DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41095-023-0369-x
تاريخ النشر: 2024-02-08
CF-DAN: التعرف على تعبيرات الوجه استنادًا إلى شبكة الانتباه المزدوجة المتقاطعة
الملخص
مؤخراً، ركز التعرف على تعبيرات الوجه (FER) بشكل أساسي على الصور في البيئات الطبيعية، بما في ذلك عوامل مثل حجب الوجه وضبابية الصورة، بدلاً من الصور المخبرية. لقد قدمت البيئات الميدانية المعقدة تحديات جديدة لـ FER. لمعالجة هذه التحديات، تقترح هذه الدراسة شبكة انتباه مزدوجة مع دمج عبر. تتكون الشبكة من ثلاثة أجزاء: (1) آلية انتباه مزدوجة مجمعة مع دمج عبر لتنقيح الميزات المحلية والحصول على معلومات عالمية؛ (2) اقتراح
1 المقدمة
الاهتمام بالمواقع الرئيسية داخل الصورة واستخراج المعلومات الرئيسية من هذه المواقع الرئيسية لإكمال مهام مختلفة. على سبيل المثال، يمكن تطبيق نموذج المحول البصري (ViT) على تصنيف الصور. ومع ذلك، في مجال التعرف على تعبيرات الوجه (FER)، لا يمكن استخدام الشبكات المشابهة لنموذج ViT مباشرة، بسبب حجم العينة المحدود. قام عويدب وآخرون بتطبيق شبكة ViT بنجاح لمهمة التعرف على التعبيرات من خلال إضافة كتلة الضغط والتحفيز (SE). بسبب قدرة الشبكة على نمذجة الاعتمادات العالمية، يمكن لآليات الانتباه الذاتي أن ترتبط بشكل أفضل مع أجزاء الوجه المختلفة عند معالجة المعلومات الدلالية البصرية عالية المستوى. ومع ذلك، تتطلب آليات الانتباه الذاتي موارد حسابية كبيرة، والتي غالبًا ما تكون غير مقبولة في العديد من السيناريوهات الواقعية. في هذه الدراسة، تناولنا هذه المشكلة من خلال اعتماد نهج التجميع وإضافة تقطير الانتباه الذاتي داخل كل مجموعة.
تمديد دالة ReLU. تتمتع دالة السجمويد والوظائف المرتبطة بها بتعقيد حسابي عالٍ بسبب تضمين عمليات القوة، مما يؤدي إلى بطء في سرعة الحساب. على الرغم من أن دالة ReLU والوظائف المرتبطة بها تتمتع بسرعات حساب سريعة، إلا أن عدم استقرارها ناتج عن عدم استمرارية المشتق من الدرجة الأولى، ويصبح الفاصل السالب صفرًا بعد التفعيل، مما يؤدي بسهولة إلى تعطيل الخلايا العصبية. لمعالجة ذلك، تقترح هذه الدراسة طريقة لبناء دالة تفعيل تستخدم التناسب لتجنب عمليات القوة مع الحفاظ على استمرارية المشتق من الدرجة الأولى. خلال عملية التناسب، يتم إجراء تعديلات على الفواصل لمنع تعطيل الخلايا العصبية. مساهمات هذه الدراسة هي كما يلي:
(1) نقترح محول ثنائي الانتباه مع دمج متقاطع يعتمد على الأبعاد المكانية والقنوية. التفاعل المحلي في البعد المكاني يكمل تحسين الميزات، ويتم توفير مجال استقبال عالمي في البعد القنوي. يحقق محول الانتباه الثنائي مع الدمج المتقاطع التكامل المتبادل لمعلومات الميزات من أبعاد مختلفة، مما يحسن دقة الميزات المعنية.
(2)قمنا بتصميم طريقة لبناء دالة تفعيل لحل المشكلات في دوال التفعيل المستخدمة بشكل شائع، مثل تعطيل الخلايا العصبية، والعبء الحسابي الكبير الذي تسببه دالة القوة، ووجود نقاط غير قابلة للاشتقاق. علاوة على ذلك، قامت هذه الدراسة ببناء
(3)لتقليل التكلفة الحسابية العالية لآلية الانتباه الذاتي، نقترح آلية مجمعة وتقطير الانتباه الذاتي. هذه العملية تقسم الانتباه إلى مجموعات مختلفة وتستخدم تقطير الانتباه الذاتي في كل مجموعة لتقليل الأبعاد المكانية لـ
2 الأعمال ذات الصلة
لقد بذل الباحثون جهودًا كبيرة لتحسين دقة التعرف تحت ظروف خلفيات معقدة وحجب الشخصيات. قام بورييل وآخرون [36] باستخراج ميزات الدرجة المكانية للأجزاء الرئيسية من الوجه للتصنيف. حققت الطرق المعتمدة على تحليل المكونات الرئيسية [37، 38] إسقاط الصور الاختبارية على الصور التدريبية باستخدام التشابه لتحقيق التعرف على التعبيرات. استخدم حمال وآخرون [39] تقسيم الصور متعدد المستويات والتحلل النادر لحل مشكلة حجب تعبيرات الوجه. تم استخدام عدة كاشفات للوجه مثل نماذج MTCNN [40] وDlib [41] للكشف عن الوجه في سيناريوهات العالم الحقيقي. علاوة على ذلك، لحل المشكلات الموجودة في سيناريوهات العالم الحقيقي، تم إجراء عدد متزايد من الدراسات المعتمدة على الرؤية متعددة الزوايا ومتعددة المقاييس. اقترح هابي وروتراي [42] وماجومدر وآخرون [43] أن تغييرات تعبير الوجه تنعكس بشكل أساسي في الأجزاء الرئيسية، مثل العينين والفم. مع التطور المستمر للتعلم العميق، حققت العديد من الدراسات المعتمدة على الشبكات العصبية التلافيفية (CNNs) تقدمًا كبيرًا في استخراج ميزات الوجه في بيئات العالم الحقيقي. يضيف نموذج SCN [44] ثلاثة وحدات إضافية إلى CNN التقليدي لأغراض وزن أهمية الانتباه الذاتي، وتنظيم الرتبة، وإعادة التسمية. يستخدم RAN [45] عمليات التلافيف لتصميم استخراج الميزات، والانتباه الذاتي، ووحدات الانتباه العلاقية. يستخدم EfficientFace [46] مستخرج ميزات محلي ومعدل مكاني للقناة لتحسين المتانة. يستخدم DMUE [47] فرعًا مساعدًا لاستخراج التوزيعات المحتملة وإجراء تقديرات حتمية زوجية. FDRL [48] هو شبكة تفكيك وإعادة بناء ميزات مرتبطة بالعواطف. يتكون DAN [49] من شبكة تجميع الميزات، والانتباه المتقاطع متعدد الرؤوس، وشبكة دمج الانتباه. تستخدم ARM وحدة تمثيل معدلة لاستبدال طبقة التجميع. يدمج CSGResNet [50] التلافيف غابور (GConv) في ResNet. يستخرج AMP-Net ميزات التعبيرات الوجهية العالمية والمحلية والبارزة بمستويات مختلفة من الدقة لتعلم التنوع الأساسي والمعلومات الرئيسية لعواطف الوجه. ومع ذلك، فإن هذه الطرق محدودة من قبل الحقول الاستقبالية الصغيرة لـ CNNs. في هذه الدراسة، نستفيد من مزايا CNN لاستخراج الميزات السطحية ونستخدم آليات الانتباه الذاتي لمعالجة المعلومات الدلالية البصرية عالية المستوى.
