الاصطناعي، والمنطق الضبابي، وتعلم الآلة. على الرغم من التقدم الكبير، تواجه هذه المجال تحديات في معالجة الفجوات الجغرافية، والمجالات غير المستكشفة، والتكيف مع الاحتياجات العالمية الناشئة. تقدم هذه الدراسة مراجعة شاملة لتطور MCDM، موحدةً الرؤى من 3,655 مقالة تمت مراجعتها من قبل الأقران تم الحصول عليها من خلالDimensions.ai وتم تحليلها باستخدام أدوات بيبليومترية مثل VOSviewer. تحدد الأبحاث اتجاهات النشر، والمساهمين الرئيسيين، والمجموعات الموضوعية، والشبكات التعاونية مع تحديد الفجوات والفرص للاستكشاف المستقبلي. تسلط هذه النتائج الرئيسية الضوء على النمو الأسي في تطبيقات MCDM، لا سيما في الطاقة المستدامة، والتخطيط الحضري، وتحسين الرعاية الصحية. تتماشى هذه التقدمات مع الأولويات العالمية، بما في ذلك أهداف التنمية المستدامة للأمم المتحدة (SDGs) مثل الطاقة النظيفة، والعمل المناخي، والمدن المستدامة. ومع ذلك، لا تزال هناك فجوات حرجة في معالجة قضايا مثل تخفيف الفقر، والمساواة بين الجنسين، والحفاظ على التنوع البيولوجي، مما يبرز الحاجة إلى تطبيقات متعددة التخصصات أوسع. تختتم هذه المراجعة بأن إمكانيات MCDM تكمن في احتضان الشمولية، والتقدم نحو التقنيات الناشئة مثل البلوك تشين والميتافيرس، وتعزيز التعاون عبر المناطق والمجالات غير الممثلة. من خلال الاستفادة من البيانات في الوقت الحقيقي، والمحاكاة الغامرة، ومنصات اتخاذ القرار الآمنة، يمكن لـ MCDM إعادة تعريف كيفية معالجة التحديات العالمية.
1. المقدمة
1.2 مراجعة الأدبيات
أساليب MCDM التقليدية مع أدوات حوسبة متقدمة مثل المنطق الضبابي، والذكاء الاصطناعي (AI)، وتعلم الآلة. قدم سعود وآخرون [9] “decideXpert”، وهو نظام اتخاذ قرار تعاوني يجمع بين AHP-TOPSIS مع المنطق الضبابي لتحسين اتخاذ القرار الجماعي. اقترح رادوليسكو ورادوليسكو [10] نموذجًا هجينيًا يدمج أساليب SAW وTOPSIS وVIKOR وCOPRAS لمشكلات اختيار إنترنت الأشياء، مما يوضح تنوع الأطر الهجينة في معالجة التحديات التكنولوجية المعقدة.
1. الهندسة: في الهندسة، كانت أساليب MCDM أساسية في تحسين تخصيص الموارد وتطوير البنية التحتية. طبق سيفالينغام وسوبارامانيام [11] نموذج AHP-TOPSIS الهجين لاختيار الروبوتات في عملية تجميع فلتر الوقود، مما يبرز أهميته العملية في الأتمتة الصناعية. طور توبال أوغلو [12] طريقة MCDM هجينة جديدة لاختيار مواقع المرافق، معالجًا التعقيدات اللوجستية في التخطيط الحضري.
iii. العلوم البيئية: تُستخدم تقنيات MCDM، وخاصةً PROMETHEE وELECTRE، على نطاق واسع في الاستدامة البيئية. وقد قامت هذه الطرق بتقييم التبادلات بين التنمية الاقتصادية والحفاظ على البيئة Zavadskas وآخرون، [8]. استعرض Stojčić وآخرون، [13] تطبيق طرق MCDM في هندسة الاستدامة، مع تسليط الضوء على دورها في التخفيف من آثار تغير المناخ وإدارة الموارد.
iii. الرعاية الصحية: استفاد قطاع الرعاية الصحية من MCDM لتحديد أولويات الموارد بكفاءة وتقييم الأداء. قدم Stević وآخرون، [14] طريقة MARCOS لتعزيز اختيار الموردين في الرعاية الصحية، بينما طبق Mahmoodirad وآخرون، [15] نموذج BCC الضبابي لتقييم أداء المستشفيات. تُظهر هذه الدراسات قدرة MCDM على التنقل في تعقيدات اتخاذ القرار في الرعاية الصحية.
iv. الأعمال والاقتصاد: تُستخدم طرق MCDM على نطاق واسع في اتخاذ القرارات الاستراتيجية، وتقييم الموردين، والتحليل المالي. طبق Karatas وآخرون، [16] تقنيات MCDM في الصناعة 4.0، مستكشفين دورها في معالجة التحديات في قطاع الرعاية الصحية. قام Pamučar وĆirović [17] بتوسيع طريقة MABAC لتحسين العمليات اللوجستية، مما يُظهر فائدتها في بيئات الأعمال.
تظهر التنوع المنهجي داخل MCDM في التمييز بين المدارس الأمريكية والأوروبية. تركز المدرسة الأمريكية على البساطة والنماذج القائمة على القيمة مثل AHP وSMART، بينما تركز المدرسة الأوروبية على تقنيات التفوق مثل PROMETHEE وELECTRE. قارن Zavadskas وآخرون، [8] بين هذه الأساليب، مسلطين الضوء على نقاط قوتها وضعفها. تسد الطرق الهجينة، مثل تلك التي اقترحها Deveci وآخرون، [18] الفجوات من خلال دمج تقنيات مكملة لتحسين اتخاذ القرار.
1.3 فجوات البحث
الأدبيات السابقة حول طرق MCDM
| المؤلفون | عنوان العمل | النتائج | المجالات |
| Zavadskas وآخرون، [8] | استطلاعات حالة الفن حول طرق MCDM/MADM | تقنيات MCDM قابلة للتكيف وتستخدم على نطاق واسع في اتخاذ القرار | تطبيقات MCDM العامة |
| Saoud وآخرون، [9] | DecideXpert: نظام تعاوني يستخدم AHP-TOPSIS وتقنيات ضبابية | تحسن اتخاذ القرار التعاوني من خلال الأنظمة الهجينة | اتخاذ القرار التعاوني |
| Radulescu وRadulescu [10] | نهج جماعي هجيني لمشكلات اختيار IoT | تتفوق النماذج الهجينة على الطرق المستقلة في اختيار IoT | اختيار IoT |
| Sivalingam وSubramaniam [11] | اختيار Cobot باستخدام AHPTOPSIS لعملية تجميع فلتر الوقود | يضمن AHP-TOPSIS اختيار Cobot الأمثل لأتمتة الصناعة | أتمتة الصناعة |
| Topaloğlu [12] | تطوير طريقة هجينة جديدة لاختيار مواقع المنشآت | تكون النماذج الهجينة فعالة في القرارات اللوجستية | تحسين اللوجستيات |
| Stojčić وآخرون، [13] | تطبيق طرق MCDM في هندسة الاستدامة: مراجعة أدبية 2008-2018 | MCDM ضروري لتقييم التبادلات في الاستدامة | هندسة الاستدامة |
| Stević وآخرون، [14] | اختيار الموردين المستدامين في صناعات الرعاية الصحية باستخدام MARCOS | يعزز MARCOS عمليات تقييم الموردين | شراء الرعاية الصحية |
| Mahmoodirad وآخرون، [15] | تقييم الأداء القائم على تحليل الانحدار للمستشفيات: تنفيذ نموذج BCC الضبابي الجديد. | تحسن طرق الضبابية من دقة التقييم | تقييم أداء المستشفى |
| Karatas وآخرون، [16] | البيانات الضخمة لصناعة الرعاية الصحية 4.0: التطبيقات، التحديات، وآفاق المستقبل | تسهل MCDM اتخاذ القرار الفعال في بيئات البيانات المعقدة | الصناعة 4.0 |
| Pamučار وĆirović [17] | اختيار موارد النقل والمناولة في مراكز اللوجستيات | تحقق MABAC المحسن نتائج أفضل في التخطيط اللوجستي | إدارة اللوجستيات |
| Deveci وآخرون، [18] | نظام دعم القرار للنقل الحضري المستدام في الميتافيرس | تحسن MCDM تخطيط النقل الحضري المستدام في البيئات الافتراضية | تقنيات الميتافيرس |
| Pamucar وآخرون، [19] | نموذج تقييم ميتافيرس للنقل المستدام | يدعم استدامة النقل الحضري باستخدام MCDM | النقل الحضري |
| Ala وآخرون، [20] | تقييم الخوارزميات لتحسين طاقة الرياح: نموذج اتخاذ قرار هجيني | تحسن النماذج الهجينة من الكفاءة في أنظمة الطاقة المتجددة | الطاقة المتجددة |
| المؤلفون | عنوان العمل | النتائج | المجالات |
| نموذج. أنظمة الخبراء مع التطبيقات | |||
| Chyad وآخرون، [21] | استكشاف التعلم العميق العدائي لتطبيقات كشف الجلد | يعزز التعلم العميق العدائي من دقة الكشف | تطبيقات الذكاء الاصطناعي وقناة الألوان المتعددة |
| Leung وZhang [22] | تحسين سرب الجسيمات LSTM للتنبؤ بأسعار الوقود | تحسن النماذج الهجينة من دقة التنبؤ | اقتصاديات الطاقة |
| Karagoz وآخرون، [23] | نهج CODAS الضبابي الجديد لتحديد مواقع مراكز التفكيك | تحسن الأساليب الضبابية من تخطيط مراكز التفكيك | إدارة النفايات |
| Simic وآخرون، [24] | نهج CODAS القائم على القرار الجماعي الضبابي لضرائب استثمارات النقل | تحسن الأساليب الضبابية من المالية العامة في أنظمة النقل | استثمارات النقل العام |
| Deveci وآخرون، [25] | الحركة الشخصية في الميتافيرس مع المركبات المستقلة باستخدام مجموعات ضبابية Q-rung | تحسين قرارات الحركة المستقلة في الفضاءات الافتراضية | الحركة في الميتافيرس |
1.4 تنظيم الدراسة
2. المنهجية
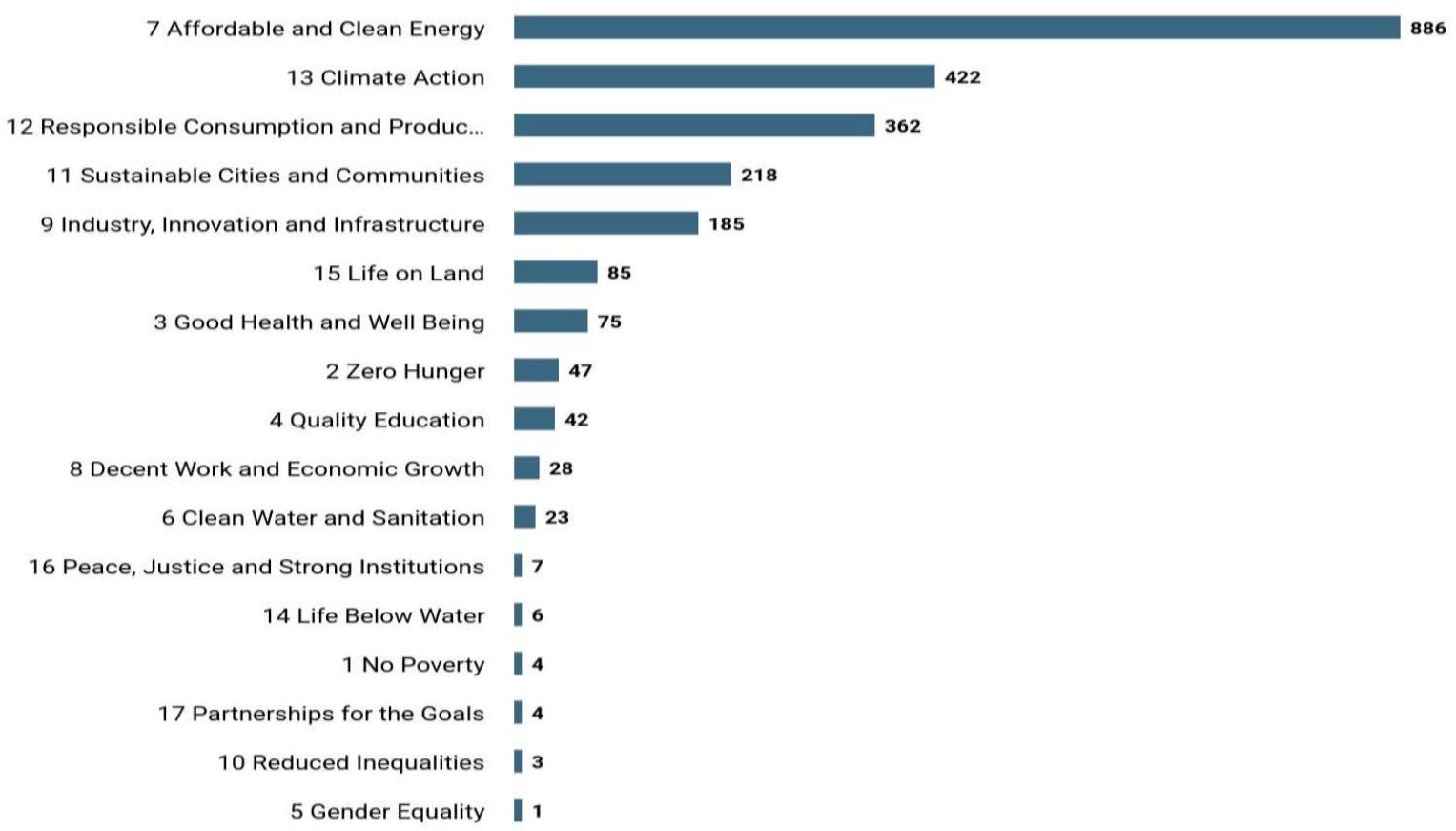
الاستدامة البيئية والطاقة. الهدف الأكثر تناولًا هو الطاقة النظيفة والميسورة (SDG 7)، مع 886 دراسة تبرز الطاقة المتجددة والتحسين. يلي ذلك العمل المناخي (SDG 13) بـ 422 دراسة، بينما يضم الاستهلاك والإنتاج المسؤولين (SDG 12) 362. تشمل المساهمات في المدن والمجتمعات المستدامة (SDG 11) والصناعة والابتكار والبنية التحتية (SDG 9) 218 و185 دراسة على التوالي. تشمل أهداف التنمية المستدامة الأقل بحثًا المساواة بين الجنسين (SDG 5)، وعدم الفقر (SDG 1)، وتقليل الفوارق (SDG 10)، مما يبرز الفجوات والفرص المستقبلية للبحث.
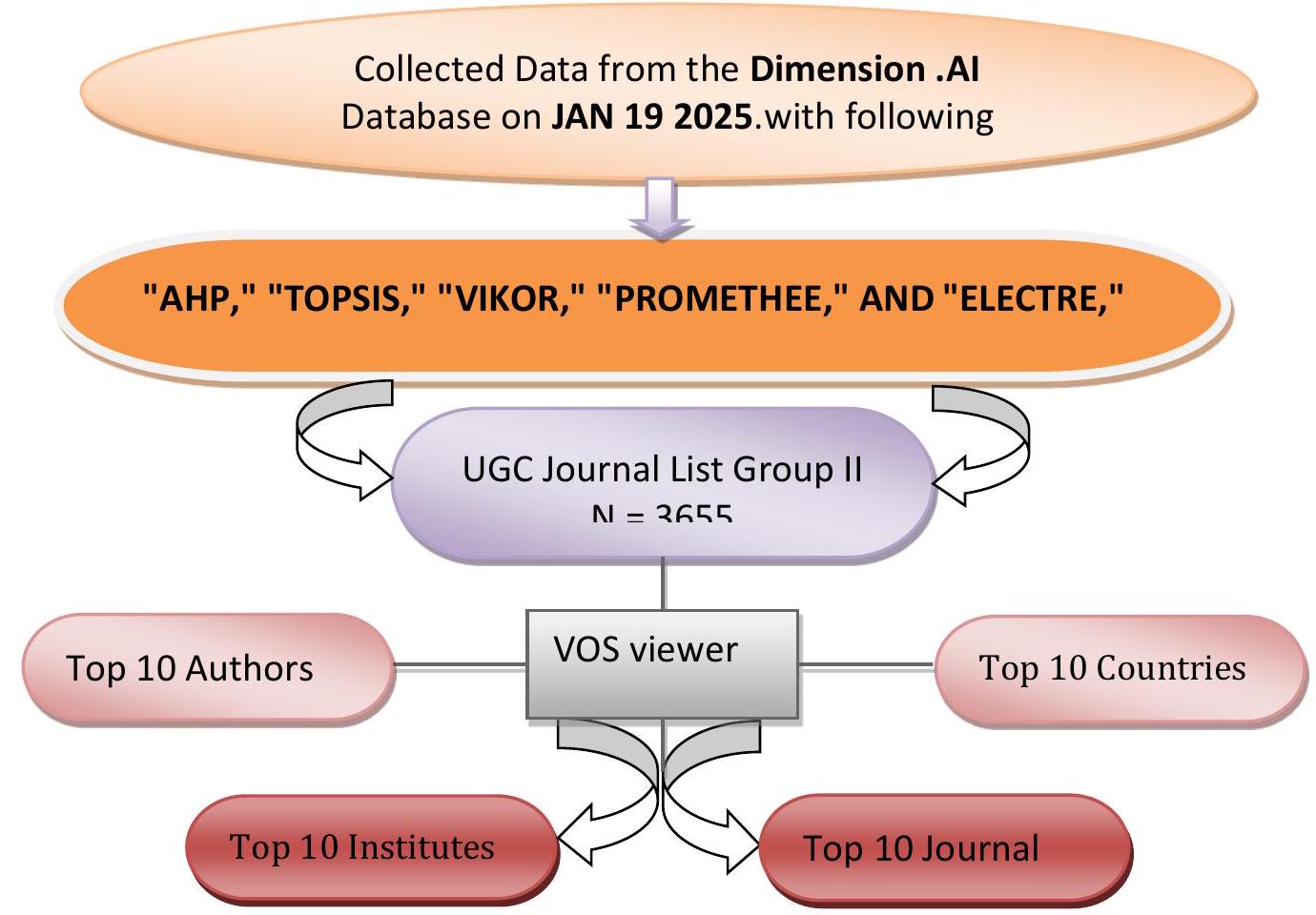

تم التصدير: 19 يناير 2025
المعايير: “‘,AHP, TOPSIS, VIKOR, PROMETHEE, ELECTRE, “‘ في البيانات الكاملة؛ سنة النشر هي 2006 أو 2007 أو 2008 أو 2009 أو 2004 أو 2010 أو 2011 أو 2012 أو 2013 أو 2014 أو 2015 أو 2016 أو 2017 أو 2018 أو 2019 أو 2020 أو 2021 أو 2022 أو 2023 أو 2024.
3. النتائج
3.1 تحليل الاتجاهات في النشر
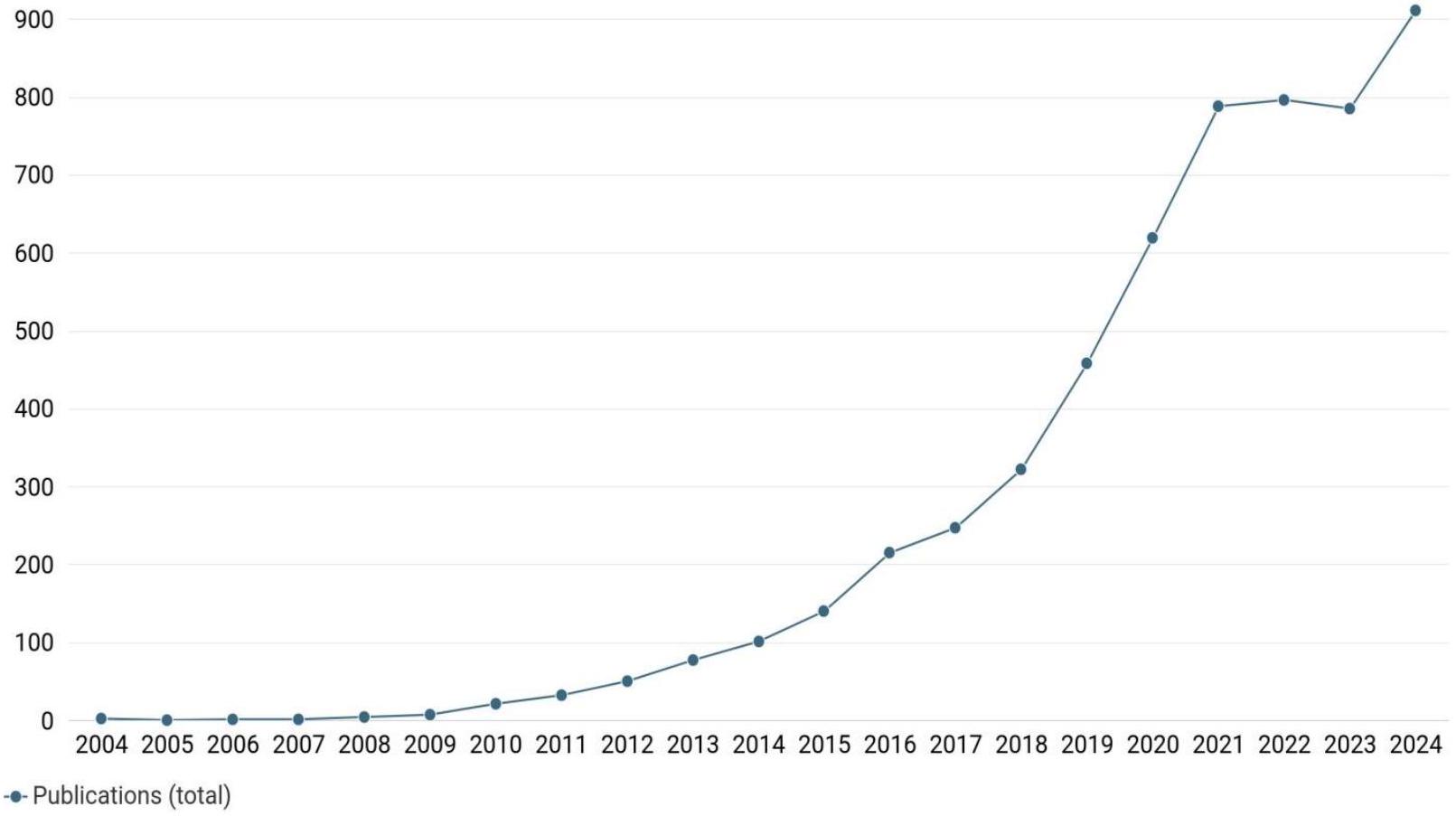
تحليل اتجاهات المنشورات (2004-2024)
| السنة | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| المنشورات | N | 0 |
|
ન | o |
|
|
으 | へ |
|
O |
|
|
|
os | 3 |
|
ゲ |
|
ন⿱⿵人一口冋 |
3.2 تحليل الاتجاهات في الاقتباسات
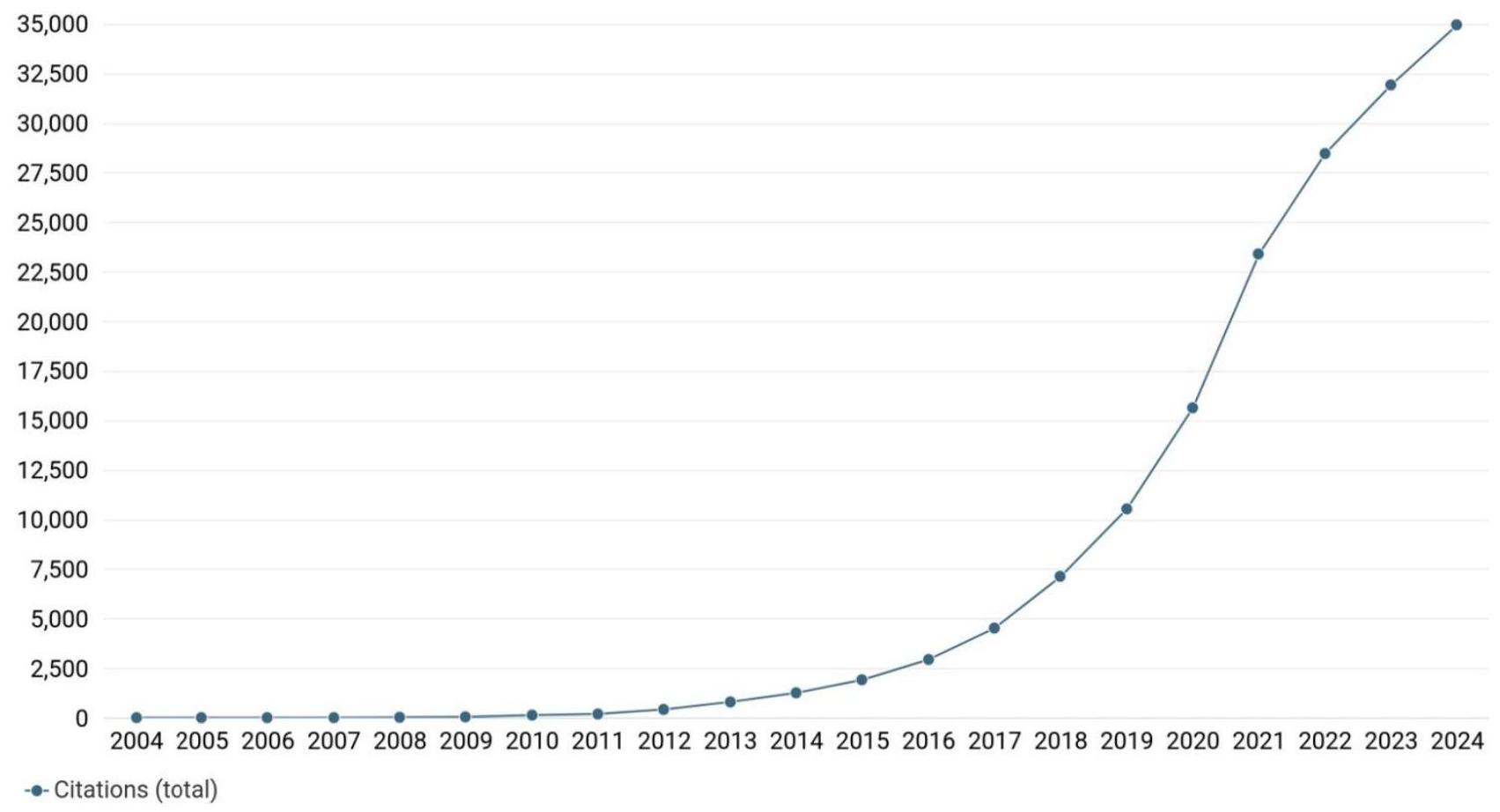
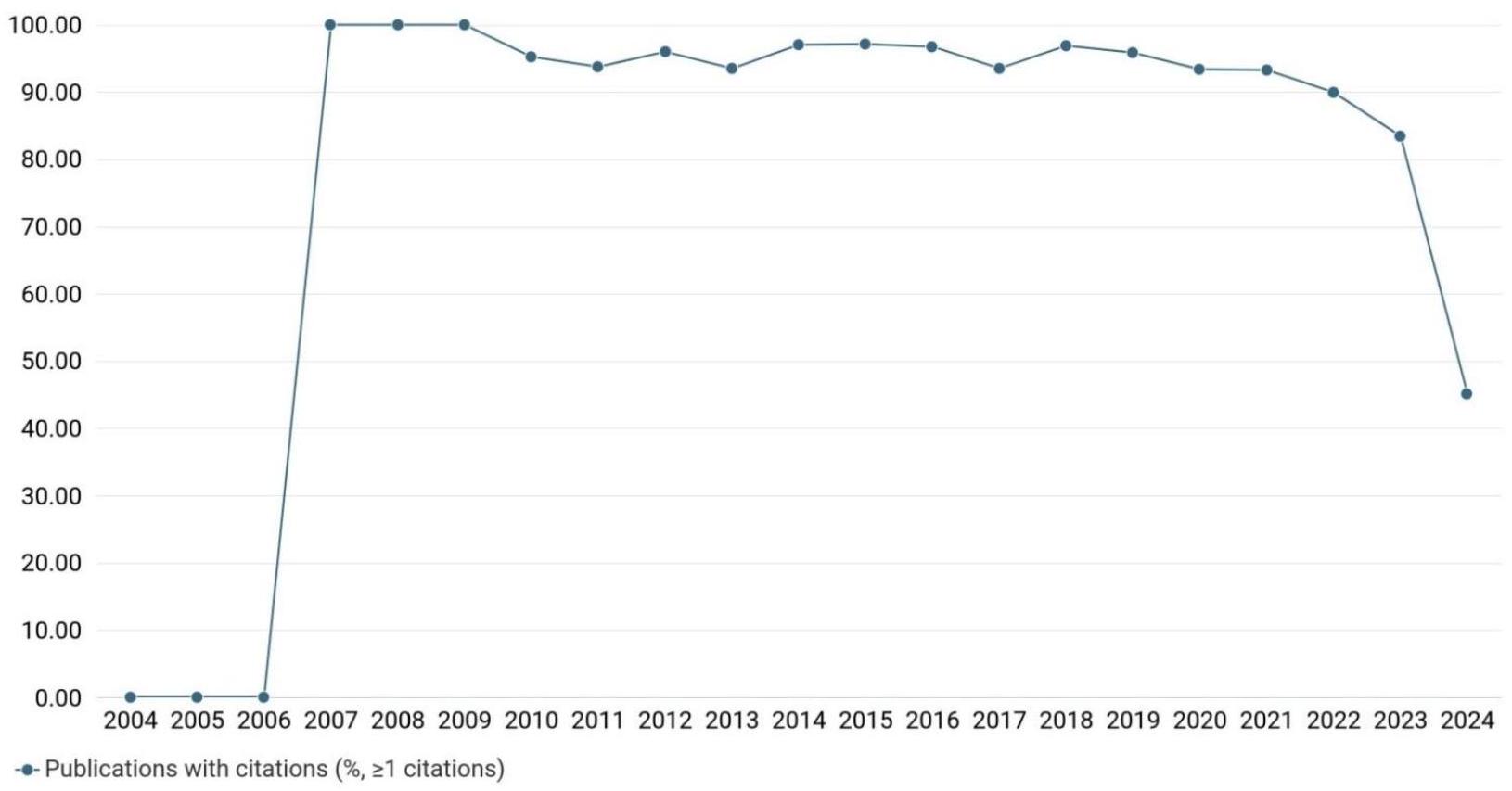
3.3 تحليل الاتجاهات في المنشورات مع الاقتباسات
3.4 تحليل التعاون في التأليف
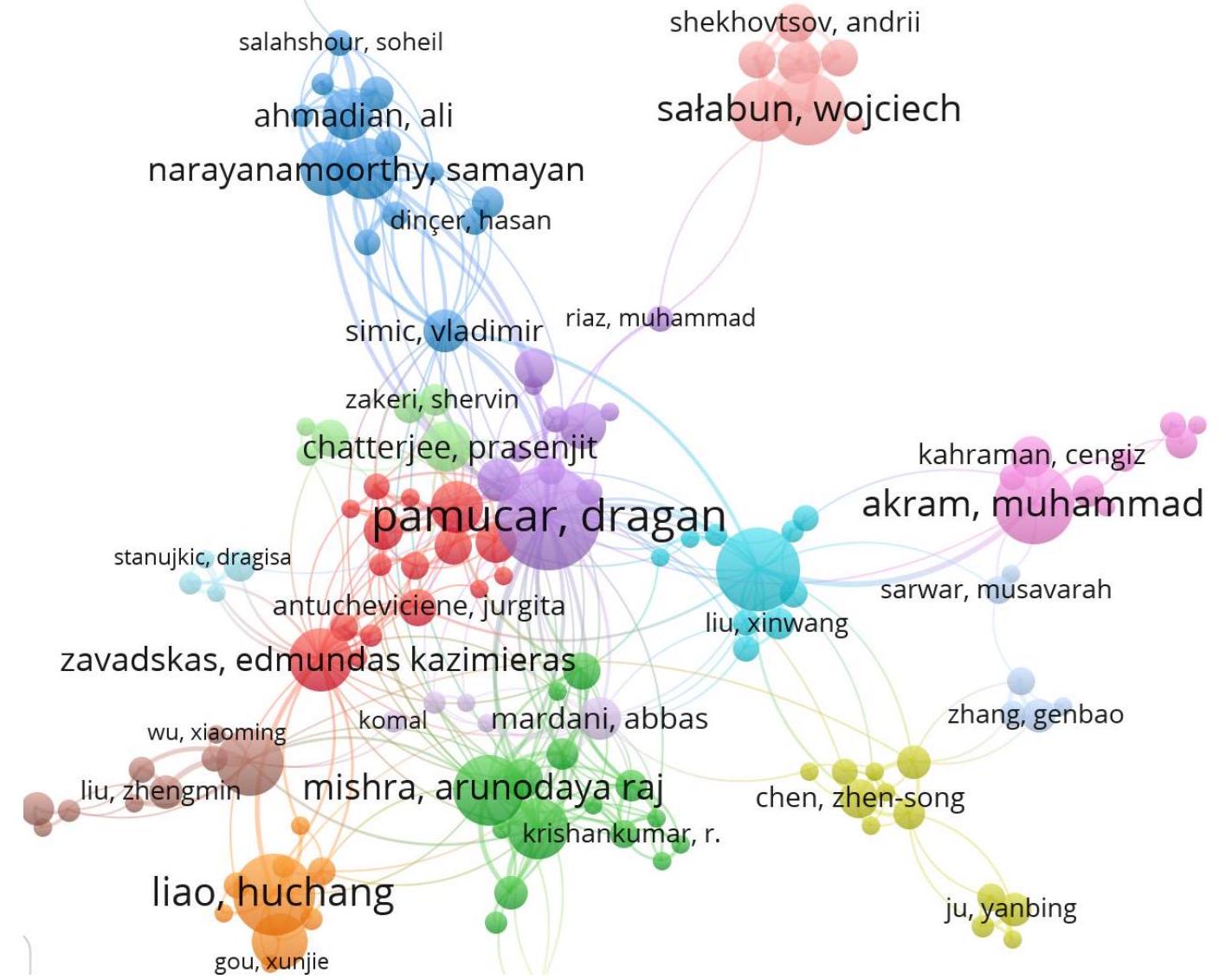
المؤلفون: تحدد هذه الدراسة 6387 مؤلفًا بعد إزالة النصوص التي تحتوي على 25 مؤلفًا كحد أقصى لكل منها. من بين هؤلاء، يتوافق 249 مؤلفًا فقط مع معايير وجود أربعة مستندات على الأقل وحد أدنى من 4 استشهادات. توضح الشكل 7 أنه من بين 249 مؤلفًا، كان لدى 141 باحثًا أعلى عدد من الأعمال المرتبطة.