في تطبيقات رؤية الكمبيوتر. تم تطبيق عدة دراسات رائدة، مثل تلك المتعلقة بأساليب iGPT [51] وViT، آلية الانتباه الذاتي مباشرة على بكسلات الصورة أو تسلسلات الرقع. مستلهمًا من ذلك، كانت المحولات البصرية التلافيفية (CVTs) [52] الأولى التي تطبق نموذج المحول على مهام FER. تستخدم CVTs خوارزمية النمط الثنائي المحلي (LBP) لإرسال صور تعبير الوجه في حالتين مختلفتين إلى شبكة ResNet للحصول على صور ميزات أصغر، ويتم استخدام نموذج المحول لإكمال مهمة FER. يولد محول رؤية القناع (MViT) [53] قناعًا بناءً على نموذج المحول لتصفية الخلفيات المعقدة وحجب صور الوجه. ترسل طريقة FER-VT [54] خرائط ميزات بمقاييس مختلفة إلى نفس نموذج المحول لإكمال دمج المعلومات. ترشد خرائط الانتباه العشوائي [55] و وحدات الانتباه الذاتي النموذج في تعلم العلاقات الغنية بين الرقع المحلية المختلفة. ومع ذلك، فإن هذه الطرق محدودة من حيث البعد المكاني ولديها قيود في الحصول على المعلومات العالمية مقارنةً بآلية الانتباه المزدوج.
3 المنهجية
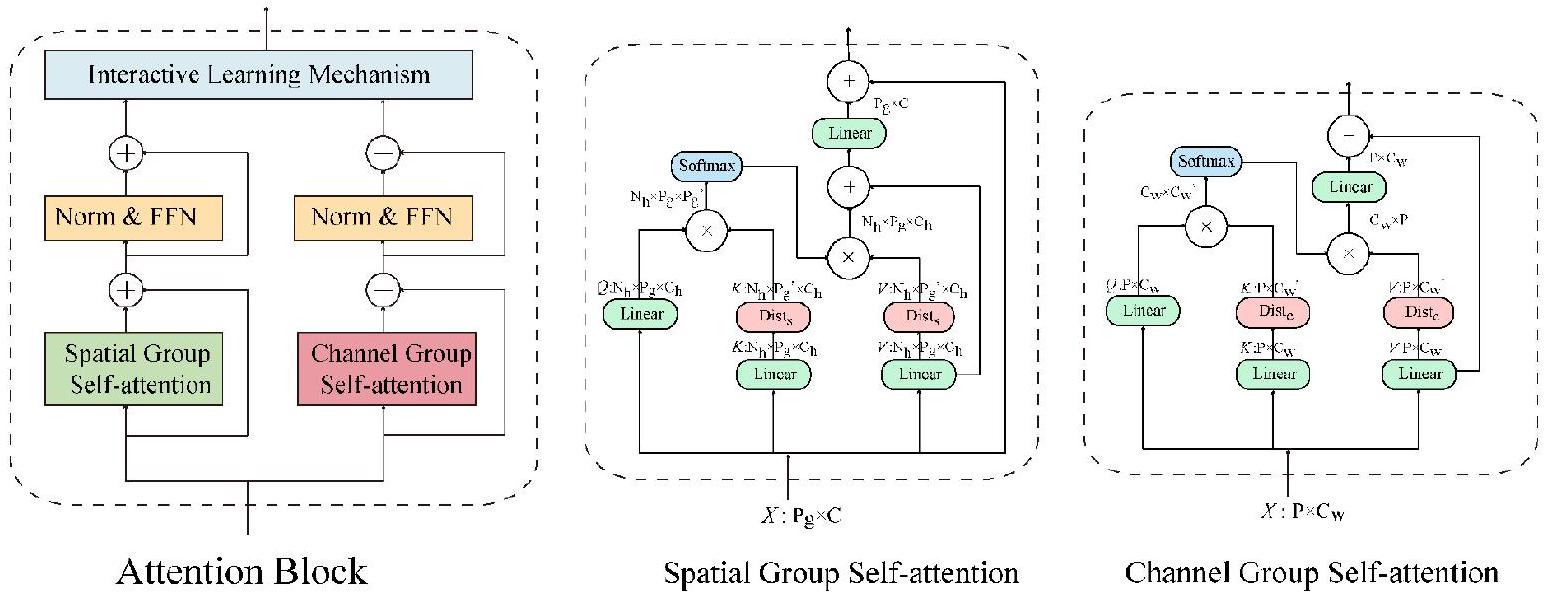

3.1 آلية الانتباه المزدوج (DAM)
الصورة المدخلة في شكل
استكمال نقل المعلومات بين الأبعاد المختلفة. القسم 3.2 يوضح ذلك بشكل أكبر.
3.2 آلية انتباه الاندماج المتقاطع
3.3 تقطير الانتباه الذاتي
عملية استخراج الميزات، مما يؤدي إلى تراجع أداء النموذج. تقترح هذه الدراسة أن آلية تقطير الانتباه الذاتي تعمل على المفاتيح والقيم، مما يقلل من حجم الأبعاد المكانية والقناة. يمكن استخراج الميزات السائدة باستخدام هذه العملية لتشكيل خريطة ميزات تتمتع بميزة مركزة في الانتباه الذاتي اللاحق، مما ي suppress التداخل من المعلومات الزائدة وتقليل توليد الضوضاء. علاوة على ذلك، لتقليل فقدان المعلومات ذات الترددات المتوسطة والعالية الناتج عن آلية تقطير الانتباه الذاتي، يتم استخدام اتصال متبقي لدمج الأصل.
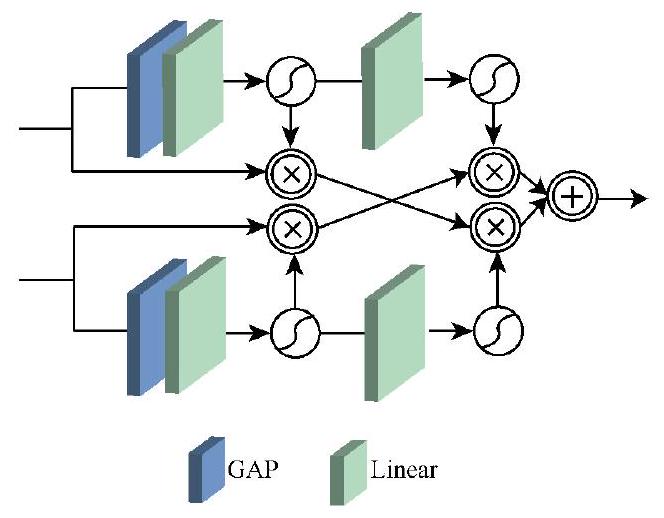
3.4 آلية التعلم التفاعلي (ILM)
المشتقات الأولى عند النقاط
أن
4 نتائج

4.1 مجموعات البيانات
4.2 تفاصيل التجربة
4.3 النتائج والتحليل
| طريقة | سنة | RAF-DB | أفيكت نت | فير بلس |
| SCN[44] | مؤتمر رؤية الكمبيوتر والأنظمة المعززة 2020 | ٨٧.٠٣ | 60.23 | ٨٩.٣٩ |
| ران[45] | نصيحة 2020 | ٨٦.٩٠ | - | ٨٩.١٦ |
| EfficientFace[46] | AAAI 2021 | ٨٨.٣٦ | ٥٩.٨٩ | - |
| DMUE[47] | مؤتمر رؤية الكمبيوتر والأنظمة المعززة 2021 | 89.42 | - | - |
| FDRL[48] | مؤتمر الرؤية الحاسوبية ونظم التعلم 2021 | ٨٩.٤٧ | - | - |
| DAN[49] | أرشيف 2021 | ٨٩.٧٠ | 62.09 | - |
| ARM[56] | أرشيف 2021 | 90.42 | ٦١.٣٣ | - |
| CSGResNet[50] | ICASSP 2022 | ٨٨.٥٩ | 61.03 | ٨٨.٩٤ |
| AMP-Net[57] | تي سي إس في تي 2022 | ٨٩.١٩ | 61.32 | ٨٩.٣٧ |
| ملصق[33] | أرشيف 2022 | 92.05 | 63.34 | 91.62 |
| خاصتنا | - | 92.78 | 63.58 | 92.02 |
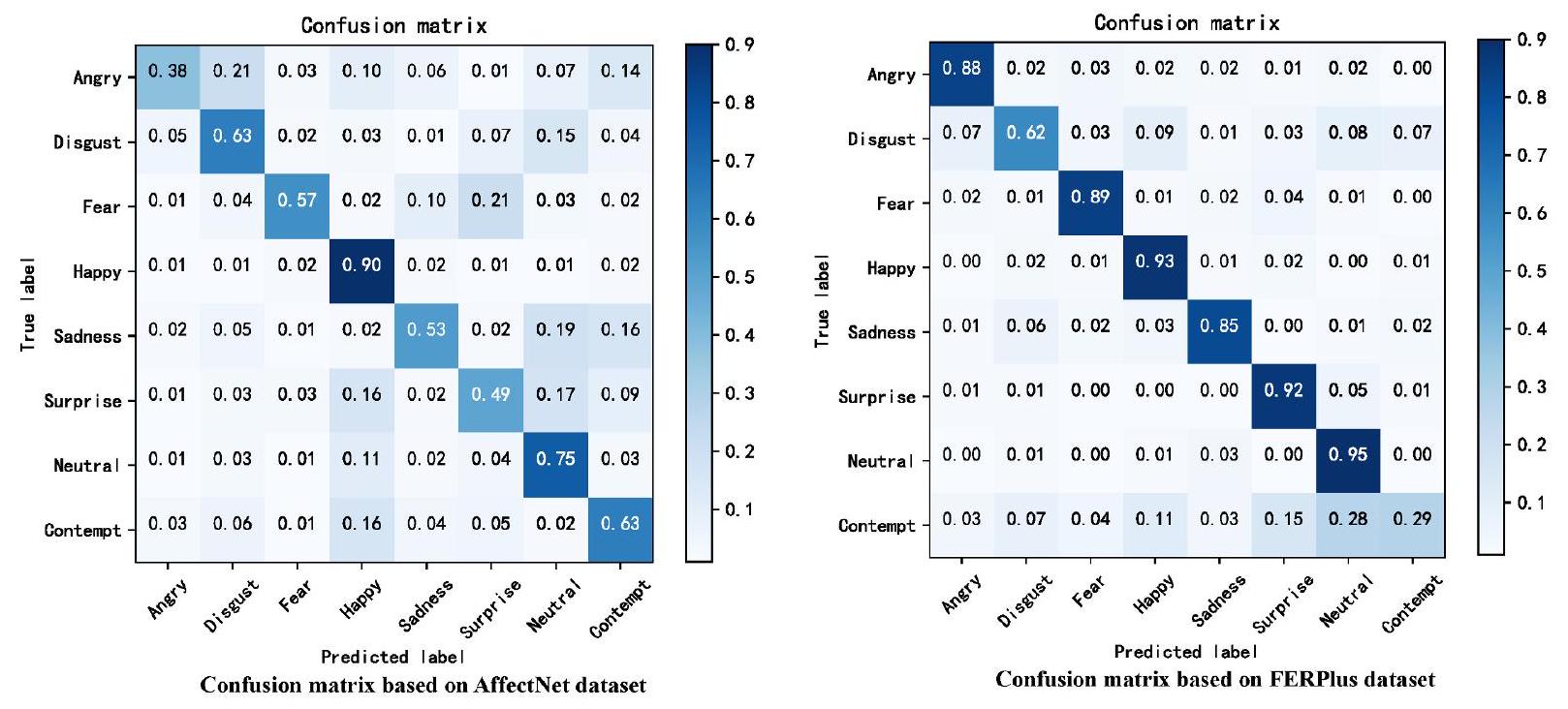
التعبير هو الأسهل في التعرف عليه من بين الثمانية تعبيرات، وذلك بفضل نطاق عرضه الكبير. كانت نسبة التعرف على السعادة في مجموعة بيانات AffectNet أعلى بكثير من تلك الخاصة بالتعبيرات الأخرى. على عكس الوجوه السعيدة، كانت الفروق في معدلات النجاح صغيرة، ويرجع ذلك أساسًا إلى أن الصور في مجموعة بيانات AffectNet تأتي من الإنترنت وتحتوي على العديد من العينات الخاطئة. في مجموعة بيانات FERPlus، كانت نسبة التعرف على السعادة أقل قليلاً من تلك الخاصة بالتعبيرات المحايدة، لأن التعبيرات المحايدة تحتوي على أكبر حجم عينة. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، احتوت مجموعة بيانات FERPlus على أقل عدد من عينات الاشمئزاز والازدراء – فقط عُشر عدد العينات للتعبيرات الأخرى – وهذه التعبيرات لها مظهر مشابه. وبالتالي، كانت دقة التعرف على الاشمئزاز والازدراء أقل بكثير من تلك الخاصة بالتعبيرات الأخرى.
تعتبر (FLOPs) ميزات رئيسية يجب أخذها بعين الاعتبار لإجراء مقارنات عادلة. كانت إحدى النقاط الأساسية في هذه الدراسة تتعلق بتقليل العدد الإجمالي لبارامترات النموذج. ولهذا الغرض، اقترحنا آليات الانتباه الذاتي المجمعة وعمليات تقطير الانتباه الذاتي. تقارن الجدول 2 بارامترات الطريقة المقترحة مع تلك الخاصة بأساليب أخرى، بما في ذلك CVT وDMUE وTransFER وPOSTER وDAN. من الواضح أن عدد البارامترات في الطريقة المقترحة لا يتجاوز ربع تلك الخاصة بالأساليب الأخرى، مع الحفاظ على أعلى دقة في التعرف على تعبيرات الوجه. من حيث سرعة التشغيل، يتطلب الأمر حوالي ساعة و20 دقيقة لإكمال التدريب على مجموعة بيانات RAF-DB التدريبية وحوالي دقيقة واحدة لاختبار جميع صور التعبير على مجموعة بيانات RAF-DB الاختبارية بعد التدريب. وهذا يوفر نموذج التعرف على تعبيرات الوجه القائم على الانتباه الذاتي بميزة كبيرة.
4.4 دراسة الاستئصال
| طريقة | سنة | معلمات | عمليات النقطة العائمة في الثانية | Acc(RAF-DB) | Acc (FERPlus) |
| CVT[52] | أرشيف 2021 | 80.1 مليون | - | ٨٧.٦١ | ٨٨.٨١ |
| DMUE[47] | مؤتمر الرؤية الحاسوبية ونظم التعلم 2021 | 78.4 مليون | 13.4 جي | ٨٩.٤٢ | - |
| TransFER[55] | مؤتمر ICCV 2021 | 65.2 مليون | 15.3G | 90.91 | 90.83 |
| ملصق[33] | أرشيف 2022 | 71.8 مليون | 15.7G | 92.05 | 91.62 |
| DAN[49] | أرشيف 2021 | 28.3 مليون | 2.6G | ٨٩.٧٠ | - |
| خاصتنا | - | 16.4 مليون | 2.0 ج | 92.78 | 92.02 |
| الطريقة | AffectNet | FERPlus | RAF-DB |
| الخط الأساسي | 59.73٪ | 89.69٪ | 90.37٪ |
| الخط الأساسي + DAM | 60.44٪ | 90.92٪ | 90.88٪ |
| الخط الأساسي + DAM + ILM | 63.12٪ | 91.55٪ | 91.63٪ |
| الخط الأساسي + DAM + ILM المتقاطع | 63.58٪ | 92.02٪ | 92.78٪ |


في الجزء السلبي من دالة تنشيط ReLU ، قمنا بتعيين المنطقة السلبية إلى منطقة سلبية أصغر
كما هو موضح في الشكل 9 ، فإن دالة التنشيط المستخدمة في هذه الدراسة قابلة للاشتقاق باستمرار عند جميع النقاط. علاوة على ذلك ، لا تتضمن دالة التنشيط المقترحة الأسس ، مما يحسن سرعة تشغيل النموذج مقارنة بدوال تنشيط السيغمويد و tanh. من حيث دقة التعرف ، قارنّا بين دوال التنشيط المختلفة على مجموعة بيانات RAF-DB؛ يقدم الجدول 4 النتائج. من الواضح أن دالة التنشيط المقترحة تؤدي بشكل أفضل في مهام FER.