تحليل أفضل 10 مؤلفين (الجدول 3) في أبحاث MCDM يبرز أدوارهم المحورية في تشكيل هذا المجال من خلال مساهماتهم الغزيرة، والاستشهادات المؤثرة، والتأثير الأكاديمي. دراغان باموكار هو رائد في الإنتاجية، حيث لديه 48 منشورًا و1,277 استشهادًا، مع الحفاظ على متوسط مشرف يبلغ 26.60 استشهادًا لكل مقال، مما يعكس مساهماته المستمرة عبر مجالات متنوعة من MCDM. بالمثل، يظهر محمد ديفيجي تأثيرًا أكاديميًا قويًا مع 34 منشورًا ومتوسط مثير للإعجاب يبلغ 31.09 استشهادًا، مما يبرز أهميته وتأثيره المستمر. ومن الجدير بالذكر أن يورغيتا أنتوكيفيتشيني تبرز كأحد الأسماء البارزة بأعلى متوسط استشهادات لكل مقال (66.60)، مما يسلط الضوء على جودة أبحاثها الاستثنائية وتأثيرها. جيانلي زو (62.90) وإدمونداس كازيميراس زافادسكس (45.52) يمثلان أيضًا التميز الأكاديمي، حيث حققا تأثيرًا كبيرًا من خلال مساهماتهما الكبيرة في تطوير المنهجيات والتطبيقات في MCDM. أرونودايا راج ميشرا يوازن بين الإنتاجية والتأثير بشكل فعال، مع 27 منشورًا ومتوسط 41.00 استشهادًا، مما يعكس حضوره الأكاديمي القوي. المؤلفون مثل هوتشانغ لياو (23.97 استشهادًا لكل مقال) وزيشوي شو (15.58) يحافظون على تأثير أكاديمي ثابت من خلال أعمالهم الأساسية والمتعددة التخصصات، مما يساهم في نمو هذا المجال وتطبيقه عبر مجالات متنوعة.
الإنتاجية والتأثير الاستثنائي. بينما يقود بعضهم، مثل باموكار د. وديفيجي م. بسجلات نشر واسعة، يحقق آخرون، مثل أنتوشتشيفيتشين وزو، تأثيرًا ملحوظًا لكل مقال، مما يبرز عمق وجودة أبحاثهم. يسلط عملهم الضوء على الأهمية المتزايدة لطرق اتخاذ القرار المتعددة المعايير (MCDM) في معالجة تحديات اتخاذ القرار المعقدة، وجسر التخصصات، ودفع التقدم النظري والتطبيقات العملية على مستوى العالم.
أفضل 10 مؤلفين من حيث المنشورات والاستشهادات ومتوسط الاستشهادات لكل مقال
| رتبة | اسم المؤلف | المطبوعات | استشهادات | متوسط الاقتباسات لكل مقال |
| 1 | دراغان باموكار | ٤٨ | ١,٢٧٧ | 27 |
| ٢ | محمد ديفجي | ٣٤ | ١٠٥٧ | 31 |
| ٣ | هو تشانغ لياو | ٣٣ | 791 | ٢٤ |
| ٤ | أرونودايا راج ميشرا | 27 | ١،١٠٧ | 41 |
| ٥ | إدمونداس كازيميراس زافادسكس | 23 | ١٠٤٧ | ٤٥ |
| ٦ | زيسوي شيو | 19 | ٢٩٦ | 16 |
| ٧ | دايكوك كانغ | 18 | ٢٨٣ | 16 |
| ٨ | علي أحمديان | 16 | 180 | 11 |
| 9 | جيانلي زو | 10 | 629 | 63 |
| 10 | يورجيتا أنتوكيفيتشيني | 10 | 666 | 67 |
أفضل 10 منظمات بناءً على المنشورات والاستشهادات وقوة الروابط الإجمالية
| رتبة | اسم المنظمة | المطبوعات | استشهادات | قوة الرابط الكلية |
| 1 | جامعة بلغراد | 70 | 1,380 | 164 |
| 2 | جامعة سيتشوان | ٥٤ | 1,388 | ٤٤ |
| ٣ | جامعة فيلنيوس غيديميناس التقنية | 50 | ١٤٧٤ | ١٠١ |
| ٤ | جامعة شتشيتسين | ٣٧ | 1,329 | 40 |
| ٥ | الأكاديمية البحرية | 32 | ٨٨٥ | ١٠٧ |
| ٦ | جامعة الدفاع | 26 | 1,913 | ٥٧ |
| ٧ | جامعة يلدز التقنية | ٢٨ | 664 | ٢٤ |
| ٨ | جامعة مولانا أبو الكلام آزاد للتكنولوجيا | 20 | ١٦١٥ | 41 |
| 9 | جامعة إسطنبول التقنية | ٢٨ | ١١٢٧ | 15 |
| 10 | جامعة أفيوك كوجاتيبé | 17 | 914 | ٣٤ |
أفضل 10 دول بناءً على المنشورات والاستشهادات ومتوسط الاستشهادات لكل مقال
| رتبة | بلد | المطبوعات | استشهادات | متوسط الاقتباسات لكل مقال |
| 1 | الصين | 570 | ١٣,٩٦٧ | ٢٤.٥١ |
| 2 | الهند | 418 | 9,442 | ٢٢.٥٩ |
| ٣ | تركيا | 385 | ٨,٨٢٨ | ٢٢.٩٣ |
| ٤ | المملكة المتحدة | ١٢٢ | ٤٥٦٥ | ٣٧.٤٢ |
| ٥ | الولايات المتحدة | 111 | ٣٤١٥ | 30.77 |
| ٦ | إسبانيا | ١٢٦ | ٣,٣١١ | ٢٦.٢٩ |
| ٧ | صربيا | ١٠٦ | ٣٤٢٦ | 32.32 |
| ٨ | المملكة العربية السعودية | ١١٩ | ٢,٢٨٢ | 19.18 |
| 9 | بولندا | 100 | ٢٦٤٧ | ٢٦.٤٧ |
| 10 | تايوان | 100 | 1,852 | 18.52 |
3.5 تحليل الاقتباسات
المستندات: تركز دراسة الاقتباسات بشكل أساسي على منشورات أكاديمية محددة، بما في ذلك مقالات المجلات، وأوراق المؤتمرات، والكتب، وبراءات الاختراع. باستخدام VOSviewer، يمكن للباحثين تحليل روابط الاقتباس بين هذه الأوراق، والعثور على المنشورات المؤثرة، وتتبع تاريخ الأفكار، واكتشاف الإطار الفكري لمجال معين من الدراسة.
تم العثور على 2504 مستندات في هذا التحليل. فقط 1945 مستندًا تلبي المعايير بحد أدنى من 3 استشهادات لكل منها. توضح الشكل 10 أنه من بين 295 مستندًا، كان لدى 129 ورقة أكبر عدد من الأشياء ذات الصلة.
تُبرز الجدول 6 أبرز 10 مؤلفين مشاركين مؤثرين بناءً على استشهاداتهم ومساهماتهم في مجالات مختلفة. يتصدر Stević وآخرون، [14] القائمة بـ 866 استشهادًا في بحوث العمليات، مما يُظهر تأثيرًا كبيرًا. يظهر Liu وآخرون، [28] بـ 631 استشهادًا، مما يعكس عملاً مؤثرًا في العلوم البيئية. يساهم Yadav وآخرون، [29] وSlebi-Acevedo وآخرون، [30] بشكل بارز في التنمية المستدامة وعلوم القرار، على التوالي. يركز Akram وآخرون، [31] وTzouramani وآخرون، [32] على تقنيات التحسين والاستدامة. يتميز Liao وآخرون، [33] بمساهماتهم في الطاقة المتجددة، بينما يركز Salimi وآخرون، [34] وRahimi وآخرون، [35] على النمذجة الرياضية وعلوم البيانات. هؤلاء المؤلفون المشاركون مرتبطون بمؤسسات مرموقة، مما يبرز الطبيعة متعددة التخصصات لأبحاثهم وتأثيرها على المناقشات الأكاديمية العالمية.
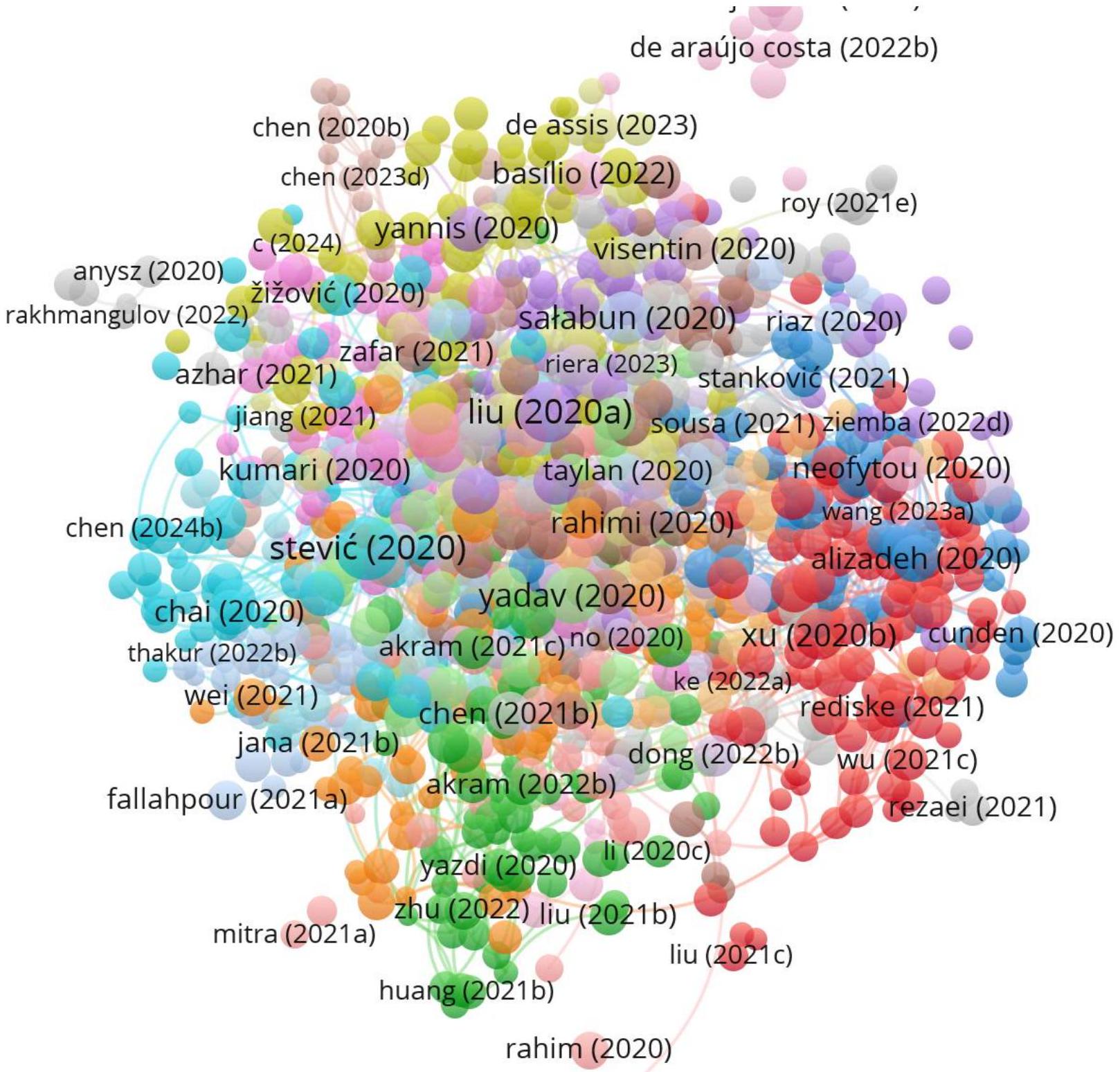
أفضل 10 مؤلفين مشاركين مع المؤسسة ومجال الدراسة
| مؤلف مشارك | استشهادات | روابط | مؤسسة | مجال الدراسة |
| ستيفيتش وآخرون، [14] | ٨٦٦ | 98 | جامعة شرق سراييفو | بحوث العمليات |
| ليو وآخرون، [28] | 631 | 17 | الأكاديمية الصينية للعلوم | علوم البيئة |
| ياداف وآخرون، [29] | ٤٥٨ | ٤ | معهد الهند للتكنولوجيا | التنمية المستدامة |
| سليبي-أسيفيدو وآخرون، [30] | ٣٥٢ | 60 | جامعة بوزنان للتكنولوجيا | علوم القرار |
| أكرم وآخرون، [31] | ١٩٧ | 23 | جامعة طهران | تقنيات التحسين |
| تزوراماني وآخرون، [32] | 143 | 17 | جامعة طهران | التنمية المستدامة |
| لياو وآخرون، [33] | 143 | 17 | جامعة تايوان الوطنية | الطاقة المتجددة |
| سليمي وآخرون، [34] | ١١٩ | ١٣ | جامعة فيينا | النمذجة الرياضية |
| رحيمي وآخرون، [35] | 67 | 14 | جامعة شريف للتكنولوجيا | علوم البيانات |
في هذا التحليل (الشكل 11). هناك 174 مصدرًا فقط تلبي الحد الأدنى المطلوب من 3 مستندات واستشهادات بالمصادر. يوضح الشكل 11 أنه من بين 174 مصدرًا، هناك 170 تحتوي على أكثر العناصر ذات الصلة.