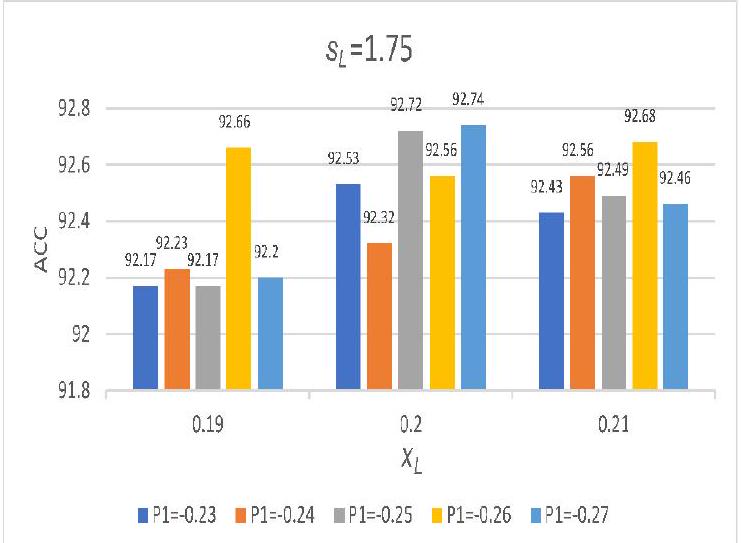
4.5 تحليل حساسية المعلمات
| PCP | سيغمويد | ReLU | tanh | ILM | ACC |
|
|
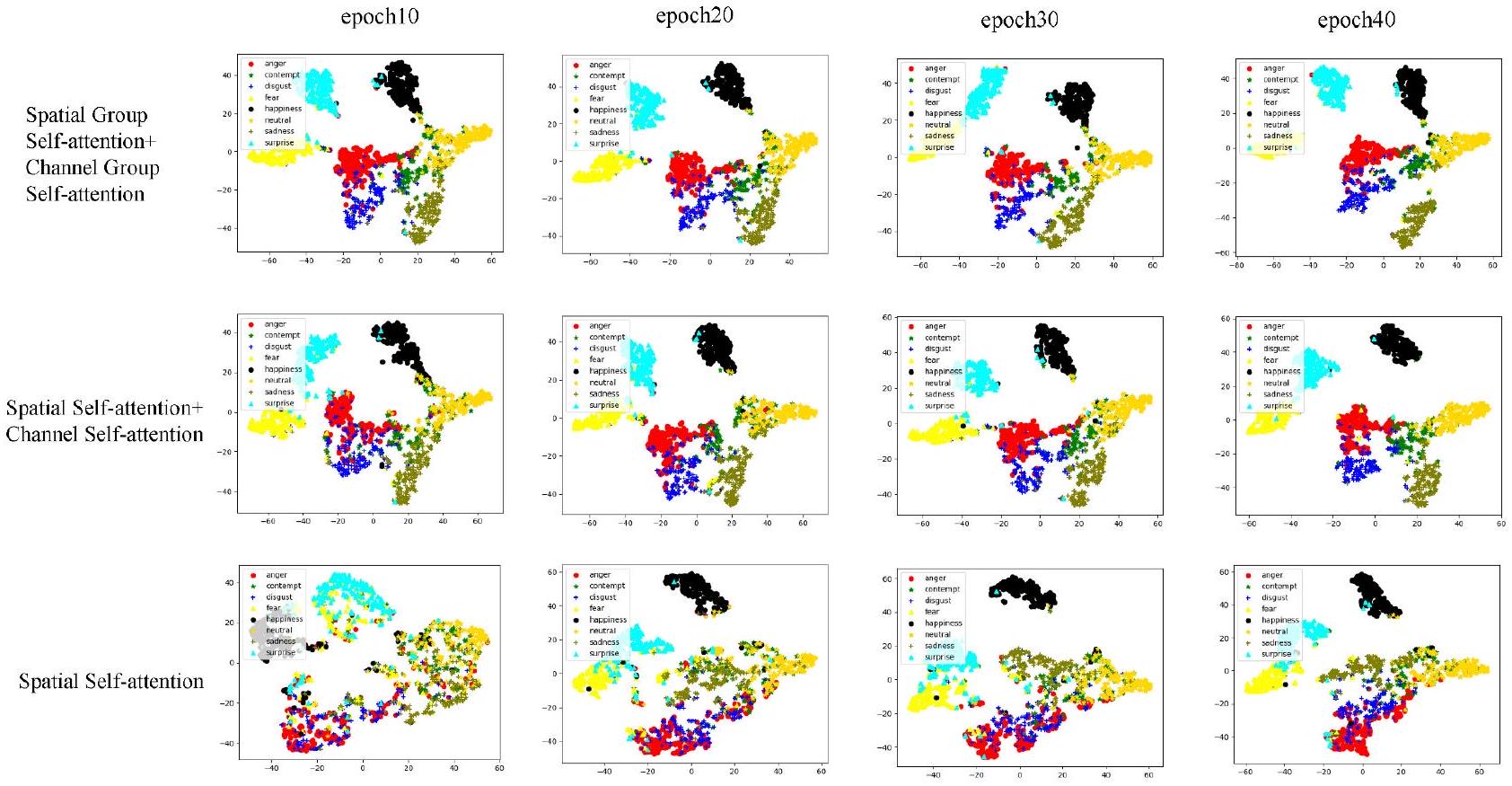
92.54 | ||||
|
|
|
92.78 | |||
|
|
91.42 | ||||
|
|
|
91.78 | |||
|
|
91.98 | ||||
|
|
|
92.26 | |||
|
|
91.75 | ||||
|
|
|
91.97 |
| الطريقة | AffectNet | FERPlus | المعلمات | FLOPs |
| بدون تقطير |
|
|
4.2 M | 0.21 G |
| مع التقطير |
|
|
4.22 M | 0.14 G |


5 الاستنتاجات
شكر وتقدير
إعلان عن تضارب المصالح
References
[2] Joshi, A.; Kyal, S.; Banerjee, S.; Mishra, T. In-the-wild drowsiness detection from facial expressions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, 207-212, 2020.
[3] Tran, L.; Yin, X.; Liu, X. M. Representation learning by rotating your faces. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence Vol. 41, No. 12, 30073021, 2019.
[4] Wu, T. F.; Bartlett, M. S.; Movellan, J. R. Facial expression recognition using Gabor motion energy filters. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition – Workshops, 42-47, 2010.
[5] Shan, C. F.; Gong, S. G.; McOwan, P. W. Facial expression recognition based on Local Binary Patterns: A comprehensive study. Image and Vision Computing Vol. 27, No. 6, 803-816, 2009.
[6] Shokoohi, Z.; Bahmanjeh, R.; Faez, K. Expression recognition using directional gradient local pattern and gradient-based ternary texture patterns. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis, 1-7, 2015.
[7] Wang, Z.; Ying, Z. L. Facial expression recognition based on local phase quantization and sparse representation. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Natural Computation, 222-225, 2012.
[8] Ali, H. B.; Powers, D. M. W.; Jia, X. B.; Zhang, Y. H. Extended non-negative matrix factorization for face and facial expression recognition. International Journal of Machine Learning and Computing Vol. 5, No. 2, 142147, 2015.
[9] Baddar, W. J.; Lee, S. M.; Ro, Y. M. On-the-fly facial expression prediction using LSTM encoded appearancesuppressed dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing Vol. 13, No. 1, 159-174, 2022.
[10] Li, Y. J.; Gao, Y. N.; Chen, B. Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, G. M.; Zhang, D. Self-supervised exclusive-inclusive interactive learning for multi-label facial expression recognition in the wild. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology Vol. 32, No. 5, 3190-3202, 2022.
[11] Zhang, X.; Zhang, F. F.; Xu, C. S. Joint expression
synthesis and representation learning for facial expression recognition. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology Vol. 32, No. 3, 16811695, 2022.
[12] Otberdout, N.; Daoudi, M.; Kacem, A.; Ballihi, L.; Berretti, S. Dynamic facial expression generation on Hilbert hypersphere with conditional Wasserstein generative adversarial nets. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence Vol. 44, No. 2, 848-863, 2022.
[13] Zhang, F. F.; Zhang, T. Z.; Mao, Q. R.; Xu, C. S. A unified deep model for joint facial expression recognition, face synthesis, and face alignment.
[14] Feffer, M.; Rudovic, O.; Picard, R. W. A mixture of personalized experts for human affect estimation. In: Machine Learning and Data Mining in Pattern Recognition. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 10935. Perner, P. Ed. Springer Cham, 316-330, 2018.