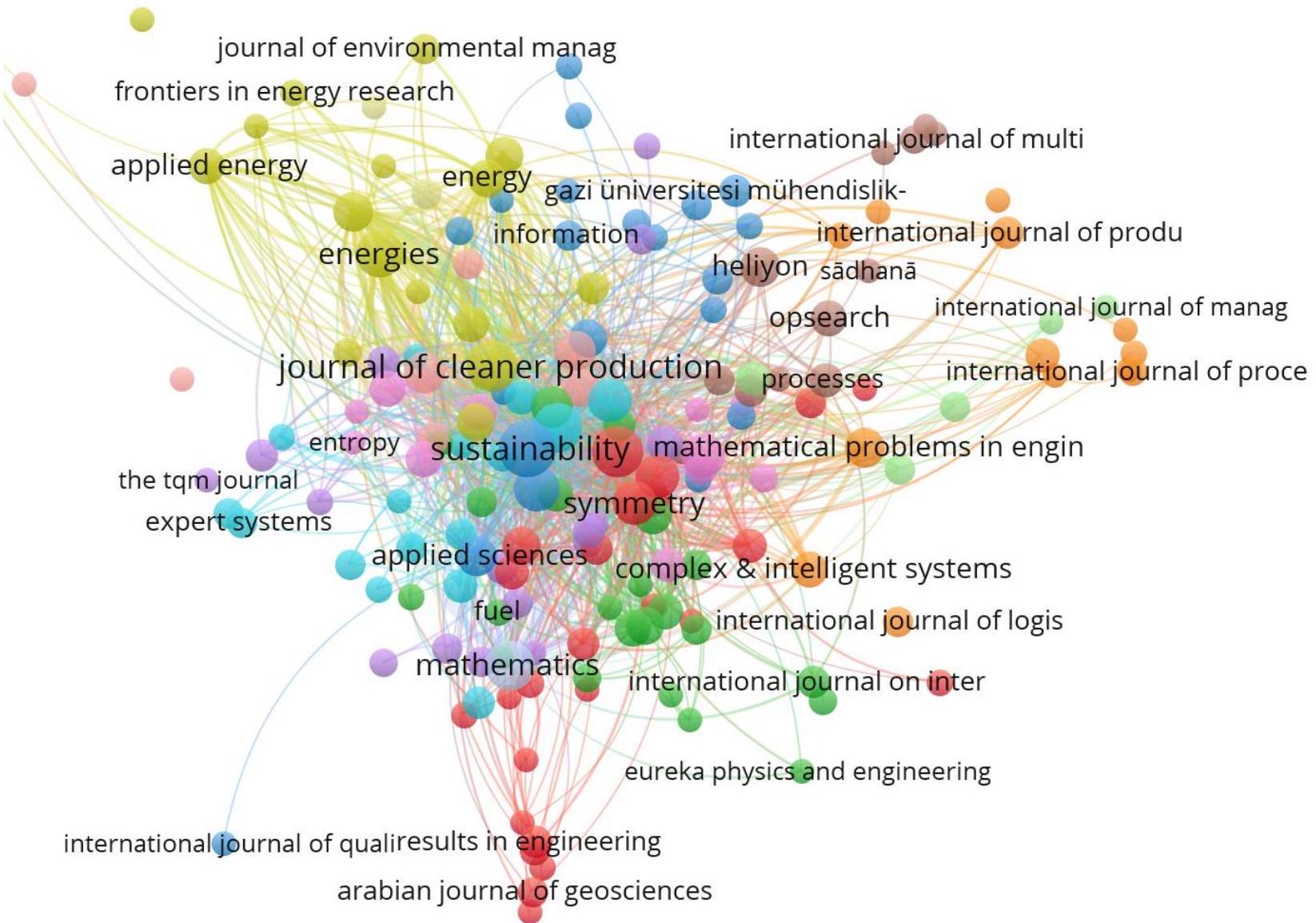
أفضل 10 مجلات بناءً على الاستشهادات
| رتبة | مصدر | مستندات | استشهادات | قوة الرابط الكلية |
| 1 | مجلة الإنتاج النظيف | 85 | ٣٧٢٩ | ٦٠٠ |
| ٢ | أنظمة الخبراء مع التطبيقات | 90 | ٣٣٧٢ | 628 |
| ٣ | الاستدامة | 152 | ٢٤٨١ | 520 |
| ٤ | تناظر | 40 | 1940 | ٣٣٢ |
| ٥ | علوم البيئة وبحوث التلوث | ٣٨ | 862 | 198 |
| ٦ | الطاقة المتجددة | ٢٥ | ١٠٩٠ | 204 |
| ٧ | الحوسبة اللينة التطبيقية | 73 | 2670 | 564 |
| ٨ | تقارير الطاقة | ١٨ | ٣٦٢ | 127 |
| 9 | IEEE Access | ٤٦ | 604 | 221 |
| 10 | الرياضيات | 77 | 1328 | 344 |
4. المناقشة
4.1 المساهمة في أهداف التنمية المستدامة
4.2 التقنيات الناشئة
الحلول في الميتافيرس، مما يوفر رؤى قيمة للتنفيذ في العالم الحقيقي. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يدعم الميتافيرس اتخاذ القرار التعاوني من خلال السماح لأصحاب المصلحة بالمشاركة في المحاكاة الافتراضية وتحليل النتائج بشكل مشترك. تسلط دراسات الحالة الضوء على التأثير العملي لهذه التقنيات. تم تنفيذ نهج الذكاء الاصطناعي-اتخاذ القرار المتعدد المعايير الهجينة بنجاح في مشاريع الطاقة المتجددة، مما يحسن اختيار المواقع لمزارع الرياح والطاقة الشمسية. لقد حسنت تطبيقات اتخاذ القرار المتعدد المعايير المدعومة بإنترنت الأشياء في الشبكات الذكية توزيع الطاقة وخفض التكاليف التشغيلية.
5. الخاتمة
شكر وتقدير
تعارض المصالح
References
[2] Kumar, R. (2024). Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Applications in Agro-based Industries for Economic Development: An Overview of Global Trends, Collaborative Patterns, and Research Gaps. Spectrum of Engineering and Management Sciences, 2(1), 247-262. https://doi.org/10.31181/sems21202431k
[3] Kumar, R. (2024). Artificial Intelligence (AI)-driven Transformation: Sustainable Development of Agro-based Industries in Bihar. International Journal for Multidisciplinary Research, 6(2). https://doi.org/10.36948/ijfmr.2024.v06i02.15935
[4] Kumar, R. & Kumari, K. (2024). Enhancing Economic Development through Inventory Management Optimization in Agro-based Industries in Bihar: A Comparative Study of EOQ and EPQ Models. International Journal for Multidisciplinary Research, 6(2). https://doi.org/10.36948/ijfmr.2024.v06i02.16892
[5] Kumar, R., Khan, A. K., & Goel, S. (2024). From farm to table: How AI is revolutionizing demand forecasting in agrobased industries. Blockchain and AI in business. Applications, Research and Insights, 81-99.
[6] Mokhtar, M. R., Abdullah, M. P., Hassan, M. Y., & Hussin, F. (2015). Combination of AHP-PROMETHEE and TOPSIS for selecting the best Demand Side Management (DSM) options. In 2015 IEEE Student Conference on Research and Development (SCOReD) (pp. 367-372). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/scored.2015.7449357
[7] Kumar, R. (2024). Global Trends and Research Patterns in Financial Literacy and Behavior: A Bibliometric Analysis. Management Science Advances., 2(1), 1-18. https://doi.org/10.31181/msa2120256
[8] Zavadskas, E. K., Turskis, Z., & Kildiené, S. (2014). STATE OF ART SURVEYS OF OVERVIEWS ON MCDM/MADM METHODS. Technological and Economic Development of Economy, 20(1), 165-179. https://doi.org/10.3846/20294913.2014.892037
[9] Saoud, A., Lachgar, M., Hanine, M., Dhimni, R. E., Azizi, K. E., & Machmoum, H. (2025). decideXpert: Collaborative system using AHP-TOPSIS and fuzzy techniques for multi-criteria group decision-making. SoftwareX, 29, 102026.
[10] Radulescu, C. Z., & Radulescu, M. (2024). A Hybrid Group Multi-Criteria Approach Based on SAW, TOPSIS, VIKOR, and COPRAS Methods for Complex IoT Selection Problems. Electronics, 13(4), 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13040789
[11] Sivalingam C, & Subramaniam, S. K. (2024). Cobot selection using hybrid AHP-TOPSIS based multi-criteria decision making technique for fuel filter assembly process. Heliyon, 10(4), e26374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26374
[12] Topaloğlu, F. (2024). Development of a new hybrid method for multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) approach: a case study for facility location selection. Operational Research, 24(4), 60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-024-00871-4
[13] Stojčić, M., Zavadskas, E., Pamučar, D., Stević, Ž., & Mardani, A. (2019). Application of MCDM Methods in Sustainability Engineering: A Literature Review 2008-2018. Symmetry, 11(3), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11030350
[14] Stević, Ž., Pamučar, D., Puška, A., & Chatterjee, P. (2020). Sustainable supplier selection in healthcare industries using a new MCDM method: Measurement of alternatives and ranking according to COmpromise solution (MARCOS). Computers & Industrial Engineering, 140, 106231. https://doi.org/10.1016/i.cie.2019.106231
[15] Mahmoodirad, A., Pamucar, D., Niroomand, S., & Simic, V. (2025). Data envelopment analysis based performance evaluation of hospitals – Implementation of novel picture fuzzy BCC model. Expert Systems with Applications, 263, 125775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2025.125775
[16] Karatas, M., Eriskin, L., Deveci, M., Pamucar, D., & Garg, H. (2022). Big Data for Healthcare Industry 4.0: Applications, challenges and future perspectives. Expert Systems with Applications, 200, 116912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.116912
[17] Pamučar, D., & Ćirović, G. (2015). The selection of transport and handling resources in logistics centers using MultiAttributive Border Approximation area Comparison (MABAC). Expert Systems with Applications, 42(6), 3016-3028. https://doi.org/10.1016/i.eswa.2014.11.057
[18] Deveci, M., Mishra, A. R., Gokasar, I., Rani, P., Pamucar, D., & Özcan, E. (2022). A Decision Support System for Assessing and Prioritizing Sustainable Urban Transportation in Metaverse. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 31(2), 475-484. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2022.3190613
[19] Pamucar, D., Deveci, M., Gokasar, I., Tavana, M., & Köppen, M. (2022). A metaverse assessment model for sustainable transportation using ordinal priority approach and Aczel-Alsina norms. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 182, 121778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.121778
[20] Ala, A., Mahmoudi, A., Mirjalili, S., Simic, V., & Pamucar, D. (2023). Evaluating the Performance of various Algorithms for Wind Energy Optimization: A Hybrid Decision-Making model. Expert Systems with Applications, 221, 119731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.119731
[21] Chyad, M., Zaidan, B. B., Zaidan, A. A., Pilehkouhi, H., Aalaa, R., Qahtan, S., Alsattar, H. A., Pamucar, D., & Simic, V. (2024). Exploring adversarial deep learning for fusion in multi-color channel skin detection applications. Information Fusion, 114, 102632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2024.102632
[22] Leung, A. Y. T., & Zhang, H. (2009). Particle swarm optimization of tuned mass dampers. Engineering Structures, 31(3), 715-728. https://doi.org/10.1016/i.engstruct.2008.11.017
[23] Karagoz, S., Deveci, M., Simic, V., Aydin, N., & Bolukbas, U. (2020). A novel intuitionistic fuzzy MCDM-based CODAS approach for locating an authorized dismantling center: a case study of Istanbul. Waste Management & Research, 38(6), 660-672. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242×19899729
[24] Simic, V., Gokasar, I., Deveci, M., & Isik, M. (2021). Fermatean Fuzzy Group Decision-Making Based CODAS Approach for Taxation of Public Transit Investments. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 70(12), 4233-4248. https://doi.org/10.1109/tem.2021.3109038
[25] Deveci, M., Pamucar, D., Gokasar, I., Koppen, M., & Gupta, B. B. (2022). Personal Mobility in Metaverse With Autonomous Vehicles Using Q-Rung Orthopair Fuzzy Sets Based OPA-RAFSI Model. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1109/tits.2022.3186294
[26] Kumar, R., & Sahoo, S. K. (2024). A Bibliometric Analysis of Agro-Based Industries: Trends and Challenges in Supply Chain Management. Decision Making Advances, 3(1), 200-215. https://doi.org/10.31181/dma31202568
[27] Kumar, R. (2025). Bibliometric Analysis: Comprehensive Insights into Tools, Techniques, Applications, and Solutions for Research Excellence. Spectrum of Engineering and Management Sciences, 3(1), 45-62. https://doi.org/10.31181/sems31202535k
[28] Liu, Y., Eckert, C. M., & Earl, C. (2020). A review of fuzzy AHP methods for decision-making with subjective judgements. Expert Systems with Applications, 161, 113738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113738
[29] Yadav, V., Kalbar, P. P., Karmakar, S., & Dikshit, A. K. (2020). A two-stage multi-attribute decision-making model for selecting appropriate locations of waste transfer stations in urban centers. Waste Management, 114, 80-88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.05.024
[30] Slebi-Acevedo, C. J., Lastra-González, P., Calzada-Pérez, M. A., & Castro-Fresno, D. (2020). Effect of Synthetic Fibers and Hydrated Lime in Porous Asphalt Mixture Using Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Techniques. Materials, 13(3), 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030675
[31] Akram, M., Kahraman, C., & Zahid, K. (2021). Group decision-making based on complex spherical fuzzy VIKOR approach. Knowledge-Based Systems, 216, 106793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2021.106793
[32] Tzouramani, I., Mantziaris, S., & Karanikolas, P. (2020). Assessing Sustainability Performance at the Farm Level: Examples from Greek Agricultural Systems. Sustainability, 12(7), 2929. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12072929
[33] Liao, H., Peng, X., & Gou, X. (2020). Medical Supplier Selection with a Group Decision-Making Method Based on Incomplete Probabilistic Linguistic Preference Relations. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 23, 280-294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-020-00885-y
[34] Salimi, A. H., Noori, A., Bonakdari, H., Masoompour Samakosh, J., Sharifi, E., Hassanvand, M., Gharabaghi, B., & Agharazi, M. (2020). Exploring the Role of Advertising Types on Improving the Water Consumption Behavior: An Application of Integrated Fuzzy AHP and Fuzzy VIKOR Method. Sustainability, 12(3), 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12031232
[35] Rahimi, S., Hafezalkotob, A., Monavari, S. M., Hafezalkotob, A., & Rahimi, R. (2020). Sustainable landfill site selection for municipal solid waste based on a hybrid decision-making approach: Fuzzy group BWM-MULTIMOORAGIS. Journal of Cleaner Production, 248, 119186. https://doi.org/10.1016/i.jclepro.2019.119186
- *Corresponding author.
E-mail address: rahul1996magadhuniversity@gmail.com
DOI: https://doi.org/10.31181/sdmap21202524
Publication Date: 2025-01-23
A Comprehensive and Systematic Review of Multi-Criteria DecisionMaking (MCDM) Methods to Solve Decision-Making Problems: Two Decades from 2004 to 2024
ARTICLE INFO
Article history:
Received in revised form 10 December 2024
Accepted 12 January 2025
Available online 23 January 2025
Keywords:
Abstract
Decision-making in complex, multifaceted scenarios has become increasingly critical across diverse sectors, necessitating robust frameworks like MultiCriteria Decision-Making (MCDM). Over the past two decades (2004-2024), MCDM has transformed from foundational methods like AHP and TOPSIS into dynamic hybrid models integrating artificial intelligence, fuzzy logic, and machine learning. Despite significant strides, the field faces challenges in addressing geographic disparities, underexplored domains and adapting to emerging global needs. This study provides a comprehensive review of MCDM’s evolution, consolidating insights from 3,655 peer-reviewed articles sourced through Dimensions.ai and analyzed using bibliometric tools like VOSviewer. The research identifies publication trends, leading contributors, thematic clusters, and collaborative networks while pinpointing gaps and opportunities for future exploration. These Key findings highlight exponential growth in MCDM applications, particularly in sustainable energy, urban planning, and healthcare optimization. These advancements align with global priorities, including the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) such as clean energy, climate action, and sustainable cities. However, critical gaps remain in addressing issues like poverty alleviation, gender equity, and biodiversity conservation, emphasizing the need for broader interdisciplinary applications. This review concludes that MCDM’s potential lies in embracing inclusivity, advancing into emerging technologies like blockchain and the metaverse, and fostering collaboration across underrepresented regions and domains. By harnessing real-time data, immersive simulations, and secure decision-making platforms, MCDM can redefine how global challenges are addressed.
1. Introduction
1.2 Literature Review
integrate traditional MCDM methods with advanced computational tools such as fuzzy logic, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning. Saoud et al., [9] introduced “decideXpert,” a collaborative decision-making system combining AHP-TOPSIS with fuzzy logic for enhanced group decision-making [9]. Radulescu and Radulescu [10] proposed a hybrid model integrating SAW, TOPSIS, VIKOR, and COPRAS methods for IoT selection problems, illustrating the versatility of hybrid frameworks in tackling complex technological challenges [10].
i. Engineering: In engineering, MCDM methods have been instrumental in optimizing resource allocation and infrastructure development. Sivalingam and Subramaniam [11] applied a hybrid AHP-TOPSIS model to cobot selection in the fuel filter assembly process, emphasizing its practical relevance in industrial automation [11]. Topaloğlu [12] developed a new hybrid MCDM method for facility location selection, addressing logistical complexities in urban planning.
ii. Environmental Sciences: MCDM techniques, particularly PROMETHEE and ELECTRE, are widely employed in environmental sustainability. These methods have evaluated tradeoffs between economic development and environmental preservation Zavadskas et al., [8]. Stojčić et al., [13] reviewed the application of MCDM methods in sustainability engineering, highlighting their role in climate change mitigation and resource management.
iii. Healthcare: The healthcare sector has leveraged MCDM for efficient resource prioritization and performance evaluation. Stević et al., [14] introduced the MARCOS method to enhance supplier selection in healthcare, while Mahmoodirad et al., [15] applied a picture fuzzy BCC model for evaluating hospital performance. These studies demonstrate MCDM’s ability to navigate the complexities of healthcare decision-making.
iv. Business and Economics: MCDM methods are extensively utilized in strategic decisionmaking, supplier evaluation, and financial analysis. Karatas et al., [16] applied MCDM techniques in Industry 4.0, exploring their role in addressing challenges in the healthcare sector. Pamučar and Ćirović [17] extended the MABAC method to improve logistics operations, showcasing its utility in business environments.
The methodological diversity within MCDM is evident in the distinction between the American and European schools. The American school emphasizes simplicity and value-based models such as AHP and SMART, while the European school focuses on outranking techniques like PROMETHEE and ELECTRE. Zavadskas et al., [8] compared these approaches, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses. Hybrid methods, such as those proposed by Deveci et al., [18], bridge the gaps by integrating complementary techniques for enhanced decision-making.
1.3 Research Gaps
Past Literature on MCDM Methods
| Authors | Title of Work | Findings | Domains |
| Zavadskas et al., [8] | State of art surveys of overviews on MCDM/MADM methods | MCDM techniques are adaptable and widely used in decision-making | General MCDM Applications |
| Saoud et al., [9] | DecideXpert: Collaborative system using AHP-TOPSIS and fuzzy techniques | Collaborative decisionmaking is improved through hybrid systems | Collaborative Decision-Making |
| Radulescu and Radulescu [10] | A Hybrid Group Multi-Criteria Approach for IoT Selection Problems | Hybrid models outperform standalone methods in IoT selection | IoT Selection |
| Sivalingam and Subramaniam [11] | Cobot selection using hybrid AHPTOPSIS for fuel filter assembly process | AHP-TOPSIS ensures optimized cobot selection for industrial automation | Industrial Automation |
| Topaloğlu [12] | Development of a new hybrid method for facility location selection | Hybrid models are effective for logistical decisions | Logistics Optimization |
| Stojčić et al., [13] | Application of MCDM methods in sustainability engineering: A Literature Review 2008-2018 | MCDM is crucial for evaluating trade-offs in sustainability | Sustainability Engineering |
| Stević et al., [14] | Sustainable supplier selection in healthcare industries using MARCOS | MARCOS enhances supplier evaluation processes | Healthcare Procurement |
| Mahmoodirad et al., [15] | Data envelopment analysis-based performance evaluation of hospitalsImplementation of novel picture fuzzy BCC model. | Picture fuzzy methods improve evaluation accuracy | Hospital Performance Evaluation |
| Karatas et al., [16] | Big Data for Healthcare Industry 4.0: Applications, challenges, and future perspectives | MCDM facilitates effective decision-making in complex data environments | Industry 4.0 |
| Pamučar and Ćirović [17] | The selection of transport and handling resources in logistics centers | Enhanced MABAC achieves better results in logistics planning | Logistics Management |
| Deveci et al., [18] | A decision support system for sustainable urban transportation in the Metaverse | MCDM improves sustainable urban transportation planning in virtual environments | Metaverse Technologies |
| Pamucar et al., [19] | A metaverse assessment model for sustainable transportation | Supports urban transportation sustainability using MCDM | Urban Transportation |
| Ala et al., [20] | Evaluating algorithms for wind energy optimization: A Hybrid Decision-Making | Hybrid models improve efficiency in renewable energy systems | Renewable Energy |
| Authors | Title of Work | Findings | Domains |
| model. Expert Systems with Applications | |||
| Chyad et al., [21] | Exploring adversarial deep learning for skin detection applications | Adversarial deep learning enhances detection accuracy | AI and Multi-Color Channel Applications |
| Leung and Zhang [22] | Particle swarm optimization tuned LSTM for fuel price forecasting | Hybrid models improve forecasting accuracy | Energy Economics |
| Karagoz et al., [23] | A novel intuitionist fuzzy CODAS approach for locating dismantling centers | Intuitionist fuzzy approaches improve dismantling center planning | Waste Management |
| Simic et al., [24] | Fermat fuzzy group decision-making based CODAS approach for taxation of transit investments | Fuzzy methods optimize public finance in transit systems | Public Transit Investments |
| Deveci et al., [25] | Personal mobility in Metaverse with autonomous vehicles using Q-rung orthopedic fuzzy sets | Optimized autonomous mobility decisions in virtual spaces | Mobility in the Metaverse |
1.4 Organization of the Study
2. Methodology
environmental sustainability and energy. The most addressed SDG is Affordable and Clean Energy (SDG 7), with 886 studies emphasizing renewable energy and optimization. Climate Action (SDG 13) follows with 422 studies, while Responsible Consumption and Production (SDG 12) has 362. Contributions to Sustainable Cities and Communities (SDG 11) and Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure (SDG 9) include 218 and 185 studies, respectively. Lesser-researched SDGs include Gender Equality (SDG 5), No Poverty (SDG 1), and Reduced Inequalities (SDG 10), highlighting gaps and future opportunities for research.



Exported: January 19, 2025
Criteria: “‘,AHP, TOPSIS, VIKOR, PROMETHEE, ELECTRE, “‘ in full data; Publication Year is 2006 or 2007 or 2008 or 2009 or 2004 or 2010 or 2011 or 2012 or 2013 or 2014 or 2015 or 2016 or 2017 or 2018 or 2019 or 2020 or 2021 or 2022 or 2023 or 2024.
3. Results
3.1 Trend Analysis of Publication

Publications Trend Analysis Table(2004-2024)
| Year | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| Publica tions | N | 0 |
|
ન | o |
|
|
으 | へ |
|
O |
|
|
|
os | 3 |
|
ゲ |
|
ন⿱⿵人一口冋 |
3.2 Trend Analysis of Citations

3.3 Trend Analysis of publications with citations

3.4 Co-authorship Analysis
I. Authors: This investigation identifies 6387 authors after removing texts with a maximum of 25 authors apiece. Of these, only 249 authors match the criteria of having at least four documents and a minimum of 4 citations. Figure 7 demonstrates that among the 249 authors, 141 researchers had the highest number of linked works.