[15] Fan, Y.; Lu, X. J.; Li, D.; Liu, Y. L. Videobased emotion recognition using CNN-RNN and C3D hybrid networks. In: Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, 445-450, 2016.
[16] Zhang, T.; Zheng, W. M.; Cui, Z.; Zong, Y.; Li, Y. Spatial-temporal recurrent neural network for emotion recognition. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics Vol. 49, No. 3, 839-847, 2019.
[17] Pang, L.; Li, N. Q.; Zhao, L.; Shi, W. X.; Du, Y. P. Facial expression recognition based on Gabor feature and neural network. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Security, Pattern Analysis, and Cybernetics, 489-493, 2018.
[18] Liu, Z.; Lin, Y. T.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. X.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. N. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 9992-10002, 2021.
[19] Kim, J. H.; Kim, N.; Won, C. S. Facial expression recognition with Swin transformer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.13472, 2022.
[20] Wang, W. H.; Xie, E. Z.; Li, X.; Fan, D. P.; Song, K. T.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pyramid vision transformer: A versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 548-558, 2021.
[21] Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y. B. ResT: An efficient transformer for visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 1547515485, 2021.
[22] Zhang, F.; Chen, G. G.; Wang, H.; Li, J. J.; Zhang, C. M. Multi-scale video super-resolution transformer with polynomial approximation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology Vol. 33, No. 9, 4496-4506, 2023.
[23] Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X. H.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16×16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929, 2020.
[24] Aouayeb, M.; Hamidouche, W.; Soladie, C.; Kpalma, K.; Seguier, R. Learning vision transformer with squeeze and excitation for facial expression recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.03107, 2021.
[25] Putro, M. D.; Nguyen, D. L.; Jo, K. H. A dual attention module for real-time facial expression recognition. In: Proceedings of the 46th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, 411-416, 2020.
[26] Song, W. Y.; Shi, S. Z.; Wu, Y. X.; An, G. Y. Dualattention guided network for facial action unit detection. IET Image Processing Vol. 16, No. 8, 2157-2170, 2022.
[27] Ding, M. Y.; Xiao, B.; Codella, N.; Luo, P.; Wang, J. D.; Yuan, L. DaViT: Dual attention vision transformers. In: Computer Vision – ECCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 13684. Avidan, S.; Brostow, G.; Cissé, M.; Farinella, G. M.; Hassner, T. Eds. Springer Cham, 74-92, 2022.
[28] Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H. J.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y. J.; Fang, Z. W.; Lu, H. Q. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 3141-3149, 2019.
[29] Li, X. Q.; Xie, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, G. T.; Tong, W. Q. Dual attention convolutional network for action recognition. IET Image Processing Vol. 14, No. 6, 10591065, 2020.
[30] Li, Y. S.; Liu, Y.; Yu, R.; Zong, H. L.; Xie, W. X. Dual attention based spatial-temporal inference network for volleyball group activity recognition. Multimedia Tools and Applications Vol. 82, No. 10, 15515-15533, 2023.
[31] Gedamu, K.; Yilma, G.; Assefa, M.; Ayalew, M. Spatiotemporal dual-attention network for view-invariant human action recognition. In: Proceedings of the SPIE 12342, 14th International Conference on Digital Image Processing, 123420Q, 2022.
[32] Ullah, H.; Munir, A. Human activity recognition using cascaded dual attention CNN and bi-directional GRU framework. arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.05034, 2022.
[33] Zheng, C.; Mendieta, M.; Chen, C. POSTER: A pyramid cross-fusion transformer network for facial expression recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204. 04083, 2022.
[34]Han,J.;Moraga,C.The influence of the sigmoid function parameters on the speed of backpropagation learning.In:Proceedings of the International Workshop on Artificial Neural Networks:From Natural to Artificial Neural Computation,195-201, 1995.
[35]Glorot,X.;Bordes,A.;Bengio,Y.Deep sparse rectifier neural networks.In:Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics,315-323, 2011.
[36]Bourel,F.;Chibelushi,C.C.;Low,A.A.Recognition of facial expressions in the presence of occlusion.In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, 1-10, 2001.
[37]Mao,X.;Xue,Y.L.;Li,Z.;Huang,K.;Lv,S.W. Robust facial expression recognition based on RPCA and AdaBoost.In:Proceedings of the 10th Workshop on Image Analysis for Multimedia Interactive Services, 113-116, 2009.
[38]Jiang,B.;Jia,K.B.Research of robust facial expression recognition under facial occlusion condition. In:Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Active Media Technology,92-100, 2011.
[39]Hammal,Z.;Arguin,M.;Gosselin,F.Comparing a novel model based on the transferable belief model with humans during the recognition of partially occluded facial expressions.Journal of Vision Vol.9,No.2,22, 2009.
[40]Zhang,K.P.;Zhang,Z.P.;Li,Z.F.;Qiao,Y.Joint face detection and alignment using multitask cascaded convolutional networks.IEEE Signal Processing Letters Vol.23,No.10,1499-1503, 2016.
[41]Amos,B.;Ludwiczuk,B.;Satyanarayanan,M. OpenFace:A general-purpose face recognition library with mobile applications.School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University,2016.Available at https://elijah.cs.cmu.edu/DOCS/CMU-CS-16-118.pdf
[42]Happy,S.L.;Routray,A.Automatic facial expression recognition using features of salient facial patches. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing Vol.6, No.1,1-12, 2015.
[43]Majumder,A.;Behera,L.;Subramanian,V.K. Automatic facial expression recognition system using deep network-based data fusion.IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics Vol.48,No.1,103-114, 2018.
[44]Wang,K.;Peng,X.J.;Yang,J.F.;Lu,S.J.; Qiao,Y.Suppressing uncertainties for large-scale facial expression recognition.In:Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,6896-6905, 2020.
[45]Wang,K.;Peng,X.J.;Yang,J.F.;Meng,D.B.;Qiao, Y.Region attention networks for pose and occlusion
robust facial expression recognition.IEEE Transactions on Image Processing Vol.29,4057-4069, 2020.
[46]Zhao,Z.Q.;Liu,Q.S.;Zhou,F.Robust light- weight facial expression recognition network with label distribution training.Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence Vol.35,No.4, 3510-3519, 2021.
[47]She,J.H.;Hu,Y.B.;Shi,H.L.;Wang,J.; Shen,Q.;Mei,T.Dive into ambiguity:Latent distribution mining and pairwise uncertainty estimation for facial expression recognition.In:Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,6244-6253, 2021.
[48]Ruan,D.L.;Yan,Y.;Lai,S.Q.;Chai,Z.H.; Shen,C.H.;Wang,H.Z.Feature decomposition and reconstruction learning for effective facial expression recognition.In:Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,7656-7665, 2021.
[49]Wen,Z.;Lin,W.;Wang,T.;Xu,G.Distract your attention:Multi-head cross attention network for facial expression recognition.arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.07270, 2021.
[50]Jiang,S.P.;Xu,X.M.;Liu,F.;Xing,X.F.;Wang, L.CS-GResNet:A simple and highly efficient network for facial expression recognition.In:Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics,Speech and Signal Processing,2599-2603, 2022.
[51]Chen,M.;Radford,A.;Child,R.;Wu,J.;Jun, H.;Luan,D.;Sutskever,I.Generative pretraining from pixels.In:Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning,1691-1703, 2020.
[52]Ma,F.;Sun,B.;Li,S.Robust facial expression recognition with convolutional visual transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.16854, 2021.
[53]Li,H.;Sui,M.;Zhao,F.;Zha,Z.;Wu,F.MVT:Mask vision transformer for facial expression recognition in the wild.arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.04520, 2021.
[54]Huang,Q.H.;Huang,C.Q.;Wang,X.Z.;Jiang,F. Facial expression recognition with grid-wise attention and visual transformer.Information Sciences Vol.580, 35-54, 2021.
[55]Xue,F.L.;Wang,Q.C.;Guo,G.D.TransFER: Learning relation-aware facial expression repre- sentations with transformers.In:Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision,3581-3590, 2021.
[56]Shi,J.;Zhu,S.;Liang,Z.Learning to amend facial expression representation via de-albino and affinity. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.10189, 2021.
[57]Liu,H.W.;Cai,H.L.;Lin,Q.C.;Li,X.F.;Xiao,
[58]Dhall,A.;Goecke,R.;Lucey,S.;Gedeon,T.Static facial expression analysis in tough conditions:Data, evaluation protocol and benchmark.In:Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops,2106-2112, 2011.
[59]Li,S.;Deng,W.H.;Du,J.P.Reliable crowdsourcing and deep locality-preserving learning for expression recognition in the wild.In:Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,2584-2593, 2017.
[60]Barsoum,E.;Zhang,C.;Ferrer,C.C.;Zhang, Z.Y.Training deep networks for facial expression recognition with crowd-sourced label distribution.In: Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction,279-283, 2016.
[61]Van Der Maaten,L.;Hinton,G.Visualizing data using t-SNE.Journal of Machine Learning Research Vol.9, 2579-2625, 2008.




Other papers from this open access journal are available free of charge from http://www.springer.com/journal/41095. To submit a manuscript,please go to https://www. editorialmanager.com/cvmj.
- 1 Shandong Technology and Business University,Shandong 264005,China.E-mail:F.Zhang,zhangfan@sdtbu.edu.cn; G.Chen,2020410018@sdtbu.edu.cn.
2 School of Information and Electrical Engineering,Ludong University,Yantai 264025,China.E-mail:hua.wang@ldu.edu.cn(
3 Shangdong University,Shandong 250100,China.E-mail: czhang@sdu.edu.cn.
Manuscript received:2023-02-21;accepted:2023-07-19 - (1)http://mohammadmahoor.com/affectnet/
(2)http://www.whdeng.cn/raf/model1.html
(3)https://www.worldlink.com.cn/osdir/ferplus.html
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41095-023-0369-x
Publication Date: 2024-02-08
CF-DAN:Facial-expression recognition based on cross-fusion dual-attention network
Abstract
Recently,facial-expression recognition(FER) has primarily focused on images in the wild,including factors such as face occlusion and image blurring,rather than laboratory images.Complex field environments have introduced new challenges to FER.To address these challenges,this study proposes a cross-fusion dual- attention network.The network comprises three parts: (1)a cross-fusion grouped dual-attention mechanism to refine local features and obtain global information;(2)a proposed
1 Introduction
attention to key positions within an image and extract key information from these key positions to complete various tasks.For example,the vision transformer(ViT)[23]model can be applied to image classification.However,in the field of FER, networks similar to the ViT model cannot be used directly,owing to the limited sample size.Aouayeb et al.[24]successfully applied a ViT network for an expression recognition task by adding a squeeze- and-excitation(SE)block.Because of the network's ability to model global dependencies,self-attention mechanisms can better correlate with various facial parts when processing high-level visual semantic information.However,self-attention mechanisms require considerable computational resources,which are often unacceptable in several real-world scenarios. In this study,we addressed this issue by adopting a grouping approach and adding self-attention distillation within each group.
extension of the ReLU function[35].Sigmoid and its related functions have high computational complexity owing to the inclusion of power operations,resulting in a slow computation speed.Although ReLU and its related functions have fast computation speeds, their poor stability is caused by the discontinuity of the first-order derivative,and the negative interval becomes zero after activation,which easily leads to neuron deactivation.To address this,this study proposes an activation function construction method that uses fitting to avoid power operations while maintaining the continuity of the first-order derivative. During the fitting process,interval adjustments are made to prevent neuron deactivation.The contributions of this study are as follows:
(1)We propose a cross-fusion dual-attention transformer based on the spatial and channel dimensions.Local interaction in the spatial dimension completes the feature refinement,and a global receptive field is provided in the channel dimension. The cross-fusion dual-attention transformer realizes the mutual complementation of feature information of different dimensions,thereby improving the accuracy of the respective features.
(2)We designed an activation function construction method to solve problems in commonly used activation functions,such as neuron deactivation, the large computational overhead introduced by the power function,and the existence of non-differentiable points.Moreover,this study constructed a
(3)To reduce the high computational cost of the self-attention mechanism,we propose a grouped mechanism and self-attention distillation.This process divides the attention into different groups and uses self-attention distillation in each group to reduce the spatial dimensions of
2 Related work
researchers have made great efforts to improve the recognition accuracy under complex background and figure occlusion conditions. Bourel et al. [36] extracted the spatial degree features of key facial parts for classification. PCA-based methods [37, 38] realized the projection of test images onto training images using similarity to realize expression recognition. Hammal et al. [39] used multilevel image segmentation and sparse decomposition to solve the facial expression occlusion problem. Multiple face detectors such as the MTCNN [40] and Dlib [41] models have been used for facial detection in realworld scenarios. Moreover, to solve problems present in real-world scenarios, an increasing number of multi-view and multiscale-based studies have been conducted. Happy and Routray [42] and Majumder et al. [43] proposed that facial expression changes are primarily reflected in key parts, such as the eyes and mouth. With the continuous development of deep learning, numerous studies based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have made significant progress in extracting facial features in real-world environments. The SCN model [44] adds three additional modules to the traditional CNN for self-attention importance weighting, rank regularization, and relabeling purposes. An RAN [45] employs convolutional operations to design feature extraction, self-attention, and relation attention modules. EfficientFace [46] uses a local feature extractor and channel spatial modulator to improve the robustness. DMUE [47] uses an auxiliary branch to mine potential distributions and perform pairwise deterministic estimations. FDRL [48] is an emotionrelated feature decomposition and reconstruction network. A DAN [49] consists of a feature-clustering, multi-head cross attention, and attention fusion network. ARM uses a modified representation module to replace the pooling layer. CSGResNet [50] integrates Gabor convolution (GConv) into ResNet. AMP-Net extracts global, local, and salient facialemotion features with different granularities to learn the underlying diversity and key information of facial emotions. However, these methods are limited by the small receptive fields of CNNs. In this study, we leverage the advantages of CNN to extract shallow features and use self-attention mechanisms to process high-level visual semantic information.
in computer vision applications. Several pioneering studies, such as those on the iGPT [51] and ViT methods, applied a self-attention mechanism directly to image pixels or patch sequences. Inspired by this, convolutional visual transformers (CVTs) [52] were the first to apply the transformer model to FER tasks. CVTs use the local binary pattern (LBP) algorithm to send facial expression images in two different states to a ResNet network to obtain smaller feature images, and the transformer model is used to complete the FER task. A mask vision transformer (MViT) [53] generates a mask based on the transformer model to filter complex backgrounds and occlusions of facial images. The FER-VT [54] method sends feature maps of different scales to the same transformer model to complete the information fusion. Transfer [55] random dropout attention maps and self-attention modules guide the model in learning the rich relationships between different local patches. However, these methods are limited by the spatial dimension and have limitations in obtaining global information compared with the dual-attention mechanism.
3 Methodology


3.1 Dual-attention mechanism(DAM)
the input image in the form of
complete the information transfer between different dimensions. Section 3.2 details this further.
3.2 Cross-fusion attention mechanism
3.3 Self-attention distillation
feature extraction process,resulting in a declining model performance.This study proposes that the self-attention distillation mechanism acts on keys and values,reducing the scale of the spatial and channel dimensions.Dominant features can be extracted using this operation to form a feature map with a focused advantage in subsequent self-attention, suppressing interference from redundant information and reducing noise generation.Moreover,to reduce the loss of middle-and high-frequency information caused by the self-attention distillation mechanism, a residual connection is used to fuse the original
3.4 Interactive learning mechanism(ILM)
The first derivatives at points
that

4 Results

4.1 Datasets
4.2 Experiment details
4.3 Results and analysis
| Method | Year | RAF-DB | AffectNet | FERPlus |
| SCN[44] | CVPR 2020 | 87.03 | 60.23 | 89.39 |
| RAN[45] | TIP 2020 | 86.90 | - | 89.16 |
| EfficientFace[46] | AAAI 2021 | 88.36 | 59.89 | - |
| DMUE[47] | CVPR 2021 | 89.42 | - | - |
| FDRL[48] | CVPR 2021 | 89.47 | - | - |
| DAN[49] | arXiv 2021 | 89.70 | 62.09 | - |
| ARM[56] | arXiv 2021 | 90.42 | 61.33 | - |
| CSGResNet[50] | ICASSP 2022 | 88.59 | 61.03 | 88.94 |
| AMP-Net[57] | TCSVT 2022 | 89.19 | 61.32 | 89.37 |
| POSTER[33] | arXiv 2022 | 92.05 | 63.34 | 91.62 |
| Ours | - | 92.78 | 63.58 | 92.02 |

expression is the easiest to recognize among the eight expressions,owing to its large display range.The recognition rate of happiness in the AffectNet dataset was considerably higher than that of other expressions. Unlike happy faces,the difference in success rates was small,primarily because the images in the AffectNet dataset originate from the Internet and contain many error samples.In the FERPlus dataset,the happy recognition rate was slightly lower than that of neutral expressions,because neutral expressions have the largest sample size.Additionally,the FERPlus dataset contained the least disgust and contempt samples in-only one tenth the number of samples of other expressions-and these expressions have similar appearances.Consequently,the recognition accuracy of disgust and contempt was substantially lower than that of the other expressions.