The analysis of the top 10 authors (Table 3 ) in MCDM research underscores their pivotal roles in shaping the field through prolific contributions, impactful citations, and academic influence. Dragan Pamucar is a leader in productivity, with 48 publications and 1,277 citations, maintaining a commendable average of 26.60 citations per article, reflecting his consistent contributions across diverse areas of MCDM. Similarly, Muhammet Deveci demonstrates strong academic influence with 34 publications and an impressive average of 31.09 citations, underscoring his relevance and consistent impact. Notably, Jurgita Antucheviciene emerges as a standout with the highest average citations per article (66.60), highlighting her exceptional research quality and influence. Jianli Zhou (62.90) and Edmundas Kazimieras Zavadskas (45.52) further exemplify academic excellence, achieving substantial impact through their significant contributions to advancing methodologies and applications in MCDM. Arunodaya Raj Mishra balances productivity and influence effectively, with 27 publications and an average of 41.00 citations, reflecting his robust academic presence. Authors like Huchang Liao ( 23.97 citations per article) and Zeshui Xu (15.58) maintain steady academic impact through foundational and interdisciplinary work, contributing to the field’s growth and its application across various domains.
productivity and exceptional influence. While some, like Pamucar D. and Deveci M. lead with extensive publication records, others, such as Antucheviciene and Zhou, achieve remarkable perarticle impact, demonstrating the depth and quality of their research. Their work highlights the growing significance of MCDM in addressing complex decision-making challenges, bridging disciplines, and driving both theoretical advancements and practical applications globally.

Top 10 Authors publications, citations, and average citation per article
| Rank | Author Name | Publications | Citations | Average Citations per Article |
| 1 | Dragan Pamucar | 48 | 1,277 | 27 |
| 2 | Muhammet Deveci | 34 | 1,057 | 31 |
| 3 | Huchang Liao | 33 | 791 | 24 |
| 4 | Arunodaya Raj Mishra | 27 | 1,107 | 41 |
| 5 | Edmundas Kazimieras Zavadskas | 23 | 1,047 | 45 |
| 6 | Zeshui Xu | 19 | 296 | 16 |
| 7 | Daekook Kang | 18 | 283 | 16 |
| 8 | Ali Ahmadian | 16 | 180 | 11 |
| 9 | Jianli Zhou | 10 | 629 | 63 |
| 10 | Jurgita Antucheviciene | 10 | 666 | 67 |

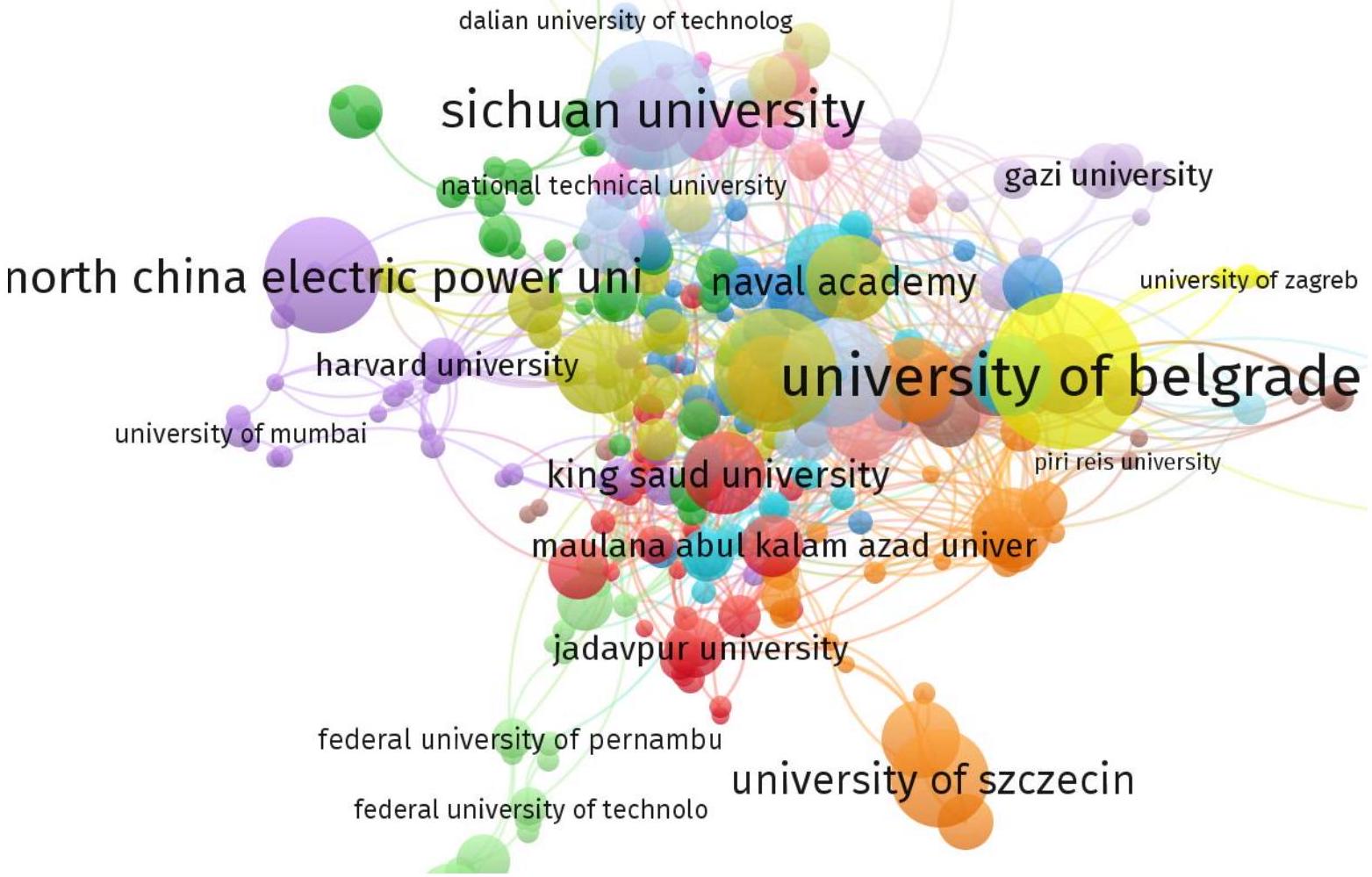
Top 10 Organizations Based on Publications, Citations, and Total Link Strength
| Rank | Organization Name | Publications | Citations | Total Link Strength |
| 1 | University of Belgrade | 70 | 1,380 | 164 |
| 2 | Sichuan University | 54 | 1,388 | 44 |
| 3 | Vilnius Gediminas Technical University | 50 | 1,474 | 101 |
| 4 | University of Szczecin | 37 | 1,329 | 40 |
| 5 | Naval Academy | 32 | 885 | 107 |
| 6 | University of Defence | 26 | 1,913 | 57 |
| 7 | Yıldız Technical University | 28 | 664 | 24 |
| 8 | Maulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology | 20 | 1,615 | 41 |
| 9 | Istanbul Technical University | 28 | 1,127 | 15 |
| 10 | AfyonKocatepe University | 17 | 914 | 34 |

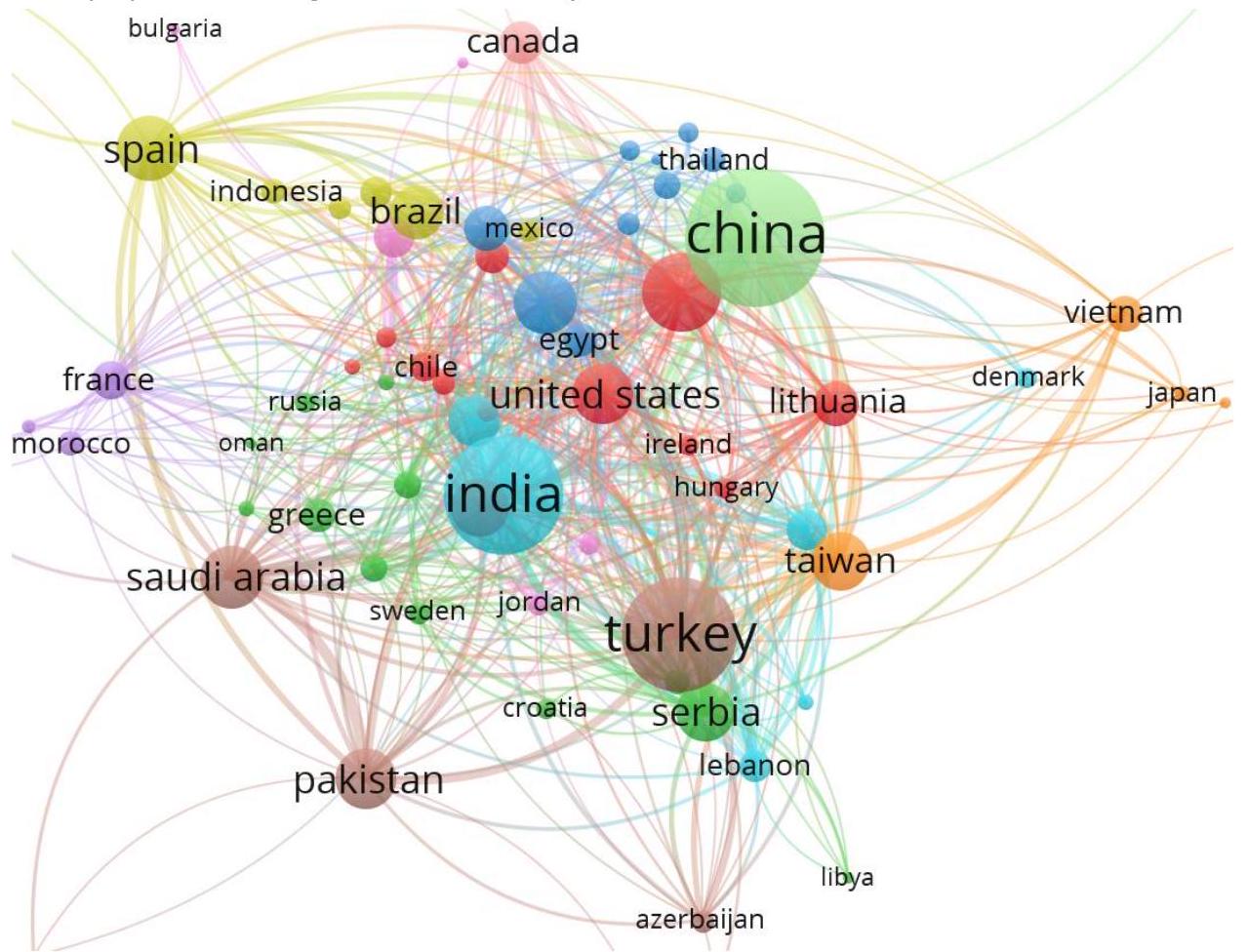
Top 10 Countries Based on Publications, Citations, and Average Citations per Article
| Rank | Country | Publications | Citations | Average Citations per Article |
| 1 | China | 570 | 13,967 | 24.51 |
| 2 | India | 418 | 9,442 | 22.59 |
| 3 | Turkey | 385 | 8,828 | 22.93 |
| 4 | United Kingdom | 122 | 4,565 | 37.42 |
| 5 | United States | 111 | 3,415 | 30.77 |
| 6 | Spain | 126 | 3,311 | 26.29 |
| 7 | Serbia | 106 | 3,426 | 32.32 |
| 8 | Saudi Arabia | 119 | 2,282 | 19.18 |
| 9 | Poland | 100 | 2,647 | 26.47 |
| 10 | Taiwan | 100 | 1,852 | 18.52 |
3.5 Citation Analysis
i. Documents: The study of citations primarily focuses on specific academic publications, including journal articles, conference papers, books, and patents. Using VOSviewer, researchers can analyze citation links among these papers, find influential publications, track the history of ideas, and discover the intellectual framework of a certain field of study.
There are 2504 documents found in this analysis. Merely 1945 documents satisfy the criterion with a minimum of 3 citations each. Figure 10 illustrates that, of the 295 documents, 129 papers had the greatest number of related things.