(FLOPs)are key features to be considered for fair comparisons.One of the starting points of this study involved reducing the overall number of model parameters.To this end,we proposed grouped self- attention and self-attention distillation mechanisms. Table 2 compares the parameters of the proposed method with those of other methods,including the CVT,DMUE,TransFER[55],POSTER,and DAN models.Evidently,the number of parameters in the proposed method is only a quarter of those for the other methods,while maintaining the highest FER accuracy.In terms of running speed,it requires approximately 1 h and 20 min to complete training on the RAF-DB training set and approximately 1 min to test all expression images on the RAF-DB test set after training.This provides the self-attention-based facial expression recognition model with a significant advantage.
4.4 Ablation study
| Method | Year | Params | FLOPs | Acc(RAF-DB) | Acc(FERPlus) |
| CVT[52] | arXiv 2021 | 80.1 M | - | 87.61 | 88.81 |
| DMUE[47] | CVPR 2021 | 78.4 M | 13.4G | 89.42 | - |
| TransFER[55] | ICCV 2021 | 65.2 M | 15.3G | 90.91 | 90.83 |
| POSTER[33] | arXiv 2022 | 71.8 M | 15.7G | 92.05 | 91.62 |
| DAN[49] | arXiv 2021 | 28.3 M | 2.6G | 89.70 | - |
| Ours | - | 16.4 M | 2.0 G | 92.78 | 92.02 |
| Method | AffectNet | FERPlus | RAF-DB |
| Baseline | 59.73% | 89.69% | 90.37% |
| Baseline+DAM | 60.44% | 90.92% | 90.88% |
| Baseline+DAM+ILM | 63.12% | 91.55% | 91.63% |
| Baseline+cross-fusion DAM+ILM | 63.58% | 92.02% | 92.78% |




in the negative part of the ReLU activation function, we mapped the negative region to a smaller negative
interval.As shown in Fig.9,the activation function used in this study is continuously differentiable at all points.Moreover,the proposed activation function does not involve exponentiation,thereby improving the model's operational speed compared with that of the sigmoid and tanh activation functions. In terms of recognition accuracy,we compared various activation functions on the RAF-DB dataset; Table 4 presents the results.Evidently,the proposed activation function performs better in FER tasks.
4.5 Parameter sensitivity analysis
| PCP | sigmoid | ReLU | tanh | ILM | ACC |
|
|
92.54 | ||||
|
|
|
92.78 | |||
|
|
91.42 | ||||
|
|
|
91.78 | |||
|
|
91.98 | ||||
|
|
|
92.26 | |||
|
|
91.75 | ||||
|
|
|
91.97 |
| Method | AffectNet | FERPlus | Params | FLOPs |
| Without distillation |
|
|
4.2 M | 0.21 G |
| With distillation |
|
|
4.22 M | 0.14 G |



5 Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Declaration of competing interest
References
[2] Joshi, A.; Kyal, S.; Banerjee, S.; Mishra, T. In-the-wild drowsiness detection from facial expressions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, 207-212, 2020.
[3] Tran, L.; Yin, X.; Liu, X. M. Representation learning by rotating your faces. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence Vol. 41, No. 12, 30073021, 2019.
[4] Wu, T. F.; Bartlett, M. S.; Movellan, J. R. Facial expression recognition using Gabor motion energy filters. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition – Workshops, 42-47, 2010.
[5] Shan, C. F.; Gong, S. G.; McOwan, P. W. Facial expression recognition based on Local Binary Patterns: A comprehensive study. Image and Vision Computing Vol. 27, No. 6, 803-816, 2009.
[6] Shokoohi, Z.; Bahmanjeh, R.; Faez, K. Expression recognition using directional gradient local pattern and gradient-based ternary texture patterns. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis, 1-7, 2015.
[7] Wang, Z.; Ying, Z. L. Facial expression recognition based on local phase quantization and sparse representation. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Natural Computation, 222-225, 2012.
[8] Ali, H. B.; Powers, D. M. W.; Jia, X. B.; Zhang, Y. H. Extended non-negative matrix factorization for face and facial expression recognition. International Journal of Machine Learning and Computing Vol. 5, No. 2, 142147, 2015.
[9] Baddar, W. J.; Lee, S. M.; Ro, Y. M. On-the-fly facial expression prediction using LSTM encoded appearancesuppressed dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing Vol. 13, No. 1, 159-174, 2022.
[10] Li, Y. J.; Gao, Y. N.; Chen, B. Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, G. M.; Zhang, D. Self-supervised exclusive-inclusive interactive learning for multi-label facial expression recognition in the wild. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology Vol. 32, No. 5, 3190-3202, 2022.
[11] Zhang, X.; Zhang, F. F.; Xu, C. S. Joint expression
synthesis and representation learning for facial expression recognition. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology Vol. 32, No. 3, 16811695, 2022.
[12] Otberdout, N.; Daoudi, M.; Kacem, A.; Ballihi, L.; Berretti, S. Dynamic facial expression generation on Hilbert hypersphere with conditional Wasserstein generative adversarial nets. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence Vol. 44, No. 2, 848-863, 2022.
[13] Zhang, F. F.; Zhang, T. Z.; Mao, Q. R.; Xu, C. S. A unified deep model for joint facial expression recognition, face synthesis, and face alignment.
[14] Feffer, M.; Rudovic, O.; Picard, R. W. A mixture of personalized experts for human affect estimation. In: Machine Learning and Data Mining in Pattern Recognition. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 10935. Perner, P. Ed. Springer Cham, 316-330, 2018.
[15] Fan, Y.; Lu, X. J.; Li, D.; Liu, Y. L. Videobased emotion recognition using CNN-RNN and C3D hybrid networks. In: Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, 445-450, 2016.
[16] Zhang, T.; Zheng, W. M.; Cui, Z.; Zong, Y.; Li, Y. Spatial-temporal recurrent neural network for emotion recognition. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics Vol. 49, No. 3, 839-847, 2019.
[17] Pang, L.; Li, N. Q.; Zhao, L.; Shi, W. X.; Du, Y. P. Facial expression recognition based on Gabor feature and neural network. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Security, Pattern Analysis, and Cybernetics, 489-493, 2018.
[18] Liu, Z.; Lin, Y. T.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. X.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. N. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 9992-10002, 2021.
[19] Kim, J. H.; Kim, N.; Won, C. S. Facial expression recognition with Swin transformer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.13472, 2022.
[20] Wang, W. H.; Xie, E. Z.; Li, X.; Fan, D. P.; Song, K. T.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pyramid vision transformer: A versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 548-558, 2021.
[21] Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y. B. ResT: An efficient transformer for visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 1547515485, 2021.
[22] Zhang, F.; Chen, G. G.; Wang, H.; Li, J. J.; Zhang, C. M. Multi-scale video super-resolution transformer with polynomial approximation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology Vol. 33, No. 9, 4496-4506, 2023.
[23] Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X. H.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16×16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929, 2020.
[24] Aouayeb, M.; Hamidouche, W.; Soladie, C.; Kpalma, K.; Seguier, R. Learning vision transformer with squeeze and excitation for facial expression recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.03107, 2021.
[25] Putro, M. D.; Nguyen, D. L.; Jo, K. H. A dual attention module for real-time facial expression recognition. In: Proceedings of the 46th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, 411-416, 2020.
[26] Song, W. Y.; Shi, S. Z.; Wu, Y. X.; An, G. Y. Dualattention guided network for facial action unit detection. IET Image Processing Vol. 16, No. 8, 2157-2170, 2022.
[27] Ding, M. Y.; Xiao, B.; Codella, N.; Luo, P.; Wang, J. D.; Yuan, L. DaViT: Dual attention vision transformers. In: Computer Vision – ECCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 13684. Avidan, S.; Brostow, G.; Cissé, M.; Farinella, G. M.; Hassner, T. Eds. Springer Cham, 74-92, 2022.
[28] Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H. J.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y. J.; Fang, Z. W.; Lu, H. Q. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 3141-3149, 2019.
[29] Li, X. Q.; Xie, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, G. T.; Tong, W. Q. Dual attention convolutional network for action recognition. IET Image Processing Vol. 14, No. 6, 10591065, 2020.
[30] Li, Y. S.; Liu, Y.; Yu, R.; Zong, H. L.; Xie, W. X. Dual attention based spatial-temporal inference network for volleyball group activity recognition. Multimedia Tools and Applications Vol. 82, No. 10, 15515-15533, 2023.
[31] Gedamu, K.; Yilma, G.; Assefa, M.; Ayalew, M. Spatiotemporal dual-attention network for view-invariant human action recognition. In: Proceedings of the SPIE 12342, 14th International Conference on Digital Image Processing, 123420Q, 2022.
[32] Ullah, H.; Munir, A. Human activity recognition using cascaded dual attention CNN and bi-directional GRU framework. arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.05034, 2022.
[33] Zheng, C.; Mendieta, M.; Chen, C. POSTER: A pyramid cross-fusion transformer network for facial expression recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204. 04083, 2022.
[34]Han,J.;Moraga,C.The influence of the sigmoid function parameters on the speed of backpropagation learning.In:Proceedings of the International Workshop on Artificial Neural Networks:From Natural to Artificial Neural Computation,195-201, 1995.
[35]Glorot,X.;Bordes,A.;Bengio,Y.Deep sparse rectifier neural networks.In:Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics,315-323, 2011.
[36]Bourel,F.;Chibelushi,C.C.;Low,A.A.Recognition of facial expressions in the presence of occlusion.In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, 1-10, 2001.
[37]Mao,X.;Xue,Y.L.;Li,Z.;Huang,K.;Lv,S.W. Robust facial expression recognition based on RPCA and AdaBoost.In:Proceedings of the 10th Workshop on Image Analysis for Multimedia Interactive Services, 113-116, 2009.
[38]Jiang,B.;Jia,K.B.Research of robust facial expression recognition under facial occlusion condition. In:Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Active Media Technology,92-100, 2011.
[39]Hammal,Z.;Arguin,M.;Gosselin,F.Comparing a novel model based on the transferable belief model with humans during the recognition of partially occluded facial expressions.Journal of Vision Vol.9,No.2,22, 2009.
[40]Zhang,K.P.;Zhang,Z.P.;Li,Z.F.;Qiao,Y.Joint face detection and alignment using multitask cascaded convolutional networks.IEEE Signal Processing Letters Vol.23,No.10,1499-1503, 2016.
[41]Amos,B.;Ludwiczuk,B.;Satyanarayanan,M. OpenFace:A general-purpose face recognition library with mobile applications.School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University,2016.Available at https://elijah.cs.cmu.edu/DOCS/CMU-CS-16-118.pdf
[42]Happy,S.L.;Routray,A.Automatic facial expression recognition using features of salient facial patches. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing Vol.6, No.1,1-12, 2015.
[43]Majumder,A.;Behera,L.;Subramanian,V.K. Automatic facial expression recognition system using deep network-based data fusion.IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics Vol.48,No.1,103-114, 2018.
[44]Wang,K.;Peng,X.J.;Yang,J.F.;Lu,S.J.; Qiao,Y.Suppressing uncertainties for large-scale facial expression recognition.In:Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,6896-6905, 2020.
[45]Wang,K.;Peng,X.J.;Yang,J.F.;Meng,D.B.;Qiao, Y.Region attention networks for pose and occlusion
robust facial expression recognition.IEEE Transactions on Image Processing Vol.29,4057-4069, 2020.
[46]Zhao,Z.Q.;Liu,Q.S.;Zhou,F.Robust light- weight facial expression recognition network with label distribution training.Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence Vol.35,No.4, 3510-3519, 2021.
[47]She,J.H.;Hu,Y.B.;Shi,H.L.;Wang,J.; Shen,Q.;Mei,T.Dive into ambiguity:Latent distribution mining and pairwise uncertainty estimation for facial expression recognition.In:Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,6244-6253, 2021.
[48]Ruan,D.L.;Yan,Y.;Lai,S.Q.;Chai,Z.H.; Shen,C.H.;Wang,H.Z.Feature decomposition and reconstruction learning for effective facial expression recognition.In:Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,7656-7665, 2021.
[49]Wen,Z.;Lin,W.;Wang,T.;Xu,G.Distract your attention:Multi-head cross attention network for facial expression recognition.arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.07270, 2021.
[50]Jiang,S.P.;Xu,X.M.;Liu,F.;Xing,X.F.;Wang, L.CS-GResNet:A simple and highly efficient network for facial expression recognition.In:Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics,Speech and Signal Processing,2599-2603, 2022.
[51]Chen,M.;Radford,A.;Child,R.;Wu,J.;Jun, H.;Luan,D.;Sutskever,I.Generative pretraining from pixels.In:Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning,1691-1703, 2020.
[52]Ma,F.;Sun,B.;Li,S.Robust facial expression recognition with convolutional visual transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.16854, 2021.
[53]Li,H.;Sui,M.;Zhao,F.;Zha,Z.;Wu,F.MVT:Mask vision transformer for facial expression recognition in the wild.arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.04520, 2021.
[54]Huang,Q.H.;Huang,C.Q.;Wang,X.Z.;Jiang,F. Facial expression recognition with grid-wise attention and visual transformer.Information Sciences Vol.580, 35-54, 2021.
[55]Xue,F.L.;Wang,Q.C.;Guo,G.D.TransFER: Learning relation-aware facial expression repre- sentations with transformers.In:Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision,3581-3590, 2021.
[56]Shi,J.;Zhu,S.;Liang,Z.Learning to amend facial expression representation via de-albino and affinity. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.10189, 2021.
[57]Liu,H.W.;Cai,H.L.;Lin,Q.C.;Li,X.F.;Xiao,
[58]Dhall,A.;Goecke,R.;Lucey,S.;Gedeon,T.Static facial expression analysis in tough conditions:Data, evaluation protocol and benchmark.In:Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops,2106-2112, 2011.
[59]Li,S.;Deng,W.H.;Du,J.P.Reliable crowdsourcing and deep locality-preserving learning for expression recognition in the wild.In:Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,2584-2593, 2017.
[60]Barsoum,E.;Zhang,C.;Ferrer,C.C.;Zhang, Z.Y.Training deep networks for facial expression recognition with crowd-sourced label distribution.In: Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction,279-283, 2016.
[61]Van Der Maaten,L.;Hinton,G.Visualizing data using t-SNE.Journal of Machine Learning Research Vol.9, 2579-2625, 2008.




Other papers from this open access journal are available free of charge from http://www.springer.com/journal/41095. To submit a manuscript,please go to https://www. editorialmanager.com/cvmj.
- 1 Shandong Technology and Business University,Shandong 264005,China.E-mail:F.Zhang,zhangfan@sdtbu.edu.cn; G.Chen,2020410018@sdtbu.edu.cn.
2 School of Information and Electrical Engineering,Ludong University,Yantai 264025,China.E-mail:hua.wang@ldu.edu.cn(
3 Shangdong University,Shandong 250100,China.E-mail: czhang@sdu.edu.cn.
Manuscript received:2023-02-21;accepted:2023-07-19 - (1)http://mohammadmahoor.com/affectnet/
(2)http://www.whdeng.cn/raf/model1.html
(3)https://www.worldlink.com.cn/osdir/ferplus.html