Table 6 highlights the top 10 influential co-authors based on their citations and contributions to various fields. Stević et al., [14] lead with 866 citations in operations research, showcasing significant influence. Liu et al., [28] appear with 631 citations, reflecting impactful work in environmental science. Yadav et al., [29] and Slebi-Acevedo et al., [30] contribute prominently to sustainable development and decision sciences, respectively. Akram et al., [31] and Tzouramani et al., [32] emphasize optimization techniques and sustainability. Liao et al., [33] stand out for contributions to renewable energy, while Salimi et al., [34] and Rahimi et al., [35] focus on mathematical modeling and data science. These co-authors are affiliated with prestigious institutions, highlighting their research’s multidisciplinary nature and impact on global academic discussions

Top 10 Co-Authors with Institution and Field of Study
| Co-Author | Citations | Links | Institution | Field of Study |
| Stević et al., [14] | 866 | 98 | University of East Sarajevo | Operations Research |
| Liu et al., [28] | 631 | 17 | Chinese Academy of Sciences | Environmental Science |
| Yadav et al., [29] | 458 | 4 | Indian Institute of Technology | Sustainable Development |
| Slebi-Acevedo et al., [30] | 352 | 60 | Poznan University of Technology | Decision Sciences |
| Akram et al., [31] | 197 | 23 | University of Tehran | Optimization Techniques |
| Tzouramani et al., [32] | 143 | 17 | University of Tehran | Sustainable Development |
| Liao et al., [33] | 143 | 17 | National Taiwan University | Renewable Energy |
| Salimi et al., [34] | 119 | 13 | University of Vienna | Mathematical Modeling |
| Rahimi et al., [35] | 67 | 14 | Sharif University of Technology | Data Science |
in this analysis (Figure 11). Merely 174 sources satisfy the required minimum of 3 documents and source citations. Figure 11 illustrates that of the 174 sources, 170 have the most related items.

Top 10 journals based on citations
| Rank | Source | Documents | Citations | Total Link Strength |
| 1 | Journal of Cleaner Production | 85 | 3729 | 600 |
| 2 | Expert Systems with Applications | 90 | 3372 | 628 |
| 3 | Sustainability | 152 | 2481 | 520 |
| 4 | Symmetry | 40 | 1940 | 332 |
| 5 | Environmental Science and Pollution Research | 38 | 862 | 198 |
| 6 | Renewable Energy | 25 | 1090 | 204 |
| 7 | Applied Soft Computing | 73 | 2670 | 564 |
| 8 | Energy Reports | 18 | 362 | 127 |
| 9 | IEEE Access | 46 | 604 | 221 |
| 10 | Mathematics | 77 | 1328 | 344 |
4. Discussion
4.1 Contribution to SDGs
4.2 Emerging Technologies
solutions in the Metaverse, offering valuable insights for real-world implementation. Additionally, the Metaverse supports collaborative decision-making by allowing stakeholders to engage in virtual simulations and jointly analyze outcomes. Case studies highlight the practical impact of these technologies. Hybrid AI-MCDM approaches have been successfully implemented in renewable energy projects, optimizing site selection for wind and solar farms. IoT-enabled MCDM applications in smart grids have improved energy distribution and reduced operational costs.
5. Conclusion
Acknowledgment
Conflicts of Interest
References
[2] Kumar, R. (2024). Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Applications in Agro-based Industries for Economic Development: An Overview of Global Trends, Collaborative Patterns, and Research Gaps. Spectrum of Engineering and Management Sciences, 2(1), 247-262. https://doi.org/10.31181/sems21202431k
[3] Kumar, R. (2024). Artificial Intelligence (AI)-driven Transformation: Sustainable Development of Agro-based Industries in Bihar. International Journal for Multidisciplinary Research, 6(2). https://doi.org/10.36948/ijfmr.2024.v06i02.15935
[4] Kumar, R. & Kumari, K. (2024). Enhancing Economic Development through Inventory Management Optimization in Agro-based Industries in Bihar: A Comparative Study of EOQ and EPQ Models. International Journal for Multidisciplinary Research, 6(2). https://doi.org/10.36948/ijfmr.2024.v06i02.16892
[5] Kumar, R., Khan, A. K., & Goel, S. (2024). From farm to table: How AI is revolutionizing demand forecasting in agrobased industries. Blockchain and AI in business. Applications, Research and Insights, 81-99.
[6] Mokhtar, M. R., Abdullah, M. P., Hassan, M. Y., & Hussin, F. (2015). Combination of AHP-PROMETHEE and TOPSIS for selecting the best Demand Side Management (DSM) options. In 2015 IEEE Student Conference on Research and Development (SCOReD) (pp. 367-372). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/scored.2015.7449357
[7] Kumar, R. (2024). Global Trends and Research Patterns in Financial Literacy and Behavior: A Bibliometric Analysis. Management Science Advances., 2(1), 1-18. https://doi.org/10.31181/msa2120256
[8] Zavadskas, E. K., Turskis, Z., & Kildiené, S. (2014). STATE OF ART SURVEYS OF OVERVIEWS ON MCDM/MADM METHODS. Technological and Economic Development of Economy, 20(1), 165-179. https://doi.org/10.3846/20294913.2014.892037
[9] Saoud, A., Lachgar, M., Hanine, M., Dhimni, R. E., Azizi, K. E., & Machmoum, H. (2025). decideXpert: Collaborative system using AHP-TOPSIS and fuzzy techniques for multi-criteria group decision-making. SoftwareX, 29, 102026.
[10] Radulescu, C. Z., & Radulescu, M. (2024). A Hybrid Group Multi-Criteria Approach Based on SAW, TOPSIS, VIKOR, and COPRAS Methods for Complex IoT Selection Problems. Electronics, 13(4), 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13040789
[11] Sivalingam C, & Subramaniam, S. K. (2024). Cobot selection using hybrid AHP-TOPSIS based multi-criteria decision making technique for fuel filter assembly process. Heliyon, 10(4), e26374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26374
[12] Topaloğlu, F. (2024). Development of a new hybrid method for multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) approach: a case study for facility location selection. Operational Research, 24(4), 60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-024-00871-4
[13] Stojčić, M., Zavadskas, E., Pamučar, D., Stević, Ž., & Mardani, A. (2019). Application of MCDM Methods in Sustainability Engineering: A Literature Review 2008-2018. Symmetry, 11(3), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11030350
[14] Stević, Ž., Pamučar, D., Puška, A., & Chatterjee, P. (2020). Sustainable supplier selection in healthcare industries using a new MCDM method: Measurement of alternatives and ranking according to COmpromise solution (MARCOS). Computers & Industrial Engineering, 140, 106231. https://doi.org/10.1016/i.cie.2019.106231
[15] Mahmoodirad, A., Pamucar, D., Niroomand, S., & Simic, V. (2025). Data envelopment analysis based performance evaluation of hospitals – Implementation of novel picture fuzzy BCC model. Expert Systems with Applications, 263, 125775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2025.125775
[16] Karatas, M., Eriskin, L., Deveci, M., Pamucar, D., & Garg, H. (2022). Big Data for Healthcare Industry 4.0: Applications, challenges and future perspectives. Expert Systems with Applications, 200, 116912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.116912
[17] Pamučar, D., & Ćirović, G. (2015). The selection of transport and handling resources in logistics centers using MultiAttributive Border Approximation area Comparison (MABAC). Expert Systems with Applications, 42(6), 3016-3028. https://doi.org/10.1016/i.eswa.2014.11.057
[18] Deveci, M., Mishra, A. R., Gokasar, I., Rani, P., Pamucar, D., & Özcan, E. (2022). A Decision Support System for Assessing and Prioritizing Sustainable Urban Transportation in Metaverse. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 31(2), 475-484. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2022.3190613
[19] Pamucar, D., Deveci, M., Gokasar, I., Tavana, M., & Köppen, M. (2022). A metaverse assessment model for sustainable transportation using ordinal priority approach and Aczel-Alsina norms. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 182, 121778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.121778
[20] Ala, A., Mahmoudi, A., Mirjalili, S., Simic, V., & Pamucar, D. (2023). Evaluating the Performance of various Algorithms for Wind Energy Optimization: A Hybrid Decision-Making model. Expert Systems with Applications, 221, 119731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.119731
[21] Chyad, M., Zaidan, B. B., Zaidan, A. A., Pilehkouhi, H., Aalaa, R., Qahtan, S., Alsattar, H. A., Pamucar, D., & Simic, V. (2024). Exploring adversarial deep learning for fusion in multi-color channel skin detection applications. Information Fusion, 114, 102632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2024.102632
[22] Leung, A. Y. T., & Zhang, H. (2009). Particle swarm optimization of tuned mass dampers. Engineering Structures, 31(3), 715-728. https://doi.org/10.1016/i.engstruct.2008.11.017
[23] Karagoz, S., Deveci, M., Simic, V., Aydin, N., & Bolukbas, U. (2020). A novel intuitionistic fuzzy MCDM-based CODAS approach for locating an authorized dismantling center: a case study of Istanbul. Waste Management & Research, 38(6), 660-672. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242×19899729
[24] Simic, V., Gokasar, I., Deveci, M., & Isik, M. (2021). Fermatean Fuzzy Group Decision-Making Based CODAS Approach for Taxation of Public Transit Investments. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 70(12), 4233-4248. https://doi.org/10.1109/tem.2021.3109038
[25] Deveci, M., Pamucar, D., Gokasar, I., Koppen, M., & Gupta, B. B. (2022). Personal Mobility in Metaverse With Autonomous Vehicles Using Q-Rung Orthopair Fuzzy Sets Based OPA-RAFSI Model. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1109/tits.2022.3186294
[26] Kumar, R., & Sahoo, S. K. (2024). A Bibliometric Analysis of Agro-Based Industries: Trends and Challenges in Supply Chain Management. Decision Making Advances, 3(1), 200-215. https://doi.org/10.31181/dma31202568
[27] Kumar, R. (2025). Bibliometric Analysis: Comprehensive Insights into Tools, Techniques, Applications, and Solutions for Research Excellence. Spectrum of Engineering and Management Sciences, 3(1), 45-62. https://doi.org/10.31181/sems31202535k
[28] Liu, Y., Eckert, C. M., & Earl, C. (2020). A review of fuzzy AHP methods for decision-making with subjective judgements. Expert Systems with Applications, 161, 113738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113738
[29] Yadav, V., Kalbar, P. P., Karmakar, S., & Dikshit, A. K. (2020). A two-stage multi-attribute decision-making model for selecting appropriate locations of waste transfer stations in urban centers. Waste Management, 114, 80-88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.05.024
[30] Slebi-Acevedo, C. J., Lastra-González, P., Calzada-Pérez, M. A., & Castro-Fresno, D. (2020). Effect of Synthetic Fibers and Hydrated Lime in Porous Asphalt Mixture Using Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Techniques. Materials, 13(3), 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030675
[31] Akram, M., Kahraman, C., & Zahid, K. (2021). Group decision-making based on complex spherical fuzzy VIKOR approach. Knowledge-Based Systems, 216, 106793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2021.106793
[32] Tzouramani, I., Mantziaris, S., & Karanikolas, P. (2020). Assessing Sustainability Performance at the Farm Level: Examples from Greek Agricultural Systems. Sustainability, 12(7), 2929. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12072929
[33] Liao, H., Peng, X., & Gou, X. (2020). Medical Supplier Selection with a Group Decision-Making Method Based on Incomplete Probabilistic Linguistic Preference Relations. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 23, 280-294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-020-00885-y
[34] Salimi, A. H., Noori, A., Bonakdari, H., Masoompour Samakosh, J., Sharifi, E., Hassanvand, M., Gharabaghi, B., & Agharazi, M. (2020). Exploring the Role of Advertising Types on Improving the Water Consumption Behavior: An Application of Integrated Fuzzy AHP and Fuzzy VIKOR Method. Sustainability, 12(3), 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12031232
[35] Rahimi, S., Hafezalkotob, A., Monavari, S. M., Hafezalkotob, A., & Rahimi, R. (2020). Sustainable landfill site selection for municipal solid waste based on a hybrid decision-making approach: Fuzzy group BWM-MULTIMOORAGIS. Journal of Cleaner Production, 248, 119186. https://doi.org/10.1016/i.jclepro.2019.119186
- *Corresponding author.
E-mail address: rahul1996magadhuniversity@gmail.com
